Last Updated On
In this tutorial, we will discuss the steps to combine the test reports in a single test report in the Robot Framework.
Table Of Contents
Prerequisite:
- Install Python
- Install PIP
- Install Robot Framework
- Install Robot framework Selenium Library
- Install PyCharm IDE
Please refer to this tutorial to install Robot Framework – How to install and setup Robot Framework for Python.
Implementation Steps
Step 1 – Create a new project
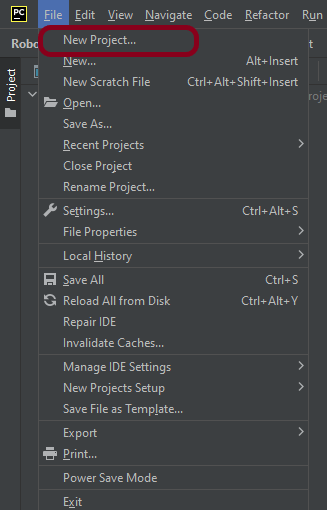
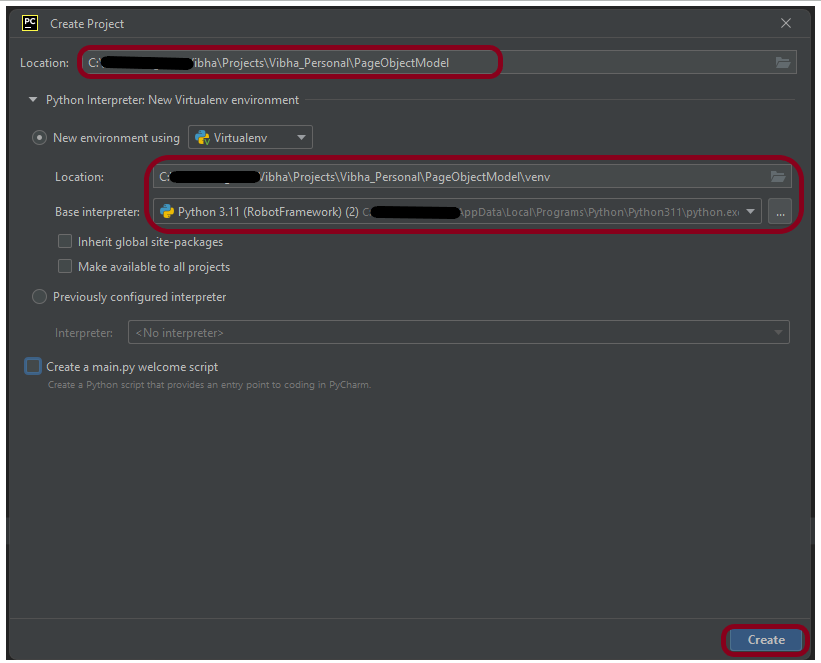
Step 1.1 – Open PyCharm and create a new project. Go to File and select New Project from the main menu.
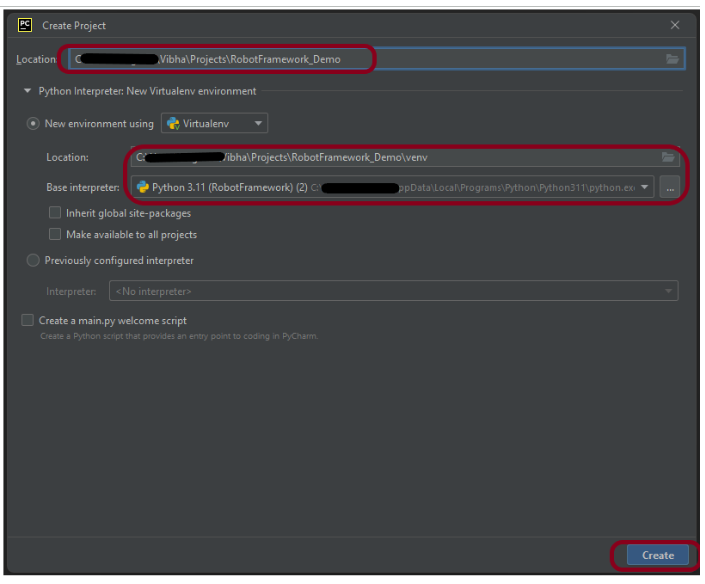
Step 1.2 – Choose the project location. Click the “Browse” button next to the Location field and specify the directory for your project.
Deselect the Create a main.py welcome script checkbox because you will create a new Python file for this tutorial.
Click on the “Create” Button.
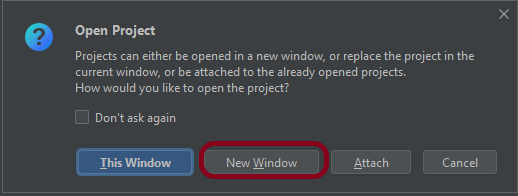
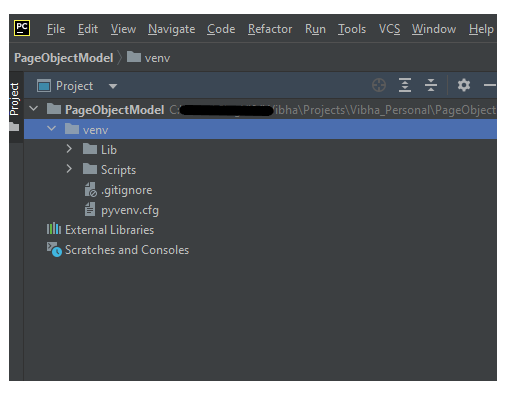
Step 1.3 – A new dialog appears asking to open the project using any one of the given options. I have selected New Window as I like to have separate windows for each project.
