Playwright is integrated with Java, Cucumber, and Junit5. This integration creates a robust and scalable test automation framework for modern web applications. It is a BDD-driven framework.
Table of Contents
- What is Playwright?
- What is Cucumber?
- What is JUnit5?
- System requirements
- High-Level Architecture
- Setting Up Cucumber BDD Framework with Playwright and JUnit5
- Create a new Maven Project
- Set Up the Environment
- Define Directory Structure
- Create a feature file under src/test/resources/features
- Create the utility package in src/test/java
- Create the hooks package in src/test/java
- Create the pages package in src/test/java
- Create the step package in src/test/java
- Create the step definition class in src/test/java
- Create a JUnit Platform Cucumber Runner class in src/test/java
- Run the test using the Junit Platform Runner File
- Run the tests from the Command Line
- Cucumber Report Generation
- Surefire Report Generation
- Recap of Key Points
What is Playwright?
Page Object Model (POM) is a design pattern used in test automation. It enhances test maintenance and reduces code duplication. In this pattern, web pages are represented as classes. The various elements on the page are defined as variables in the class. All possible user interactions can then be implemented as methods in the class.
What is Cucumber?
Cucumber is Behavior Driven Development (BDD). It is a methodology that integrates non-technical stakeholders, testers, and developers into the same conversation. This is achieved by using clearly defined specifications.
In behavior-driven development with Cucumber, test cases are written in Gherkin syntax. They use a Given-When-Then structure. This structure closely mirrors user stories and business rules.
Benefits of Using Cucumber with Playwright
1. Readable, business-friendly tests: Cucumber’s Gherkin syntax (Given–When–Then) makes test scenarios easy to understand for non-technical stakeholders, bridging the gap between QA, developers, and business teams.
2. Better Test Maintainability: With standardized step definitions and modularized test architecture, scaling up your test suite is effortless. Altering the suite won’t harm the entire framework.
3. Clear reporting and traceability: Cucumber’s reports map test results directly to feature files. They map directly to scenarios. This makes it easier to track coverage and failures against requirements.
4. Cross-browser and cross-platform coverage: When combined with Playwright, Cucumber scenarios can be executed across Chromium, Firefox, and WebKit without changing feature files
5. Scales well in CI/CD pipelines: The combination supports parallel execution. It offers tagging and selective test runs. This makes it suitable for continuous testing in CI environments.
What is JUnit5?
JUnit5 is a test execution engine. It discovers and runs Cucumber tests. It enhances integration testing with advanced annotations, nested tests, and parameterized testing. It simplifies test execution in Maven, Gradle, and Spring Boot with better assertions, Java dependency injection, and parallel execution.
System requirements
The following prerequisites are required to be installed on the machine to begin with a smooth setup and installation.
- Java 11 or higher
- IntelliJ IDE or any other IDE to create a project
- Maven
- Browsers on which tests need to be run, like Chrome, Firefox, etc.
- Cucumber is installed
High-Level Architecture
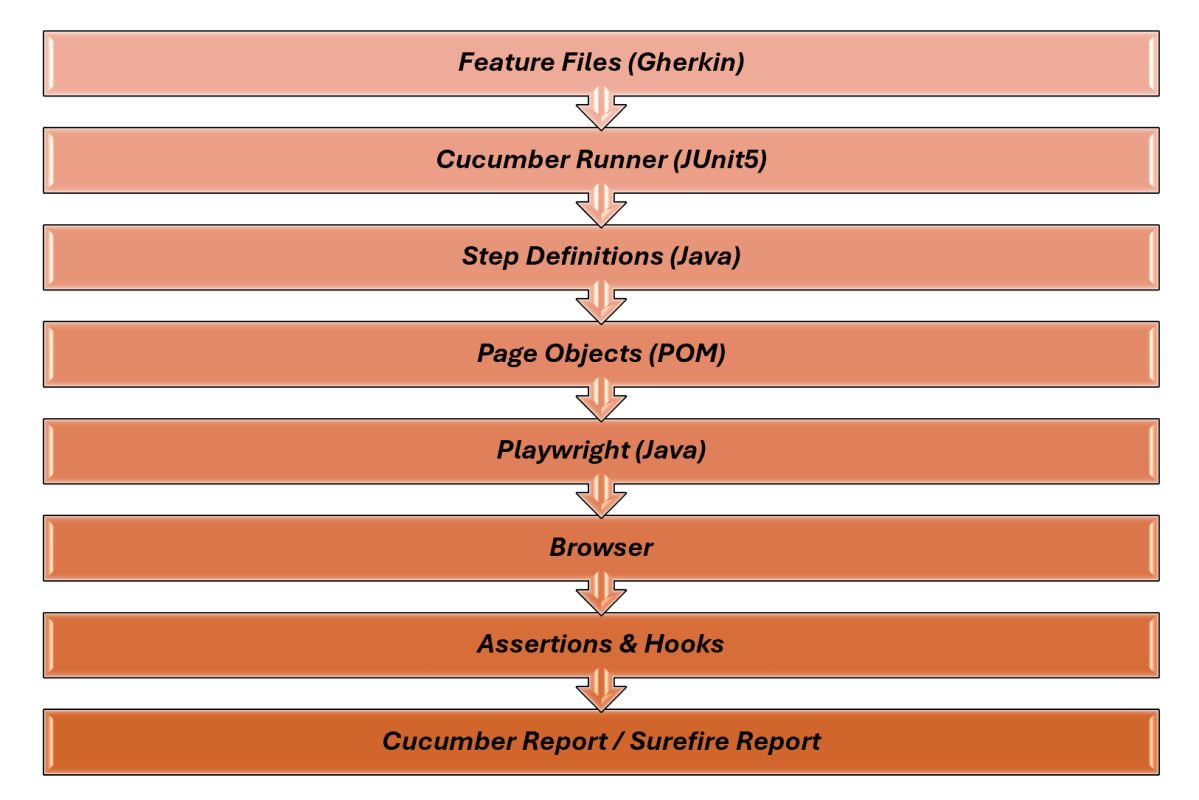
Setting Up Cucumber BDD Framework with Playwright and JUnit5
1. Create a new Maven Project
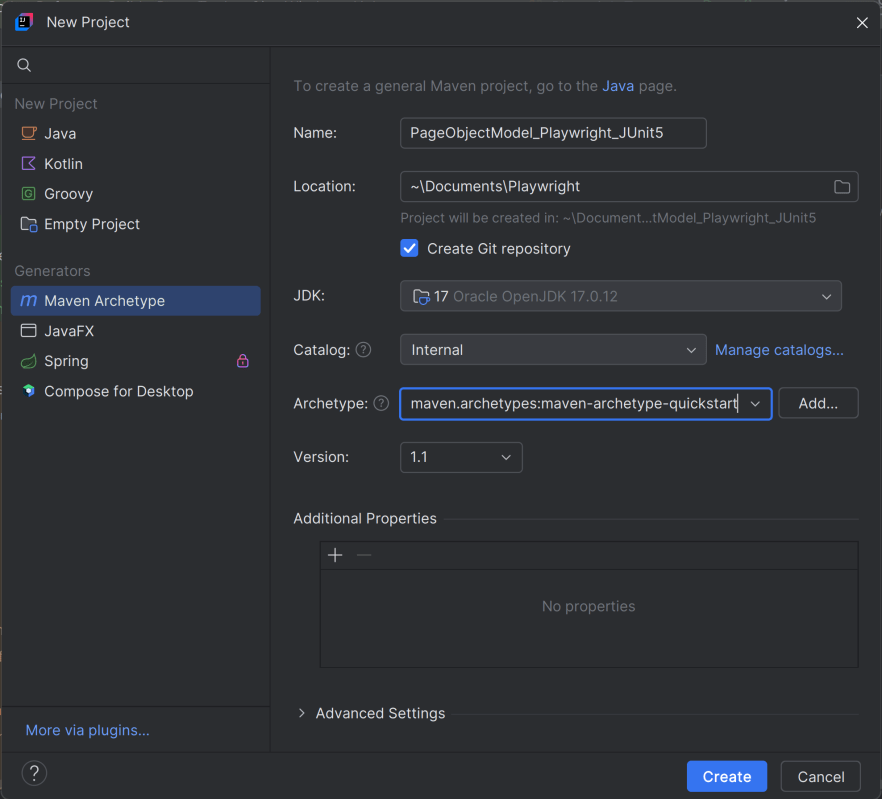
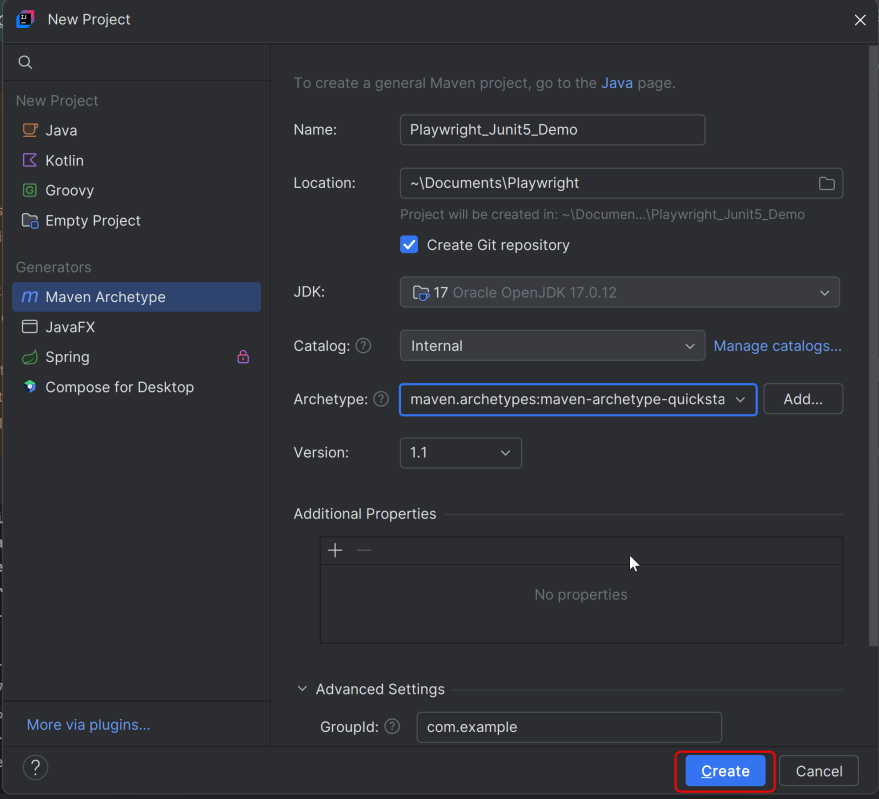
The first step in setup is to create a new Maven project. I will be using IntelliJ in this tutorial. The following steps need to be followed to create a new Maven project :
Open IntelliJ, Navigate to File >> New >> Project

2. In the New Project window, enter the following details:
- Name of the Project – Cucumber_Playwright_JUnit5
- Location/path where the project needs to be saved – Documents/Playwright (my location)
- Select JDK version — I am using JDK 17
- Archetype — Search for “quickstart” and select maven-archetype-quickstart from the results
Click on the Create button to create the project.
