Allure Framework is a lightweight, flexible multi-language test report tool that not only displays a very concise representation of what has been tested in a neat web report form, but also allows everyone involved in the development process to extract the most useful information from everyday test execution.
JUnit5
Difference between JUnit4 and JUnit5
In this article, we’ll see an overview of the differences between the two versions of the library.
Table of Contents
- Architecture
- JDK Version
- Imports
- Assertions
- Assumptions
- Conditional Test Execution
- Extending JUnit
- Non-public Test Methods are Allowed
- Repeat Tests
- Parameterized Tests
1. Architecture
JUnit 4 has everything bundled into a single jar file whereas JUnit 5 is composed of 3 sub-projects i.e. JUnit Platform, JUnit Jupiter, and JUnit Vintage.
JUnit4
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
JUnit Platform: It defines the TestEngine API for developing new testing frameworks that run on the platform.
JUnit Jupiter: It has all new JUnit annotations and TestEngine implementation to run tests written with these annotations.
JUnit Vintage: To support running JUnit 3 and JUnit 4 written tests on the JUnit 5 platform.
JUnit5
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-engine</artifactId>
<version>5.9.0-M1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId>
<version>5.9.0-M1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
<version>5.9.0-M1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
2. JDK Version
JUnit 4 requires Java 5 (or higher) whereas JUnit 5 requires Java 8 (or higher).
3. Imports
JUnit 5 uses the org.JUnit package for its annotations and classes whereas JUnit 5 uses the new org.JUnit.jupiter package for its annotations and classes. For example, org.JUnit.Test becomes org.JUnit.jupiter.api.Test.
@Before annotation of JUnit4 is renamed to @BeforeEach in JUnit5
@After annotation of JUnit4 is renamed to @AfterEach in JUnit5
@BeforeClass annotation of JUnit4 is renamed to @BeforeAll in JUnit5
@AfterClass annotation of JUnit4 is renamed to @AfterAll in JUnit5
4. Assertions
JUnit 5 assertions are now in org.JUnit.jupiter.api.Assertions whereas JUnit4 assertions are in org.JUnit.Assert. Most of the common assertions, like assertEquals() and assertNotNull() look the same as before, but there are a few key differences:
- The error message is now the last argument, for example, assertEquals(“my message”, 1, 2) would be assertEquals(1, 2, “my message”)
- Most assertions now accept a lambda that constructs the error message, which is only called when the assertion fails.
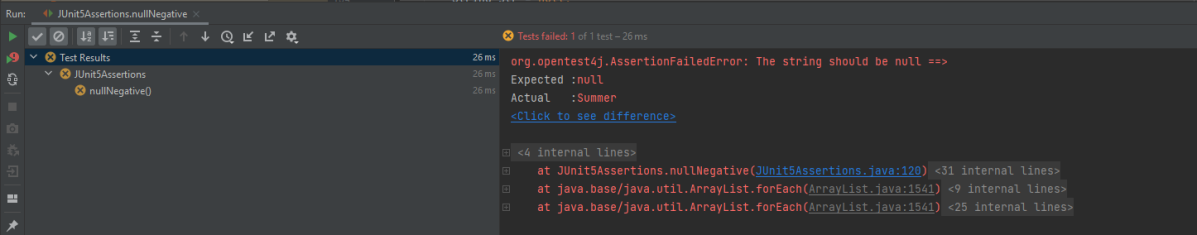
Below is an example of the same.
@Test
void nullNegative() {
String str = "Summer";
Assertions.assertNull(str, () -> "The string should be null");
}
The output of the above program is
- assertTimeout() and assertTimeoutPreemptively() have replaced the @Timeout annotation (note that there is a @Timeout annotation in JUnit 5, but it works differently than JUnit 4).
- There are several new assertions in JUnit5- assertAll(), assertIterableEquals(), assertLinesMatch(), assertThrows() and assertDoesNotThrow(). To know more about assertions in JUnit5, please refer to this tutorial – JUnit5 Assertions Example
5. Assumptions
In Junit 4, org.junit.Assume contains methods for stating assumptions about the conditions in which a test is meaningful. It has the following five methods:
- assumeFalse()
- assumeNoException()
- assumeNotNull()
- assumeThat()
- assumeTrue()
JUnit5 has the following three methods:
- assumeFalse()
- assumingThat()
- assumeTrue()
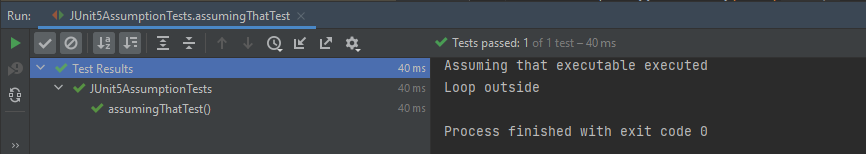
Below is an example of assumeThat() annotation in JUnit5.
@Test
void assumingThatTest() {
System.setProperty("ENV", "UAT");
assumingThat(
"UAT".equals(System.getProperty("ENV")),
() -> {
// Since the condition is true, this assertion will get executed
System.out.println("Assuming that executable executed");
assertEquals((num1+num2),num4,"The product of "+ num1 +" and "+ num2 +" is not equal to "+num4);
});
System.out.println("Loop outside");
assertEquals((num5-num2),num6,"The difference of "+ num5 +" and "+num2+" is not equal to " + num6);
}
The output of the above program is
6. Conditional Test Execution
In JUnit4, @Ignore is used to skip the execution of a test whereas @Disabled or one of the other built-in execution conditions is used to skip the execution of the test in JUnit5. To know more about skipping the tests in JUnit5, please refer to this tutorial – How to disable tests in JUnit5 – @Disabled.
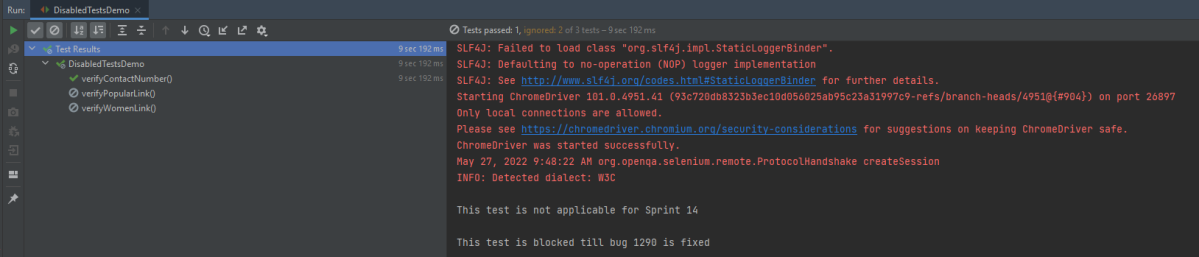
Below is an example of @Disabled in JUnit5.
import io.github.bonigarcia.wdm.WebDriverManager;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.*;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeOptions;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
class DisabledTestsDemo {
WebDriver driver;
@BeforeEach
public void setUp() {
WebDriverManager.chromedriver().setup();
ChromeOptions chromeOptions = new ChromeOptions();
driver = new ChromeDriver(chromeOptions);
driver.manage().window().fullscreen();
driver.get("http://automationpractice.com/index.php");
}
@Disabled("This test is not applicable for Sprint 14")
@Test
void verifyPopularLink() {
boolean displayed = driver.findElement(By.xpath("//*[@id='home-page-tabs']/li[1]/a")).isDisplayed();
assertTrue(displayed);
}
@Test
void verifyContactNumber() {
String contactDetail = driver.findElement(By.xpath("//span[@class='shop-phone']/strong")).getText();
assertEquals("0123-456-789", contactDetail);
}
@Disabled("This test is blocked till bug 1290 is fixed")
@Test
void verifyWomenLink() {
boolean enabled = driver.findElement(By.xpath("//*[@id='block_top_menu']/ul/li[1]/a")).isEnabled();
assertTrue(enabled);
}
@AfterEach
public void tearDown() {
driver.close();
}
}
The output of the above program is
JUnit 5 provides the ExecutionCondition extension API to enable or disable a test or container (test class) conditionally. This is like using @Disabled on a test but it can define custom conditions. There are multiple built-in conditions, such as:
- @EnabledOnOs and @DisabledOnOs: Enables a test only on specified operating systems.
- @EnabledOnJre and @DisabledOnJre: Specifies the test should be enabled or disabled for specific versions of Java.
- @EnabledIfSystemProperty: Enables a test based on the value of a JVM system property.
- @EnabledIf: Uses scripted logic to enable a test if scripted conditions are met.
7. Extending JUnit
@RunWith no longer exists; superseded by @ExtendWith in JUnit5.
In JUnit 4, customizing the framework generally meant using a @RunWith annotation to specify a custom runner. Using multiple runners was problematic, and usually required chaining or using a @Rule. This has been simplified and improved in JUnit 5 using extensions.
import net.serenitybdd.core.Serenity;
import net.serenitybdd.junit5.SerenityJUnit5Extension;
import net.thucydides.core.annotations.Managed;
import net.thucydides.core.annotations.Steps;
import net.thucydides.core.annotations.Title;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
@ExtendWith(SerenityJUnit5Extension.class)
class ApplicationLoginJUnit5Tests {
@Managed
WebDriver driver;
@Steps
NavigateAction navigateAction;
@Steps
StepLoginPage loginPage;
@Test
@Title("Login to application with valid credentials navigates to DashBoard page")
void successfulLogin() {
navigateAction.toTheHomePage();
// When
loginPage.inputUserName("Admin");
loginPage.inputPassword("admin123");
loginPage.clickLogin();
// Then
Serenity.reportThat("Passing valid credentials navigates to DashBoard page",
() -> assertThat(dashboardPage.getHeading()).isEqualToIgnoringCase("DashBoard"));
}
}
8. Non-public Test Methods are Allowed
JUnit 5 test classes and test methods are not required to be public. We can now make them package protected.
JUnit internally uses reflection to find test classes and test methods. Reflection can discover them even if they have limited visibility, so there is no need for them to be public.
9. Repeat Tests
JUnit Jupiter provides the ability to repeat a test a specified number of times by annotating a method with @RepeatedTest and specifying the total number of repetitions desired. To know more about RepestedTest, please refer to this tutorial – How to Retry Test in JUnit5 – @RepeatedTest
Below is the example of @RepeatedTest in JUnit5.
@RepeatedTest(3)
void repeatedTestWithRepetitionInfo1(RepetitionInfo repetitionInfo) {
assertEquals(3, repetitionInfo.getTotalRepetitions());
}
The output of the above program is