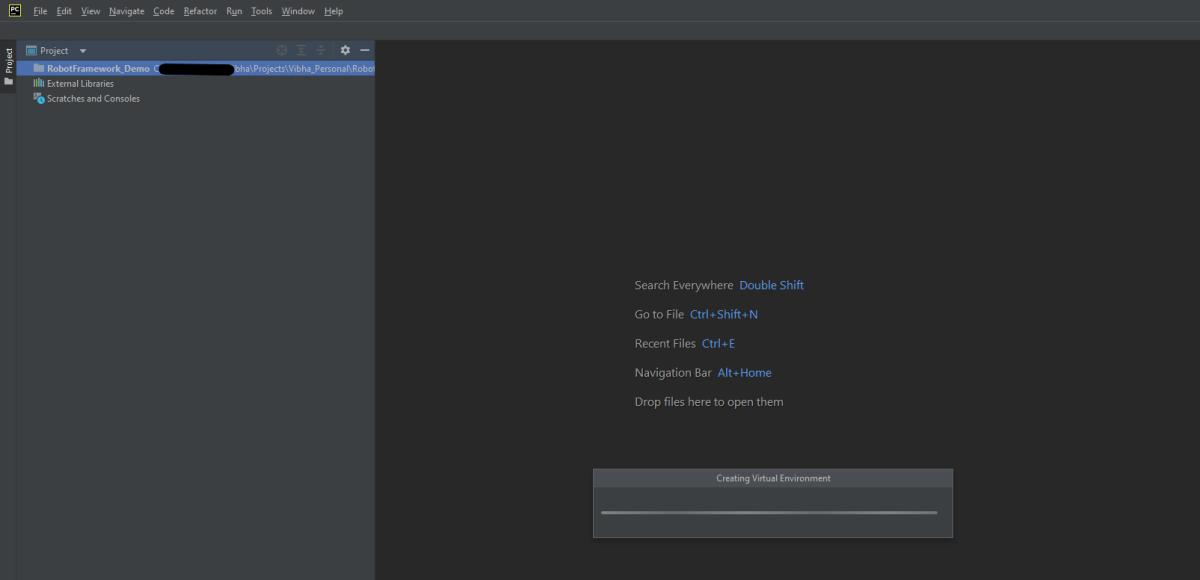
Below is the image of the new project created in PyCharms.

Step 2 – Create 3 new directories in the new project
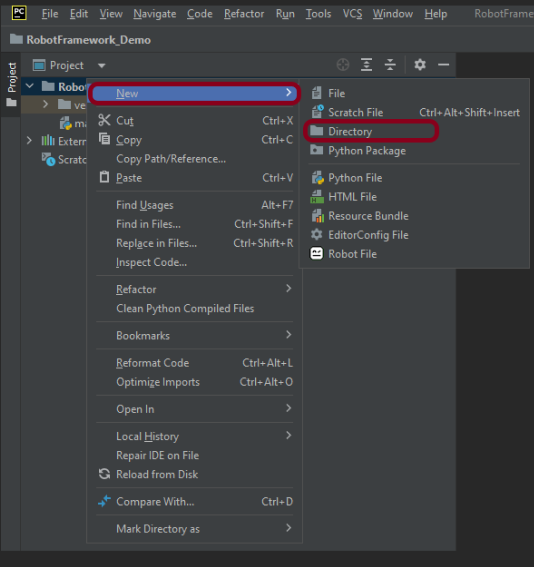
Right-Click on the project, select New->Directory, and provide the name as Tests, Drivers, and Resources
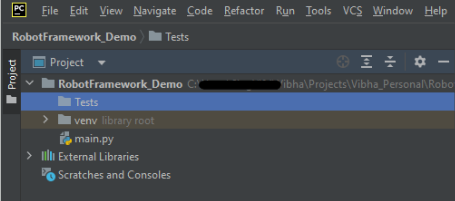
Below is the image of the new directories.

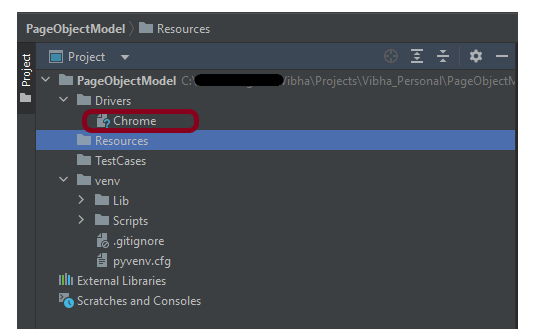
Step 3 – Download ChromeBinaries, Geckodriver and msedgedriver binaries
Download ChromeBinaries, Geckodriver and msedgedriver binaries and place in Drivers directory. This directory contains the browser binary in it. As we are using Chrome, will keep chromedriver.exe here.
The tests are going to use the Chrome browser, Firefox and Edge browsers, so we need to download the corresponding driver binaries to open a blank browser.
https://chromedriver.chromium.org/
Releases · mozilla/geckodriver
Microsoft Edge WebDriver | Microsoft Edge Developer
I will rename chromedriver.exe to Chrome, msedgedriver.exe to Edge and geckodriver.exe to Firefox.

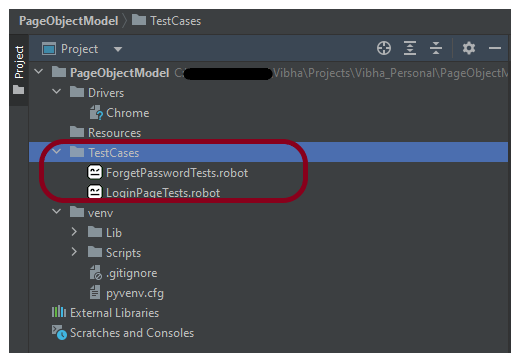
Step 4 – Create Test Files
This directory contains multiple test case files consisting of test steps.
