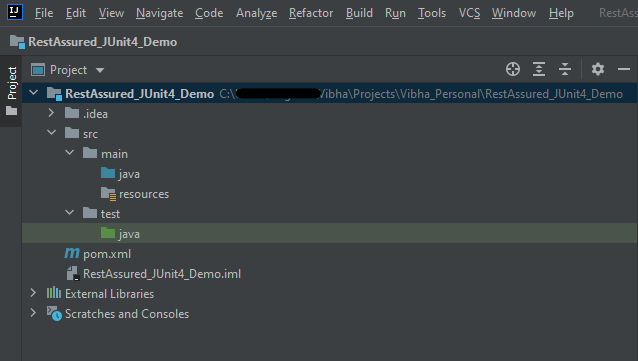
In this tutorial, I’ll explain about API & Rest Assured.
Table of Contents
What is API?
API stands for Application Programming Interface. It comprises a set of functions that can be accessed and executed by another software system. Thus, it serves as an interface between different software systems and establishes their interaction and data exchange. APIs can be used in various contexts, including web development, mobile app development, and software integration. For example, web APIs allow websites to interact with external services, such as third-party payment services or storing the information in a database.
What is API Testing?
API testing is a type of software testing that focuses on verifying the functionality, reliability, performance, and security of Application Programming Interfaces (APIs).
Testing the API’s functionality involves verifying that the API behaves as expected according to its specifications. This includes testing different API methods, parameters, headers, and payloads to ensure they produce the correct responses.
In the modern development world, many web applications are designed based on a three-tier architecture model. These are
- Presentation Tier – User Interface (UI)
- Logic Tier – Business logic is written in this tier. It is also called Business Tier. (API)
- Data Tier – Here information and data are stored and retrieved from a Database. (DB) Ideally, these three layers (tiers) should not know anything about the platform, technology, and structure of each other.
We can test UI with GUI testing tools, and we can test logic tier (API) with API testing tools. The logic tier comprises all the business logic, and it has more complexity than the other tiers the test executed on this tier is called API Testing. API Testing tests the logic tier directly and checks expected functionality, reliability, performance, and security.
What is Rest API?
REST is an architectural style that uses simple HTTP calls for inter-machine communication. REST does not contain an additional messaging layer and focuses on design rules for creating stateless services. A client can access the resource using the unique URI and a representation of the resource is returned. With each new resource representation, the client is said to transfer state. While accessing RESTful resources with HTTP protocol, the URL of the resource serves as the resource identifier, and GET, PUT, DELETE, POST and HEAD are the standard HTTP operations to be performed on that resource.
REST API Testing with Rest Assured
What is Rest Assured?
REST Assured is a Java DSL for simplifying the testing of REST-based services built on top of HTTP Builder. It supports POST, GET, PUT, DELETE, OPTIONS, PATCH, and HEAD requests and can be used to validate and verify the response of these requests.