10. Parameterized Tests
Test parameterization existed in JUnit 4 with built-in libraries like JUnit4Parameterized or third-party libraries like JUnitParams. In JUnit 5, parameterized tests are completely built-in and adopt some of the best features from JUnit4Parameterized and JUnitParams. To know more about the parameterized tests in JUnit5, please refer to this tutorial – How to parameterized Tests in JUnit5.
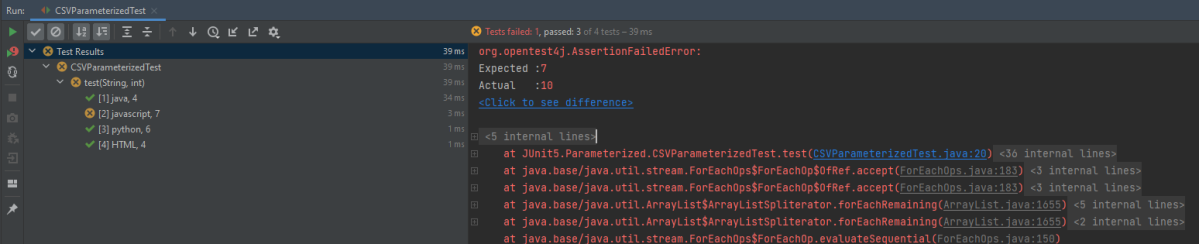
Below is an example of parameterized Test in JUnit5.
public class CSVParameterizedTest {
@ParameterizedTest
@CsvSource({
"java, 4",
"javascript, 7",
"python, 6",
"HTML, 4",
})
void test(String str, int length) {
assertEquals(length, str.length());
}
}
The output of the above program is
Congratulations. We have gone through the differences between JUnit4 and JUnit5. Happy Learning!!
Integration of Serenity with Cucumber and JUnit5
In the previous tutorial, I explained the Serenity BDD with Cucumber for Web Application using Junit4. In this tutorial, I will explain the same Test Framework using Serenity, Cucumber, and JUnit5. This tutorial gives a clear picture of the initial setup of a BDD Framework.
Table of Contents
- What is JUnit5?
- Dependency List
- Implementation Steps
- Download and Install Java
- Download and setup Eclipse IDE on the system
- Setup Maven and create a new Maven Project
- Update Properties section in Maven pom.xml
- Add repositories and pluginRepository to Maven pom.xml
- Add Serenity, Serenity Cucumber, and JUnit dependencies to POM.xml
- Update the Build Section of pom.xml
- Create a feature file under src/test/resources
- Create junit-platform.properties file under src/test/resources (optional)
- Create the Step Definition class or Glue Code
- Create a Serenity-Cucumber Runner class
- Create serenity.conf file under src/test/resources
- Create serenity.properties file at the root of the project
- Run the tests from Command Line
- Test Execution Status
- Serenity Report Generation
- Cucumber Report Generation (Optional)
What is JUnit5?
JUnit 5 is composed of several different modules from three different sub-projects.
JUnit 5 = JUnit Platform + JUnit Jupiter + JUnit Vintage
The JUnit Platform serves as a foundation for launching testing frameworks on the JVM. It also defines the TestEngine API for developing a testing framework that runs on the platform.
JUnit Jupiter is the combination of the new programming model and extension model for writing tests and extensions in JUnit 5. The Jupiter sub-project provides a TestEngine for running Jupiter based tests on the platform.
JUnit Vintage provides a TestEngine for running JUnit 3 and JUnit 4 based tests on the platform. It requires JUnit 4.12 or later to be present on the class/module path.
JUnit5 is not completely integrated with Serenity with Cucumber. So, it is advisable to use jupiter-vintage-engine for the Cucumber TestRunner classes.
Dependency List:
- Serenity – 4.0.28
- JUnit Jupiter – 5.10.1
- JUnit Vintage – 5.10.1
- JUnit Platform Suite – 1.10.1
- Cucumber JUnit Platform – 7.15.0
- Java 17
- Maven – 3.9.5
- Maven Compiler Plugin – 3.11.0
- Maven Surefire Plugin – 3.2.1
- Maven FailSafe Plugin – 3.2.1
Implementation Steps
Step 1- Download and Install Java
Click here to know How to install Java.
Step 2 – Download and setup Eclipse IDE on the system
The Eclipse IDE (integrated development environment) provides strong support for Java developers which is needed to write Java code. Click here to know How to install Eclipse.
Step 3 – Setup Maven and create a new Maven Project
Click here to know How to install Maven.
Click here to know How to create a Maven project
Below is the Maven project structure. Here,
Group Id – com.example
Artifact Id – SerenityCucumberJunit5Demo
Version – 0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
Package – com. example. SerenityCucumberJunit5Demo
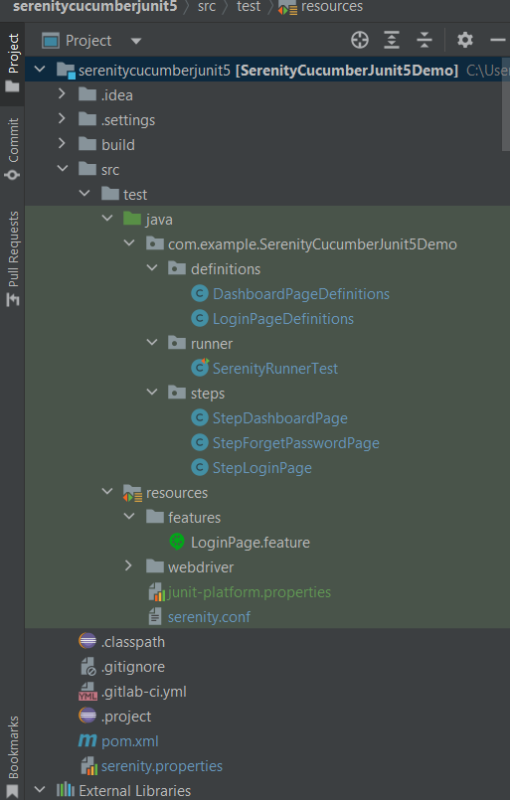
Step 4 – Update Properties section in Maven pom.xml
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<serenity.version>4.0.28</serenity.version>
<junit.jupiter.version>5.10.1</junit.jupiter.version>
<junit.vintage.version>5.10.1</junit.vintage.version>
<junit-platform-suite.version>1.10.1</junit-platform-suite.version>
<cucumber-junit-platform-engine.version>7.15.0</cucumber-junit-platform-engine.version>
<maven.compiler.plugin.version>3.11.0</maven.compiler.plugin.version>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
<maven.surefire.plugin.version>3.2.1</maven.surefire.plugin.version>
<maven.failsafe.plugin.version>3.2.1</maven.failsafe.plugin.version>
<tags></tags>
</properties>
Step 5 – Add repositories and pluginRepository to Maven pom.xml
<repositories>
<repository>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
<id>central</id>
<name>bintray</name>
<url>https://jcenter.bintray.com</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<pluginRepositories>
<pluginRepository>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
<id>central</id>
<name>bintray-plugins</name>
<url>https://jcenter.bintray.com</url>
</pluginRepository>
</pluginRepositories>
Step 6 – Add Serenity, Serenity Cucumber, and JUnit dependencies to POM.xml
<dependencies>
<!-- JUnit 5 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-engine</artifactId>
<version>${junit.jupiter.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
<version>${junit.vintage.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Serenity -->
<dependency>
<groupId>net.serenity-bdd</groupId>
<artifactId>serenity-core</artifactId>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.serenity-bdd</groupId>
<artifactId>serenity-cucumber</artifactId>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.serenity-bdd</groupId>
<artifactId>serenity-screenplay-webdriver</artifactId>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.platform</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-platform-suite</artifactId>
<version>${junit-platform-suite.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.cucumber</groupId>
<artifactId>cucumber-junit-platform-engine</artifactId>
<version>${cucumber-junit-platform-engine.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Step 7 – Update the Build Section of pom.xml
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.surefire.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<skip>true</skip>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-failsafe-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.failsafe.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<includes>
<include>**/*.java</include>
</includes>
<parallel>methods</parallel>
<useUnlimitedThreads>true</useUnlimitedThreads>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>integration-test</goal>
<goal>verify</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.compiler.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<source>${maven.compiler.source}</source>
<target>${maven.compiler.target}</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>net.serenity-bdd.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>serenity-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.serenity-bdd</groupId>
<artifactId>serenity-single-page-report</artifactId>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<configuration>
<tags>${tags}</tags>
<reports>single-page-html</reports>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>serenity-reports</id>
<phase>post-integration-test</phase>
<goals>
<goal>aggregate</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
The complete pom.xml is
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>SerenityCucumberJunit5Demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>SerenityCucumberJunit5Demo</name>
<!-- FIXME change it to the project's website -->
<url>http://www.example.com</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<serenity.version>4.0.28</serenity.version>
<junit.jupiter.version>5.10.1</junit.jupiter.version>
<junit.vintage.version>5.10.1</junit.vintage.version>
<junit-platform-suite.version>1.10.1</junit-platform-suite.version>
<cucumber-junit-platform-engine.version>7.15.0</cucumber-junit-platform-engine.version>
<maven.compiler.plugin.version>3.11.0</maven.compiler.plugin.version>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
<maven.surefire.plugin.version>3.2.1</maven.surefire.plugin.version>
<maven.failsafe.plugin.version>3.2.1</maven.failsafe.plugin.version>
<tags></tags>
</properties>
<repositories>
<repository>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
<id>central</id>
<name>bintray</name>
<url>https://jcenter.bintray.com</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<pluginRepositories>
<pluginRepository>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
<id>central</id>
<name>bintray-plugins</name>
<url>https://jcenter.bintray.com</url>
</pluginRepository>
</pluginRepositories>
<dependencies>
<!-- JUnit 5 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-engine</artifactId>
<version>${junit.jupiter.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
<version>${junit.vintage.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Serenity -->
<dependency>
<groupId>net.serenity-bdd</groupId>
<artifactId>serenity-core</artifactId>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.serenity-bdd</groupId>
<artifactId>serenity-cucumber</artifactId>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.serenity-bdd</groupId>
<artifactId>serenity-screenplay-webdriver</artifactId>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.platform</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-platform-suite</artifactId>
<version>${junit-platform-suite.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.cucumber</groupId>
<artifactId>cucumber-junit-platform-engine</artifactId>
<version>${cucumber-junit-platform-engine.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.surefire.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<skip>true</skip>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-failsafe-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.failsafe.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<includes>
<include>**/*.java</include>
</includes>
<parallel>methods</parallel>
<useUnlimitedThreads>true</useUnlimitedThreads>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>integration-test</goal>
<goal>verify</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.compiler.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<source>${maven.compiler.source}</source>
<target>${maven.compiler.target}</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>net.serenity-bdd.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>serenity-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.serenity-bdd</groupId>
<artifactId>serenity-single-page-report</artifactId>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<configuration>
<tags>${tags}</tags>
<reports>single-page-html</reports>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>serenity-reports</id>
<phase>post-integration-test</phase>
<goals>
<goal>aggregate</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Step 8 – Create a feature file under src/test/resources
The purpose of the Feature keyword is to provide a high-level description of a software feature, and to group related scenarios. To know more about the Feature file, please refer this tutorial.
Feature: Login to HRM
@ValidCredentials
Scenario: Login with valid credentials
Given User is on Home page
When User enters username as "Admin"
And User enters password as "admin123"
Then User should be able to login successfully
@InValidCredentials
Scenario Outline: Login with invalid credentials
Given User is on Home page
When User enters username as '<username>'
And User enters password as '<password>'
Then User should be able to see error message '<errorMessage>'
Examples:
|username |password |errorMessage |
|admin |admin |Invalid credentials |
|abc |admin123 |Invalid credentials |
|abc |abc123 |Invalid credentials |
|1$£" | 45£"% |Invalid credentials |
@ForgetPassword
Scenario: Verify Forget Password Functionality
Given User is on Home page
When User clicks on Forgot your password link
Then User should be able to see new page which contains Reset Password button
Step 9 – Create junit-platform.properties file under src/test/resources (optional)
This is an optional step. Cucumber of version 6.7 and above provides the functionality to generate a beautiful cucumber report. For this, it is needed to add a file junit-platform.properties under src/test/resources.
cucumber.publish.enabled = true
Step 10 – Create the Step Definition class or Glue Code
A Step Definition is a Java method with an expression that links it to one or more Gherkin steps. When Cucumber executes a Gherkin step in a scenario, it will look for a matching step definition to execute. You can have all of your step definitions in one file, or in multiple files.
LoginPageDefinitions
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
import com.example.SerenityCucumberJunit5Demo.steps.StepDashboardPage;
import com.example.SerenityCucumberJunit5Demo.steps.StepForgetPasswordPage;
import com.example.SerenityCucumberJunit5Demo.steps.StepLoginPage;
import io.cucumber.java.en.Given;
import io.cucumber.java.en.Then;
import io.cucumber.java.en.When;
import net.serenitybdd.annotations.Steps;
public class LoginPageDefinitions {
@Steps
StepLoginPage loginPage;
@Steps
StepDashboardPage dashPage;
@Steps
StepForgetPasswordPage forgetpasswordPage;
@Given("User is on Home page")
public void openApplication() {
loginPage.open();
}
@When("User enters username as {string}")
public void enterUsername(String userName) {
loginPage.inputUserName(userName);
}
@When("User enters password as {string}")
public void enterPassword(String passWord) {
loginPage.inputPassword(passWord);
loginPage.clickLogin();
}
@Then("User should be able to login successfully")
public void clickOnLoginButton() {
dashPage.loginVerify();
}
@Then("User should be able to see error message {string}")
public void unsucessfulLogin(String expectedErrorMessage) {
String actualErrorMessage = loginPage.errorMessage();
System.out.println("Actual Error Message :" + actualErrorMessage);
assertEquals(expectedErrorMessage, actualErrorMessage);
}
@When("User clicks on Forgot your password link")
public void clickForgetPasswordLink() {
loginPage.clickForgetPasswordLink();
}
@Then("User should be able to see new page which contains Reset Password button")
public void verifyForgetPasswordPage() {
assertTrue(forgetpasswordPage.ForgetPasswordPage());
}
}
Assertions in JUnit-Vintage Engine are imported from the below package:-
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
DashboardPageDefinitions
import com.example.SerenityCucumberJunit5Demo.steps.StepDashboardPage;
import net.serenitybdd.annotations.Step;
import net.serenitybdd.annotations.Steps;
public class DashboardPageDefinitions {
@Steps
StepDashboardPage dashPage;
@Step
public void verifyAdminLogin() {
dashPage.loginVerify();
}
}
The corresponding Test Step classes are – StepLoginPage and StepDashboardPage.
There are multiple ways to identify a web element on the web page – one of the ways is to use @FindBy or $(By.).
I prefer to use @FindBy as I need not find the same element multiple times. Using @FindBy, I have identified a web element and defined a WebElementFacacde for the same which is reusable.
StepLoginPage
import net.serenitybdd.annotations.Step;
import net.serenitybdd.core.annotations.findby.FindBy;
import net.serenitybdd.core.pages.PageObject;
import net.serenitybdd.core.pages.WebElementFacade;
public class StepLoginPage extends PageObject {
@FindBy(name = "username")
WebElementFacade username;
@FindBy(name = "password")
WebElementFacade password;
@FindBy(xpath = "//*[@id='app']/div[1]/div/div[1]/div/div[2]/div[2]/form/div[3]/button")
WebElementFacade submitButton;
@FindBy(xpath = "//*[@id='app']/div[1]/div/div[1]/div/div[2]/div[2]/div/div[1]/div[1]/p")
WebElementFacade errorMessage;
@FindBy(xpath = "//*[@id='app']/div[1]/div/div[1]/div/div[2]/div[2]/form/div[4]/p")
WebElementFacade linkText;
@Step("Enter Username")
public void inputUserName(String userName) {
username.sendKeys((userName));
}
@Step("Enter Password")
public void inputPassword(String passWord) {
password.sendKeys((passWord));
}
@Step("Click Submit Button")
public void clickLogin() {
submitButton.click();
}
@Step("Error Message on unsuccessful login")
public String errorMessage() {
String actualErrorMessage = errorMessage.getText();
System.out.println("Actual Error Message :" + actualErrorMessage);
return actualErrorMessage;
}
@Step("Click Forget Password Link")
public void clickForgetPasswordLink() {
linkText.click();
System.out.println("Clicked on Forgot Password Link");
}
}
StepDashboardPage
import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.containsString;
import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
import net.serenitybdd.annotations.Step;
import net.serenitybdd.core.annotations.findby.FindBy;
import net.serenitybdd.core.pages.PageObject;
import net.serenitybdd.core.pages.WebElementFacade;
public class StepDashboardPage extends PageObject {
@FindBy(xpath = "//*[@id='app']/div[1]/div[1]/header/div[1]/div[1]/span/h6")
WebElementFacade dashboardText;
@Step("Successful login")
public void loginVerify() {
String dashboardTitle = dashboardText.getText();
assertThat(dashboardTitle, containsString("Dashboard"));
}
}
StepForgetPasswordPage
import net.serenitybdd.annotations.Step;
import net.serenitybdd.core.annotations.findby.FindBy;
import net.serenitybdd.core.pages.PageObject;
import net.serenitybdd.core.pages.WebElementFacade;
public class StepForgetPasswordPage extends PageObject {
@FindBy(xpath = "//*[@id='app']/div[1]/div[1]/div/form/h6")
WebElementFacade forgetLink;
@Step("Verify Forget Password Page ")
public boolean ForgetPasswordPage() {
Boolean resetPasswordButton = forgetLink.isDisplayed();
return resetPasswordButton;
}
}
Step 11 – Create a Serenity-Cucumber Runner class
Cucumber runs the feature files via JUnit and needs a dedicated test runner class to actually run the feature files. When you run the tests with Serenity, you use the CucumberWithSerenity test runner. You also need to use the @CucumberOptions class to provide the root directory where the feature files can be found.
import static io.cucumber.junit.platform.engine.Constants.GLUE_PROPERTY_NAME;
import static io.cucumber.junit.platform.engine.Constants.PLUGIN_PROPERTY_NAME;
import org.junit.platform.suite.api.ConfigurationParameter;
import org.junit.platform.suite.api.IncludeEngines;
import org.junit.platform.suite.api.SelectClasspathResource;
import org.junit.platform.suite.api.Suite;
@Suite
@IncludeEngines("cucumber")
@SelectClasspathResource("/features")
@ConfigurationParameter(key = GLUE_PROPERTY_NAME, value = "com.example.SerenityCucumberJunit5Demo.definitions")
@ConfigurationParameter(key = PLUGIN_PROPERTY_NAME, value = "io.cucumber.core.plugin.SerenityReporterParallel,pretty,timeline:build/test-results/timeline")
public class SerenityRunnerTest {
}
Step 12 – Create serenity.conf file under src/test/resources
The serenity configuration file is used to configure the drivers so the test cases can run successfully. This file contains an operating system-specific binary. The binary file sits between your test and the browser. It acts as an intermediary, an interface between your tests and the browser you are using.
You can also configure the webdriver.base.url property for different environments in the serenity.conf configuration file.
headless.mode = false
webdriver {
driver = chrome
capabilities {
browserName = "chrome"
acceptInsecureCerts = true
"goog:chromeOptions" {
args = ["remote-allow-origins=*","test-type", "no-sandbox", "ignore-certificate-errors", "--window-size=1000,800",
"incognito", "disable-infobars", "disable-gpu", "disable-default-apps", "disable-popup-blocking",
"disable-dev-shm-usage", "disable-extensions", "disable-web-security", "disable-translate", "disable-logging"]
}
}
}
#
# Define drivers for different platforms. Serenity will automatically pick the correct driver for the current platform
#
environments {
default {
webdriver.base.url = "https://opensource-demo.orangehrmlive.com/"
}
dev {
webdriver.base.url = "https://opensource-demo.orangehrmlive.com/dev"
}
staging {
webdriver.base.url = "https://opensource-demo.orangehrmlive.com/staging"
}
prod {
webdriver.base.url = "https://opensource-demo.orangehrmlive.com/prod"
}
}
Step 13 – Create serenity.properties file at the root of the project
serenity.project.name = Serenity and Cucumber and JUnit5 Demo
Step 14 – Run the tests from Command Line
Open the command line and go to the location where pom.xml of the project is present and type the below command.
mvn clean verify
Step 15 – Test Execution Status

