When running your Jenkins automation jobs, you may need to pass some parameters to your scripts. These parameters can be a URL, a browser name, or even the test user’s credentials. This tutorial will walk you through the process of creating a parameterized Jenkins job for Robot Framework.
It is recommended to go through these tutorials, before creating a parameterized Jenkins job:-
Download and install Jenkins on Windows10
Configure JAVA_HOME and MAVEN_HOME
Types of parameters
Jenkins supports several parameter types. Below is a list of the most common ones, but keep in mind that different plugins may add new parameter types:
- String: any combination of characters and numbers
- Choice: a pre-defined set of strings from which a user can pick a value
- Credentials: a pre-defined Jenkins credential
- File: the full path to a file on the filesystem
- Multi-line String: same as String, but allows newline characters
- Password: similar to the Credentials type, but allows us to pass a plain text parameter specific to the job or pipeline
- Run: an absolute URL to a single run of another job

Implementation Steps
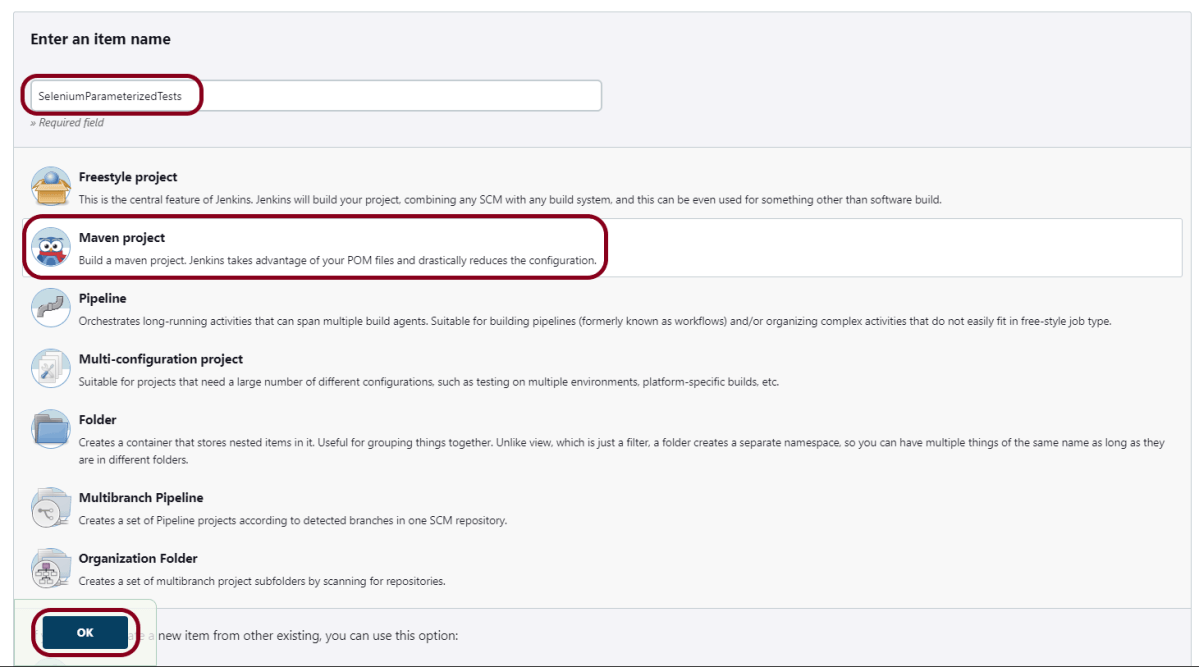
Step 1: Create a new FreeStyle project
- Give the Name of the project – RobotFramework_Demo.
- Click on the FreeStyle project.
- Click on the OK button.

Step 2: Description of the project
In the General section, enter the project description in the Description box.
Check the option – This project is parameterized.

Click on Add Parameter, and we can select any option as shown in the above image.