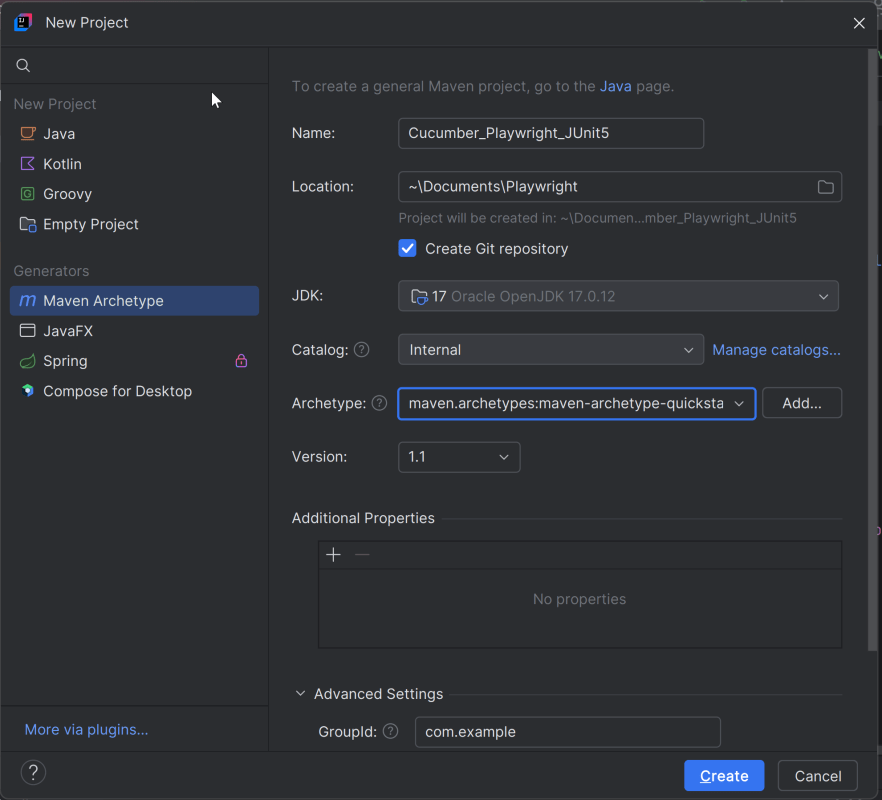
This will create a a new project in IntelliJ.
2. Set Up the Environment
2.1 Add the Cucumber, Playwright Java, and JUnit5 dependencies
Add the Cucumber, Playwright Java, and JUnit5 dependencies to the pom.xml. The latest dependency can be found here.
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<java.version>17</java.version>
<cucumber.version>7.33.0</cucumber.version>
<playwright.version>1.57.0</playwright.version>
<lombok.version>1.18.30</lombok.version>
<junit.jupiter.engine.version>6.1.0-M1</junit.jupiter.engine.version>
<junit.jupiter.version>6.1.0-M1</junit.jupiter.version>
<maven.compiler.plugin.version>3.14.1</maven.compiler.plugin.version>
<maven.compiler.source.version>17</maven.compiler.source.version>
<maven.compiler.target.version>17</maven.compiler.target.version>
<maven.surefire.plugin.version>3.5.4</maven.surefire.plugin.version>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
<maven.site.plugin.version>4.0.0-M16</maven.site.plugin.version>
<maven.surefire.report.plugin.version>3.5.4</maven.surefire.report.plugin.version>
<cucumber.junit.platform.engine>7.14.0</cucumber.junit.platform.engine>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.microsoft.playwright</groupId>
<artifactId>playwright</artifactId>
<version>${playwright.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-engine</artifactId>
<version>${junit.jupiter.engine.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId>
<version>${junit.jupiter.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-params</artifactId>
<version>${junit.jupiter.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Cucumber with Java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.cucumber</groupId>
<artifactId>cucumber-java</artifactId>
<version>${cucumber.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Cucumber with Junit5 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.cucumber</groupId>
<artifactId>cucumber-junit-platform-engine</artifactId>
<version>${cucumber.junit.platform.engine}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- JUnit Platform -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.platform</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-platform-suite</artifactId>
<version>${junit.jupiter.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2.2 Add Maven Compiler Plugin and Surefire Plugin
The compiler plugin is used to compile the source code of a Maven project. This plugin has two goals, which are already bound to specific phases of the default lifecycle:
- compile – compile main source files
- testCompile – compile test source files
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.compiler.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<source>${maven.compiler.source.version}</source>
<target>${maven.compiler.target.version}</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.surefire.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<testFailureIgnore>true</testFailureIgnore>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
2.3 Add Maven Site Plugin to generate Surefire Report
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-site-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.site.plugin.version}</version>
</plugin>
<reporting>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-report-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.surefire.report.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<outputName>JUnit5 Report</outputName>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</reporting>
The entire POM.xml file is shown below:-
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>Cucumber_Playwright_JUnit5</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>Cucumber_Playwright_JUnit5</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<java.version>17</java.version>
<cucumber.version>7.33.0</cucumber.version>
<playwright.version>1.57.0</playwright.version>
<lombok.version>1.18.30</lombok.version>
<junit.jupiter.engine.version>6.1.0-M1</junit.jupiter.engine.version>
<junit.jupiter.version>6.1.0-M1</junit.jupiter.version>
<maven.compiler.plugin.version>3.14.1</maven.compiler.plugin.version>
<maven.compiler.source.version>17</maven.compiler.source.version>
<maven.compiler.target.version>17</maven.compiler.target.version>
<maven.surefire.plugin.version>3.5.4</maven.surefire.plugin.version>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
<maven.site.plugin.version>4.0.0-M16</maven.site.plugin.version>
<maven.surefire.report.plugin.version>3.5.4</maven.surefire.report.plugin.version>
<cucumber.junit.platform.engine>7.14.0</cucumber.junit.platform.engine>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.microsoft.playwright</groupId>
<artifactId>playwright</artifactId>
<version>${playwright.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-engine</artifactId>
<version>${junit.jupiter.engine.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId>
<version>${junit.jupiter.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-params</artifactId>
<version>${junit.jupiter.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Cucumber with Java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.cucumber</groupId>
<artifactId>cucumber-java</artifactId>
<version>${cucumber.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Cucumber with Junit5 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.cucumber</groupId>
<artifactId>cucumber-junit-platform-engine</artifactId>
<version>${cucumber.junit.platform.engine}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- JUnit Platform -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.platform</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-platform-suite</artifactId>
<version>${junit.jupiter.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.compiler.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<source>${maven.compiler.source.version}</source>
<target>${maven.compiler.target.version}</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.surefire.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<testFailureIgnore>true</testFailureIgnore>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-site-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.site.plugin.version}</version>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
<reporting>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-report-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.surefire.report.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<outputName>JUnit5 Report</outputName>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</reporting>
</project>
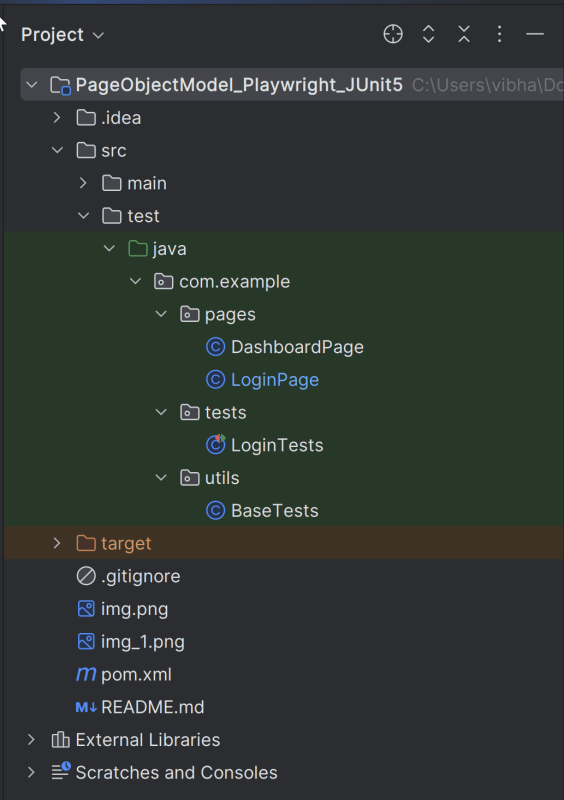
3. Define Directory Structure
Creating a well-organized project structure is crucial for maintaining a scalable and efficient automation framework.
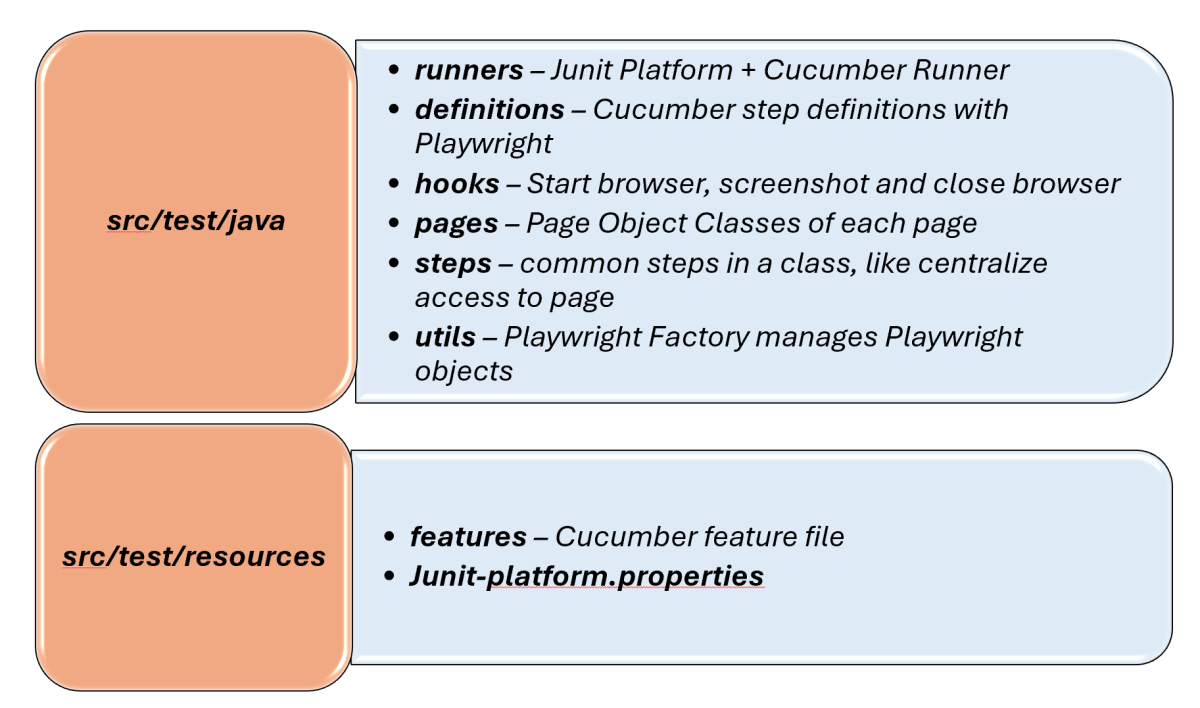
1. Maven Configuration (pom.xml): This file manages project dependencies, plugins, and other configurations.
2. Features (src/test/resources/…/features): It contains Gherkin feature files written in plain English.
3. StepDefinition (src/test/java/.../tests/): Here, you write your actual test cases, utilizing the page classes. Cucumber steps are implemented.
