In this tutorial, we will create a project in PyCharms and enter data in TextBox in Robot Framework
Prerequisite:
- Install Python
- Install PIP
- Install Robot Framework
- Install Robot framework Selenium Library
- Install PyCharm IDE
Please refer to this tutorial to install Robot Framework – How to install and setup Robot Framework for Python.
Implementation Steps:
Step 1 – Create a new Project
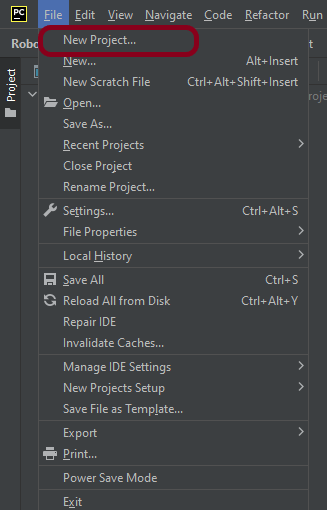
Step 1.1 – Open PyCharm and create a new project. Go to File and select New Project from the main menu.
Step 1.2 – Choose the project location. Click the Browse button next to the Location field and specify the directory for your project.
Deselect the Create a main.py welcome script checkbox because you will create a new Python file for this tutorial.

Click on the Create Button.
Step 1.3 – A new dialog will appear asking to Open the project using any one of the given options. I have selected New Window as I like to have separate windows for each project.
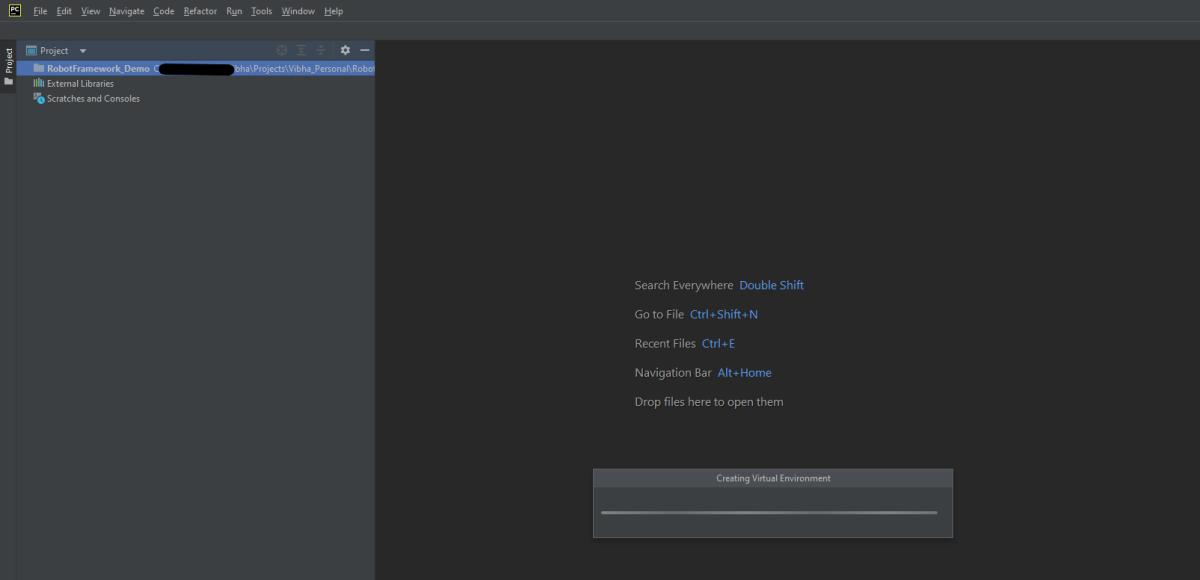
Below is the image of the new project created in PyCharms.
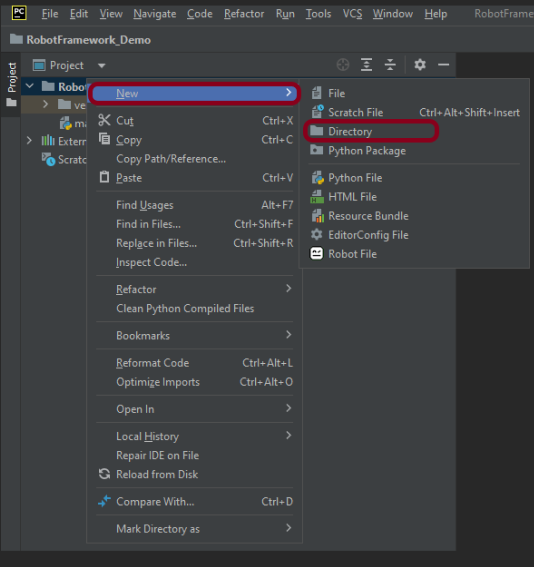
Step 2 – Create a new directory in the new project
Right-Click on the project, select New->Directory and provide name as Tests
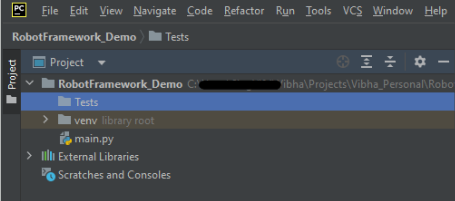
Below is the image of the new directory.