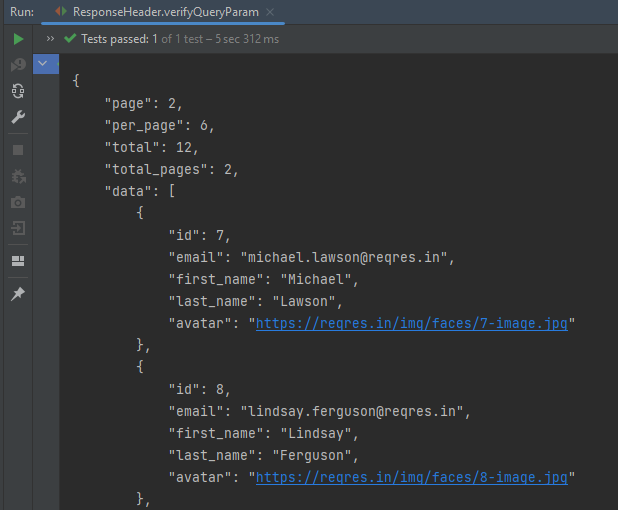
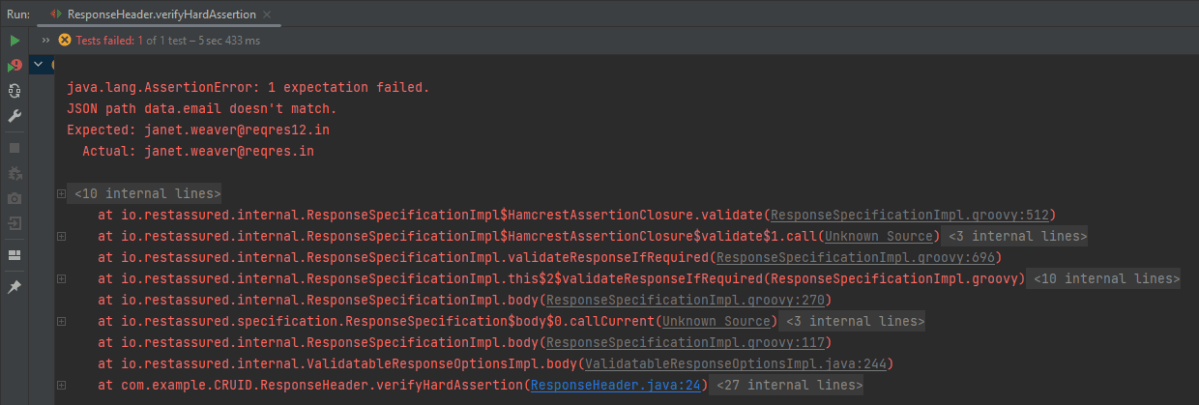
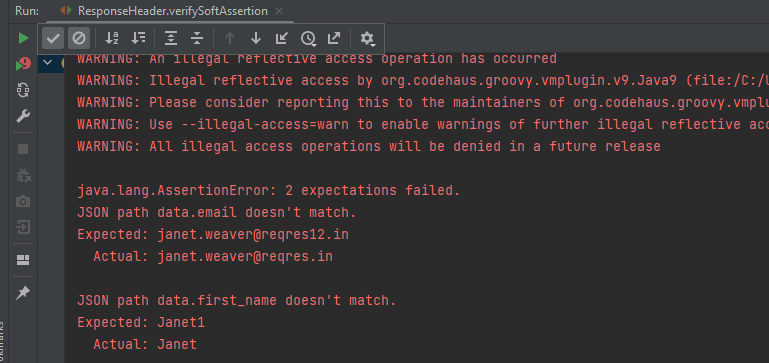
Rest-Assured library also provides the ability to validate the HTTP Responses received from the server. For e.g. we can verify the Status code, Status message, Headers, and even the Body of the response. This makes Rest-Assured a very flexible library that can be used for testing.
REST Assured can be used to test XML as well as JSON-based web services. REST Assured can be integrated with JUnit and TestNG frameworks for writing test cases for our application.
HTTP Methods for REST API Automation Testing
REST API uses five HTTP methods to request a command:
GET: To retrieve the information at a particular URL.
PUT: To update the previous resource or create new information at a particular URL.
PATCH: For partial updates.
POST: It is used to develop a new entity. Moreover, it is also used to send information to the server, such as uploading a file, customer information, etc.
DELETE: To delete all current representations at a specific URL.
HTTP Status Codes
Status codes are the responses given by a server to a client’s request. They are classified into five categories:
- 1xx (100 – 199): The response is informational
- 2xx (200 – 299): Assures successful response
- 3xx (300 – 399): You are required to take further action to fulfill the request
- 4xx (400 – 499): There’s a bad syntax and the request cannot be completed
- 5xx (500 – 599): The server entirely fails to complete the request
Advantages of Rest Assured
- It is an Open source Tool i.e. free.
- It requires less coding compared to Apache Http Client.
- Easy parsing and validation of response in JSON and XML.
- The extraction of values and asserting is quite easy using inbuilt Hemcrest Matchers.
- It follows BDD keywords like given(), when(), then() which makes code readable and supports clean coding. This feature is available from version 2.0.
- It supports quick assertion for status code and response time.
- It supports assertion to Status Code, Response Time, Headers, cookies, Content-Type, etc.
- It has a powerful logging mechanism.
- It can be easily integrated with other Java libraries like TestNG, JUnit as Test Framework and Extent Report, and Allure Report for reporting purposes.
- It provides quite good support for different authentication mechanisms for APIs.
- It can be integrated with Selenium-Java to achieve End-to-end automation.
- It supports JSONPath and XmlPath which helps in parsing JSON and XML response. Rest Assured integrates both by default.
- It can be used to verify JSON Schema using JSON Schema Validation library and XML schema validation
- It can be integrated with Build Tools like Maven or Gradle and supports CI/CD also.
- It supports multi-part form data and Spring Mock Mvc, Spring Web Test Client, Scala and Kotlin.