The image displayed above shows the execution status.
The feature file contains 3 test cases. Test Case 2 is a Test Scenario that has 4 examples. So, in total we have 6 tests. This information is clearly mentioned in the new version of Serenity.
Step 16 – Serenity Report Generation
The best part about Serenity is the report generation by it. The Reports contain all possible types of information, you can think of with minimal extra effort. There are multiple types of reports are generated. We are interested in index.html and serenity-summary.html. To know more about Serenity Reports, please refer to tutorials for Index.html and Serenity-Summary.html. Below is the new Serenity Report.
- index.html

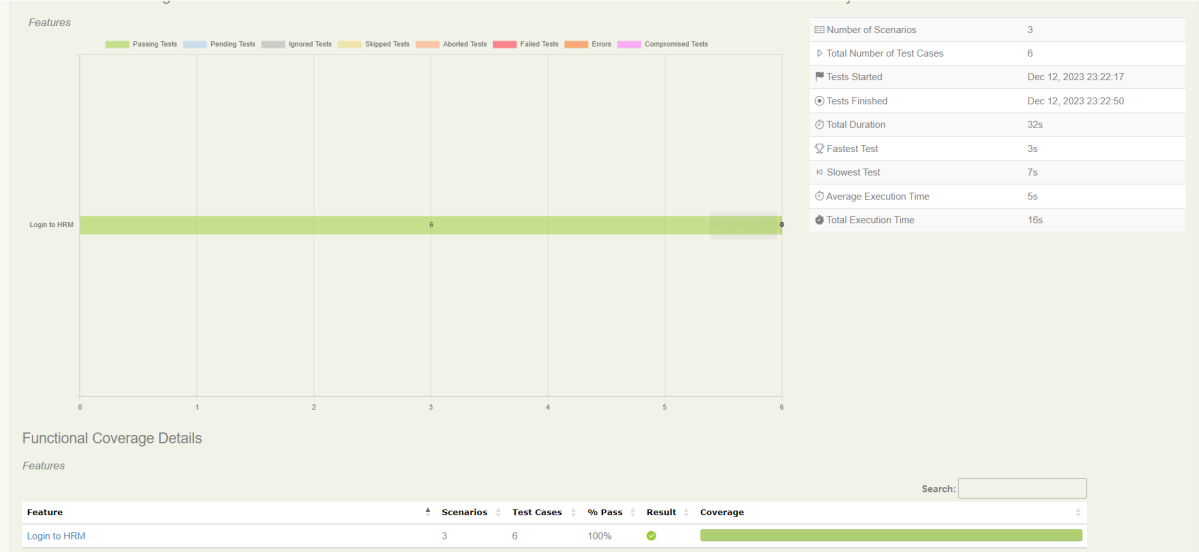
2. serenity-summary.html

Step 17 – Cucumber Report Generation (Optional)

Every Test Execution generates a Cucumber Report (Version 6.7.0) and above as shown in the image.
Copy the URL and paste it to a browser and it shows the report as shown below:

To know more about Cucumber Reports, refer to this tutorial.
We are done! Congratulations on making it through this tutorial and hope you found it useful! Happy Learning!!
Extent Reports Version 5 for Cucumber7 and JUnit5
The previous tutorial explained the steps to generate ExtentReports Version for Cucumber7 with TestNG. This tutorial explains the steps needed to be followed to generate an ExtentReports Version5 for Cucumber 7 with JUnit5.
Table of Contents
Prerequisite:
- Java 17
- Maven or Gradle
- JAVA IDE (like Eclipse, IntelliJ, or so on)
- Cucumber Eclipse plugin (in case using Eclipse)
Project Structure
There is a tutorial that explains the steps to integrate Cucumber 7 with JUnit5. Please refer to this tutorial – Integration of Cucumber7 with Selenium and JUnit5.
Now, let us add the extra steps needed to generate the ExtentRport Version5.
New Features in ExtentReports Version 5
Report Attachments
To add attachments, like screen images, two settings need to be added to the extent.properties. Firstly property, named screenshot.dir, is the directory where the attachments are stored. Secondly is screenshot.rel.path, which is the relative path from the report file to the screenshot directory.
extent.reporter.spark.out=Reports/Spark.html
screenshot.dir=/Screenshots/
screenshot.rel.path=../Screenshots/
Extent PDF Reporter
The PDF reporter summarizes the test run results in a dashboard and other sections with the feature, scenario, and, step details. The PDF report needs to be enabled in the extent.properties file.
#PDF Report
extent.reporter.pdf.start=true
extent.reporter.pdf.out=PdfReport/ExtentPdf.pdf
Ported HTML Reporter
The original HTML Extent Reporter was deprecated in 4.1.3 and removed in 5.0.0. The HTML report available in the adapter is based on the same code base and is similar in appearance. The major changes are in the Freemarker template code which has been modified to work with the Extent Reports version 5. The HTML report needs to be enabled in the extent.properties file.
#HTML Report
extent.reporter.html.start=true
extent.reporter.html.out=HtmlReport/ExtentHtml.html
Customized Report Folder Name
To enable the report folder name with date and\or time details, two settings need to be added to the extent.properties. These are basefolder.name and basefolder.datetimepattern. These will be merged to create the base folder name, inside which the reports will be generated.
#FolderName
basefolder.name=ExtentReports/SparkReport_
basefolder.datetimepattern=d_MMM_YY HH_mm_ss
Attach Image as Base64 String
This feature can be used to attach images to the Spark report by setting the src attribute of the img tag to a Base64 encoded string of the image. When this feature is used, no physical file is created. There is no need to modify any step definition code to use this. To enable this, use the below settings in extent.properties, which is false by default.
extent.reporter.spark.base64imagesrc=true
Environment or System Info Properties
It is now possible to add environment or system info properties in the extent.properties or pass them in the maven command line.
#System Info
systeminfo.os=windows
systeminfo.version=10
As mentioned above, refer to this tutorial.
Implementation Steps
Step 1 – Add Maven dependencies to the POM
Add ExtentReport dependency
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aventstack</groupId>
<artifactId>extentreports</artifactId>
<version>5.1.1</version>
</dependency>
Add tech grasshopper maven dependency for Cucumber.
<dependency>
<groupId>tech.grasshopper</groupId>
<artifactId>extentreports-cucumber7-adapter</artifactId>
<version>1.14.0</version>
</dependency>
The complete POM.xml will look like as shown below with other Selenium and JUnit5 dependencies.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>ExtentReports5CucumberJUnit5</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>ExtentReports5CucumberJUnit5</name>
<!-- FIXME change it to the project's website -->
<url>http://www.example.com</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<cucumber.version>7.14.0</cucumber.version>
<selenium.version>4.15.0</selenium.version>
<junit.jupiter.version>5.10.1</junit.jupiter.version>
<extentreports.cucumber7.adapter.version>1.14.0</extentreports.cucumber7.adapter.version>
<extentreports.version>5.1.1</extentreports.version>
<maven.compiler.plugin.version>3.11.0</maven.compiler.plugin.version>
<maven.surefire.plugin.version>3.2.1</maven.surefire.plugin.version>
<maven.compiler.source.version>17</maven.compiler.source.version>
<maven.compiler.target.version>17</maven.compiler.target.version>
</properties>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.cucumber</groupId>
<artifactId>cucumber-bom</artifactId>
<version>${cucumber.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-bom</artifactId>
<version>${junit.jupiter.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.cucumber</groupId>
<artifactId>cucumber-java</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.cucumber</groupId>
<artifactId>cucumber-junit-platform-engine</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- JUnit Platform -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.platform</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-platform-suite</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-engine</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Selenium -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.seleniumhq.selenium</groupId>
<artifactId>selenium-java</artifactId>
<version>${selenium.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Cucumber ExtentReport Adapter -->
<dependency>
<groupId>tech.grasshopper</groupId>
<artifactId>extentreports-cucumber7-adapter</artifactId>
<version>${extentreports.cucumber7.adapter.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Extent Report -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aventstack</groupId>
<artifactId>extentreports</artifactId>
<version>${extentreports.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.compiler.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<source>${maven.compiler.source.version}</source>
<target>${maven.compiler.target.version}</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.surefire.plugin.version}</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-engine</artifactId>
<version>${junit.jupiter.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Step 2 – Create extent.properties file in src/test/resources
We need to create the extent.properties file in the src/test/resources folder for the grasshopper extent report adapter to recognize it. Using a property file for reporting is quite helpful if you want to define several different properties.
#Extent Report
extent.reporter.spark.start=true
extent.reporter.spark.out=Reports/Spark.html
#PDF Report
extent.reporter.pdf.start=true
extent.reporter.pdf.out=PdfReport/ExtentPdf.pdf
#HTML Report
extent.reporter.html.start=true
extent.reporter.html.out=HtmlReport/ExtentHtml.html
#FolderName
basefolder.name=ExtentReports/SparkReport_
basefolder.datetimepattern=d_MMM_YY HH_mm_ss
#Screenshot
screenshot.dir=/Screenshots/
screenshot.rel.path=../Screenshots/
#Base64
extent.reporter.spark.base64imagesrc=true
#System Info
systeminfo.os=windows
systeminfo.version=10
Step 3 – Create a Cucumber Test Runner class in src/test/java
Add the extent report cucumber adapter to the runner class.
import static io.cucumber.junit.platform.engine.Constants.GLUE_PROPERTY_NAME;
import static io.cucumber.junit.platform.engine.Constants.PLUGIN_PROPERTY_NAME;
import org.junit.platform.suite.api.ConfigurationParameter;
import org.junit.platform.suite.api.IncludeEngines;
import org.junit.platform.suite.api.SelectClasspathResource;
import org.junit.platform.suite.api.Suite;
@Suite
@IncludeEngines("cucumber")
@SelectClasspathResource("features")
@SelectClasspathResource("com.example")
@ConfigurationParameter(key = PLUGIN_PROPERTY_NAME, value = "com.aventstack.extentreports.cucumber.adapter.ExtentCucumberAdapter:")
@ConfigurationParameter(key = GLUE_PROPERTY_NAME, value = "com.example")
public class CucumberRunnerTests {
}
Step 4 – Execute the code
To execute the code, run the tests from the command line by using the below command
mvn clean test
The output of the above program is
Step 5 – View ExtentReport
Refresh the project and will see a new folder – SparkReport_ which further contains 4 folders – HtmlReport, PdfReport, Reports, and Screenshots.
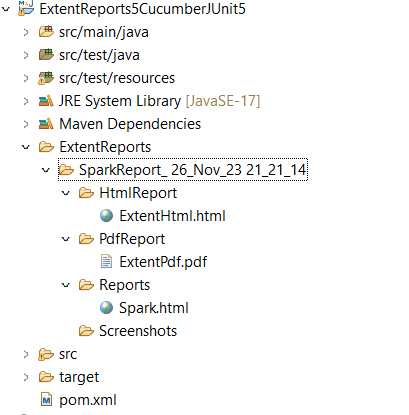
The ExtentReport will be present in the Reports folder with the name Spark.html. PDF Report is present in the PdfReport folder and HTML Report is present in the HtmlReport folder. We can see that the Screenshots folder is empty because we have used the base64imagesrc feature which resulted in no physical screenshots. The screenshots are embedded in the reports.
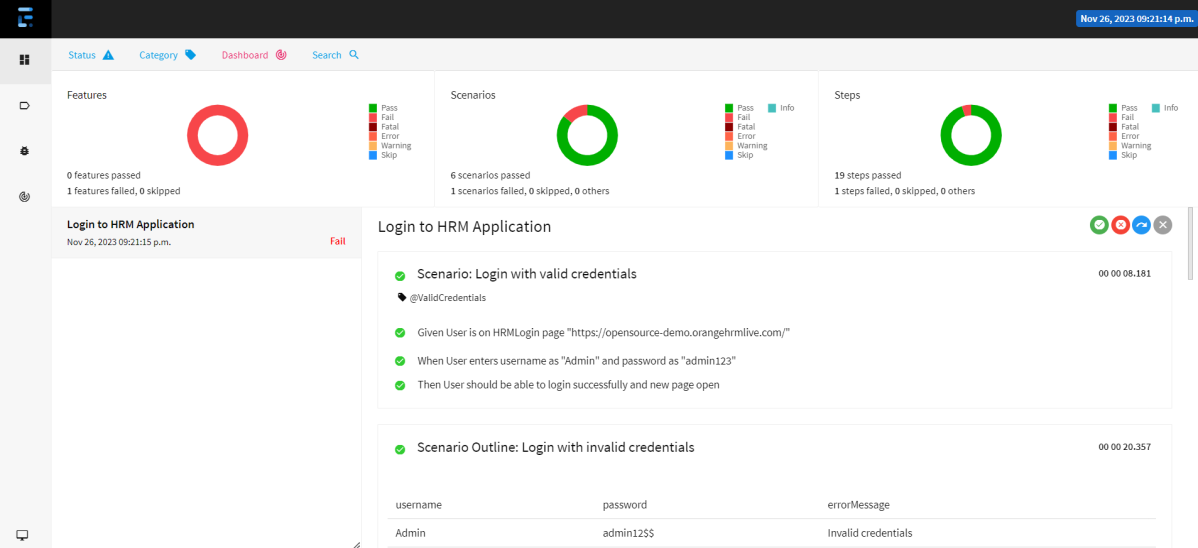
Right-click and open the ExtentHtml.html report with Web Browser. The report also has a summary section that displays the summary of the execution. The summary includes the overview of the pass/fail using a pictogram, start time, end time, and pass/fail details of features as shown in the image below.
ExtentHtml
This is the image of the Dashboard of the ExtentReport.
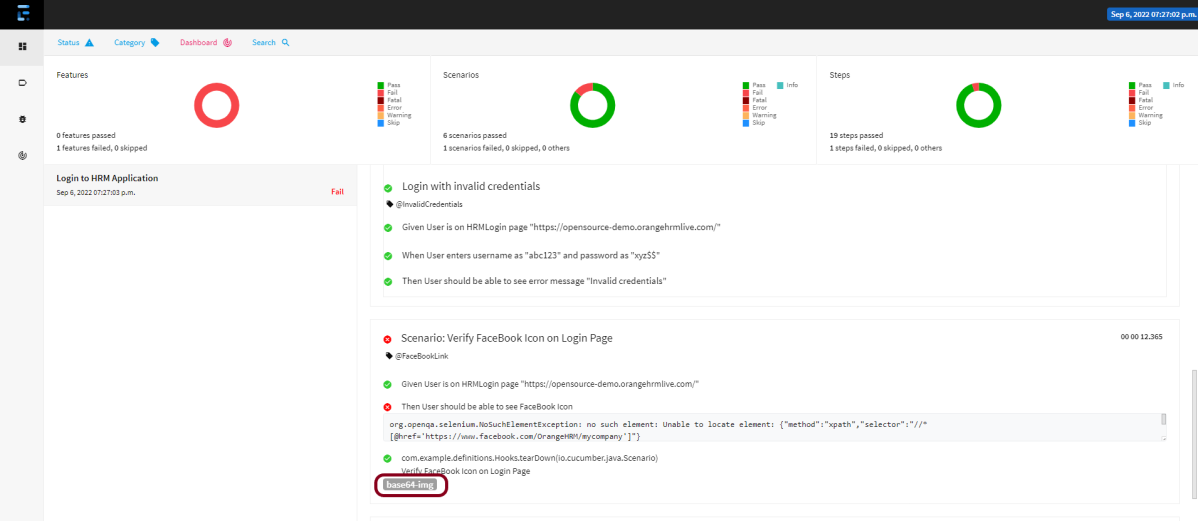
The failed test has a screenshot embedded in it. Double-click on base64 image and it will open the screenshot in full screen.