Right-click on the new directory and select New File and provide the name as LoginPageTests.robot as shown below:

Below is the code for LoginPageTests.robot
*** Settings ***
Documentation Tests to login to Login Page
Library SeleniumLibrary
Test Setup Open the Browser with URL
Test Teardown Close Browser Session
Resource ../Resources/GenericResources.robot
Resource ../Resources/LoginResources.robot
*** Test Cases ***
Validate Unsuccessful Login using invalid credentials
LoginResources.Fill the login form ${valid_username} ${invalid_password}
LoginResources.Verify the error message is correct
Validate successful Login
LoginResources.Fill the login form ${valid_username} ${valid_password}
DashboardResources.Verify Dashboard page opens
Settings
Documentation: Allows to add the description about the Login Test page.
Library: Import SeleniumLibrary for browser interactions.
Test Setup: Open the Browser with URL keyword to setup the browser before each test
Test Teardown: Capture Screenshot On Failure keyword to capture screenshots if the test fails
Suite Teardown: Close Browser Session keyword close all the browsers at the end of the test suite.
Resource: Provide the path of the resource file that contains the reusable keywords, variables and other settings.
Step 5 – Create Resources file for each page
It maintains the files which contain page elements as well as corresponding keywords.
Right-click on the new directory and select New File and provide the name as LoginResources.robot, DashboardResources.robot and GenericResources.robot as shown below:

GenericResources.robot contains the keywords that are common to all the tests, like the opening of the browser or closing of the browser.
*** Settings ***
Documentation A resource file with reusable keywords and variables.
Library SeleniumLibrary
*** Variables ***
${valid_username} Admin
${valid_password} admin123
${invalid_username} 1234
${invalid_password} 45678
${url} https://opensource-demo.orangehrmlive.com/web/index.php/auth/login
${browser} Chrome #Default browser, if no browser provided
*** Keywords ***
Open the Browser with URL
Open Browser ${url} ${browser} executable_path=C:/Users/vibha/Documents/Automation/Python/CrossBrowser_RobotFramework/Drivers/${browser}
Maximize Browser Window
Set Selenium Implicit Wait 5
Close Browser Session
Close Browser
Variables used in GenericResources.robot
${valid_username}, ${valid_password}, ${invalid_username}, ${invalid_password}: Assign values
${url}: The URL to navigate to
${browser_name}: Browser will be used to run the tests
Below is the code for LoginResources.robot
*** Settings ***
Documentation All the page objects and keywords of landing page
Library SeleniumLibrary
*** Variables ***
${login_error_message} css:.oxd-alert-content--error
${dashboard_title} css:.oxd-topbar-header-breadcrumb-module
${missing_username_error_message} xpath://*[@class='oxd-form']/div[1]/div/span
${missing_password_error_message} xpath://*[@class='oxd-form']/div[2]/div/span
${forgot_password_link} xpath://div[@class='orangehrm-login-forgot']/p
*** Keywords ***
Fill the login form
[Arguments] ${username} ${password}
Input Text css:input[name=username] ${username}
Input Password css:input[name=password] ${password}
Click Button css:.orangehrm-login-button
Verify the error message is correct
Element Text Should Be ${login_error_message} Invalid credentials
Below is the code for DashboardResources.robot
*** Settings ***
Documentation All the page objects and keywords of Dashboard page
Library SeleniumLibrary
*** Variables ***
${dashboard_title} css:.oxd-topbar-header-breadcrumb-module
*** Keywords ***
Verify Dashboard page opens
Element Text Should Be ${dashboard_title} Dashboard
All the below-mentioned keywords are derived from SeleniumLibrary. The functionality of keywords mentioned above:
1. Open Browser − The keyword opens a new browser instance to the optional url.
2. Maximize Browser Window – This keyword maximizes the current browser window.
3. Set Selenium Implicit Wait – This keyword sets the implicit wait value used by Selenium.
4. Close Browser – Close the current browser.
5. Input Text − This keyword is used to type the given text in the specified textbox identified by the locator name:username.
6. Input Password – This keyword is used to type the given text in the specified password identified by the locator name:password.
The difference compared to Input Text is that this keyword does not log the given password on the INFO level.
7. Click button – This keyword is used to click the button identified by the locator. In this case, it is “Login” button.
8. Element Text Should Be – This keyword is used to verify that the current page contains the exact text identified by the locator. Here, we are checking the exact text “Invalid Credentials”.
These keywords are present in SeleniumLibrary. To know more about these keywords, please refer to this document – https://robotframework.org/SeleniumLibrary/SeleniumLibrary.html.
To run this script, go to the command line and go to directory tests.