4. Runner (src/main/java/…runner/): It connects Cucumber feature files with Junit Platform and triggers execution.
5. Hooks (src/test/java/…/hooks): Hooks manage test lifecycle events like Launch browser before scenario, Close browser after scenario, Capture screenshots on failure
6. Page Classes (src/main/java/.../pages/): Each web page in your application should have a corresponding page class. This class encapsulates all the functionalities of the web page, following the Page Object Model.
7. Steps (src/test/java/…/steps): It is an extra abstraction layer between step definitions and pages. It contains code that is common across scenarios.
8. Utility Classes (src/main/java/.../utils/): These classes can include various utilities like configuration readers, browser factory, helper methods for common tasks, etc.
9. junit-platform.properties: It contains global configuration for Junit Platform.
4. Create a feature file under src/test/resources/features
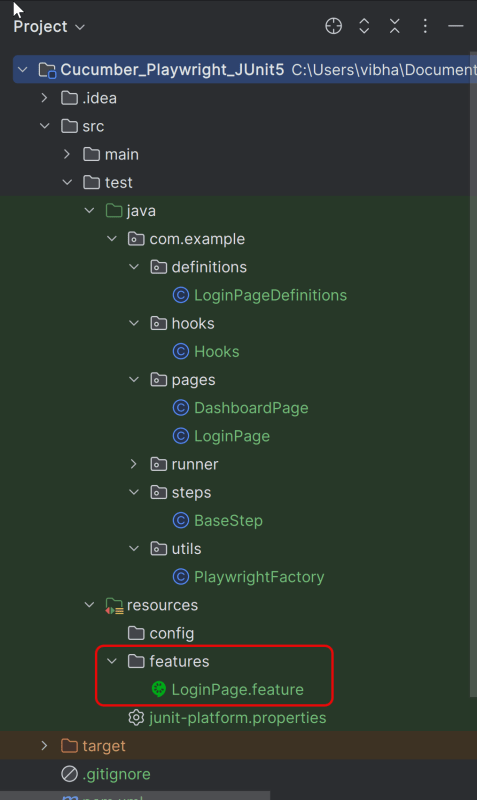
It is recommended to create a features folder in the src/test/resources directory. Create all the feature files in this features folder. Feature file should be saved as an extension of .feature. The test scenarios in the Feature file are written in Gherkins language. Add the test scenarios in this feature file. I have added sample test scenarios.
Feature: Login to HRM Application
Background:
Given User is on HRMLogin page "https://opensource-demo.orangehrmlive.com/"
@ValidCredentials
Scenario: Login with valid credentials
When User enters username as "Admin" and password as "admin123"
Then User should be able to login successfully and new page opens with heading "Dashboard"
@InvalidCredentials
Scenario Outline: Login with invalid credentials
When User enters username as "<username>" and password as "<password>"
Then User should be able to see error message "<errorMessage>"
Examples:
| username | password | errorMessage |
| Admin | admin12$$ | Invalid credentials |
| admin$$ | admin123 | Invalid credentials |
| abc123 | xyz$$ | Invalid credentials |
@MissingUsername
Scenario: Login with blank username
When User enters username as " " and password as "admin123"
Then User should be able to see a message "Required" below Username
5. Create the utility package in src/test/java
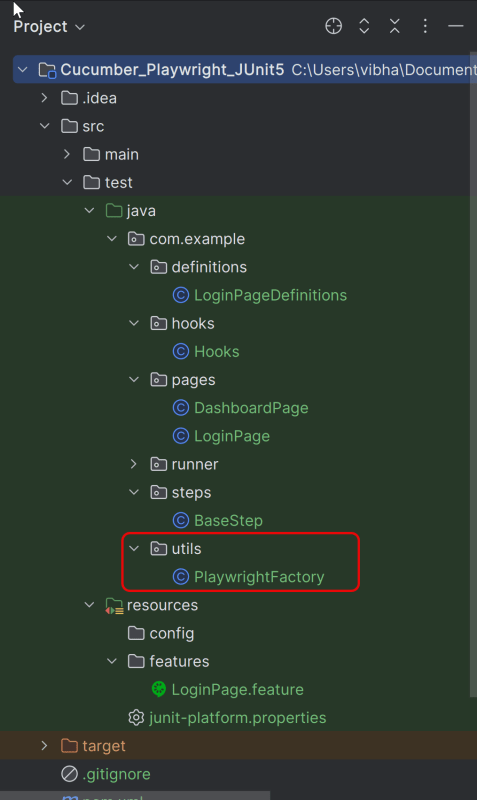
Create a Playwright Factory that includes methods to start and close the browser.
package com.example.utils;
import com.microsoft.playwright.*;
public class PlaywrightFactory {
private static Playwright playwright;
private static Browser browser;
private static BrowserContext context;
private static Page page;
public static void initBrowser() {
playwright = Playwright.create();
browser = playwright.chromium().launch(new BrowserType.LaunchOptions().setHeadless(false));
context = browser.newContext();
page = context.newPage();
}
public static Page getPage() {
return page;
}
public static void closeBrowser() {
if (page != null) page.close();
if (context != null) context.close();
if (browser != null) browser.close();
if (playwright != null) playwright.close();
}
}
6. Create the hooks package in src/test/java
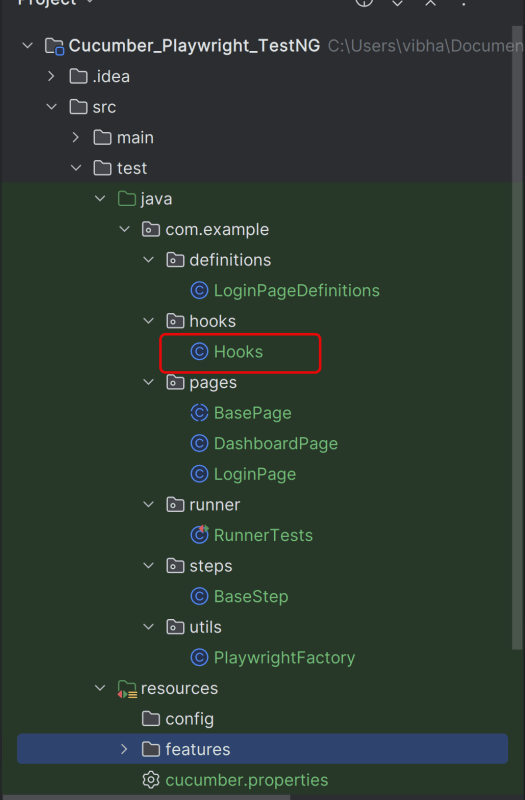
Create a Hook class that contains the code that runs before or after each scenario. Here, it is responsible for
- Starting the Playwright browser before a scenario
- Closing the browser after the scenario finishes
Below is the sample code.
package com.example.hooks;
import com.example.utils.PlaywrightFactory;
import com.microsoft.playwright.*;
import io.cucumber.java.After;
import io.cucumber.java.Before;
import io.cucumber.java.Scenario;
public class Hooks {
@Before
public void beforeScenario(Scenario scenario) {
System.out.println("Starting scenario: " + scenario.getName());
PlaywrightFactory.initBrowser();
}
@After
public void afterScenario(Scenario scenario) {
Page page = PlaywrightFactory.getPage();
if (page != null && scenario.isFailed()) {
scenario.attach(page.screenshot(), "image/png", scenario.getName());
}
PlaywrightFactory.closeBrowser();
System.out.println("Finished scenario: " + scenario.getName());
}
}
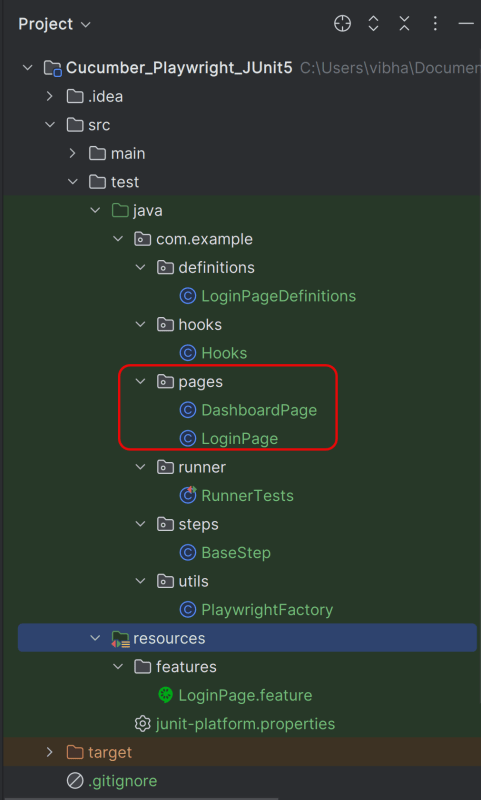
7. Create the pages package in src/test/java
Each web page in your application should have a corresponding page class. This class encapsulates all the functionalities of the web page, following the Page Object Model.