Step 3: Select the Choice Parameter
Choice Parameter
As I want to run my tests on different browsers, I have selected Choice Parameter.
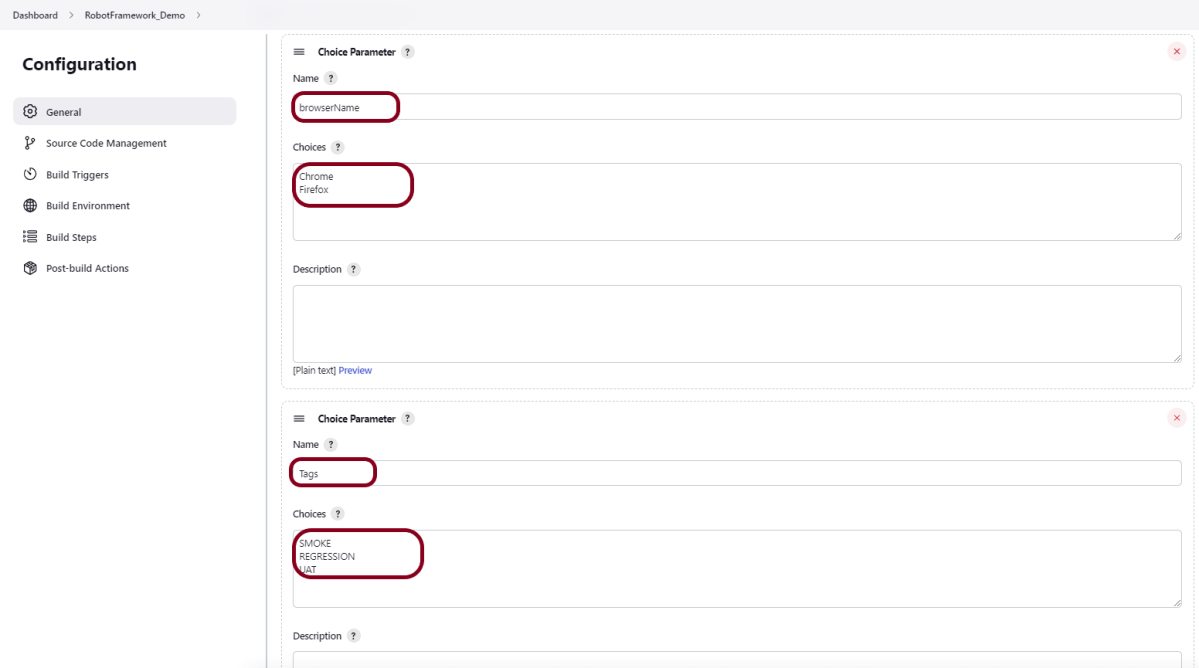
- Give the Name of the Parameter.
- Give the Choices of the Parameter – Chrome, Firefox, IE
- Give the Description of the Parameter – Select any browser to run the tests (optional).
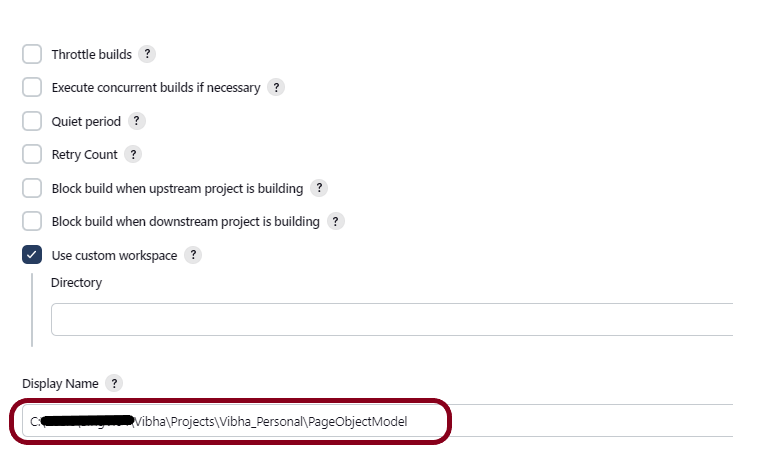
Step 4: Select a custom workspace
Mention the full path of the project in the Use custom workspace.