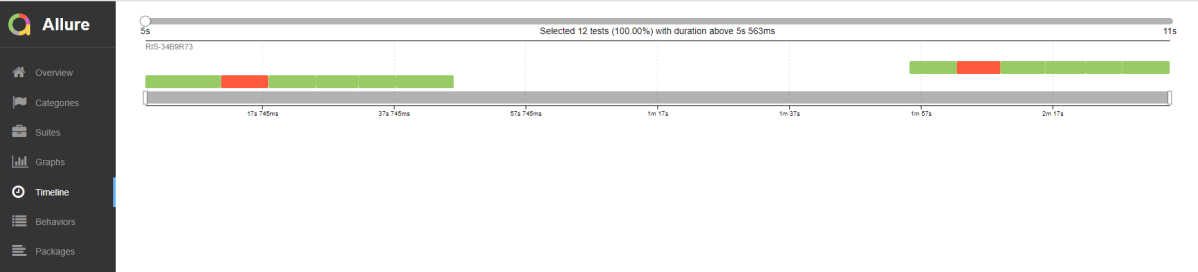
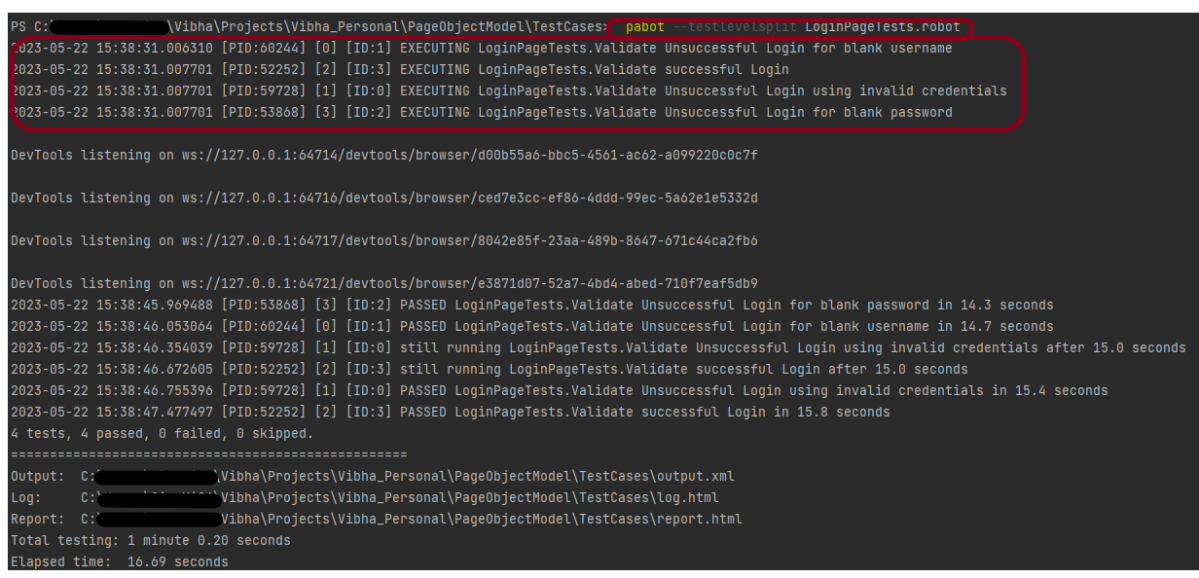
Step 6 – Execute the tests
Run your tests separately for each browser (e.g., Chrome, Firefox, Edge), generating an individual output XML file for each. For example, use the below command to run the tests using the Chrome browser:
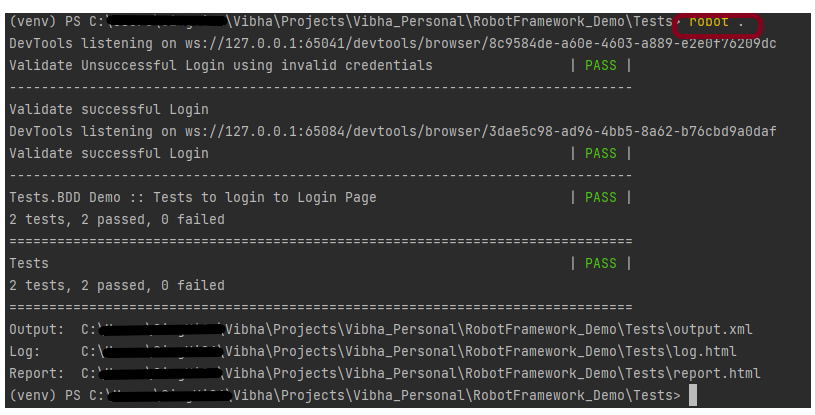
robot --variable browser:Chrome --output output_chrome.xml .
The output of the above program is
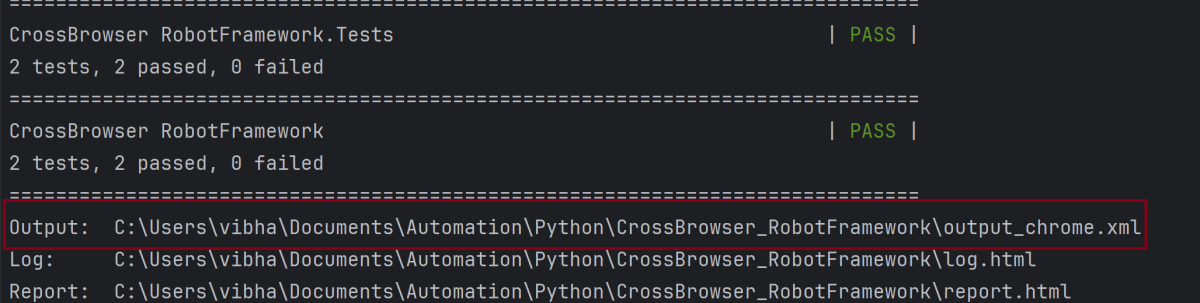
Similarly, use the below commands to run the tests using the firefox and edge browsers
robot --variable browser:Firefox --output output_firefox.xml .
robot --variable browser:Edge --output output_edge.xml .
This will create separate output_chrome.xml, output_firefox.xml, and output_edge.xml files.