LoginPage
package com.example.pages;
import com.microsoft.playwright.*;
public class LoginPage {
private Page page;
// Locators
private final Locator usernameLocator;
private final Locator passwordLocator;
private final Locator submitLocator;
private final Locator invalidCredentialsLocator;
private final Locator missingUsernameLocator;
public LoginPage(Page page) {
this.page = page;
this.usernameLocator = page.locator("input[name='username']");
this.passwordLocator = page.locator("input[name='password']");
this.submitLocator = page.locator("button[type='submit']");
this.invalidCredentialsLocator = page.locator("//p[contains(@class, "oxd-text oxd-text--p oxd-alert-content-text")]");
this.missingUsernameLocator = page.locator("//span[contains(@class, 'oxd-text oxd-text--span oxd-input-field-error-message oxd-input-group__message')]");
}
public void login(String user, String pass){
usernameLocator.fill(user);
passwordLocator.fill(pass);
submitLocator.click();
}
public void getUrl(String url){
page.navigate(url);
}
public String getMissingUsernameErrorMessage() {
return missingUsernameLocator.textContent();
}
public String getErrorMessage () {
return invalidCredentialsLocator.textContent();
}
}
DashboardPage
package com.example.pages;
import com.microsoft.playwright.Locator;
import com.microsoft.playwright.Page;
public class DashboardPage {
private Page page;
private final Locator headingLocator;
public DashboardPage(Page page){
this.page = page;
this.headingLocator = page.locator("//h6[contains(@class, "oxd-topbar-header-breadcrumb-module")]");
}
public String getDashboardPageHeading() {
return headingLocator.textContent();
}
}
8. Create the step package in src/test/java
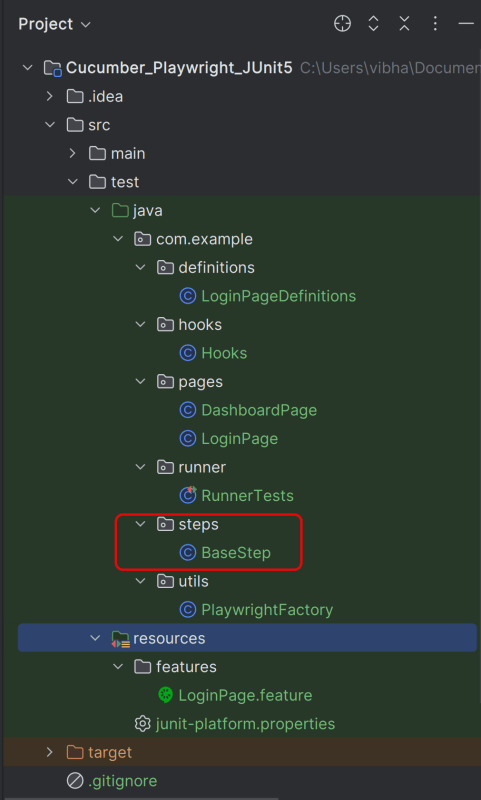
package com.example.steps;
import com.example.utils.PlaywrightFactory;
import com.microsoft.playwright.Page;
public class BaseStep {
protected Page getPage() {
Page page = PlaywrightFactory.getPage();
if (page == null) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Page is NULL. Ensure @Before hook ran and glue includes hooks package."
);
}
return page;
}
}
9. Create the step definition class in src/test/java
Create the step definition class corresponding to the feature file to test the scenarios in the src/test/java directory. The StepDefinition files should be created in this definitions directory within the folder called definitions.
Below is the step definition of the LoginPage feature file.
package com.example.definitions;
import com.example.pages.DashboardPage;
import com.example.pages.LoginPage;
import com.example.steps.BaseStep;
import io.cucumber.java.en.Given;
import io.cucumber.java.en.Then;
import io.cucumber.java.en.When;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions;
public class LoginPageDefinitions extends BaseStep {
private LoginPage loginPage;
private DashboardPage dashboardPage;
@Given("User is on HRMLogin page {string}")
public void userIsOnHRMLoginPage(String baseUrl) {
loginPage = new LoginPage(getPage());
loginPage.getUrl(baseUrl);
