In the previous tutorial, I explained Hooks in Cucumber. In this tutorial, I will explain Condition Hooks in Cucumber.
Hooks can be conditionally selected for execution based on the tags of the scenario. These are called Condition or Tagged Hooks.
Tagged Hooks are much like the scenario hooks, but the only difference is that they are executed before and after the specified tag.
These tagged hooks will be very specific to the particular tags, so these are not common for all scenarios.
So basically, they can also be run in the following two ways:
- Before (‘tagName’)
- After (‘tagName’)
Why do we need Tagged Hooks?
Suppose there are 3 different sets of scenarios. The prerequisites of these scenarios are different, like they have to open different browsers. So, we don’t want to have a common hook for all the scenarios. In this case, we can create a tagged hook to satisfy the requirement of each scenario.
In the below example, there are 3 tags – ChromeBrowser, FireFoxBrowser, and EdgeBrowser. I want to run the hook which has the specified tag for that scenario. For Example, I want @After and @Before hooks related to Chrome Browser should be executed for the tag – @ChromeBrowser.
Below is the feature file which has 3 different scenarios.
Feature: Conditional or Tagged Hooks
@ChromeBrowser
Scenario: Open Chrome Browser
Given I want to open Google Chrome Browser
@FireFoxBrowser
Scenario: Open Firefox Browser
Given I want to open Mozilla Firefox Browser
@EdgeBrowser
Scenario: Open Edge Browser
Given I want to open Microsoft Edge Browser
Below is the Step Definition for the above feature file.
import io.cucumber.java.en.Given;
public class ConditionalHooksExampleDefinitions {
@Given("I want to open Google Chrome Browser")
public void chrome() throws Throwable {
System.out.println("I want to open Google Chrome Browser");
}
@Given("I want to open Mozilla Firefox Browser")
public void firefox() throws Throwable {
System.out.println("I want to open Mozilla Firefox Browser");
}
@Given("I want to open Microsoft Edge Browser")
public void edge() throws Throwable {
System.out.println("I want to open Microsoft Edge Browser");
}
}
Hooks can be defined in the same class or different. I have defined Hooks in a separate class.
import io.cucumber.java.After;
import io.cucumber.java.AfterStep;
import io.cucumber.java.Before;
import io.cucumber.java.BeforeStep;
public class Hooks {
@BeforeStep
public void beforeStep(){
System.out.println("@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@ Before Step @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@");
}
@AfterStep
public void afterStep(){
System.out.println("@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@ After Step @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@");
}
@Before("@ChromeBrowser")
public void beforeGoogle(){
System.out.println("******* before Chrome *******");
}
@Before("@FireFoxBrowser")
public void beforeFirefox(){
System.out.println("$$$$$$$$$$ before FireFox $$$$$$$$$$");
}
@Before("@EdgeBrowser")
public void beforeEdge(){
System.out.println("============ before Edge =============");
}
@After("@ChromeBrowser")
public void afterGoogle(){
System.out.println("********* After Google *********");
}
@After("@FireFoxBrowser")
public void afterFireFox(){
System.out.println("$$$$$$$$$$$ After FireFox $$$$$$$$$$");
}
@After("@EdgeBrowser")
public void afterEdge(){
System.out.println("============ After Edge ==============");
}
}
There is no change in the Test Runner Class.
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import io.cucumber.junit.Cucumber;
import io.cucumber.junit.CucumberOptions;
@RunWith(Cucumber.class)
@CucumberOptions(monochrome = true, plugin = "pretty", features = "src/test/resources/features/ConditionalHooks.feature", tags = {
"" })
public class MyRunnerTests {
}
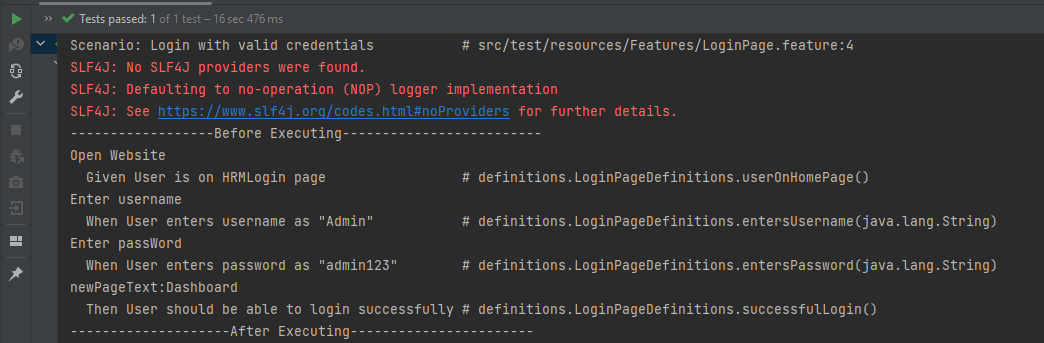
The output of the above execution is

- At the start of execution, @Before(“@ChromeBrowser”) {Scenario Hook} is executed.
- After that @BeforeStep (Step Hook) hook is executed.
- The given statement of the @ChromeBrowser tag is executed in the third step.
- The fourth step is to execute @AfterStep.
- Now, at last, the @After(“@ChromeBrowser”) hook is executed. Similarly, the same sequence is followed for FireFox and Edge Scenarios.
Congratulations on making it through this tutorial and hope you found it useful! Happy Learning!! Cheers!!