Step 3 – Create a robot Test File
Right-click on the new directory and select New File and provide the name as Test_Demo.robot as shown below:

Step 4 – Download ChromeBinaries from the below location
The tests are going to use the Chrome browser, so we need to download the ChromeBinaries to open a blank browser in Chrome.
https://chromedriver.chromium.org/
The chromedriver and geckodriver are placed in a folder name drivers in the RobotFramework_Demo project. I have renamed chromedriver to Chrome and geckodriver to Firefox.
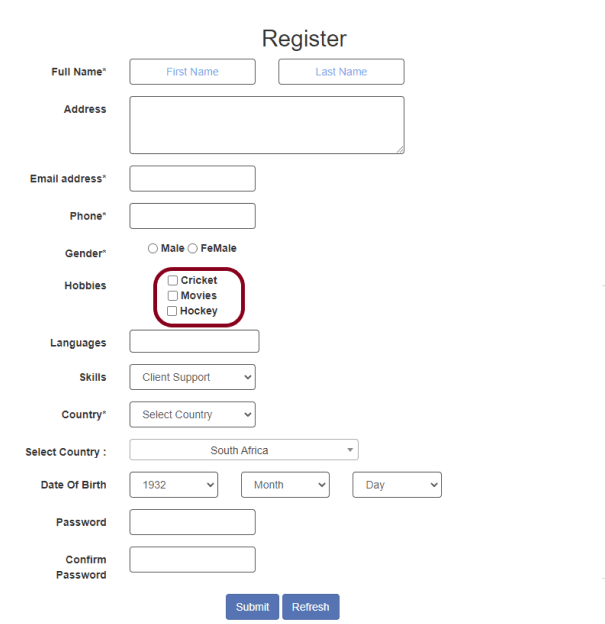
Step 5 – Enter Data in Textbox
We are now going to write test cases. The test case details will be as follows:
- Open browser − URL − https://opensource-demo.orangehrmlive.com/web/index.php/auth/login in Chrome
- Enter username and password in the search textbox
- Click Search Button
- Verify the error message
To work with the textbox, we need a locator. A locator is an identifier for the textbox like id, name, class, xpath, css selector, etc.
To know more about locators, refer to these Selenium Tutorials:
Locators in Selenium – Locate by ID, ClassName, Name, TagName, LinkText, PartialLinkText
Dynamic XPath in Selenium WebDriver
CSS Selector in Selenium WebDriver
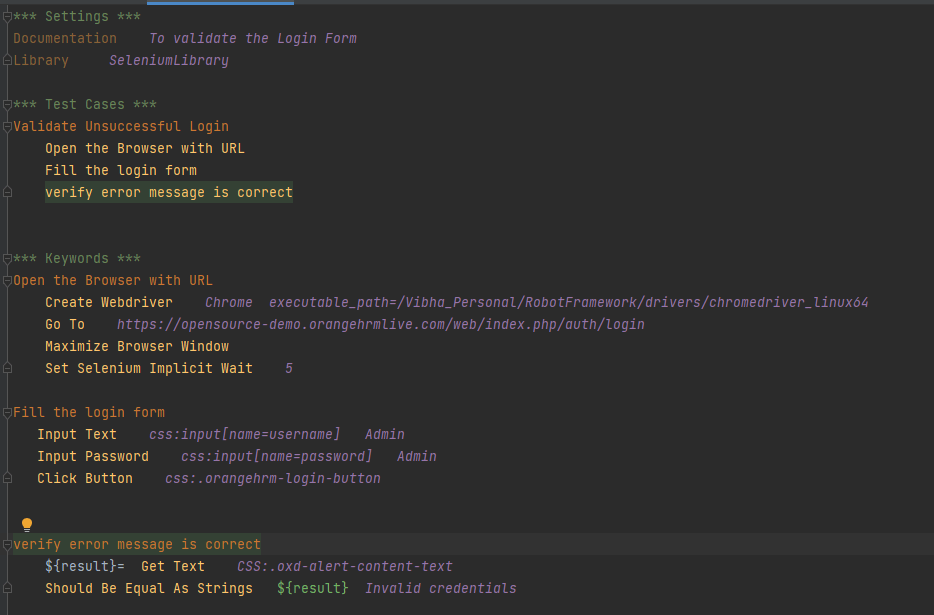
Below is an example of entering data in TextBox.