Step 5: Source Code Management
In the Source Code Management section, select None.
Step 6: Build Management
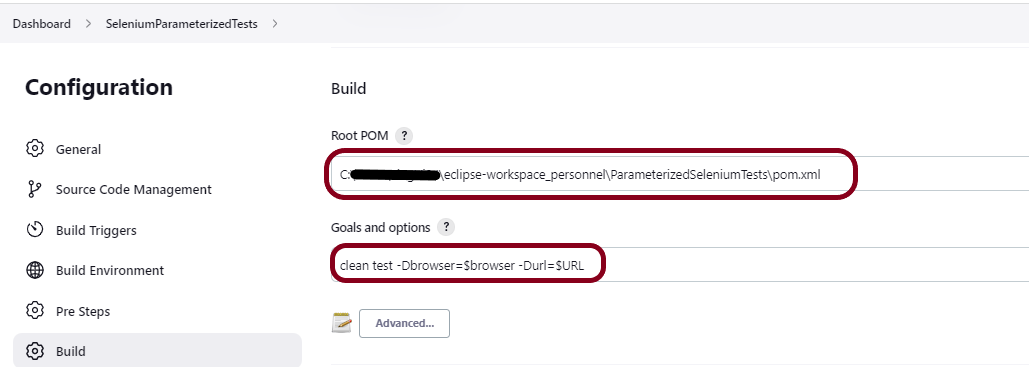
Go to the Build section of the new job. Select “Execute Windows batch command”.
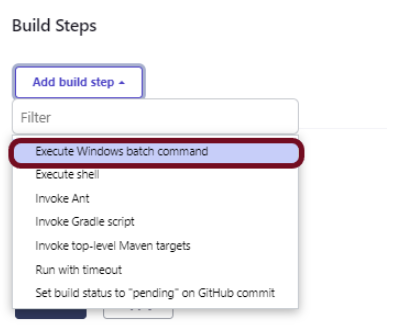
Mention the command needed to execute the tests. In this case, I have to execute all the tests, so used the below command:
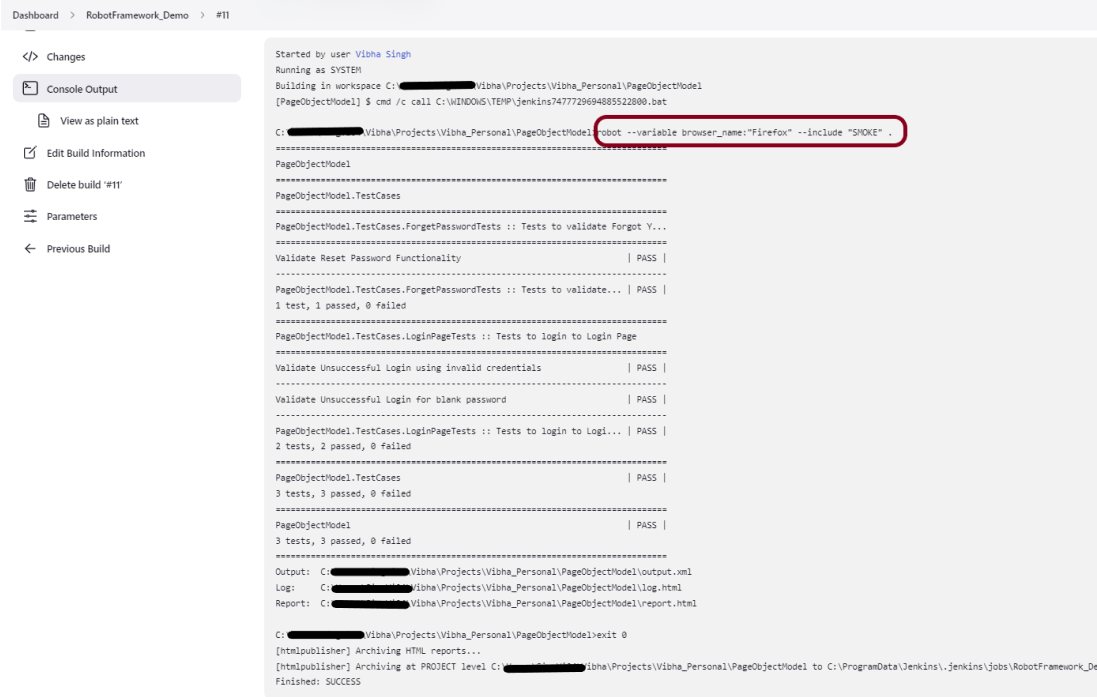
robot --variable browser_name:"%browserName%" --include "%Tags%" .