}
@When("User enters username as {string} and password as {string}")
public void userEntersUsernameAsAndPasswordAs(String username, String password) {
loginPage.login(username, password);
}
@Then("User should be able to see error message {string}")
public void userShouldBeAbleToSeeErrorMessage(String expectedErrorMessage) {
Assertions.assertEquals(expectedErrorMessage, loginPage.getErrorMessage());
}
@Then("User should be able to see a message {string} below Username")
public void userShouldBeAbleToSeeAMessageBelowUsername(String expectedErrorMessage) {
Assertions.assertEquals(expectedErrorMessage, loginPage.getMissingUsernameErrorMessage());
}
@Then("User should be able to login successfully and new page opens with heading {string}")
public void userShouldBeAbleToLoginSuccessfullyAndNewPageOpen(String expectedHeading) {
dashboardPage = new DashboardPage(getPage());
Assertions.assertEquals(expectedHeading, dashboardPage.getDashboardPageHeading());
}
}
10. Create a JUnit Platform Cucumber Runner class in src/test/java
We need to create a class called Runner class to run the tests.
This JUnit 5 runner configures and launches Cucumber scenarios by selecting feature files, defining glue code packages, and executing them via the Cucumber engine on the JUnit Platform.
package com.example.runner;
import static io.cucumber.junit.platform.engine.Constants.GLUE_PROPERTY_NAME;
import org.junit.platform.suite.api.ConfigurationParameter;
import org.junit.platform.suite.api.IncludeEngines;
import org.junit.platform.suite.api.SelectClasspathResource;
import org.junit.platform.suite.api.Suite;
@Suite
@IncludeEngines("cucumber")
@SelectClasspathResource("features")
@ConfigurationParameter(
key = GLUE_PROPERTY_NAME, value = "com.example"
)
public class RunnerTests {
}
1. @Suite – Marks this class as a JUnit 5 test suite. Acts as the entry point for test execution
2. @IncludeEngines(“cucumber”) – Tells JUnit Platform to use the Cucumber engine
3. @SelectClasspathResource(“features”) – Specifies the location of feature file
4. @ConfigurationParameter – Tells Cucumber where to find step definitions and hooks
11. Run the test using the Junit Platform Runner File
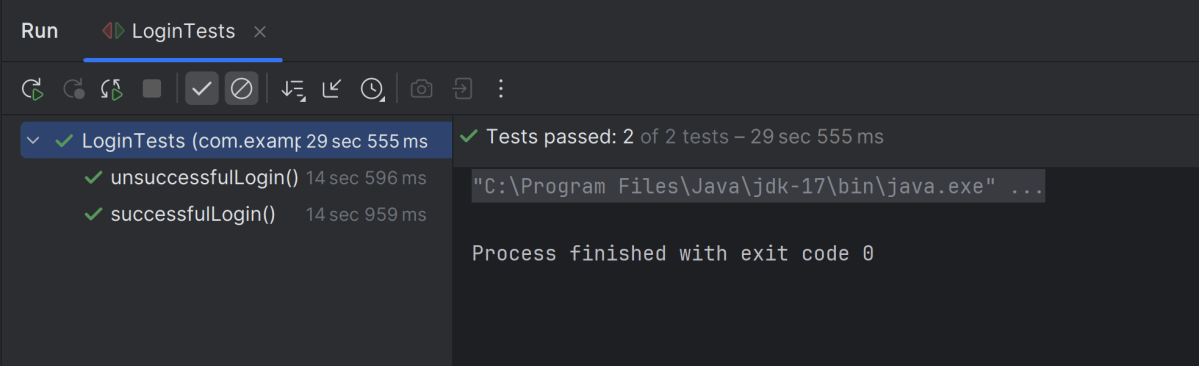
Go to the Runner class and right-click and select Run ‘RunnerTests’. The tests will run in IntelliJ.
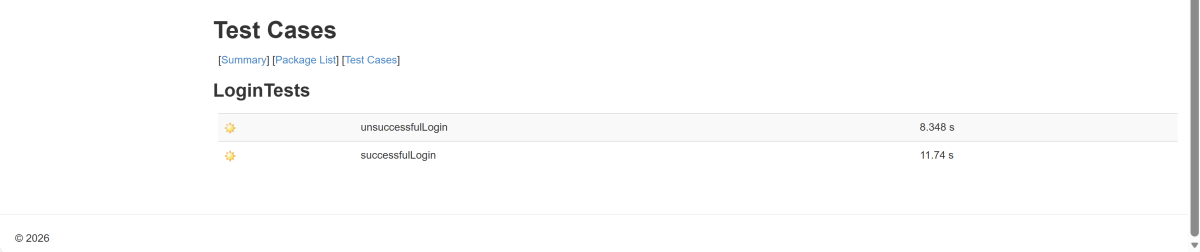
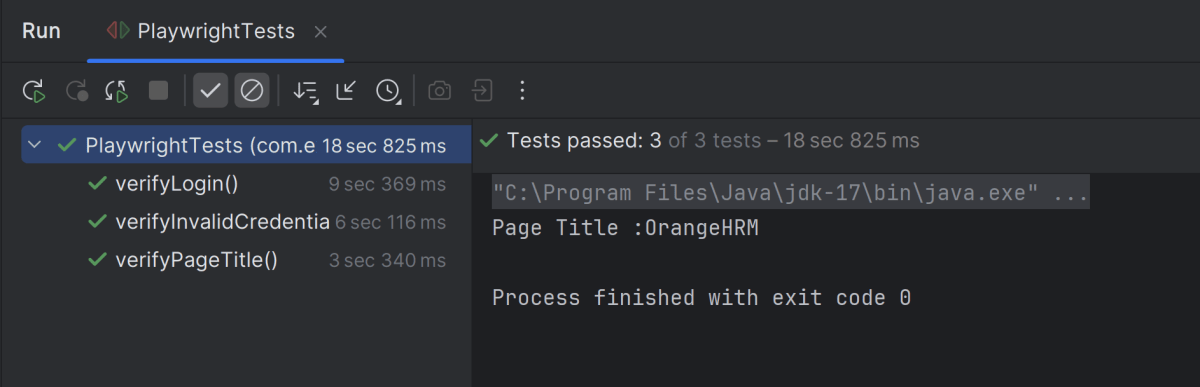
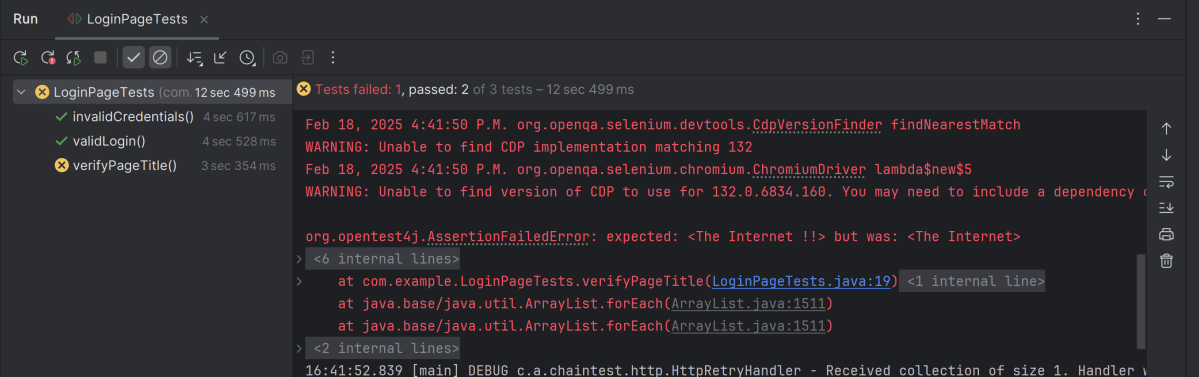
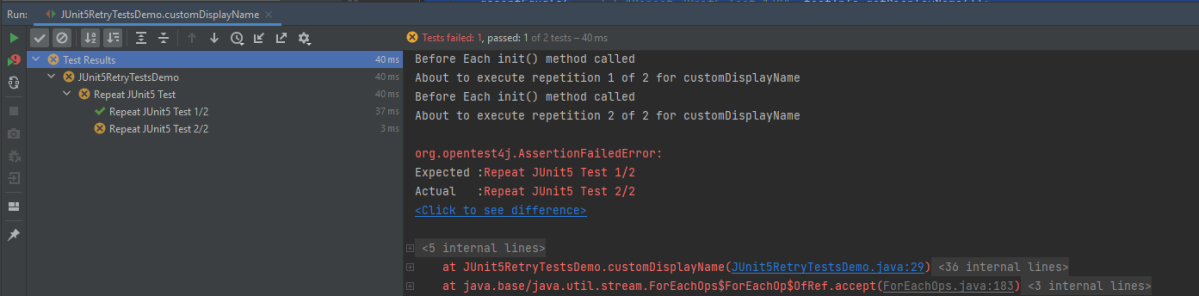
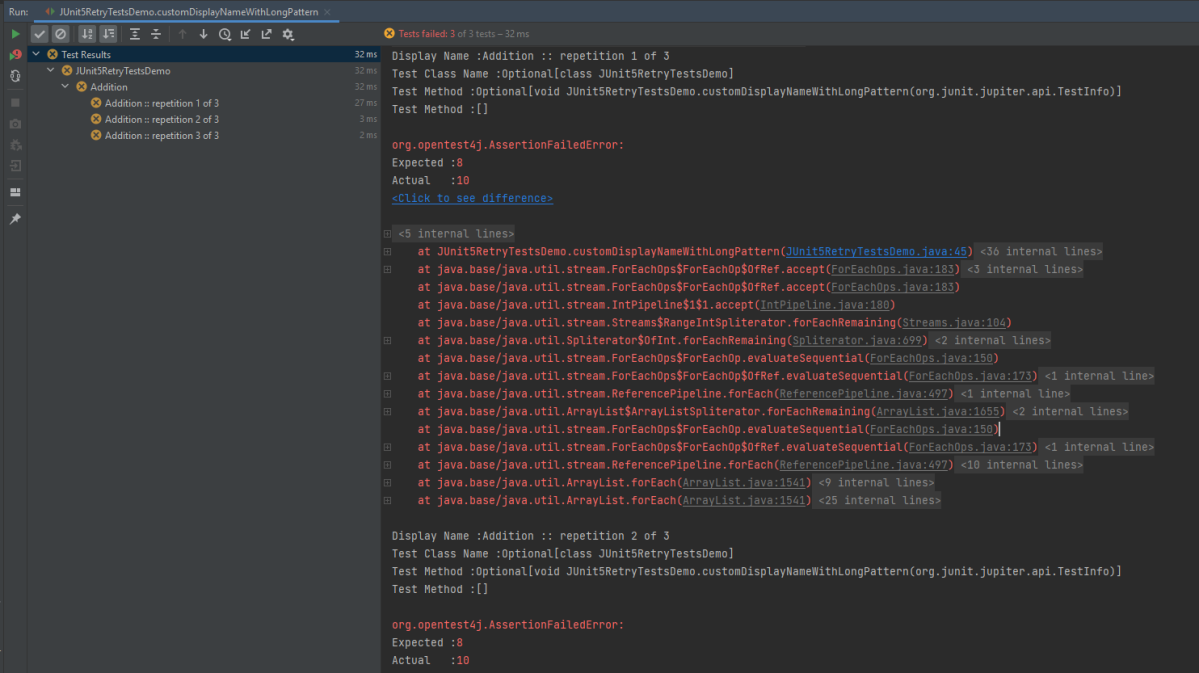
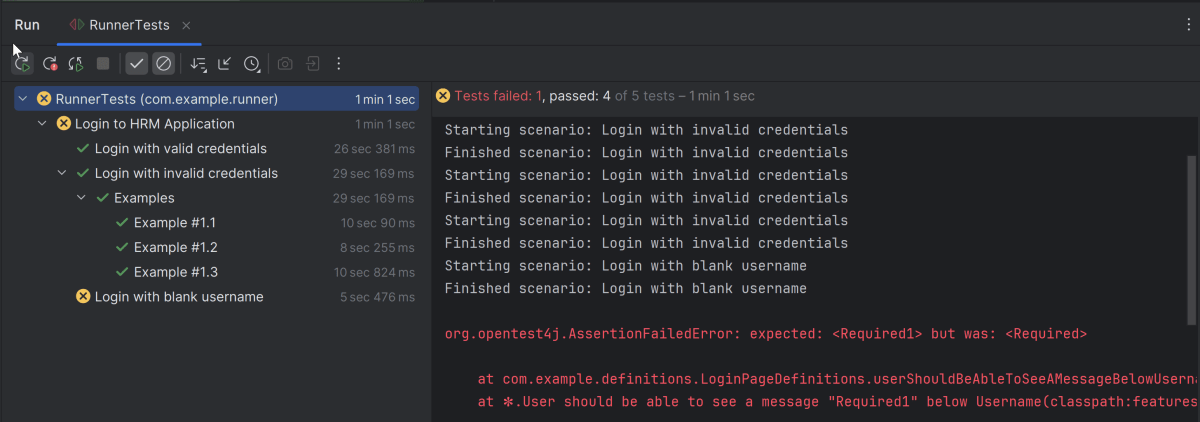
Below is the test execution result. 1 test is failed intentionally to show the status of test execution in the report.
12. Run the tests from the Command Line
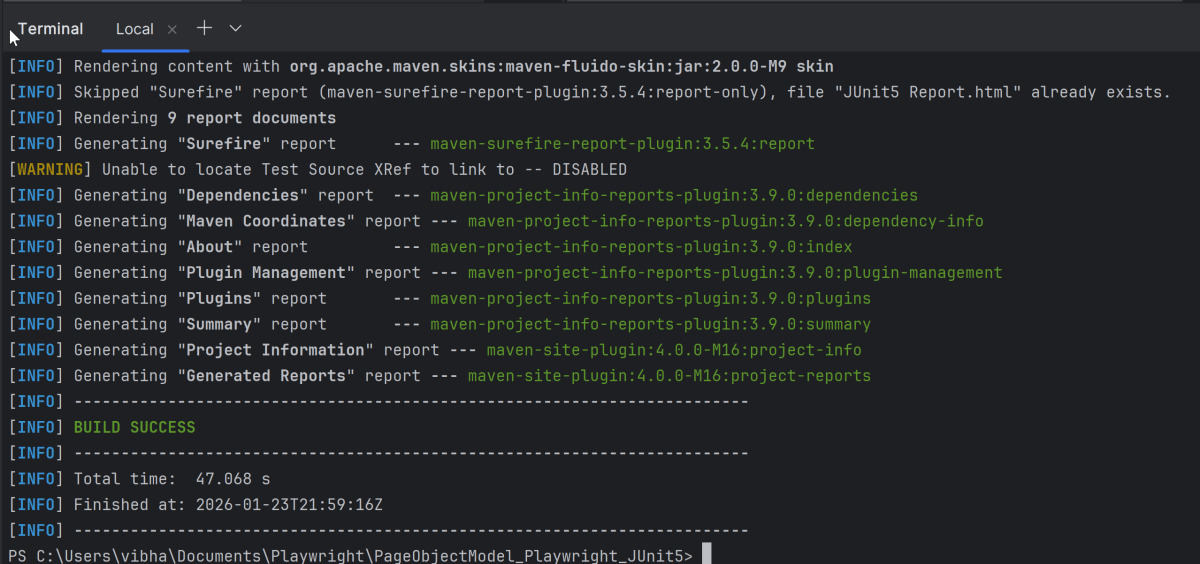
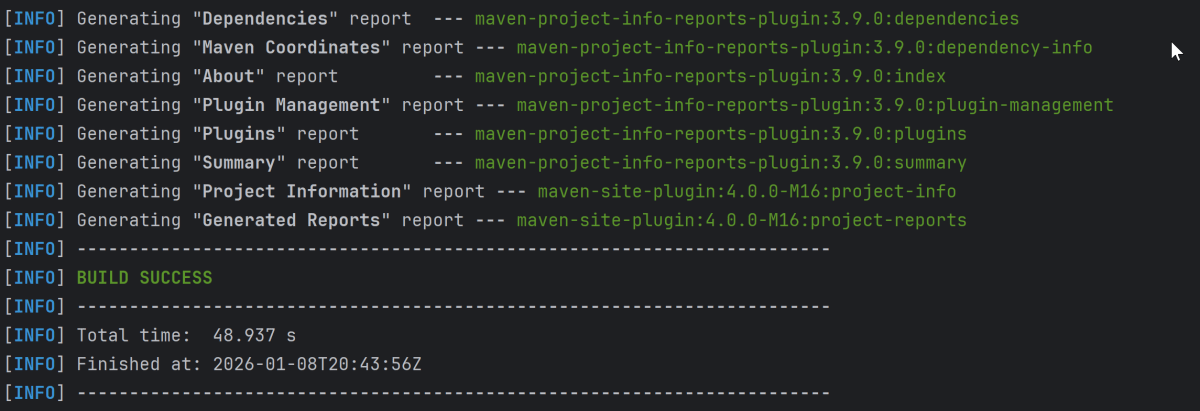
Run the command below in the command prompt to run the tests and to get the test execution report.
mvn clean site test
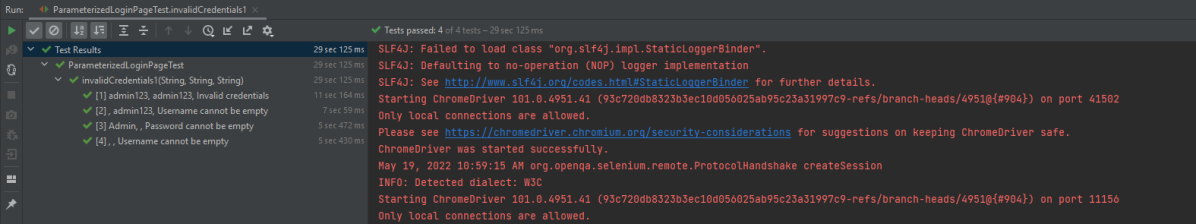
The execution screen looks like something as shown below.