PDF Report
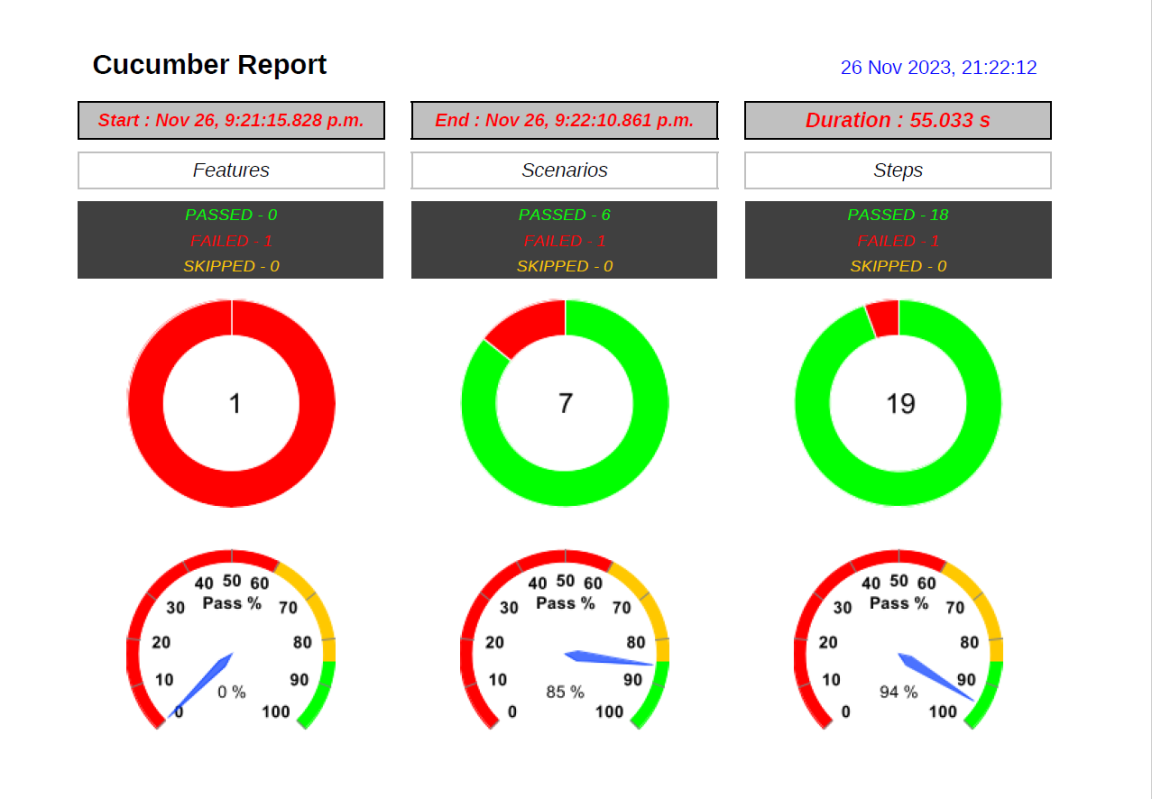
Spark Report
Right-click and open the Spark.html report with Web Browser.
The complete code can be found on GitHub.
We are done! Congratulations on making it through this tutorial and hope you found it useful! Happy Learning!!
Advance Selenium Tutorials
If you are planning to learn Selenium WebDriver and if you have completed Basic Selenium tutorial, then you can start Advanced Selenium Tutorials which will talk about different frameworks, tools integration, external data reading from different sources, and so on.
Handling Excels
| Chapter 1 How to download and install Apache POI | |
| Chapter 2 Reading Excel Data with Apache POI in Java | |
| Chapter 3 How to Write Data to Excel File in Java using Apache POI | |
| Chapter 4 How to update existing excel in Java | |
| Chapter 5 Change Font Style in Excel with Apache POI – NEW |
Handling PDFs
| Chapter 1 Download PDF in Chrome with Selenium Java |
| Chapter 2 Download PDF in Firefox with Selenium Java |
| Chapter 3 Download PDF in Edge with Selenium Java |
| Chapter 4 Read PDF Files with Selenium in Java |
| Chapter 5 How to Write in PDF with Selenium and Java |
| Chapter 6 Merge PDF Files in Selenium with Java |
Selenium – Capture Screenshots
Advance Selenium
Docker
| Chapter 1 How to run Selenium 3 on Docker |
Selenium with Cucumber
| Chapter 1 Integration of Cucumber with Selenium and JUnit | |
| Chapter 2 Integration of Cucumber with Selenium and TestNG | |
| Chapter 3 Integration of Cucumber7 with Selenium and JUnit5 |
Selenium with Serenity
Gradle Projects with Selenium
| Chapter 1 How to create Gradle project with Selenium and TestNG | |
| Chapter 2 How to create Gradle project with Selenium and JUnit4 |
Frameworks
Selenium 4
| Chapter 1 New Features in Selenium 4 | |
| Chapter 2 Selenium Tests failing on Chrome Version 111 | |
| Chapter 3 How to run Chrome tests in headless mode in Selenium4 |
Selenium Grid
| Chapter 1 Selenium 4 Grid : How to use Standalone Grid |
| Chapter 2 Selenium 4 Grid – Parallel Testing |
| Chapter 3 Selenium Grid 4 with Docker |
| Chapter 4 Cross Browser Testing with Selenium Grid 4 and Docker |
Reports
| Chapter 1 Integration of Allure Report with Selenium and JUnit4 | |
| Chapter 2 Integration of Allure Report with Selenium and JUnit5 | |
| Chapter 3 Integration of Allure Report with Selenium and TestNG |
Database
| Chapter 1 How to connect to SQL Server using Java |
CI/CD
Basic Selenium Tutorials
Selenium Multiple Choice Questions – MCQ1
Selenium Multiple Choice Questions – MCQ2
Selenium Multiple Choice Questions – MCQ3
Selenium Interview Questions and Answers
Advanced Selenium Interview Questions and Answers
Integration of Cucumber7 with Selenium and JUnit5
I have created a lot of tutorials on creating Test Frameworks by integrating JUnit4 with Selenium, Cucumber, Serenity, Rest API, Springboot. This tutorial explain the steps to Integrate Cucumber7 with JUnit5.
JUnit 5 is composed of several different modules from three different sub-projects.
JUnit 5 = JUnit Platform + JUnit Jupiter + JUnit Vintage
We can use the JUnit Platform to execute Cucumber scenarios.
Add the cucumber-junit-platform-engine dependency to your pom.xml:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.cucumber</groupId>
<artifactId>cucumber-junit-platform-engine</artifactId>
<version>${cucumber.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
This will allow IntelliJ IDEA, Eclipse, Maven, Gradle, etc, to discover, select and execute Cucumber scenarios.
Table of Contents
- Prerequisite
- Dependency List
- Project Structure
- Implementation Steps
- Download and Install Java
- Download and setup Eclipse IDE on the system
- Setup Maven
- Install Cucumber Eclipse Plugin (Only for Eclipse IDE)
- Create a new Maven Project
- Add Maven dependencies to the POM
- Create a feature file in src/test/resources
- Create cucumber.properties file in src/test/resources
- Create a Helper class in src/main/java
- Create Locator classes in src/main/java
- Create Action classes in src/main/java
- Create a Step Definition file in src/test/java
- Create Hook class in src/test/java
- Create a Cucumber Test Runner class in src/test/java
- Run the tests from Maven or Command Line
- Cucumber Report Generation
Prerequisite
- Java Version 17 installed
- Eclipse or IntelliJ installed
- Maven or Gradle installed and setup
- Cucumber Eclipse Plugin installed
Dependency List
- Cucumber – 7.14.0
- Selenium – 4.15.0
- Java – 17
- WebDriverManager – 5.5.3
- Junit Jupiter – 5.10.1
- Maven Compiler – 3.11.0
- Maven Surefire – 3.2.1
Project Structure
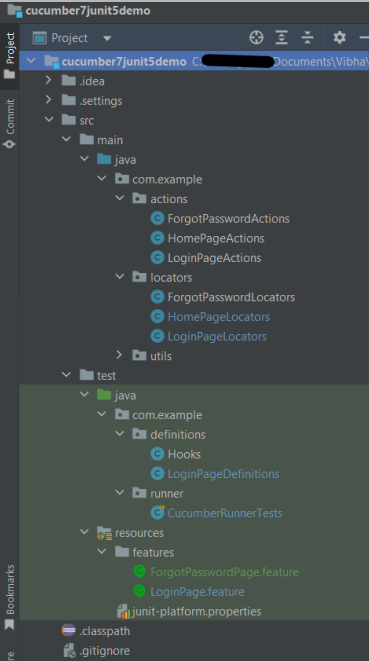
Implementation Steps
Step 1- Download and Install Java
Cucumber and Selenium need Java to be installed on the system to run the tests. Click here to know How to install Java.
Step 2 – Download and setup Eclipse IDE on the system
The Eclipse IDE (integrated development environment) provides strong support for Java developers, which is needed to write Java code. Click here to know How to install Eclipse.
Step 3 – Setup Maven
To build a test framework, we need to add a number of dependencies to the project. It is a very tedious and cumbersome process to add each dependency manually. So, to overcome this problem, we use a build management tool. Maven is a build management tool that is used to define project structure, dependencies, build, and test management. Click here to know How to install Maven.
Step 4 – Install Cucumber Eclipse Plugin (Only for Eclipse IDE)
The Cucumber Eclipse plugin is a plugin that allows eclipse to understand the Gherkin syntax. The Cucumber Eclipse Plugin highlights the keywords present in Feature File. Click here to know more – Install Cucumber Eclipse Plugin.
Step 5 – Create a new Maven Project
Click here to know How to create a Maven project
Below is the Maven project structure. Here,
Group Id – com.example
Artifact Id – Cucumber7JUnit5Demo
Version – 0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
Package – com. example. Cucumber7JUnit5Demo
Step 6 – Add Maven dependencies to the POM
Add the dependencies to the POM.xml.
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>Cucumber7JUnit5Demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<cucumber.version>7.14.0</cucumber.version>
<selenium.version>4.15.0</selenium.version>
<webdrivermanager.version>5.5.3</webdrivermanager.version>
<junit.jupiter.version>5.10.1</junit.jupiter.version>
<maven.compiler.plugin.version>3.11.0</maven.compiler.plugin.version>
<maven.surefire.plugin.version>3.2.1</maven.surefire.plugin.version>
<maven.compiler.source.version>17</maven.compiler.source.version>
<maven.compiler.target.version>17</maven.compiler.target.version>
</properties>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.cucumber</groupId>
<artifactId>cucumber-bom</artifactId>
<version>${cucumber.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-bom</artifactId>
<version>${junit.jupiter.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.cucumber</groupId>
<artifactId>cucumber-java</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.cucumber</groupId>
<artifactId>cucumber-junit-platform-engine</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- JUnit Platform -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.platform</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-platform-suite</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-engine</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Selenium -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.seleniumhq.selenium</groupId>
<artifactId>selenium-java</artifactId>
<version>${selenium.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Web Driver Manager -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.github.bonigarcia</groupId>
<artifactId>webdrivermanager</artifactId>
<version>${webdrivermanager.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.compiler.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<source>${maven.compiler.source.version}</source>
<target>${maven.compiler.target.version}</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.surefire.plugin.version}</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-engine</artifactId>
<version>${junit.jupiter.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Step 7 – Create a feature file in src/test/resources
Below is a sample feature file. Feature file should be saved as an extension of .feature. Add the test scenarios in this feature file. I have added sample test scenarios. The test scenarios are written in Gherkins language.
LoginPage.feature
@LoginPage
Feature: Login to HRM Application
Background:
Given User is on HRMLogin page "https://opensource-demo.orangehrmlive.com/"
@ValidCredentials
Scenario: Login with valid credentials
When User enters username as "Admin" and password as "admin123"
Then User should be able to login successfully and new page open
@InvalidCredentials
Scenario Outline: Login with invalid credentials
When User enters username as "<username>" and password as "<password>"
Then User should be able to see error message "<errorMessage>"
Examples:
| username | password | errorMessage |
| Admin | admin12$$ | Invalid credentials |
| admin$$ | admin123 | Invalid credentials |
| abc123 | xyz$$ | Invalid credentials |
@FaceBookLink
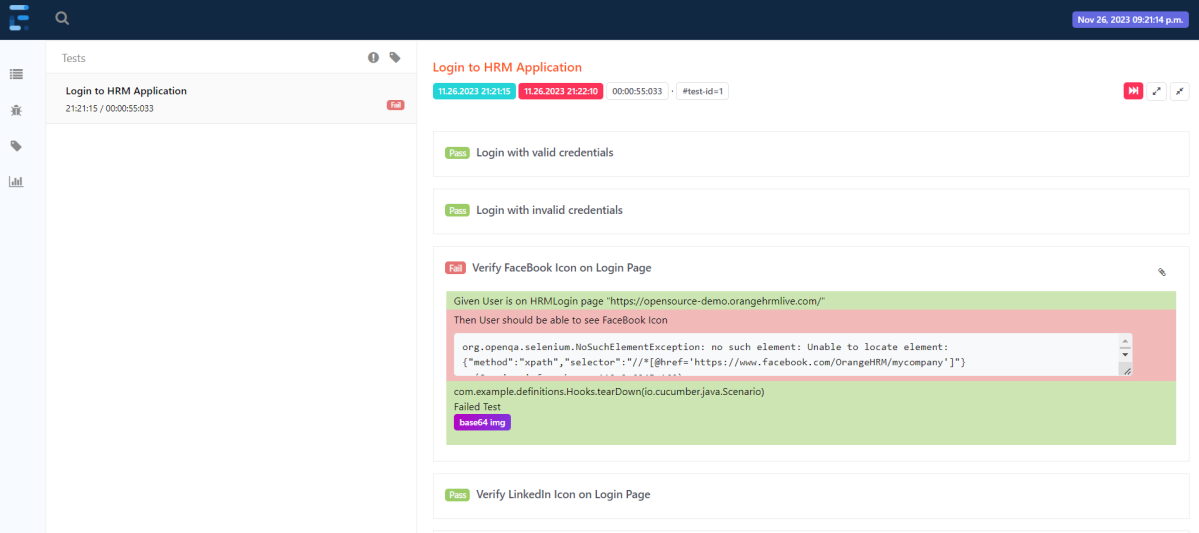
Scenario: Verify FaceBook Icon on Login Page
Then User should be able to see FaceBook Icon
@LinkedInLink
Scenario: Verify LinkedIn Icon on Login Page
Then User should be able to see LinkedIn Icon
ForgetPasswordPage.feature
@ForgetPassword
Feature: Login to ForgotPassword Page
Background:
Given User is on HRMLogin page "https://opensource-demo.orangehrmlive.com/"
@ForgetPasswordLink
Scenario: Verify ForgetPassword link on Login Page
When User clicks on Forgot your Password Link
Then User should navigate to a new page
Step 8 – Create cucumber.properties file in src/test/resources
We need to create the junit-platform.properties file in the src/test/resources folder. Using a property file for reporting is quite helpful if you want to define several different properties.
cucumber.publish.enabled=true
Step 9 – Create a Helper class in src/main/java
We have used Page Object Model with Cucumber and TestNG. Create a Helper class where we are initializing the web driver, initializing the web driver wait, defining the timeouts, and creating a private constructor of the class, it will declare the web driver, so whenever we create an object of this class, a new web browser is invoked.
import java.time.Duration;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import io.github.bonigarcia.wdm.WebDriverManager;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeOptions;
public class HelperClass {
private static HelperClass helperClass;
private static WebDriver driver;
public final static int TIMEOUT = 5;
private HelperClass() {
WebDriverManager.chromedriver().setup();
ChromeOptions options = new ChromeOptions();
options.addArguments("--start-maximized");
driver = new ChromeDriver(options);
driver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(Duration.ofSeconds(TIMEOUT));
}
public static void openPage(String url) {
driver.get(url);
}
public static WebDriver getDriver() {
return driver;
}
public static void setUpDriver() {
if (helperClass==null) {
helperClass = new HelperClass();
}
}
public static void tearDown() {
if(driver!=null) {
driver.quit();
}
helperClass = null;
}
}
Step 10 – Create Locator classes in src/main/java
Create a locator class for each page that contains the detail of the locators of all the web elements. Here, I’m creating 3 locator classes – LoginPageLocators, HomePageLocators, and ForgotPasswordLocators.
LoginPageLocators
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.FindBy;
public class LoginPageLocators {
@FindBy(name = "username")
public WebElement userName;
@FindBy(name = "password")
public WebElement password;
@FindBy(id = "logInPanelHeading")
public WebElement titleText;
@FindBy(xpath = "//*[@id='app']/div[1]/div/div[1]/div/div[2]/div[2]/form/div[3]/button")
public WebElement login;
@FindBy(xpath = "//*[@id='app']/div[1]/div/div[1]/div/div[2]/div[2]/div/div[1]/div[1]/p")
public WebElement errorMessage;
@FindBy(xpath = "//*[@href='https://www.linkedin.com/company/orangehrm/mycompany/']")
public WebElement linkedInIcon;
@FindBy(xpath = "//*[@href='https://www.facebook.com/OrangeHRM/']")
public WebElement faceBookIcon;
@FindBy(xpath = "//*[@id='app']/div[1]/div/div[1]/div/div[2]/div[2]/form/div[4]/p")
public WebElement ForgotYourPasswordLink;
}
HomePageLocators
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.FindBy;
public class HomePageLocators {
@FindBy(xpath = "//*[@id='app']/div[1]/div[2]/div[2]/div/div[1]/div[1]/div[1]/h5")
public WebElement homePageUserName;
}
ForgotPasswordLocators
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.FindBy;
public class ForgotPasswordLocators {
@FindBy(xpath = "//*[@id='app']/div[1]/div[1]/div/form/h6")
public WebElement ForgotPasswordHeading;
}
Step 11 – Create Action classes in src/main/java
Create the action classes for each web page. These action classes contain all the methods needed by the step definitions. In this case, I have created 2 action classes – LoginPageActions, HomePageActions, and ForgotPasswordActions.
LoginPageActions
In this class, the very first thing will do is to create the object of the LoginPageLocators class so that we should be able to access all the PageFactory elements. Secondly, create a public constructor of LoginPageActions class.
import org.openqa.selenium.support.PageFactory;
import com.example.locators.LoginPageLocators;
import com.example.utils.HelperClass;
public class LoginPageActions {
LoginPageLocators loginPageLocators = null;
public LoginPageActions() {
this.loginPageLocators = new LoginPageLocators();
PageFactory.initElements(HelperClass.getDriver(),loginPageLocators);
}
// Set user name in textbox
public void setUserName(String strUserName) {
loginPageLocators.userName.sendKeys(strUserName);
}
// Set password in password textbox
public void setPassword(String strPassword) {
loginPageLocators.password.sendKeys(strPassword);
}
// Click on login button
public void clickLogin() {
loginPageLocators.login.click();
}
// Get the title of Login Page
public String getLoginTitle() {
return loginPageLocators.titleText.getText();
}
// Get the title of Login Page
public String getErrorMessage() {
return loginPageLocators.errorMessage.getText();
}
// LinkedIn Icon is displayed
public Boolean getLinkedInIcon() {
return loginPageLocators.linkedInIcon.isDisplayed();
}
// FaceBook Icon is displayed
public Boolean getFaceBookIcon() {
return loginPageLocators.faceBookIcon.isDisplayed();
}
// Click on Forget Your Password link
public void clickOnForgetYourPasswordLink() {
loginPageLocators.ForgotYourPasswordLink.click();
}
public void login(String strUserName, String strPassword) {
// Fill user name
this.setUserName(strUserName);
// Fill password
this.setPassword(strPassword);
// Click Login button
this.clickLogin();
}
}
HomePageActions
import org.openqa.selenium.support.PageFactory;
import com.example.locators.HomePageLocators;
import com.example.utils.HelperClass;
public class HomePageActions {
HomePageLocators homePageLocators = null;
public HomePageActions() {
this.homePageLocators = new HomePageLocators();
PageFactory.initElements(HelperClass.getDriver(),homePageLocators);
}
// Get the User name from Home Page
public String getHomePageText() {
return homePageLocators.homePageUserName.getText();
}
}
ForgotPasswordActions
import org.openqa.selenium.support.PageFactory;
import com.example.locators.ForgotPasswordLocators;
import com.example.utils.HelperClass;
public class ForgotPasswordActions {
ForgotPasswordLocators forgotPasswordLocators = null;
public ForgotPasswordActions() {
this.forgotPasswordLocators = new ForgotPasswordLocators();
PageFactory.initElements(HelperClass.getDriver(),forgotPasswordLocators);
}
// Get the Heading of Forgot Password page
public String getForgotPasswordPageText() {
return forgotPasswordLocators.ForgotPasswordHeading.getText();
}
}
Step 12 – Create a Step Definition file in src/test/java
Create the corresponding Step Definition file of the feature file.
LoginPageDefinitions
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions;
import com.example.actions.ForgotPasswordActions;
import com.example.actions.HomePageActions;
import com.example.actions.LoginPageActions;
import com.example.utils.HelperClass;
import io.cucumber.java.en.Given;
import io.cucumber.java.en.Then;
import io.cucumber.java.en.When;
public class LoginPageDefinitions{
LoginPageActions objLogin = new LoginPageActions();
HomePageActions objHomePage = new HomePageActions();
ForgotPasswordActions objForgotPasswordPage = new ForgotPasswordActions();
@Given("User is on HRMLogin page {string}")
public void loginTest(String url) {
HelperClass.openPage(url);
}
@When("User enters username as {string} and password as {string}")
public void goToHomePage(String userName, String passWord) {
// login to application
objLogin.login(userName, passWord);
// go the next page
}
@When("User clicks on Forgot your Password Link")
public void goToForgotYourPasswordPage() {
objLogin.clickOnForgetYourPasswordLink();
}
@Then("User should be able to login sucessfully and new page open")
public void verifyLogin() {
// Verify home page
Assertions.assertTrue(objHomePage.getHomePageText().contains("Employee Information"));
}
@Then("User should be able to see error message {string}")
public void verifyErrorMessage(String expectedErrorMessage) {
// Verify home page
Assertions.assertEquals(objLogin.getErrorMessage(),expectedErrorMessage);
}
@Then("User should be able to see LinkedIn Icon")
public void verifyLinkedInIcon( ) {
Assertions.assertTrue(objLogin.getLinkedInIcon());
}
@Then("User should be able to see FaceBook Icon")
public void verifyFaceBookIcon( ) {
Assertions.assertTrue(objLogin.getFaceBookIcon());
}
@Then("User should navigate to a new page")
public void verfiyForgetYourPasswordPage() {
Assertions.assertEquals(objForgotPasswordPage.getForgotPasswordPageText(), "Reset Password");
}
}
Step 13 – Create Hook class in src/test/java
Create the hook class that contains the Before and After hook to initialize the web browser and close the web browser.
import org.openqa.selenium.OutputType;
import org.openqa.selenium.TakesScreenshot;
import com.example.utils.HelperClass;
import io.cucumber.java.After;
import io.cucumber.java.Before;
import io.cucumber.java.Scenario;
public class Hooks {
@Before
public static void setUp() {
HelperClass.setUpDriver();
}
@After
public static void tearDown(Scenario scenario) {
//validate if scenario has failed
if(scenario.isFailed()) {
final byte[] screenshot = ((TakesScreenshot) HelperClass.getDriver()).getScreenshotAs(OutputType.BYTES);
scenario.attach(screenshot, "image/png", scenario.getName());
}
HelperClass.tearDown();
}
}
Step 14 – Create a Cucumber Test Runner class in src/test/java
Cucumber needs a TestRunner class to run the feature files. It is suggested to create a folder with the name of the runner in the src/test/java directory and create the Cucumber TestRunner class in this folder. Below is the code of the Cucumber TestRunner class.
import static io.cucumber.junit.platform.engine.Constants.GLUE_PROPERTY_NAME;
import org.junit.platform.suite.api.ConfigurationParameter;
import org.junit.platform.suite.api.IncludeEngines;
import org.junit.platform.suite.api.SelectClasspathResource;
import org.junit.platform.suite.api.Suite;
@Suite
@IncludeEngines("cucumber")
@SelectClasspathResource("com.example")
@ConfigurationParameter(key = GLUE_PROPERTY_NAME, value = "com.example")
public class CucumberRunnerTests {
}
Step 15 – Run the tests from Maven or Command Line
Use the below command to run the tests.
mvn clean verify