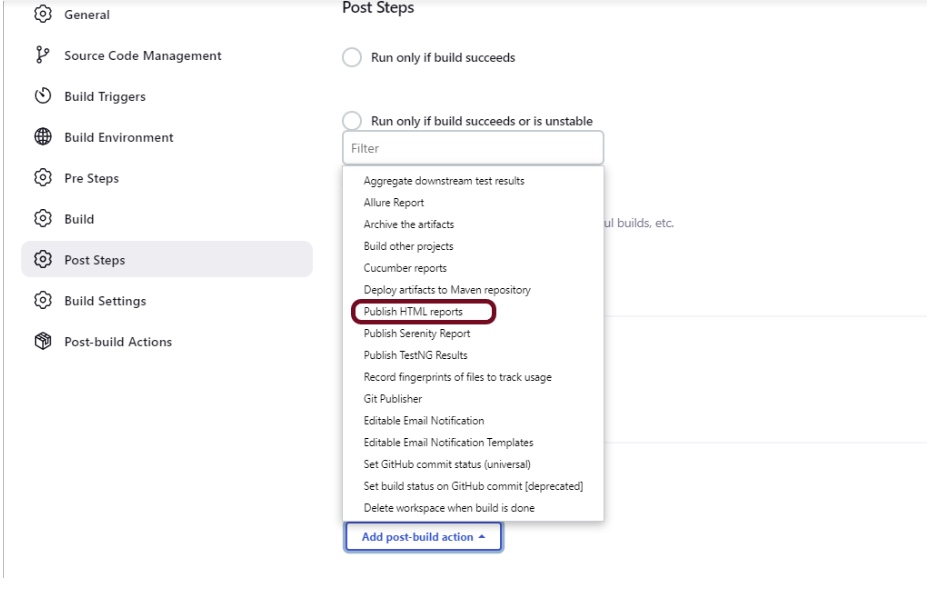
Step 7: Select “HTML Reports” from “Post Build Actions“
Scroll down to “Post Build Actions” and click on the “Add Post Build Actions” drop-down list.
Select “Publish HTML Reports“.
Enter the HTML directory to archive – Empty, Index page[s] – report.html, and Report title – HTML Report.