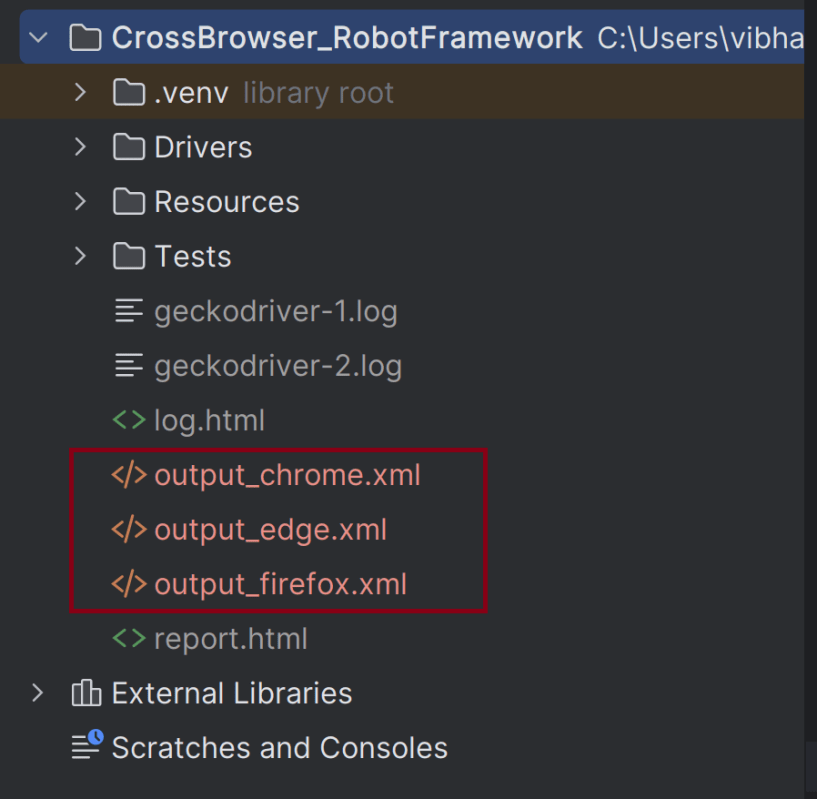
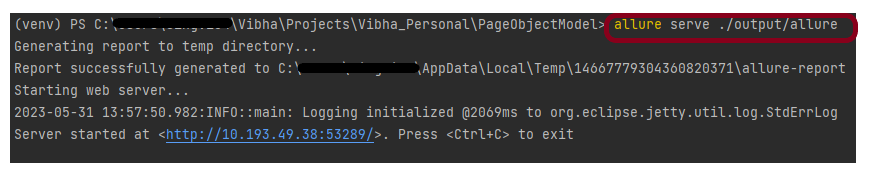
Step 7 – Combine Reports with Rebot
Use rebot to combine the output XML files into a single, consolidated report. Here’s the command:
rebot --outputdir Report --report Consolidated_Report.html