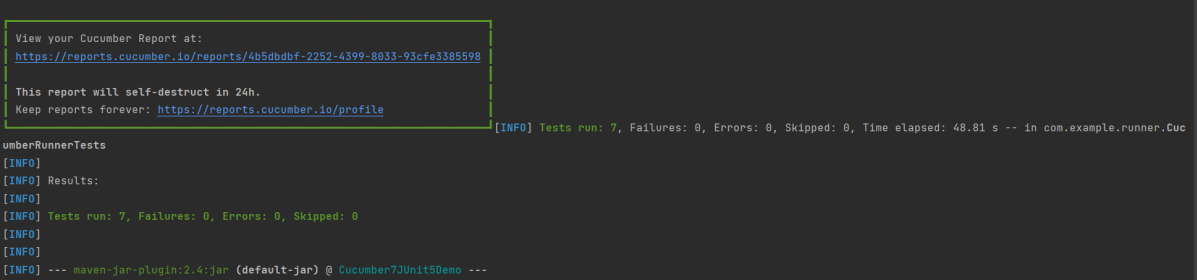
Step 16 – Cucumber Report Generation
Below is the image of the Cucumber Report generated using the Cucumber Service.
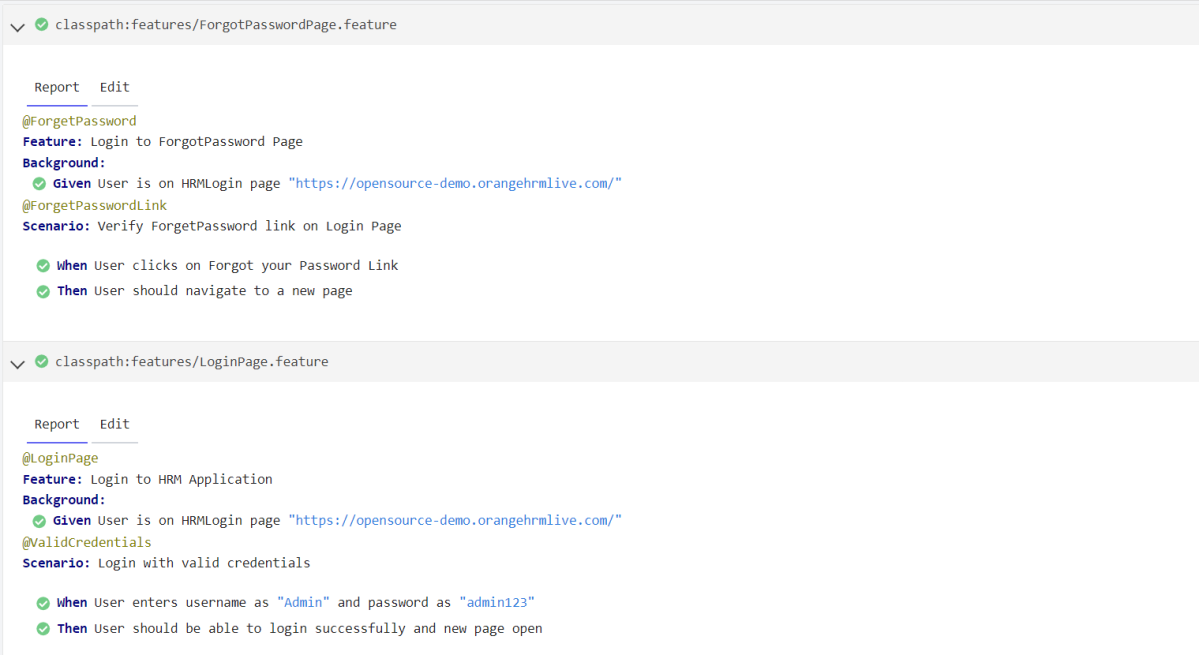
Below is the image of the Cucumber Report.