*** Settings ***
Documentation To validate the Login Form
Library SeleniumLibrary
*** Test Cases ***
Validate Unsuccessful Login
Open the Browser with URL
Fill the login form
Verify error message is correct
*** Keywords ***
Open the Browser with URL
Create Webdriver Chrome executable_path=/Vibha_Personal/RobotFramework_Demo/drivers/chromedriver_linux64
Go To https://opensource-demo.orangehrmlive.com/web/index.php/auth/login
Maximize Browser Window
Set Selenium Implicit Wait 5
Fill the login form
Input Text css:input[name=username] Admin
Input Password css:input[name=password] Admin
Click Button css:.orangehrm-login-button
Verify error message is correct
${result}= Get Text CSS:.oxd-alert-content-text
Should Be Equal As Strings ${result} Invalid credentials
All the below-mentioned keywords are derived from SeleniumLibrary except the last one. The functionality of keywords mentioned above:
1. Create Webdriver − The keyword creates an instance of Selenium WebDriver.
2. Go To – This keyword navigates the current browser window to the provided url.
3. Maximize Browser Window – This keyword maximizes the current browser window.
4. Set Selenium Implicit Wait – This keyword sets the implicit wait value used by Selenium.
5. Input Text − This keyword is used to type the given text in the specified textbox identified by the locator name:username.
6. Input Password – This keyword is used to type the given text in the specified password identified by the locator name:password.
The difference compared to Input Text is that this keyword does not log the given password on the INFO level.
7. Click button – This keyword is used to click on the button with location css:.orangehrm-login-button.
8. ${result} – This is a variable that holds the text value of the error message that is located by css:.oxd-alert-content-text
9. Get Text – This keyword returns the text value of the element identified by located by css:.oxd-alert-content-text.
10. Should Be Equal As Strings – This keyword is used from builtIn keyword. This keyword returns false if objects are unequal after converting them to strings.
Step 6 – Execute the tests
To run this script, go to the command line and go to directory tests.
We need the below command to run the Robot Framework script.
robot Test_Demo.robot

The output of the above program is

Step 7 – View Report and Log
We have the test case passed. The Robot Framework generates log.html, output.xml, and report.html by default.

Let us now see the report and log details.
Report
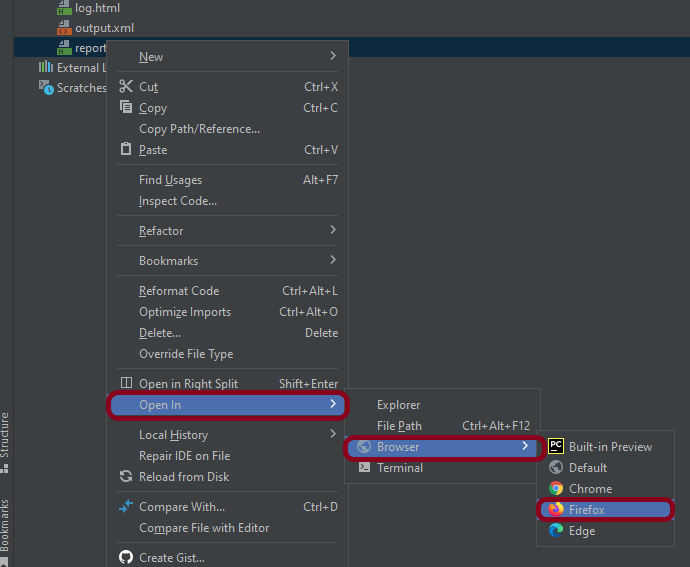
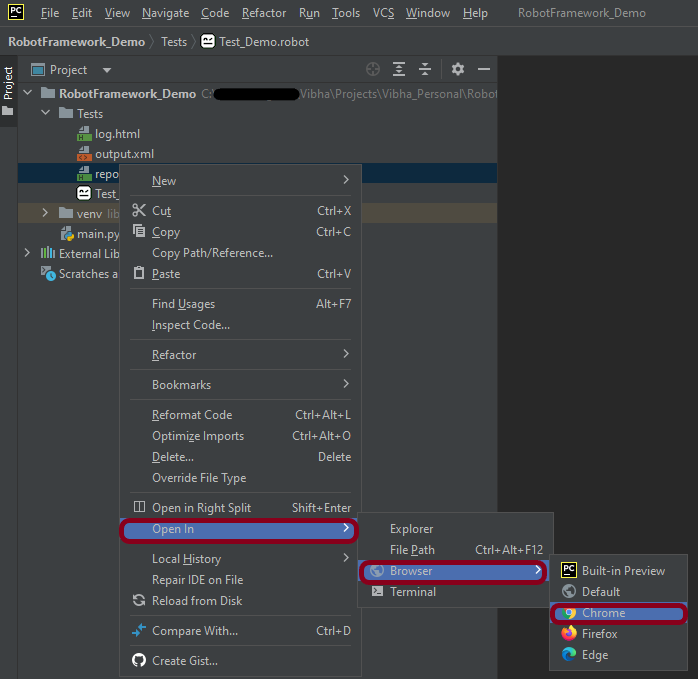
Right-click on report.html. Select Open In->Browser->Chrome(any browser of your wish).