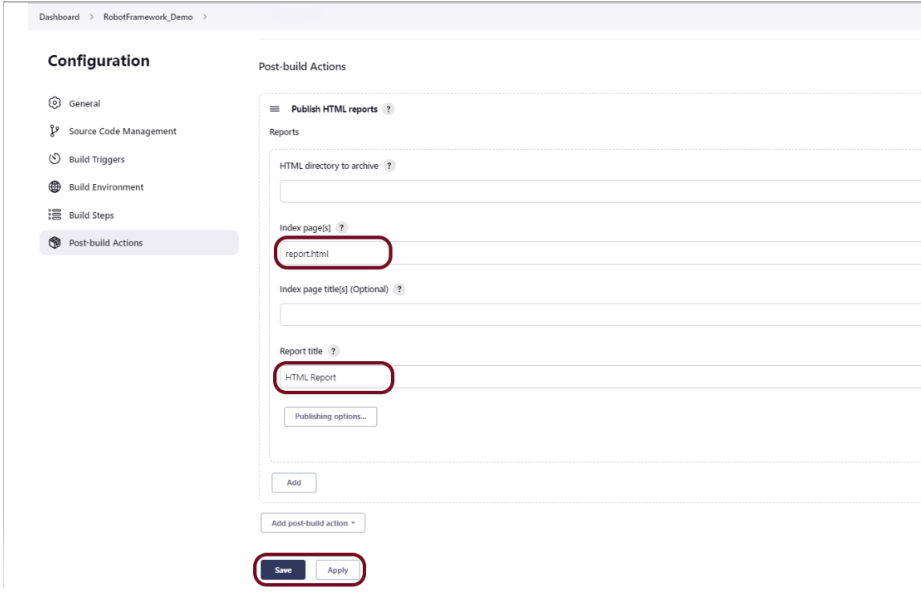
Click on the Apply and Save buttons.
If you want to see where the report is saved in Jenkins, go to the Dashboard -> RobotFramework_Demo -> Workspace -> report.html.
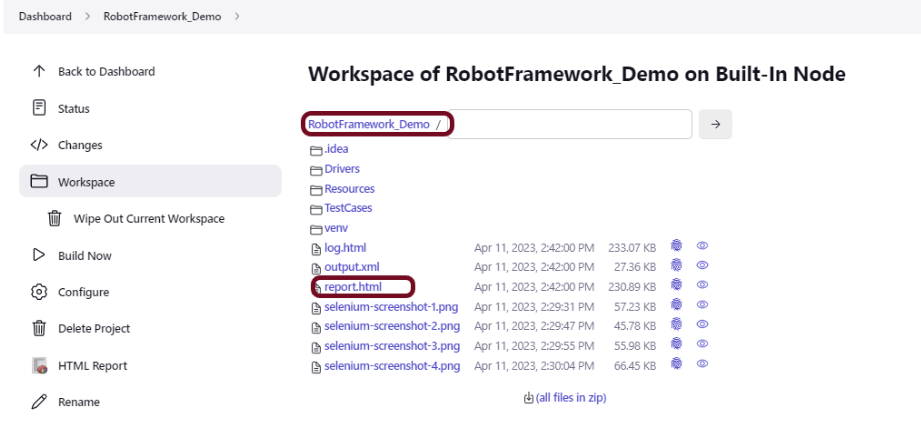
We have created a new project “RobotFramework_Demo“.