The complete code can be found on GitHub.
Congratulations!! We have built the framework using Cucumber 7 with JUnit5.
Parallel Execution of Cucumber with Serenity and JUnit5
In the previous tutorial, I explained the Serenity BDD with Cucumber for Web Application using Junit4. In this tutorial, I will explain the parallel execution of Cucumber Scenarios with Serenity and JUnit5. This tutorial gives a clear picture of the initial setup of a BDD Framework.
Starting with version 3.6.0 is possible to run the Cucumber scenarios in parallel.
We need to mention these in the junit-platform.properties to run the Cucumber scenarios parallelly.
cucumber.execution.parallel.enabled=true
cucumber.execution.parallel.config.strategy=fixed
cucumber.execution.parallel.config.fixed.parallelism=2
cucumber.plugin=io.cucumber.core.plugin.SerenityReporterParallel
Table of Contents
- Dependency List
- Project Structure
- Implementation Steps
- Download and Install Java
- Download and setup Eclipse IDE on the system
- Setup Maven and create a new Maven Project
- Update Properties section in Maven pom.xml
- Add dependencies to POM.xml
- Update the Build Section of pom.xml
- Create a feature file in src/test/resources
- Create the Step pages for StepDefinition class
- Create the Step Definition class or Glue Code
- Create a Serenity-Cucumber Runner class
- Create cucumber.properties file under src/test/resources (optional)
- Create junit-platform.properties in src/test/resources
- Create serenity.conf file under src/test/resources
- Create serenity.properties file at the root of the project
- Run the tests from Command Line
- Run the tests from CucumberRunner
- Serenity Report Generation
Dependency List:
- Serenity – 4.0.18
- Serenity Cucumber – 4.0.18
- JUnit Jupiter – 5.9.2
- Java 17
- Maven – 3.8.1
- Maven Compiler Plugin – 3.11.0
- Maven Surefire Plugin – 3.2.1
- Maven FailSafe Plugin – 3.2.1
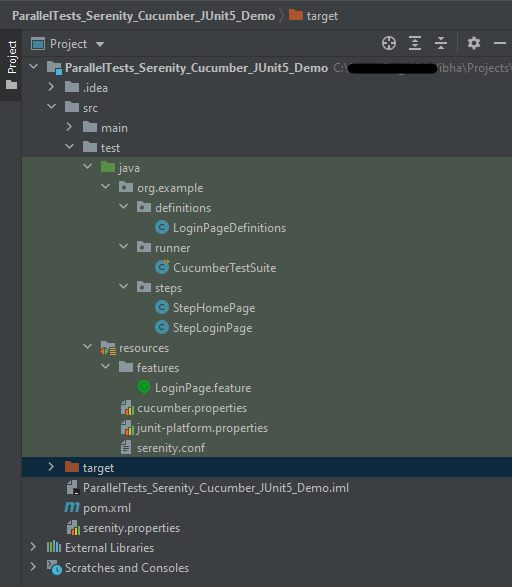
Project Structure
Implementation Steps
Step 1- Download and Install Java
Click here to know How to install Java.
Step 2 – Download and setup Eclipse IDE on the system
The Eclipse IDE (integrated development environment) provides strong support for Java developers which is needed to write Java code. Click here to know How to install Eclipse.
Step 3 – Setup Maven and create a new Maven Project
Click here to know How to install Maven.
Click here to know How to create a Maven project
Below is the Maven project structure. Here,
Group Id – org.example
Artifact Id – ParallelTests_Serenity_Cucumber_Junit5_Demo
Version – 0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
Package – org.example. ParallelTests_Serenity_Cucumber_Junit5_Demo
Step 4 – Update Properties section in Maven pom.xml
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<serenity.version>4.0.18</serenity.version>
<serenity.cucumber.version>4.0.18</serenity.cucumber.version>
<junit.platform.version>1.10.0</junit.platform.version>
<cucumber.version>7.14.0</cucumber.version>
<maven.compiler.plugin.version>3.11.0</maven.compiler.plugin.version>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
<maven.surefire.plugin.version>3.2.1</maven.surefire.plugin.version>
<maven.failsafe.plugin.version>3.2.1</maven.failsafe.plugin.version>
</properties>
Step 5 – Add dependencies to POM.xml
Add Serenity, Serenity-Cucumber, and JUnit5 dependencies to POM.xml
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.serenity-bdd</groupId>
<artifactId>serenity-core</artifactId>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.serenity-bdd</groupId>
<artifactId>serenity-junit5</artifactId>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.serenity-bdd</groupId>
<artifactId>serenity-screenplay</artifactId>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.serenity-bdd</groupId>
<artifactId>serenity-cucumber</artifactId>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.cucumber</groupId>
<artifactId>cucumber-junit-platform-engine</artifactId>
<version>${cucumber.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.platform</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-platform-suite</artifactId>
<version>${junit.platform.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Step 6 – Update the Build Section of pom.xml
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.surefire.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<skip>true</skip>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-failsafe-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.failsafe.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<includes>
<include>**/*.java</include>
</includes>
<parallel>methods</parallel>
<useUnlimitedThreads>true</useUnlimitedThreads>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>integration-test</goal>
<goal>verify</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.compiler.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<source>${maven.compiler.source}</source>
<target>${maven.compiler.target}</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>net.serenity-bdd.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>serenity-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.serenity-bdd</groupId>
<artifactId>serenity-single-page-report</artifactId>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<configuration>
<reports>single-page-html</reports>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>serenity-reports</id>
<phase>post-integration-test</phase>
<goals>
<goal>aggregate</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
The complete POM.xml looks like as shown below:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>ParallelTests_Serenity_Cucumber_JUnit5_Demo</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<serenity.version>4.0.18</serenity.version>
<serenity.cucumber.version>4.0.18</serenity.cucumber.version>
<junit.platform.version>1.10.0</junit.platform.version>
<cucumber.version>7.14.0</cucumber.version>
<maven.compiler.plugin.version>3.11.0</maven.compiler.plugin.version>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
<maven.surefire.plugin.version>3.2.1</maven.surefire.plugin.version>
<maven.failsafe.plugin.version>3.2.1</maven.failsafe.plugin.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.serenity-bdd</groupId>
<artifactId>serenity-core</artifactId>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.serenity-bdd</groupId>
<artifactId>serenity-junit5</artifactId>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.serenity-bdd</groupId>
<artifactId>serenity-screenplay</artifactId>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.serenity-bdd</groupId>
<artifactId>serenity-cucumber</artifactId>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.cucumber</groupId>
<artifactId>cucumber-junit-platform-engine</artifactId>
<version>${cucumber.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.platform</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-platform-suite</artifactId>
<version>${junit.platform.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.surefire.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<skip>true</skip>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-failsafe-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.failsafe.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<includes>
<include>**/*.java</include>
</includes>
<parallel>methods</parallel>
<useUnlimitedThreads>true</useUnlimitedThreads>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>integration-test</goal>
<goal>verify</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.compiler.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<source>${maven.compiler.source}</source>
<target>${maven.compiler.target}</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>net.serenity-bdd.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>serenity-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.serenity-bdd</groupId>
<artifactId>serenity-single-page-report</artifactId>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<configuration>
<reports>single-page-html</reports>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>serenity-reports</id>
<phase>post-integration-test</phase>
<goals>
<goal>aggregate</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Step 7 – Create a feature file in src/test/resources
The purpose of the Feature keyword is to provide a high-level description of a software feature and to group related scenarios. To know more about the Feature files, please refer this tutorial.
Feature: Login to HRM
@ValidCredentials
Scenario: Login with valid credentials
Given User is on Home page
When User enters username as "Admin"
And User enters password as "admin123"
Then User should be able to login successfully
@InValidCredentials
Scenario: Login with invalid credentials
Given User is on Home page
When User enters username as "Admin1"
And User enters password as "Admin123"
Then User should be able to see error message "Invalid credentials"
@BlankUsername
Scenario: Login with blank username
Given User is on Home page
When User enters username as ""
And User enters password as "Admin123"
Then User should be able to see error message "Required" below username
Step 8 – Create the Step pages for StepDefinition class
In Serenity, tests are broken down into reusable steps. An important principle behind Serenity is the idea that it is easier to maintain a test that uses several layers of abstraction to hide the complexity behind different parts of a test. So, in Step class, we will declare the locators of the web elements and the actions performed on these web elements.
There are multiple ways to identify a web element on the web page – one of the ways is to use @FindBy or $(By.).
I prefer to use @FindBy as I do need not to find the same element multiple times. Using @FindBy, I have identified a web element and defined a WebElementFacacde for the same which is reusable.
StepLoginPage
import net.serenitybdd.core.pages.PageObject;
import net.serenitybdd.core.pages.WebElementFacade;
import net.thucydides.core.annotations.Step;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.FindBy;
public class StepLoginPage extends PageObject {
@FindBy(name = "username")
WebElementFacade username;
@FindBy(name = "password")
WebElementFacade password;
@FindBy(xpath = "//*[@id='app']/div[1]/div/div[1]/div/div[2]/div[2]/form/div[3]/button")
WebElementFacade submitButton;
@FindBy(xpath = "//*[@id='app']/div[1]/div/div[1]/div/div[2]/div[2]/div/div[1]/div[1]/p")
WebElementFacade errorMessage;
@FindBy(xpath = "//*[@id='app']/div[1]/div/div[1]/div/div[2]/div[2]/form/div[1]/div/span")
WebElementFacade missingUsername;
@Step("Enter Username")
public void inputUserName(String userName) {
username.sendKeys((userName));
}
@Step("Enter Password")
public void inputPassword(String passWord) {
password.sendKeys((passWord));
}
@Step("Click Submit Button")
public void clickLogin() {
submitButton.click();
}
@Step("Error Message on unsuccessful login")
public String errorMessage() {
String actualErrorMessage = errorMessage.getText();
return actualErrorMessage;
}
@Step("Error Message for missing username")
public String missingUsernameErrorMessage() {
String actualErrorMessage = missingUsername.getText();
return actualErrorMessage;
}
}
StepHomePage
import net.serenitybdd.core.pages.PageObject;
import net.serenitybdd.core.pages.WebElementFacade;
import net.thucydides.core.annotations.Step;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.FindBy;
public class StepHomePage extends PageObject {
@FindBy(xpath = "//*[@id='app']/div[1]/div[1]/header/div[1]/div[1]/span/h6")
WebElementFacade dashboardText;
@Step("Successful login")
public String getHomPageTitle() {
String dashboardTitle = dashboardText.getText();
return dashboardTitle;
}
}
Step 9 – Create the Step Definition class or Glue Code
A Step Definition is a Java method with an expression that links it to one or more Gherkin steps. When Cucumber executes a Gherkin step in a scenario, it will look for a matching step definition to execute. You can have all of your step definitions in one file, or in multiple files.
LoginPageDefinitions
package org.example.definitions;
import io.cucumber.java.en.Given;
import io.cucumber.java.en.Then;
import io.cucumber.java.en.When;
import net.serenitybdd.annotations.Steps;
import org.example.steps.StepHomePage;
import org.example.steps.StepLoginPage;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
public class LoginPageDefinitions {
@Steps
StepLoginPage loginPage;
@Steps
StepHomePage homePage;
@Given("User is on Home page")
public void openApplication() {
loginPage.open();
}
@When("User enters username as {string}")
public void enterUsername(String userName) {
loginPage.inputUserName(userName);
}
@When("User enters password as {string}")
public void enterPassword(String passWord) {
loginPage.inputPassword(passWord);
loginPage.clickLogin();
}
@Then("User should be able to login successfully")
public void clickOnLoginButton() {
assertTrue(homePage.getHomPageTitle().contains("Dashboard"));
}
@Then("User should be able to see error message {string}")
public void unsuccessfulLogin(String expectedErrorMessage) {
String actualErrorMessage = loginPage.errorMessage();
assertEquals(expectedErrorMessage, actualErrorMessage);
}
@Then("User should be able to see error message {string} below username")
public void missingUsername (String expectedErrorMessage) {
String actualErrorMessage = loginPage.missingUsernameErrorMessage();
assertEquals(expectedErrorMessage, actualErrorMessage);
}
}
Assertions in JUnit-Jupiter are imported from the below package:-
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
Step 10 – Create a Serenity-Cucumber Runner class
Cucumber runs the feature files via JUnit and needs a dedicated test runner class to actually run the feature files.
import static io.cucumber.junit.platform.engine.Constants.GLUE_PROPERTY_NAME;
import org.junit.platform.suite.api.ConfigurationParameter;
import org.junit.platform.suite.api.IncludeEngines;
import org.junit.platform.suite.api.SelectClasspathResource;
import org.junit.platform.suite.api.Suite;
@Suite
@IncludeEngines("cucumber")
@SelectClasspathResource("org.example")
@SelectClasspathResource("/features")
@ConfigurationParameter(key = GLUE_PROPERTY_NAME, value = "org.example")
public class CucumberTestSuite {
}
Step 11 – Create cucumber.properties file under src/test/resources (optional)
This is an optional step. Cucumber of version 6.7 and above provides the functionality to generate a beautiful cucumber report. For this, it is needed to add a file cucumber.properties under src/test/resources.
cucumber.publish.enabled = true
Step 12 – Create junit-platform.properties in src/test/resources
cucumber.execution.parallel.enabled=true
cucumber.execution.parallel.config.strategy=fixed
cucumber.execution.parallel.config.fixed.parallelism=3
cucumber.plugin=io.cucumber.core.plugin.SerenityReporterParallel
Step 13 – Create serenity.conf file under src/test/resources
The serenity configuration file is used to configure the drivers so the test cases can run successfully. This file contains an operating system-specific binary. The binary file sits between your test and the browser. It acts as an intermediary, an interface between your tests and the browser you are using.
You can also configure the webdriver.base.url property for different environments in the serenity.conf configuration file.
webdriver {
driver = chrome
}
serenity.browser.maximized = true
#
# Define drivers for different platforms. Serenity will automatically pick the correct driver for the current platform
#
environments {
default {
webdriver.base.url = "https://opensource-demo.orangehrmlive.com/"
}
dev {
webdriver.base.url = "https://opensource-demo.orangehrmlive.com/dev"
}
staging {
webdriver.base.url = "https://opensource-demo.orangehrmlive.com/staging"
}
prod {
webdriver.base.url = "https://opensource-demo.orangehrmlive.com/prod"
}
}
Step 14 – Create serenity.properties file at the root of the project
serenity.project.name = Parallel Execution of Cucumber Scenarios with Serenity
Step 15 – Run the tests from Command Line
Open the command line and go to the location where the pom.xml of the project is present and type the below command.
mvn clean verify
Below is the test result of the test execution.
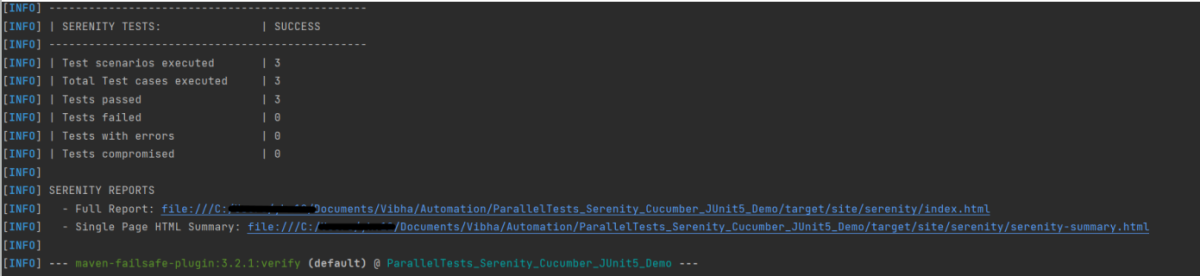
Step 16 – Run the tests from CucumberRunner
Right-click on the Ruuner class (CucumberTestSuite) and select Run ‘CucumberTestSuite’. (This is an image of IntelliJ Runner class).
The below image shows that 3 browsers open simultaneously.
Below is the test result of the test execution.
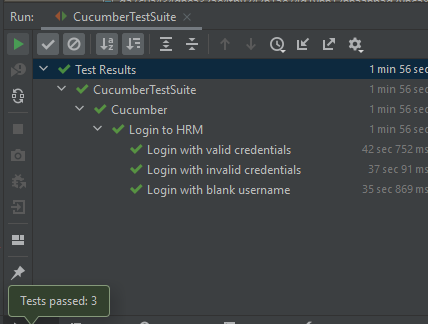
Step 17 – Serenity Report Generation
The best part about Serenity is the report generation by it. The Reports contain all possible types of information, you can think of with minimal extra effort. There is multiple types of reports are generated. We are interested in index.html and serenity-summary.html. To know more about Serenity Reports, please refer to tutorials for Index.html and Serenity-Summary.html. Below is the new Serenity Report.
Index.html
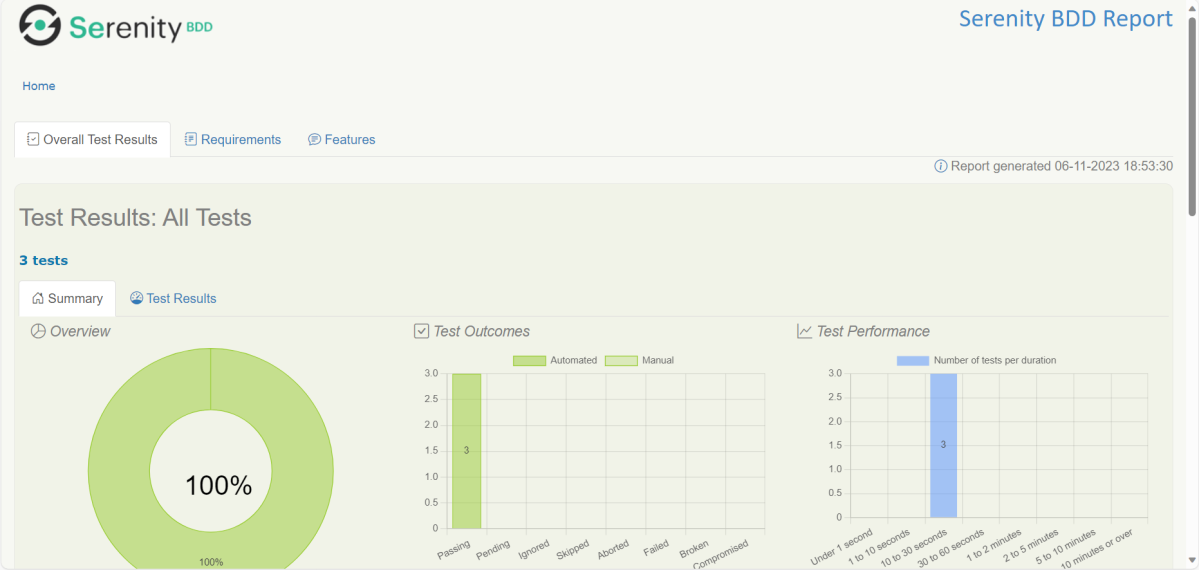