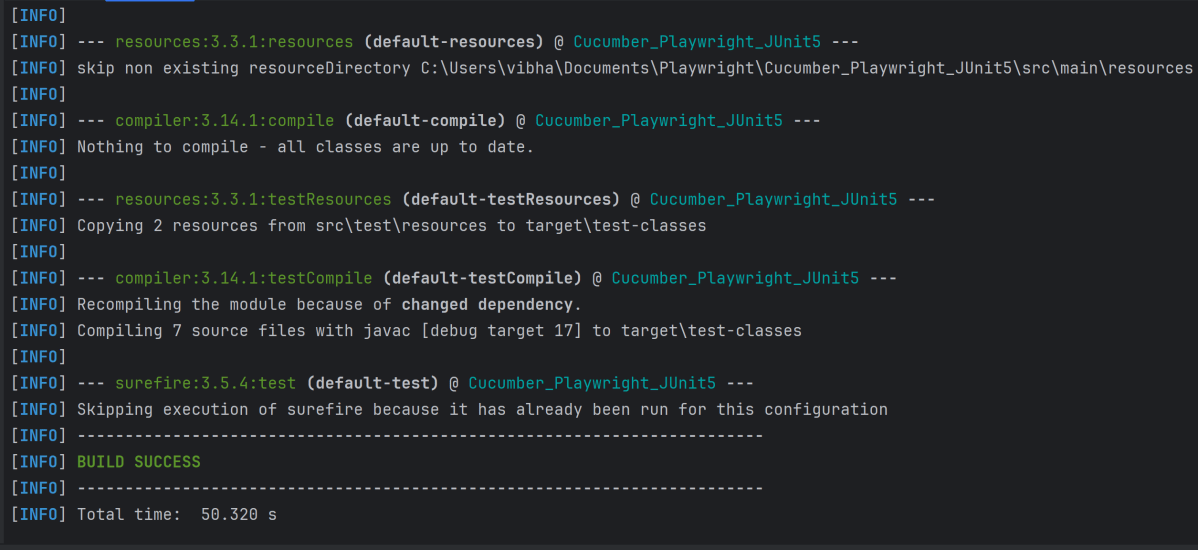
13. Cucumber Report Generation
Add junit-platform.properties under src/test/resources and add the below instructions in the file.
cucumber.publish.enabled=true
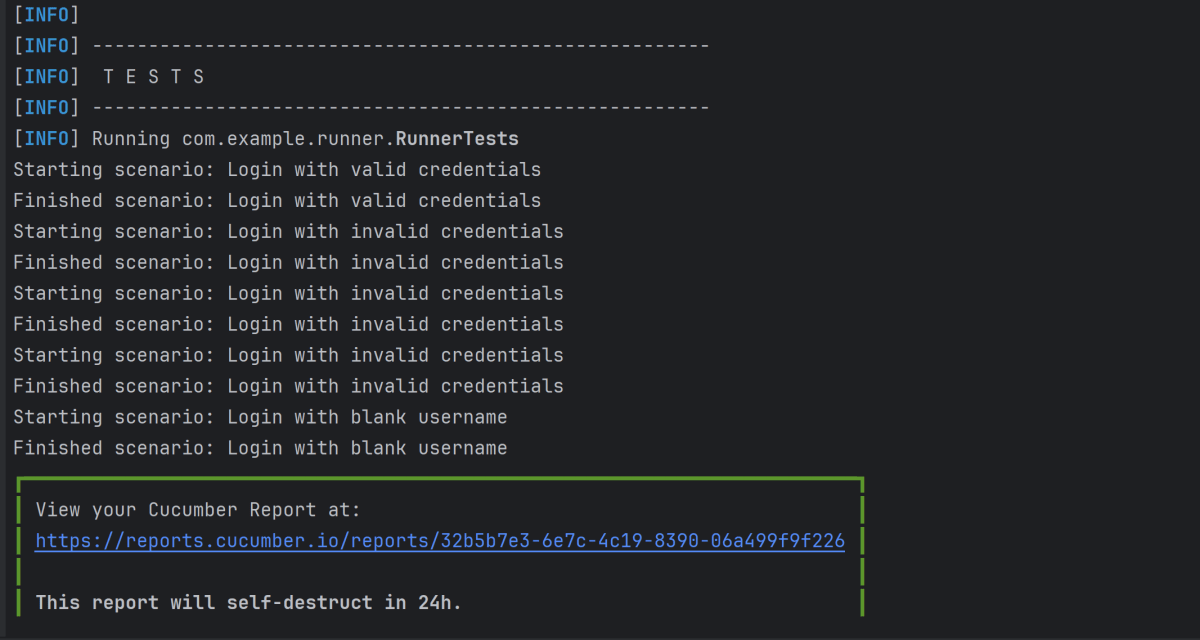
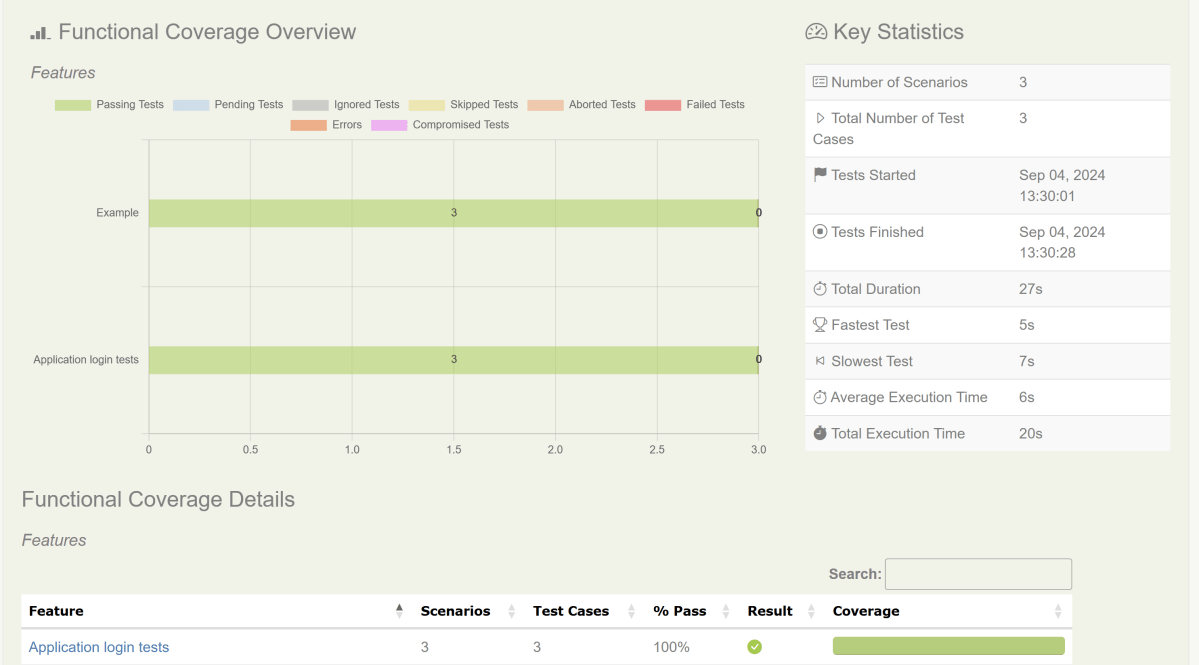
Below is the image of the Cucumber Report generated using the Cucumber Service.
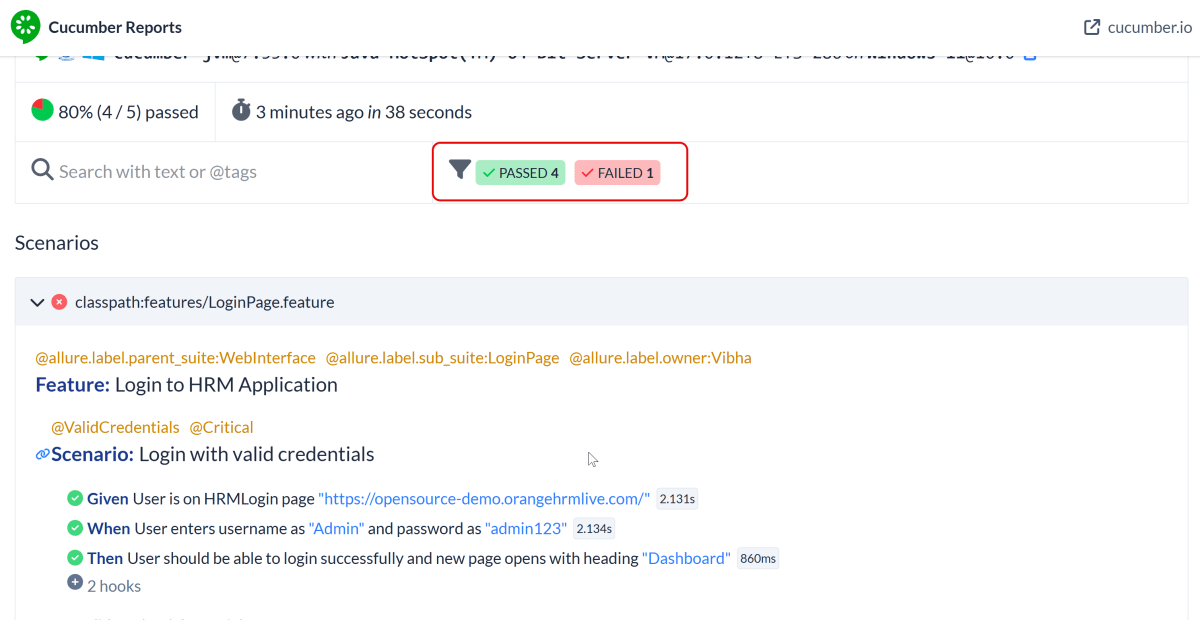
We can see the details of the failed test in the Report.
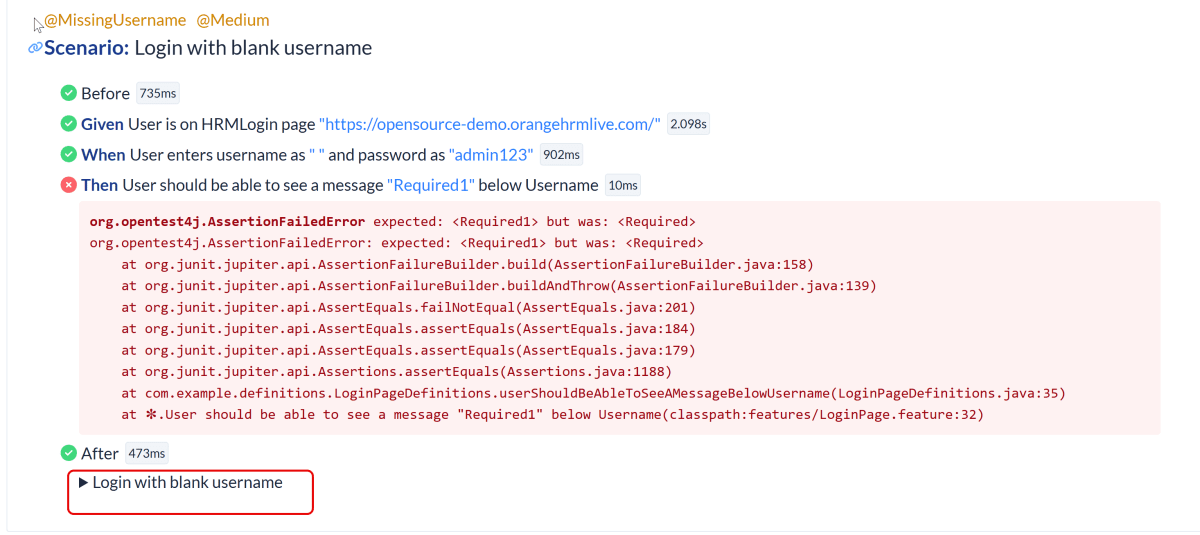
The highlighted part holds the screenshot of the failed test.
