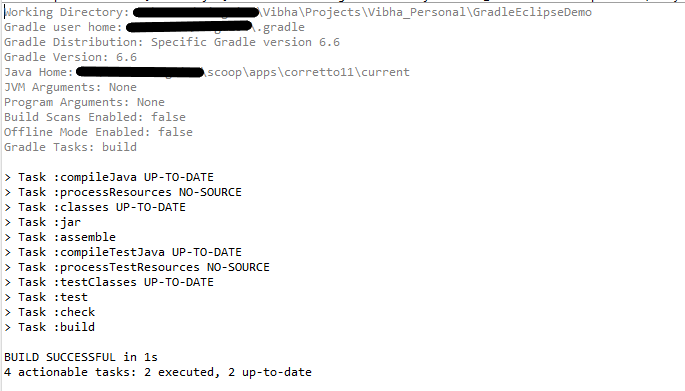
In the previous tutorial, I have provided the Introduction of Rest Assured. In this tutorial, I will explain how to setup basic Rest Assured Gradle project in Eclipse IDE. Before going through this tutorial, it is recommended to go through previous tutorial to know about Rest Assured.
What is Gradle?
Gradle is an open-source build automation tool that is designed to be flexible enough to build almost any type of software. A build automation tool is used to automate the creation of applications. The building process includes compiling, linking, and packaging the code. The process becomes more consistent with the help of building automation tools.
Steps to setup Rest Assured Gradle Project in Eclipse
- Download and Install Java on the system
- Download and setup Eclipse IDE on the system
- Setup Gradle on System
- Create a new Gradle Project
- Add Rest-Assured dependencies to the project
Step 1- Download and Install Java
Rest-Assured needs Java to be installed on the system to run the tests. Check if Java is installed on your machine or not by using the below command on Command Prompt.
java -version
If Java is not installed, then click here to know How to install Java.
Step 2 – Download and setup Eclipse IDE on the system
The Eclipse IDE (integrated development environment) provides strong support for Java developers. If Eclipse IDE is already not present on your system, then click here to know How to install Eclipse.
Step 3 – Setup Gradle
To build a test framework, we need to add several dependencies to the project. This can be achieved by any build Tool. I have used Gradle Build Tool. Click here to know How to install Gradle.
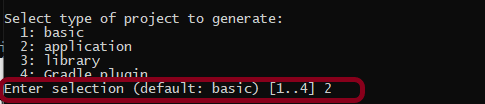
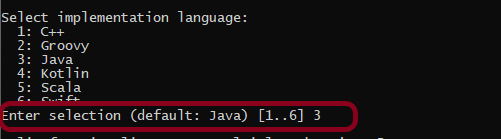
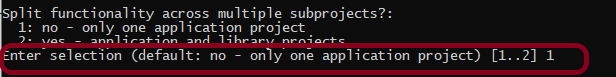
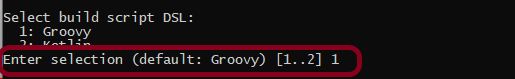
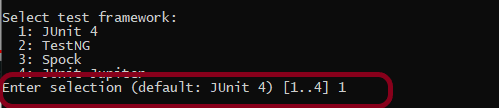
Step 4 – Create a new Gradle Project
To know, in detail, how to create a Gradle project in Eclipse, refer to this link.