output_chrome.xml output_edge.xml output_firefox.xml
In this example:
1. –outputdir Report specifies the directory where the consolidated report will be saved.
2. –report “Consolidated Report.html” sets the name of the report of the Consolidated Report.
3. The list of XML files (output_chrome.xml, output_edge, output_firefox) are the individual report files that will be merged.
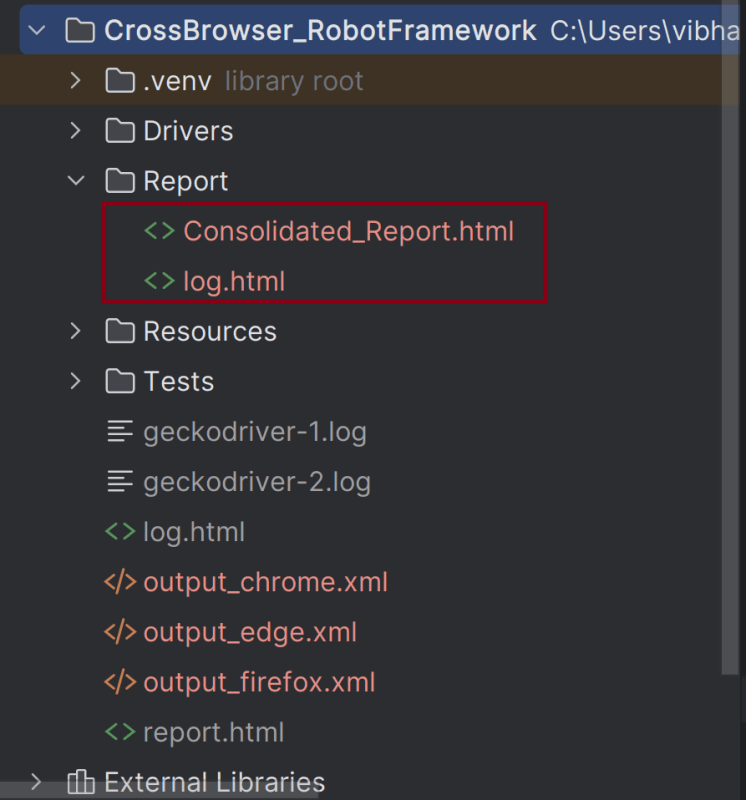
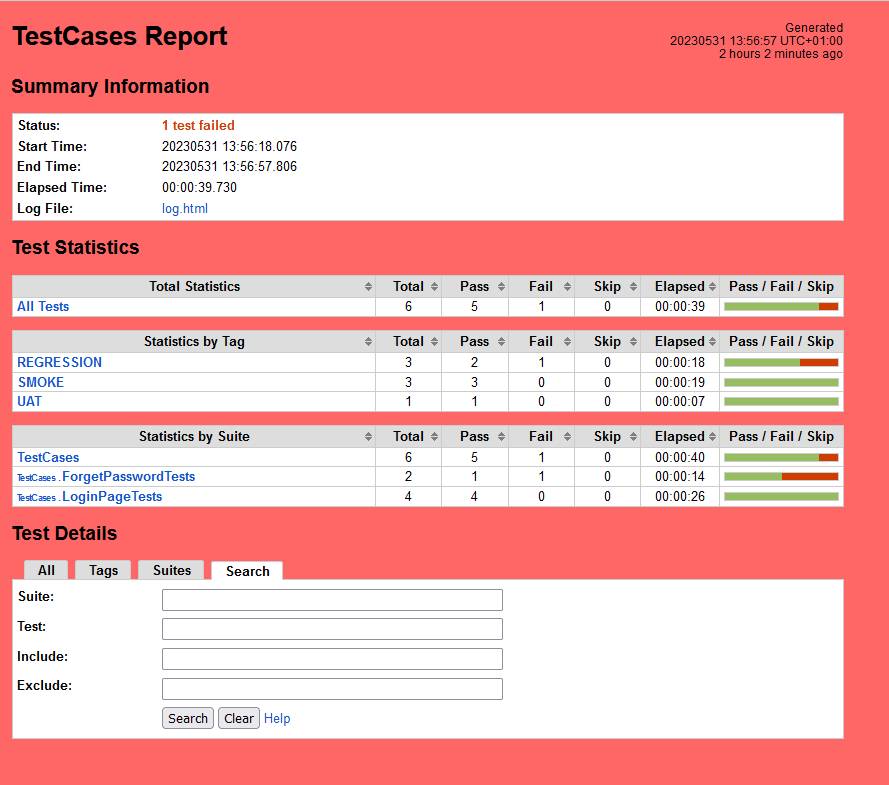
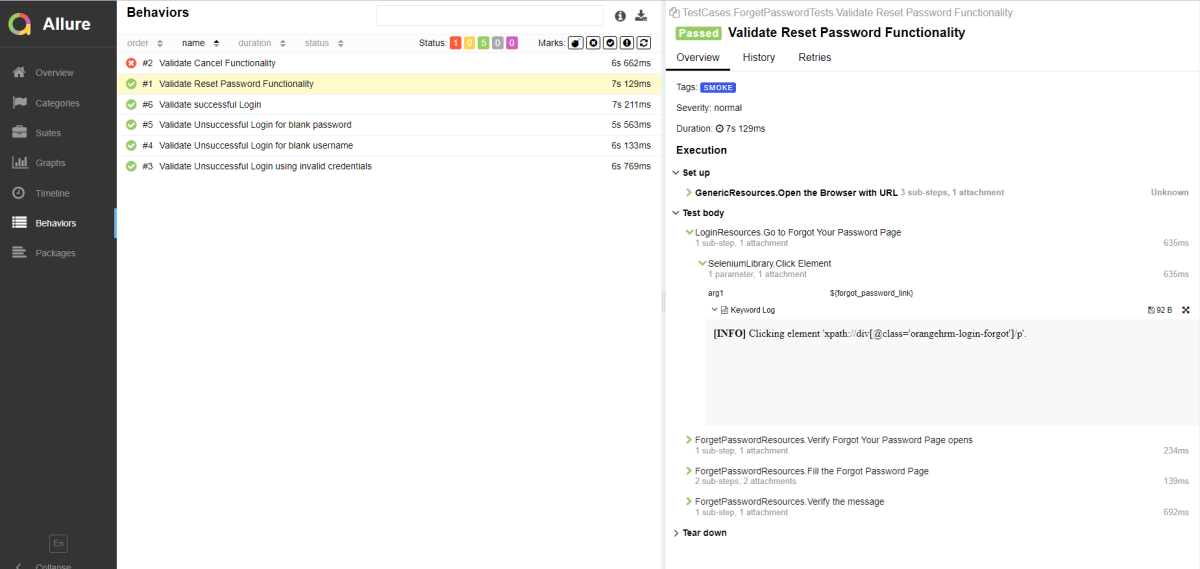