serenity-summary.html
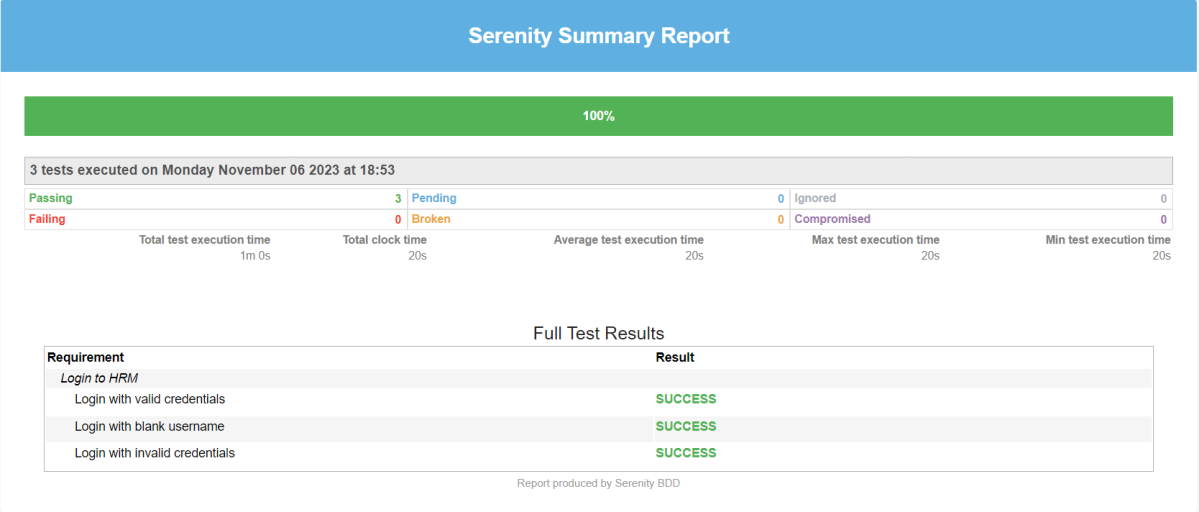
If you want to control the number of browsers open in the test, then add the below-mentioned parameters in the junit-platform.properties:
cucumber.execution.parallel.config.fixed.parallelism=2
cucumber.execution.parallel.config.fixed.max-pool-size=2
Here, count=3 is the number of browsers that will open.
Please also remove <useUnlimitedThreads>true</useUnlimitedThreads> from pom.xml.
Note: While .fixed.max-pool-size effectively limits the maximum number of concurrent threads, Cucumber does not guarantee that the number of concurrently executing scenarios will not exceed this. This is from JUnit-Platform documentation.
We are done! Congratulations on making it through this tutorial and hope you found it useful! Happy Learning!!
You can see this framework in GitHub.
Serenity BDD Tutorials
Serenity BDD is an open-source library that aims to make the idea of living documentation a reality.
Serenity BDD helps you write cleaner and more maintainable automated acceptance and regression tests faster. Serenity also uses the test results to produce illustrated, narrative reports that document and describe what your application does and how it works. Serenity tells you not only what tests have been executed, but more importantly, what requirements have been tested