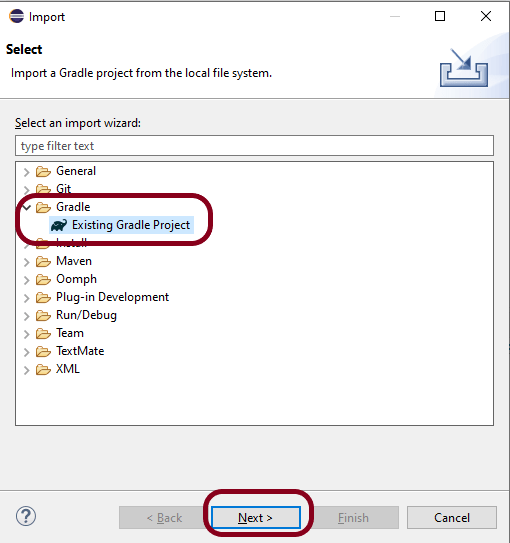
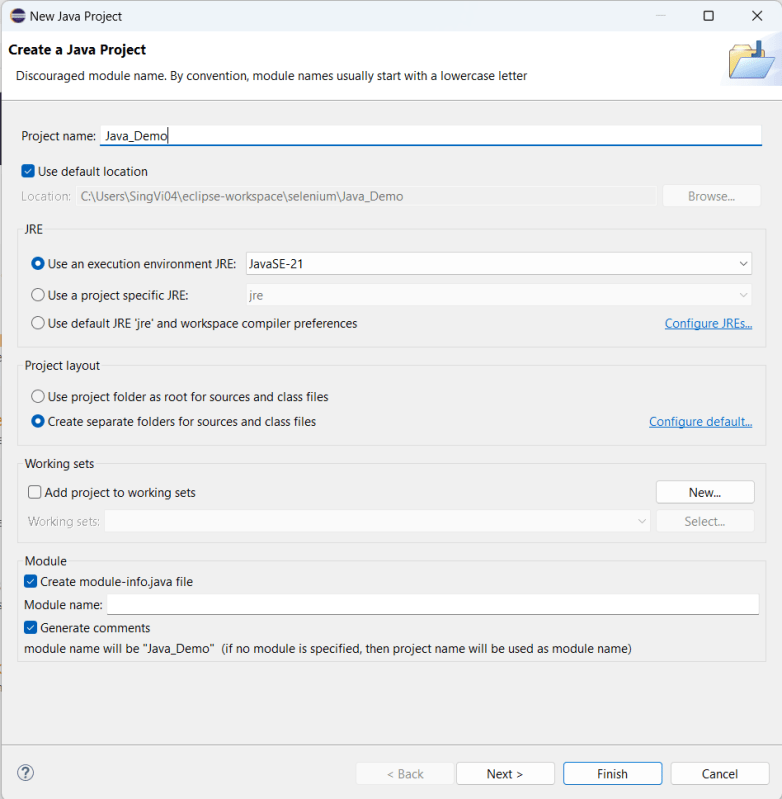
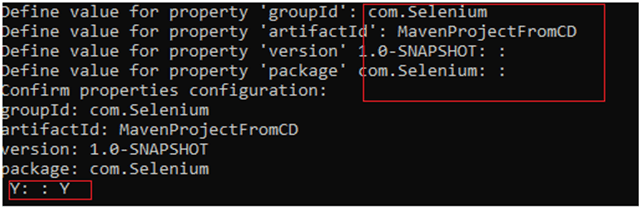
File ->New Project ->Gradle Project ->Next.

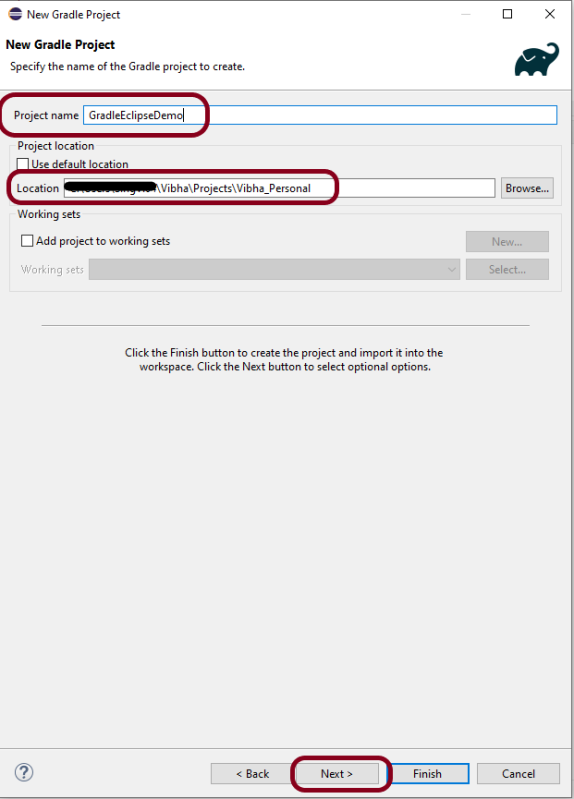
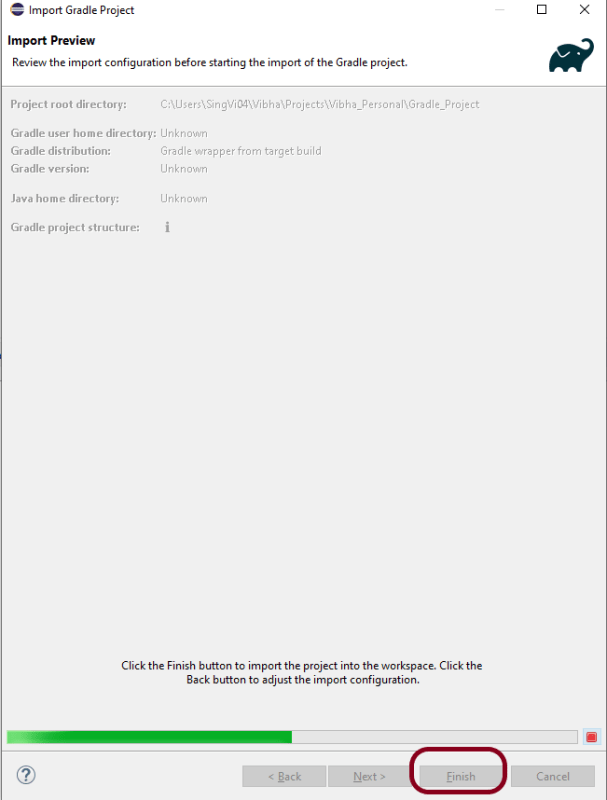
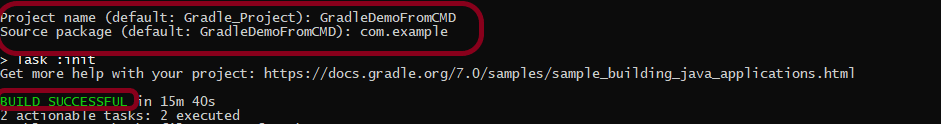