Step 8: Execute the tests
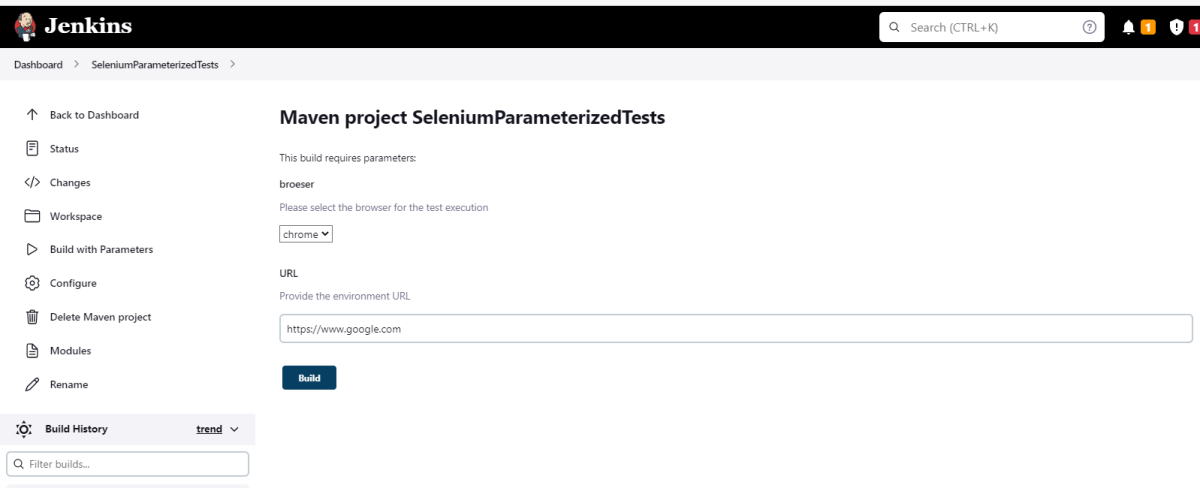
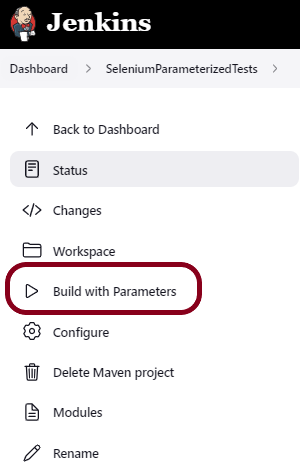
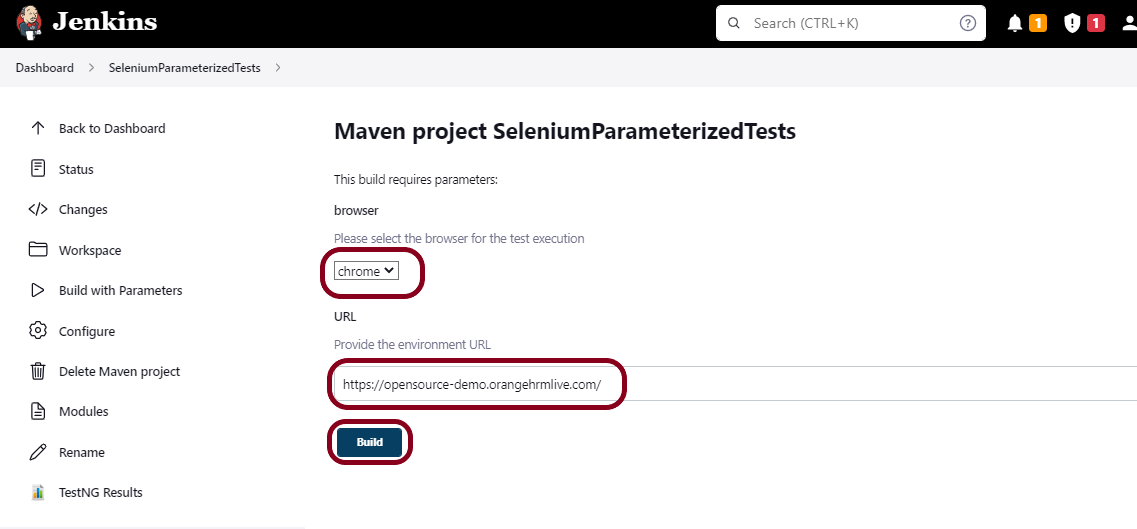
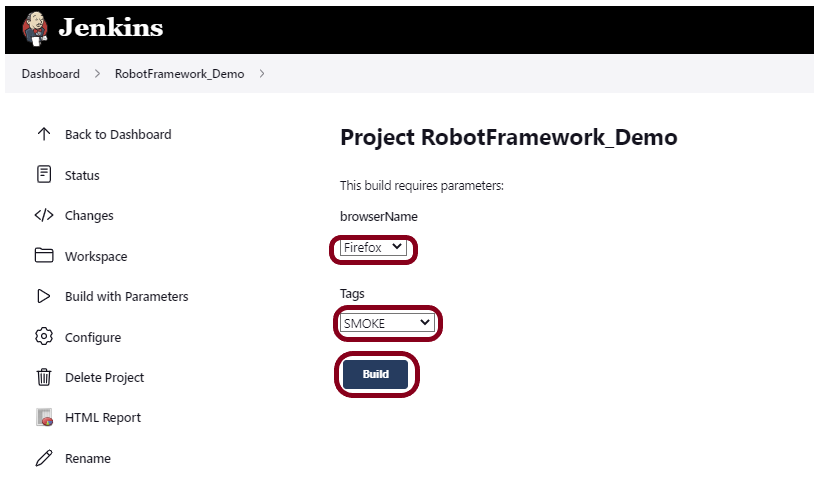
Let’s execute it now by clicking on the “Build with Parameters” button.