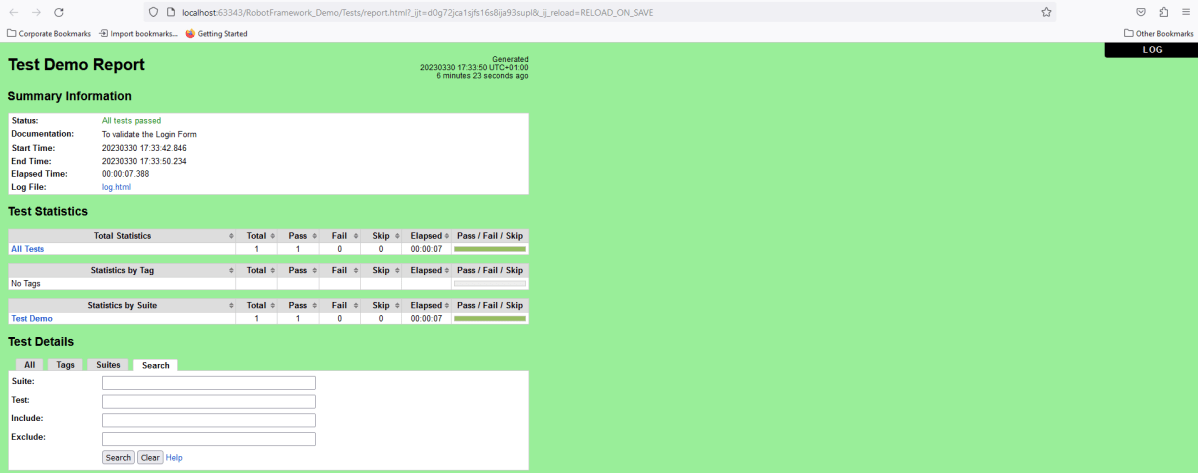
The Report generated by the framework is shown below:
Log
Robot Framework has multiple log levels that control what is shown in the automatically generated log file. The default Robot Framework log level is INFO.
Right-click on log.html. Select Open In->Browser->Chrome(any browser of your wish).
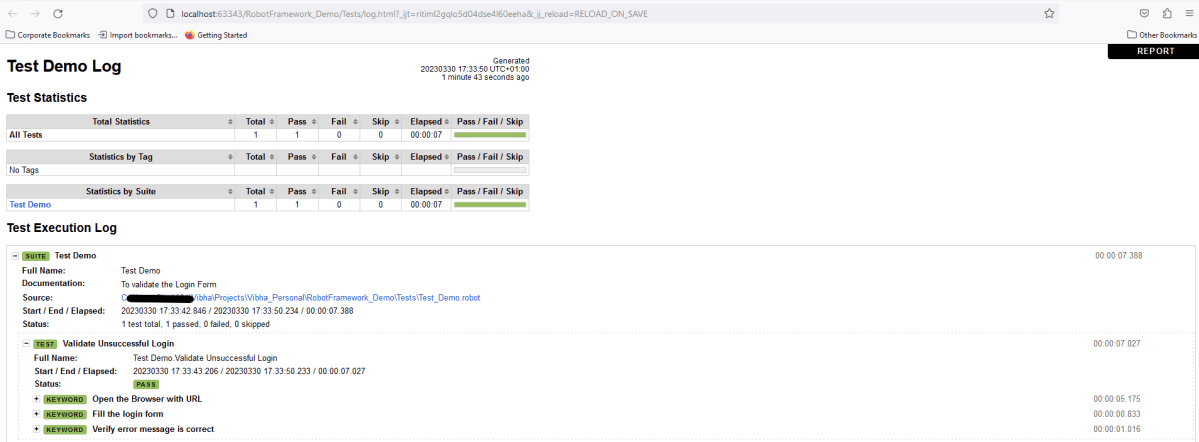
In the below image of the log, we can see that the text entered by the user is shown here, whereas the password does not show the value of the password.

That’s it! Congratulations on making it through this tutorial and hope you found it useful! Happy Learning!!