Provide projectname and location where you want to save the project on your system. Click the Finish Button.

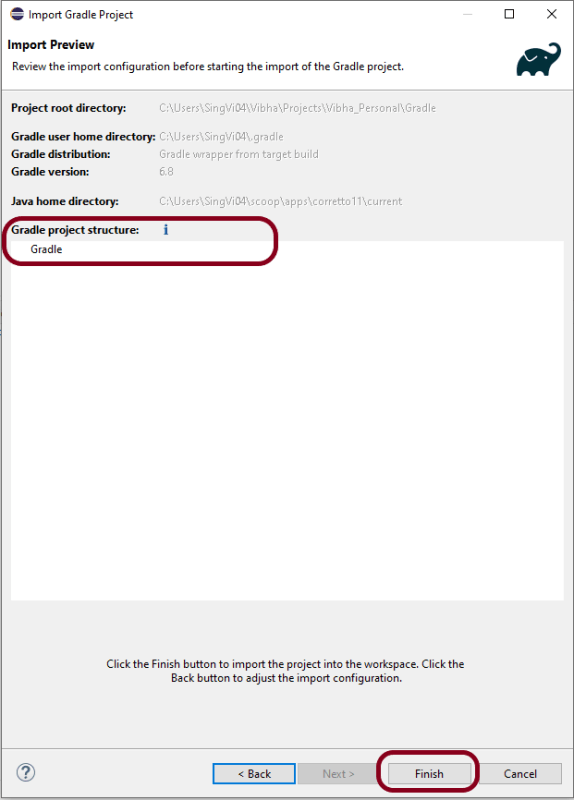
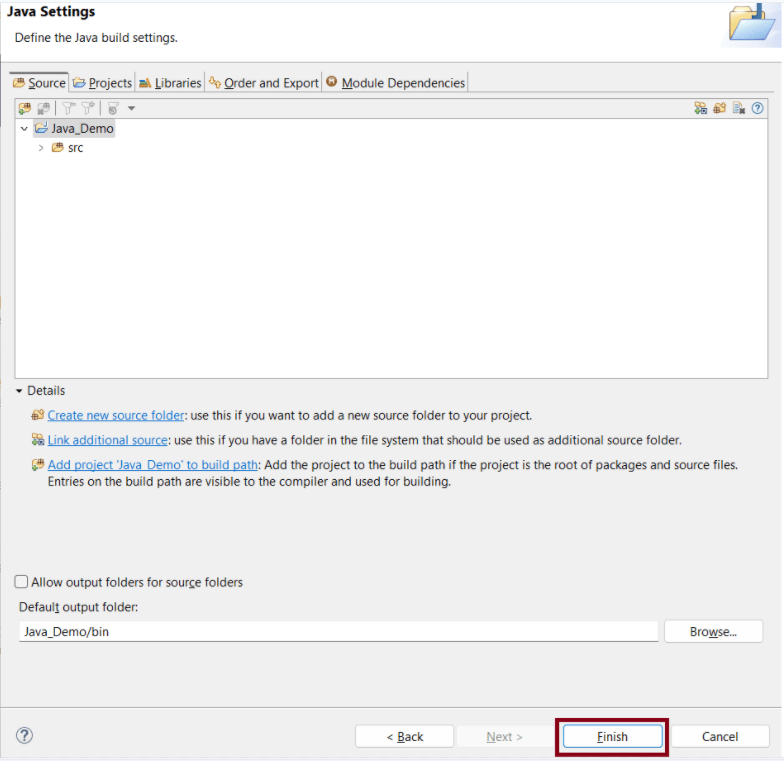
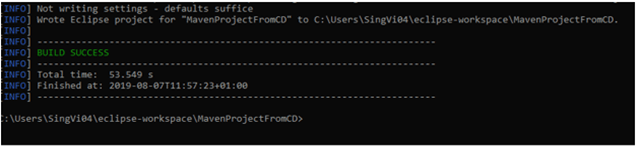