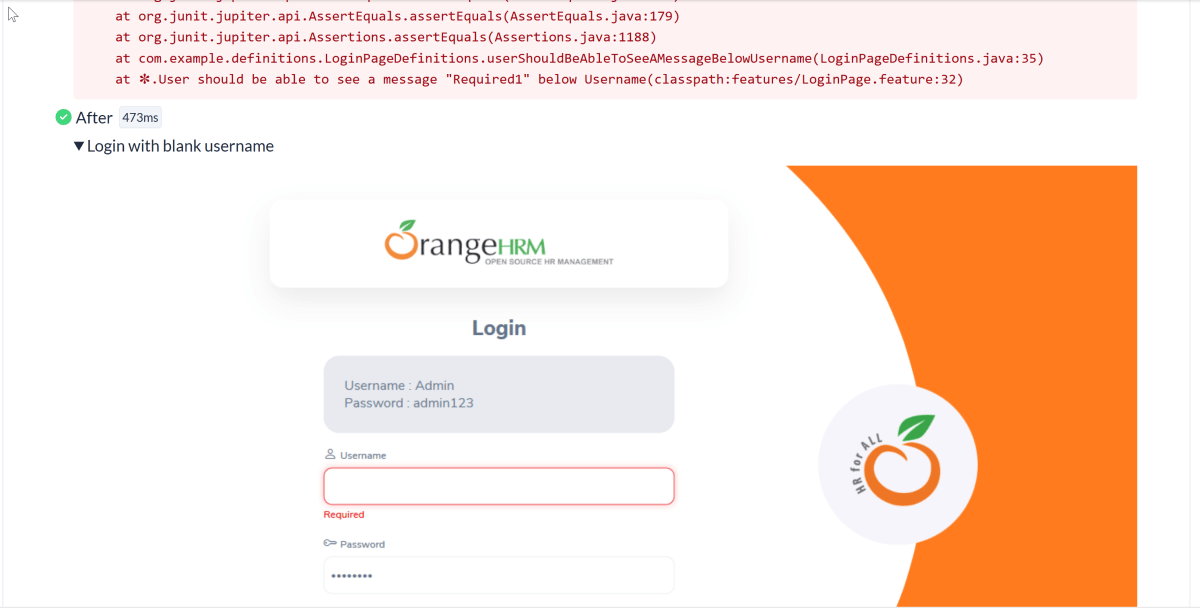
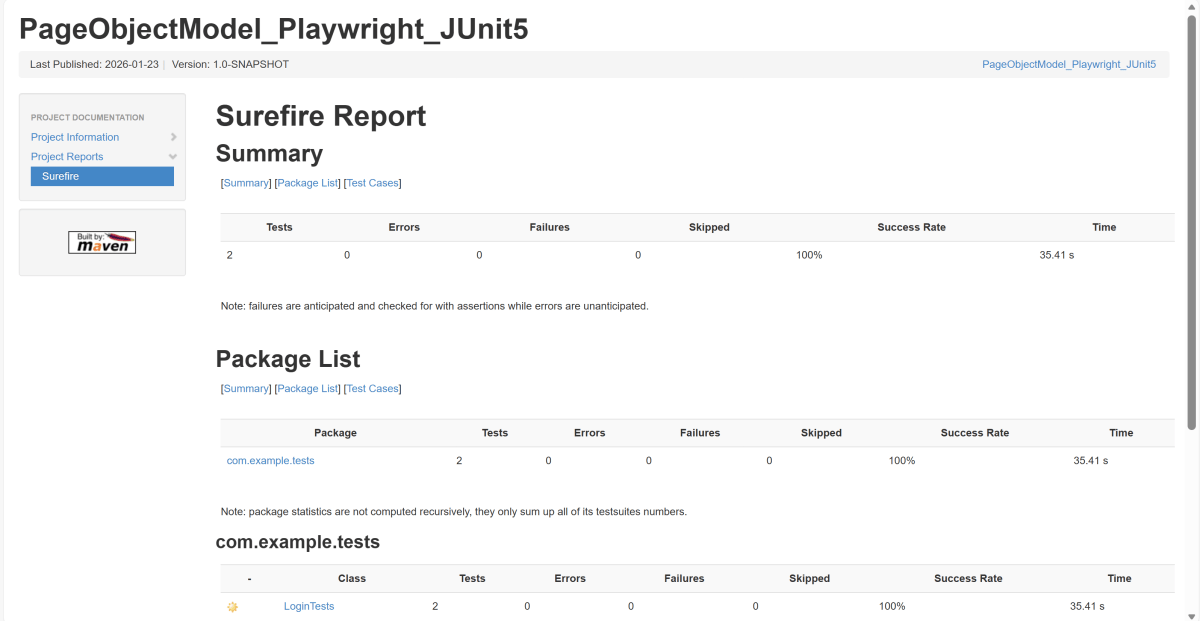
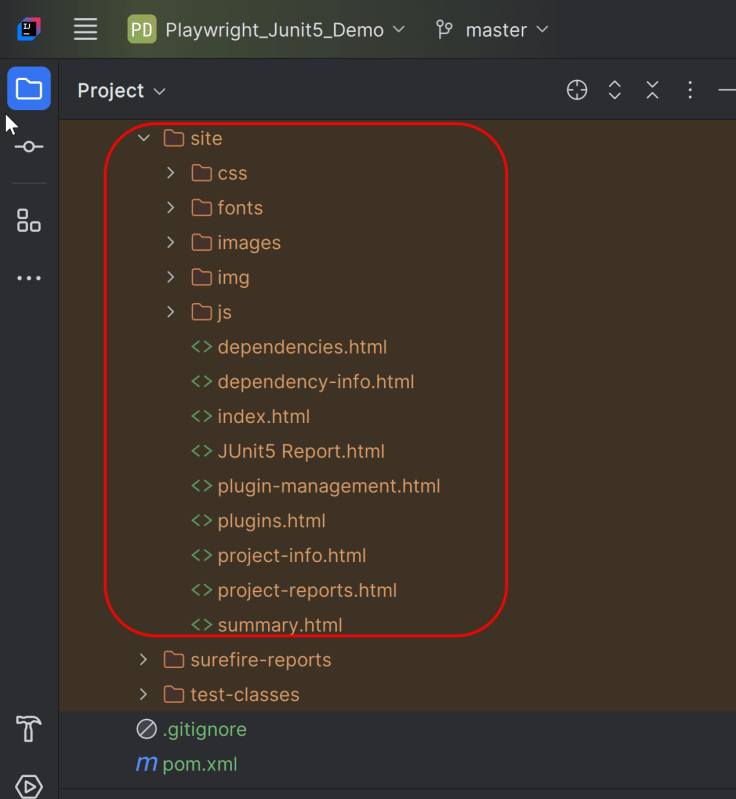
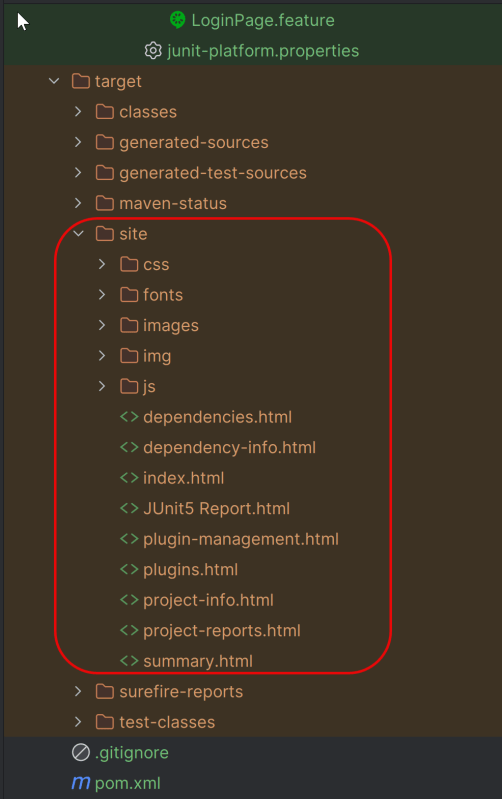
14. Surefire Report Generation
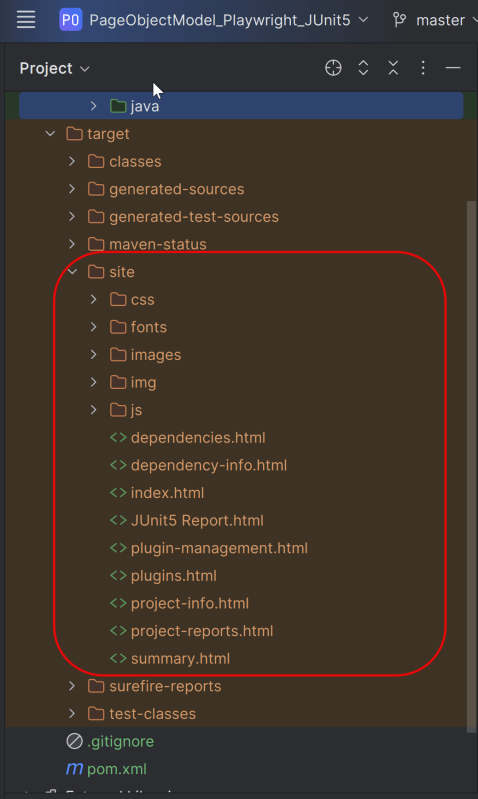
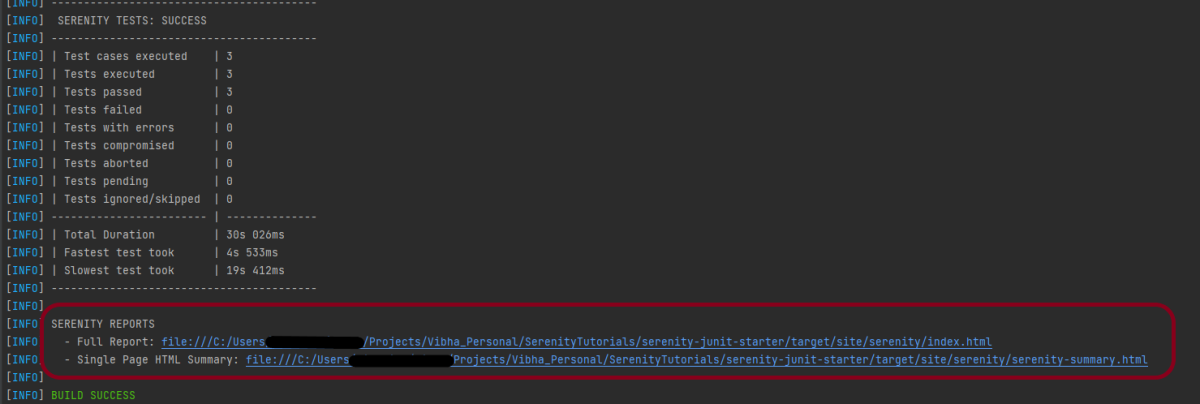
Maven Site Plugin creates a folder – site under the target directory.