This screen contains the parameters which we have to select. The browser was a choice parameter and selecting a parameter from it and Tags was also a Choice parameter, so mention the tags in it and click on the “Build” button.
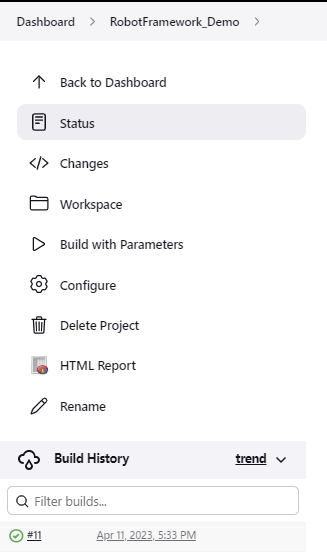
Right-click on Build Number (here in my case it is #11).
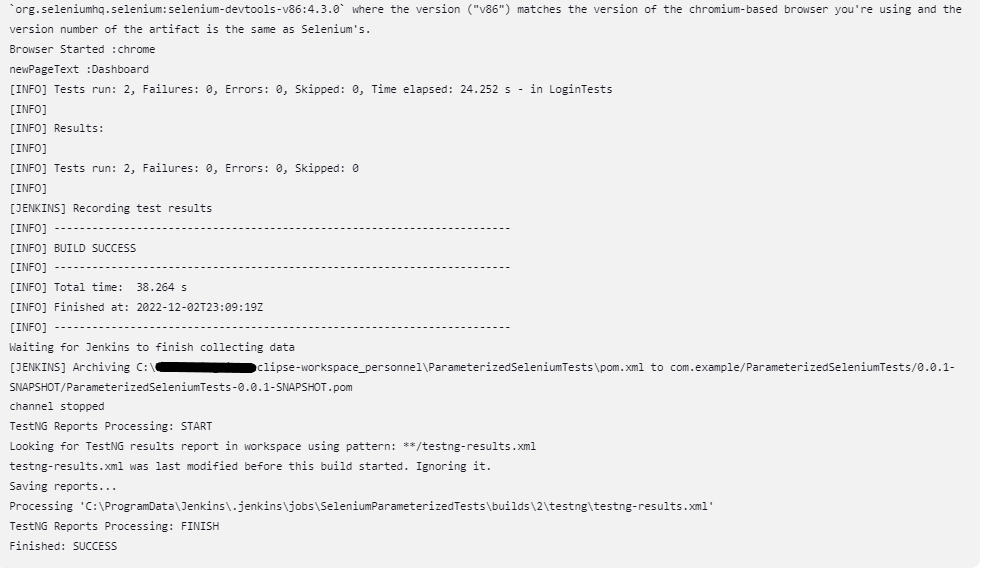
Click on Console Output to see the result.
Step 9: View the HTML Report
Once the execution is completed, click on go “Back to Project“, and we could see a link to view the “HTML Report“.
Click on the HTML Report. It displays the summary of the tests.

Congratulations on making it through this tutorial and hope you found it useful! Happy Learning!! Cheers!!
Additional Tutorials