Verify the Gradle Version and Gradle project structure name. Click the Finish Button.

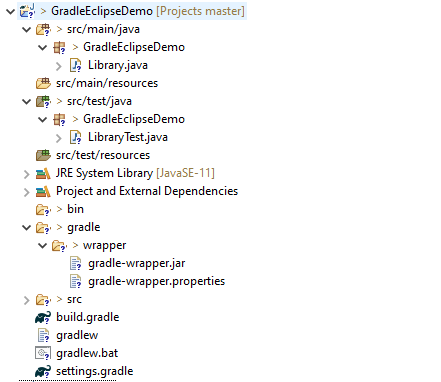
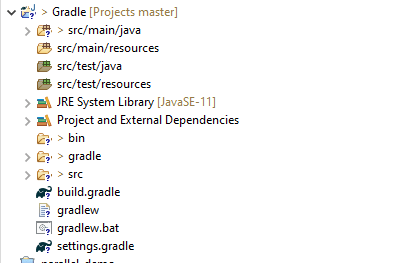
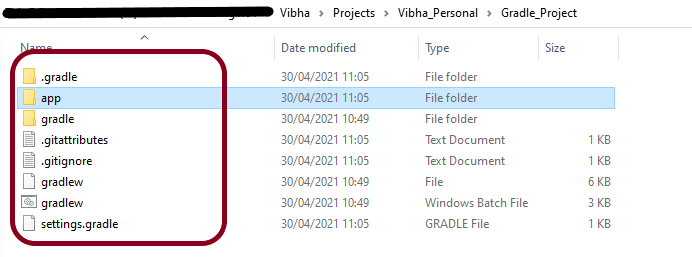
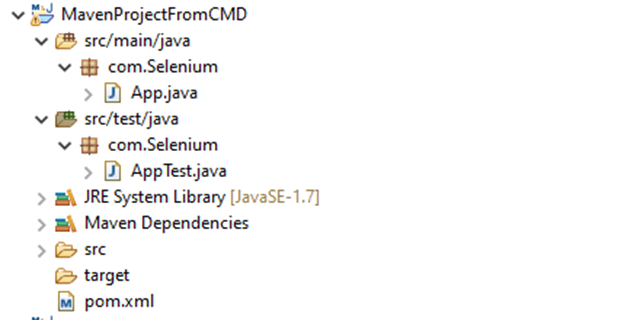
Below is the structure of the new Gradle project.