Basics of Serenity
| Chapter 1 How to run Serenity BDD tests in Chrome Browser | |
| Chapter 2 How to run Serenity BDD tests in Edge Browser | |
| Chapter 3 Testing of Web Application using Serenity with JUnit4 | |
| Chapter 4 Integration of Serenity with JUnit5 | |
| Chapter 5 Manual Tests in Serenity with JUnit5 | |
| Chapter 6 Integration of Serenity with Rest Assured | |
| Chapter 7 Data Driven Tests in Serenity with JUnit | |
| Chapter 8 Data Driven Tests using CSV file in Serenity | |
| Chapter 9 Implicit Wait in Serenity | |
| Chapter 10 Explicit Wait in Serenity | |
| Chapter 11 Fluent Wait in Serenity – NEW | |
| Chapter 12 Serenity Testing on Different Browsers – NEW |
Serenity with Cucumber
Serenity Reports
Serenity with Gradle
| Chapter 1 Serenity BDD with Gradle and Cucumber for Web Application | |
| Chapter 2 Serenity BDD with Cucumber and Rest Assured in Gradle |
Serenity with CI/CD
| Chapter 1 Serenity with Jenkins | |
| Chapter 2 How to create Jenkins pipeline for Serenity tests | |
| Chapter 3 How to run Serenity tests with GitHub Actions | |
| Chapter 4 Run Serenity Tests in GitLab CI/CD |
Parallel Testing
Cucumber Tutorials
BDD is a set of practices that helps to reduce the rework caused by misunderstanding or vague requirements, narrow the communication gaps between the development team, testing team, and customers, and promote continuous communication among them. Cucumber is one such open-source tool, which supports Behaviour Driven Development(BDD). In simple words, Cucumber can be defined as a testing framework, driven by plain English. It serves as documentation, automated tests, and a development aid – all in one.

Cucumber Introduction, Installation, and Configuration
| Chapter 1 Introduction of Cucumber Testing Tool (BDD Tool) | |
| Chapter 2 How to install Cucumber Eclipse Plugin | |
| Chapter 3 How to setup Cucumber with Eclipse | |
| Chapter 4 Cucumber – What is Gherkin |
Cucumber Scenario, Features & Step Definition
| Chapter 1 Cucumber – What is Feature File in Cucumber | |
| Chapter 2 Step Definition in Cucumber | |
| Chapter 3 Cucumber – JUnit Test Runner Class |
Cucumber – Hooks & Tags
| Chapter 1 Hooks in Cucumber | |
| Chapter 2 Tags in Cucumber | |
| Chapter 3 Conditional Hooks in Cucumber | |
| Chapter 4 What is CucumberOptions in Cucumber? | |
| Chapter 5 Background in Cucumber | |
| Chapter 6 Monochrome in Cucumber | |
| Chapter 7 What is Glue in Cucumber? | |
Cucumber – Data Driven Testing
| Chapter 1 Data Driven Testing using Scenario Outline in Cucumber | |
| Chapter 2 DataTables in Cucumber |
Cucumber Integration with Selenium – Maven
Cucumber Integration with Selenium – Gradle
| Chapter 1 Gradle Project with Cucumber, Selenium and TestNG |
| Chapter 2 Gradle Project with Cucumber, Selenium and JUnit4 |
Cucumber – Command Line Execution
| Chapter 1 Run Cucumber Test from Command Line | |
| Chapter 2 Run Gradle Cucumber Tests from Command Line |
Cucumber Integration with Rest API
| Chapter 1 Rest API Test in Cucumber BDD | |
| Chapter 2 How To Create Gradle Project with Cucumber to test Rest API |
Cucumber Integration with SpringBoot
| Chapter 1 Integration Testing of Springboot with Cucumber and JUnit4 | |
| Chapter 2 Integration Testing of Springboot with Cucumber and TestNG |
Cucumber – Reporting
Cucumber Integration with Allure Reports
Cucumber Integration with Extent Reports
Cucumber – Parallel Execution
| Chapter 1 Parallel Testing in Cucumber with JUnit | |
| Chapter 2 Parallel Testing in Cucumber with TestNG | |
| Chapter 3 Dependency Injection in Cucumber using Pico-Container |
Interview Questions
How to tag and filter JUnit5 tests – @Tag
This tutorial explains how to run the specific tests in JUnit5 using @Tag annotation. Imagine, there are 500 test cases for different functionalities. Out of 500 test cases, 350 tests are related to the Integration test and the rest 150 are for the E2E test. We want to run only Integration tests. How this can be achieved? To overcome this problem, JUnit5 provides a filtering mechanism – @Tag annotation. We can apply the @Tag annotation on a test class test method, or both.
The JUnit Platform enforces the following rules for Tag:
- A tag must not be null or blank.
- A trimmed tag must not contain whitespace.
- A trimmed tag must not contain ISO control characters.
- A trimmed tag must not contain any of the following reserved characters.
- ,: comma
- (: left parenthesis
- ): right parenthesis
- &: ampersand
- |: vertical bar
- !: exclamation point
Table of Contents
- Annotating JUnit Test Class with Tag
- Annotating JUnit Test Methods with Tag
- Filtering Tags with Maven Surefire Plugin
- Creating your own custom tag annotation
1. Annotating JUnit Test Class with Tag
Scenario 1 – Apply @Tag on the test class. It will run all the tests present within this test class.
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Tag;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
@Tag("Sprint-5")
class JUnit5TagsTests {
@Test
void test_Addition() {
System.out.println("test_Add()");
assertEquals(18, 3 + 7 + 8);
}
@Test
void test_Subtraction() {
System.out.println("test_Subtraction()");
assertEquals(18, 26 - 8);
}
@Test
void test_Calculator() {
System.out.println("test_Calculator()");
assertEquals(18, 10 + 8);
assertEquals(2, 10 - 8);
}
@Test
void test_Functions() {
System.out.println("test_Functions()");
assertEquals(8, Math.sqrt(64));
assertEquals(64, Math.pow(8,2));
}
@Test
void test_IsEven() {
System.out.println("test_IsEven()");
assertEquals(0, 16%2);
}
}
Let us say we have a number of classes, and we want to execute only this specific test class that is tagged as – @Sprint-5.
Go to the command line or in the case of IntelliJ to the terminal.
mvn clean test -Dgroups="Sprint-5"
In case of windows, use the below command.
mvn clean test -D"groups=Sprint-5"
The result of the above program is

2. Annotating JUnit Test Methods with Tag
With JUnit 5 we can filter tests by tagging a subset of them under a unique tag name.
Scenario 2 – Let’s say we have 5 tests, and we want to run 3 tests in the development environment, 1 test in both development and QA, 1 test in Production, and 1 test In-Progress. So we will tag the tests as below:
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Tag;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
class JUnit5TagsTests {
@Test
@Tag("Development")
void test1() {
System.out.println("This test is for Development");
}
@Test
@Tag("Development")
void test2() {
System.out.println("This test is for Development");
}
@Test
@Tag("Development")
@Tag("QA")
void test3() {
System.out.println("This test is for Development & QA");
}
@Test
@Tag("Production")
void test4() {
System.out.println("This test is for Production");
}
@Test
@Tag("Regression")
@Tag("QA")
void test5() {
System.out.println("This is Regression Test for QA");
}
}
To run the tests tagged with “production” in IntelliJ. Edit the configuration. Click on the Run and select “Edit Configurations”.

Select Tags from a list of components and mention the name of the tag you want to execute. Apply the changes by clicking on the “Apply” button and then click on the “OK” button.

Now, this creates a new Configuration as shown in the below image.

Click on this configuration. It will only run the test method tagged with @Production.
2. We can apply multiple tags on a single test case as well. Here, the test method – test_Calculator() is tagged with @Development and @QA.
@Test
@Tag("Development")
@Tag("QA")
void test_Calculator() {
System.out.println("test_Calculator()");
assertEquals(18, 10 + 8);
assertEquals(2, 10 - 8);
}
To run the above test, edit the configuration as shown below.
The output of the above program is
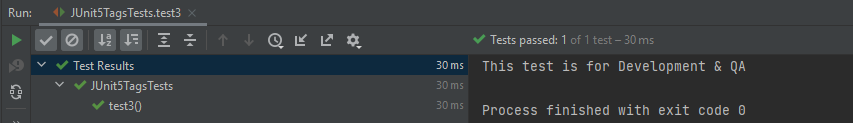
3. Filtering Tags with Maven Surefire Plugin
In Maven, we can run tests based on tags via the configuration parameters of the maven-surefire-plugin.
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0-M5</version>
<configuration>
<!-- Include tags -->
<groups>Development,QA,Production</groups>
<!-- Exclude tags -->
<excludedGroups>In-Progress</excludedGroups>
</configuration>
</plugin>
If we now execute this plugin, it will execute all tests that are tagged as Development, QA, Production.
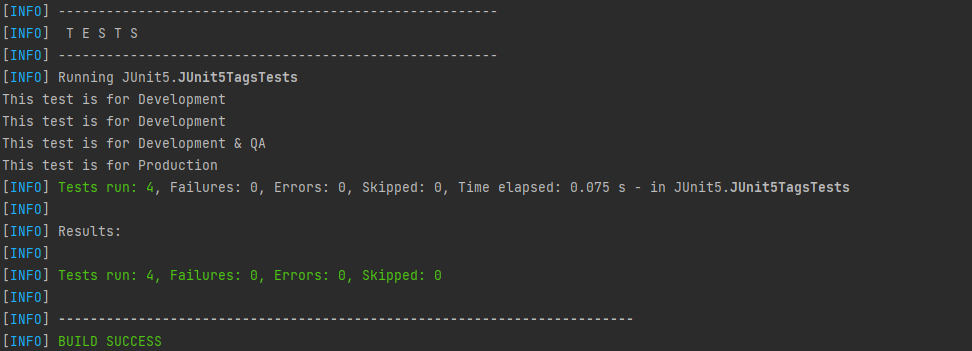
If we want to exclude any specific test from the test execution, mention it with <excludeGroups>
The below-mentioned command will run all the tests except the test tagged with “In-Progress”.
mvn clean test -DexcludeGroups="In-Progress"
4. Creating your own custom tag annotation
If we are using the same tag @Tag(“Security”) or a combination with @Tag(“QA”) in several tests, instead of copying and pasting @Tag(“Security”), @Tag(“QA”) throughout your code base, you can create a custom composed annotation named @SecurityQATest as follows. @SecurityQATest can then be used instead, using 2 annotations every time.
The following example shows you how to create custom tag annotation for @Tag(“Security”), @Tag(“QA”).
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Tag;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.TestTemplate;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE,ElementType.METHOD})
@Tag("Security")
@Tag("QA")
@Test
public @interface SecurityQATest {
}
@SecurityQATest
void test6() {
System.out.println("This is Security Testing for QA");
}
To run this test, use the below command:
mvn clean test -Dgroups="Security&QA"
The result of the above program is

Congratulations. We have understood the usage of @Tag annotation. Happy Learning!!