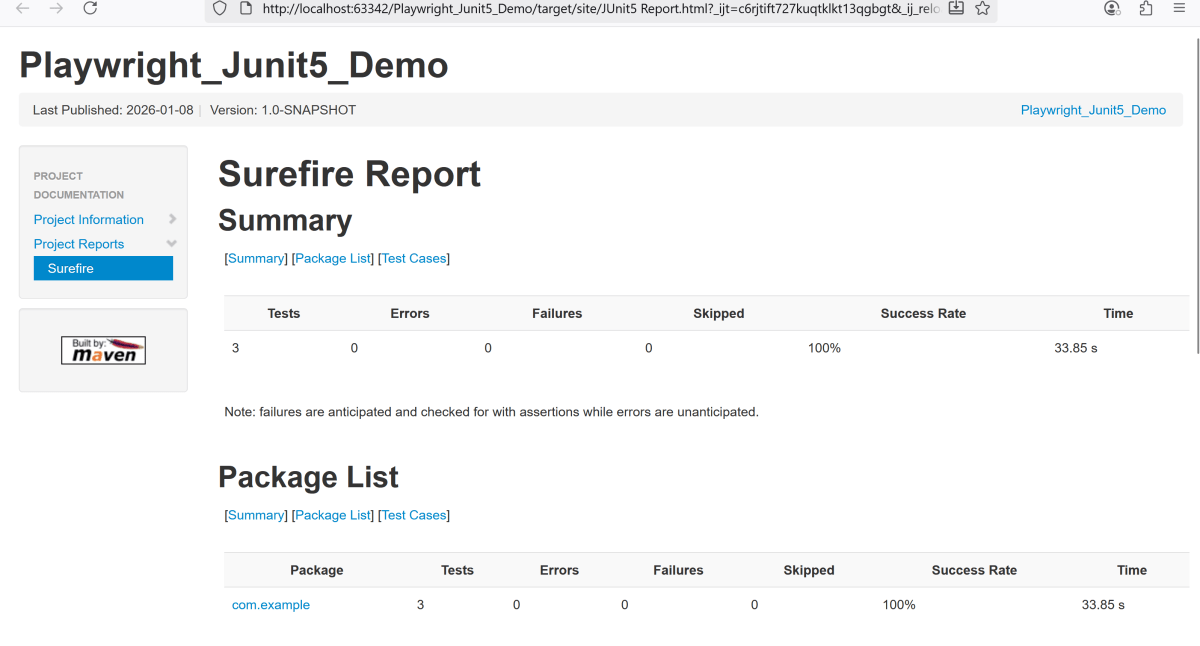
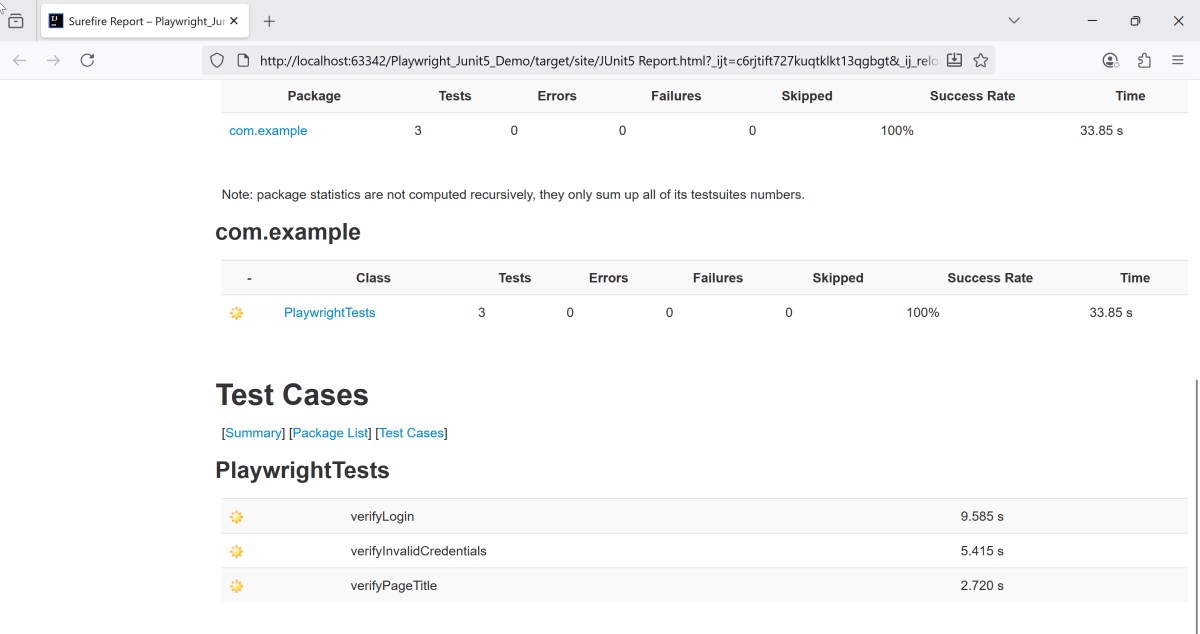
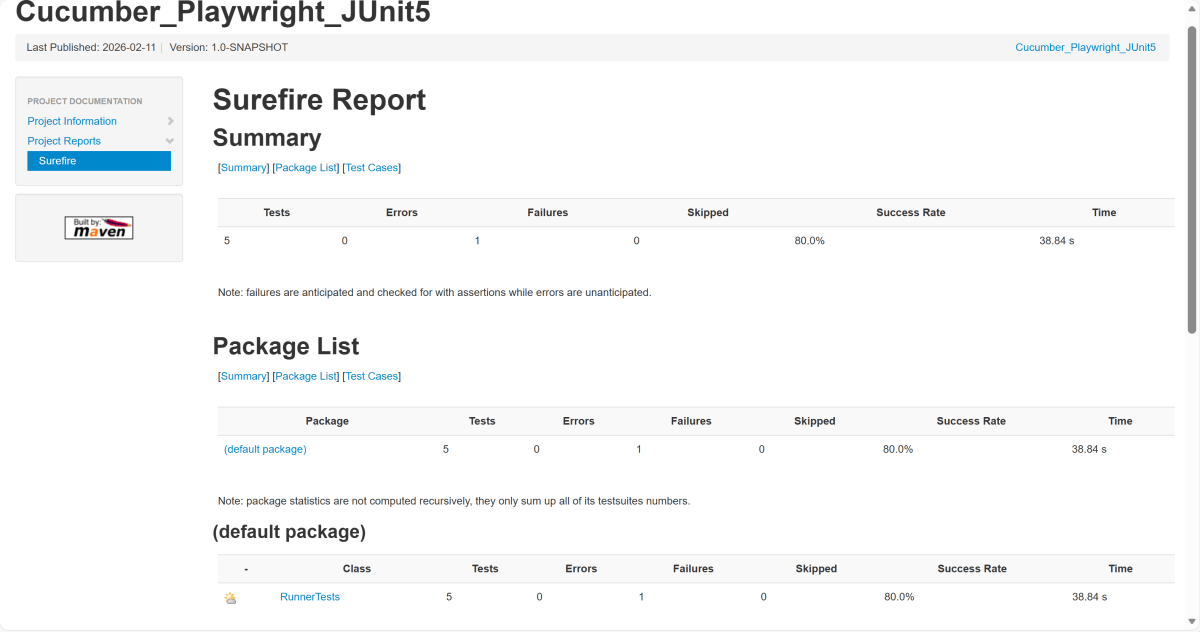
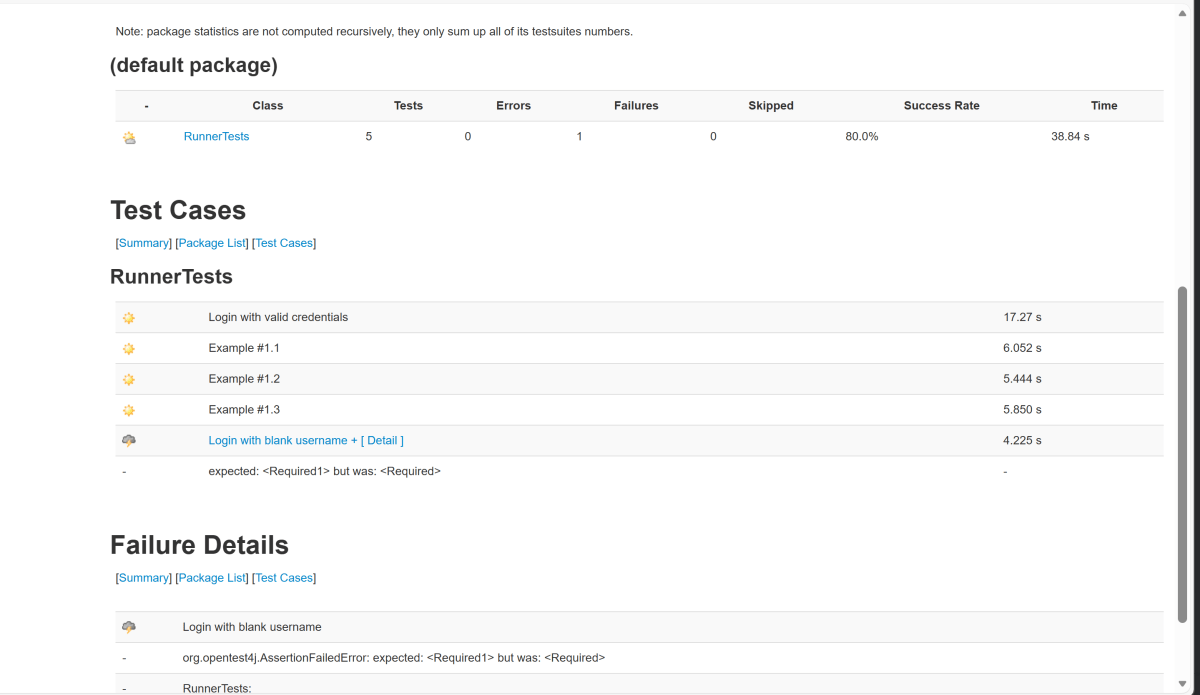
Junit also produces an “index.html” report, and it resides under the target folder. The below image shows the index.html report. This is the latest theme of the report.
Recap of Key Points:
- Playwright and Java: We explored the powerful combination of Playwright with Java. We highlighted the benefits of this duo in automated testing.
- Build: Maven manage the dependencies and execution.
- Cucumber (BDD Framework): It enables Behavior-Driven Development (BDD).
- Feature: It uses Gherkin feature file to create the scenarios.
- StepDefinition: Stepdefinition file contains the test code related to the feature file. When Cucumber executes a Gherkin step in a scenario, it will look for a matching step definition to execute.
- Test Runner: It acts as a bridge between the feature and StepDefinition file.
- JUnit5: It controls the test execution lifecycle. It integrates with Cucumber via Junit Platform runner.
- Hooks: Hooks manage browser setup, teardown, and failure handling