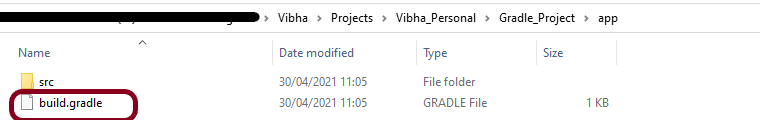
Below is the structure and content of the build.gradle of the new project.
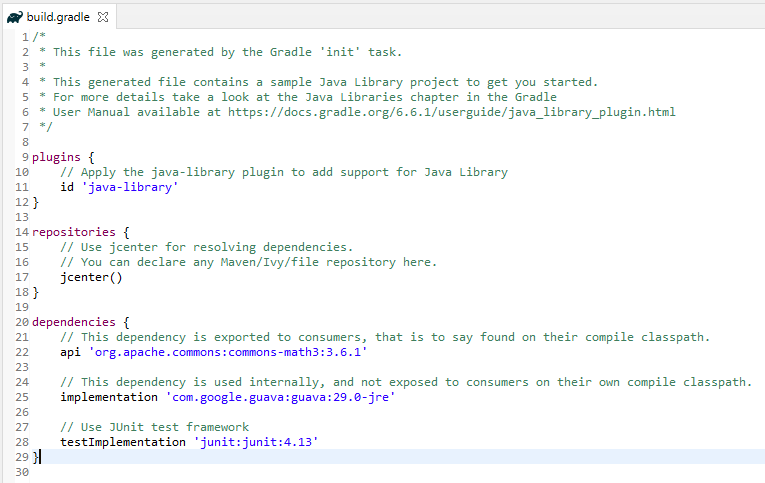
Step 5 – Add Rest-Assured dependencies to the project
Add Rest-Assured, JSON Schema Validator, and JUnit dependencies to the project.
// Use rest assured
testImplementation 'io.rest-assured:rest-assured:4.3.3'
testImplementation 'io.rest-assured:json-schema-validator:4.3.3'
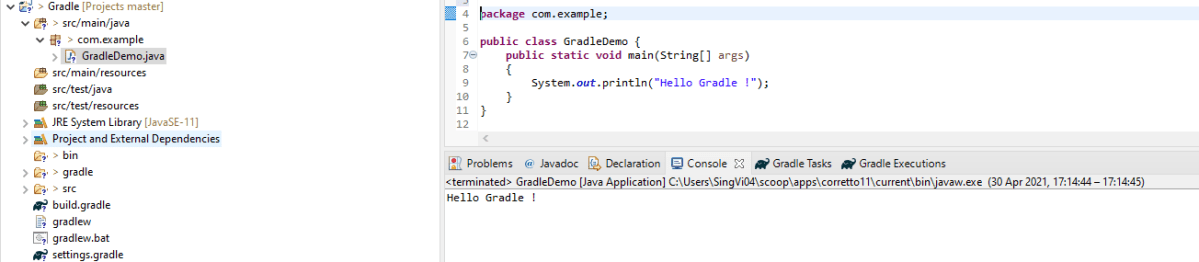
Step 6 – Below are the Rest Assured, json schema validator, junit jar files present under Maven Dependencies.
Make sure you right-click on project -> Select Gradle ->Refresh Gradle Project. It is needed to see the new jar files in the project.

That’s it! Congratulations on making it through this tutorial and hope you found it useful! Happy Learning!! Cheers