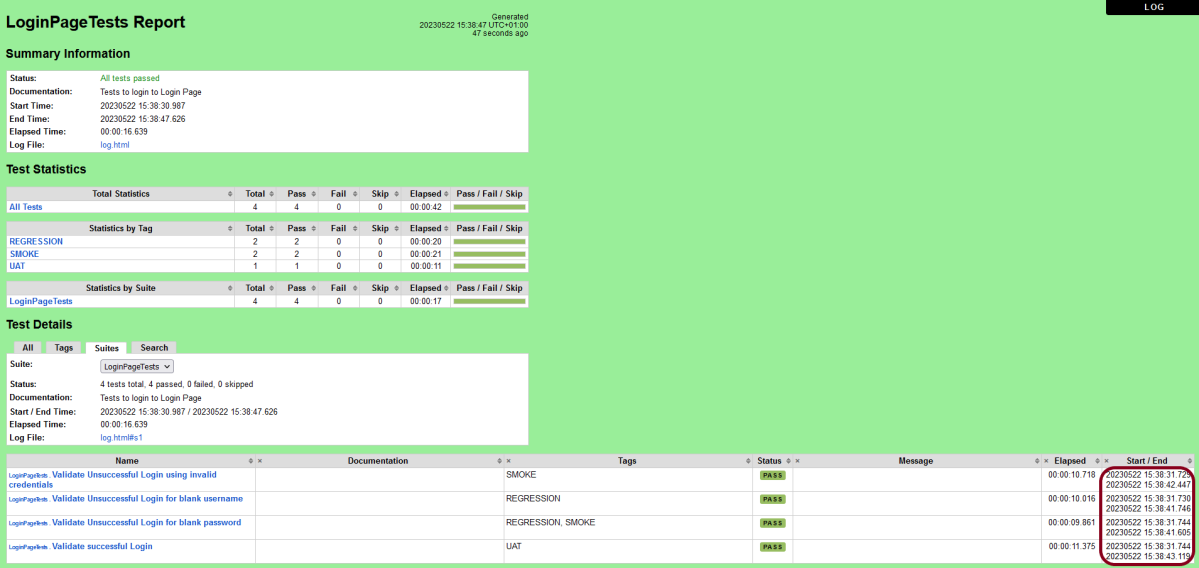
Step 8 – View Report and Log
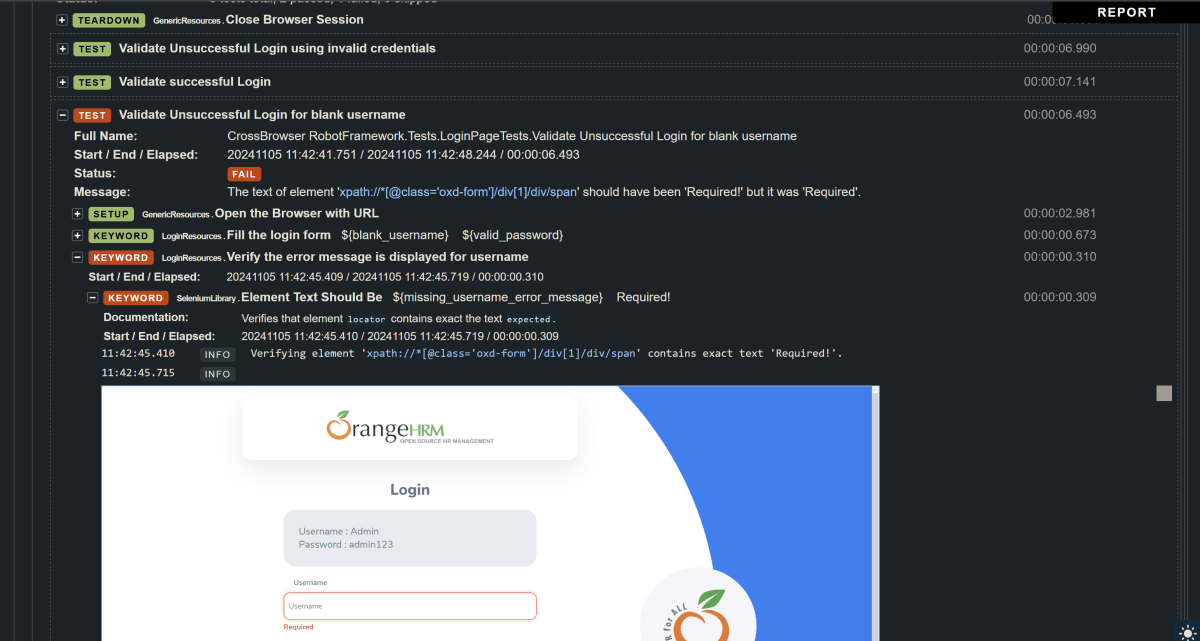
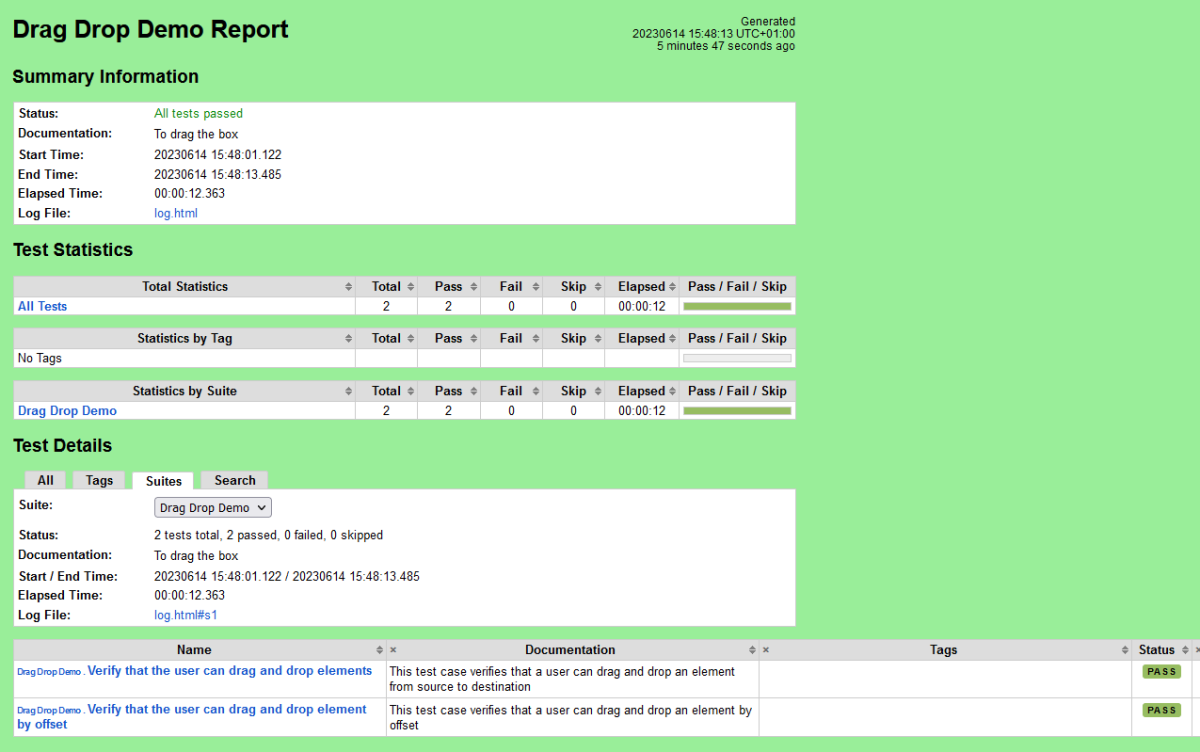
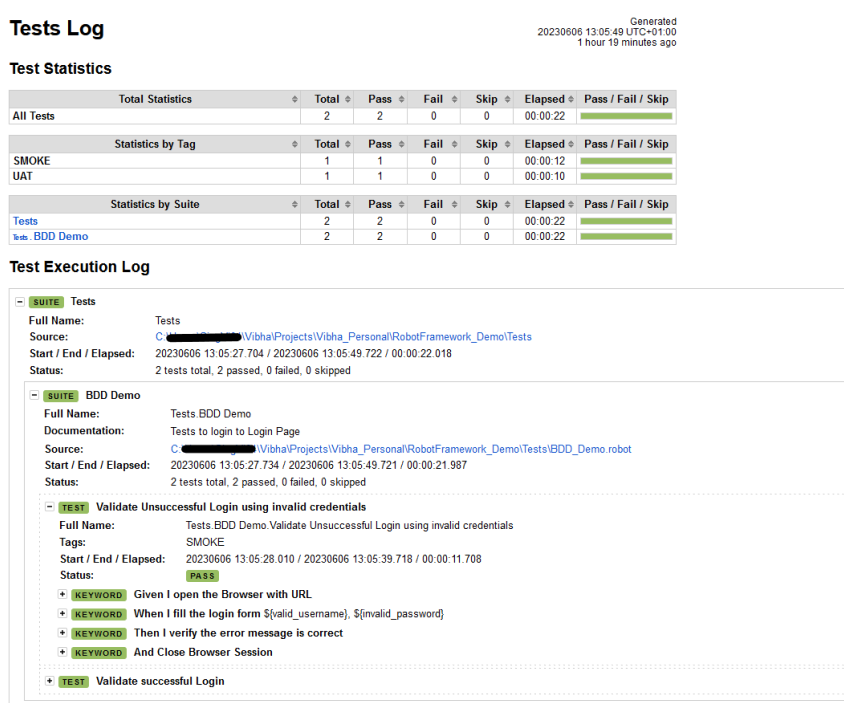
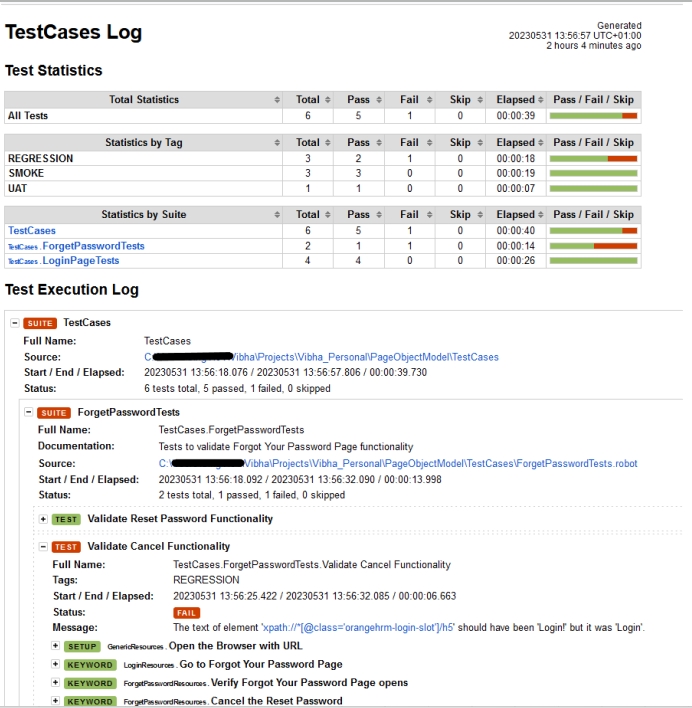
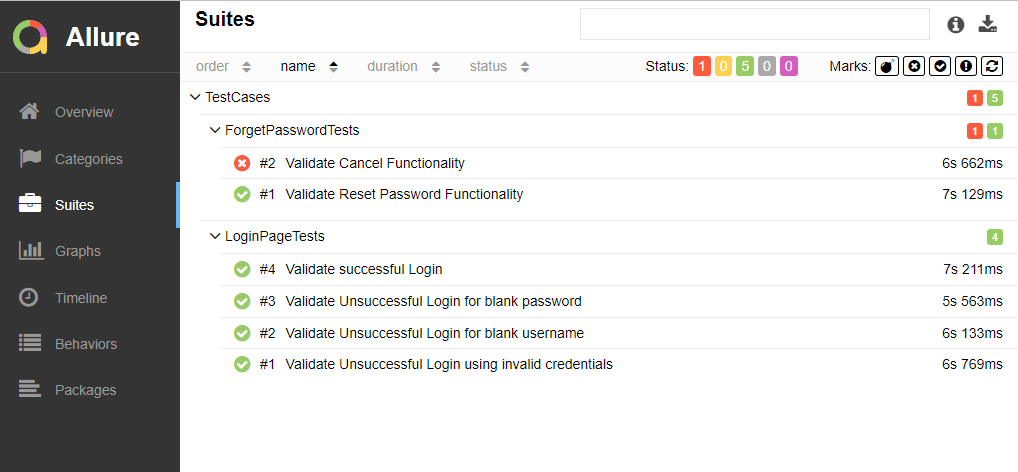
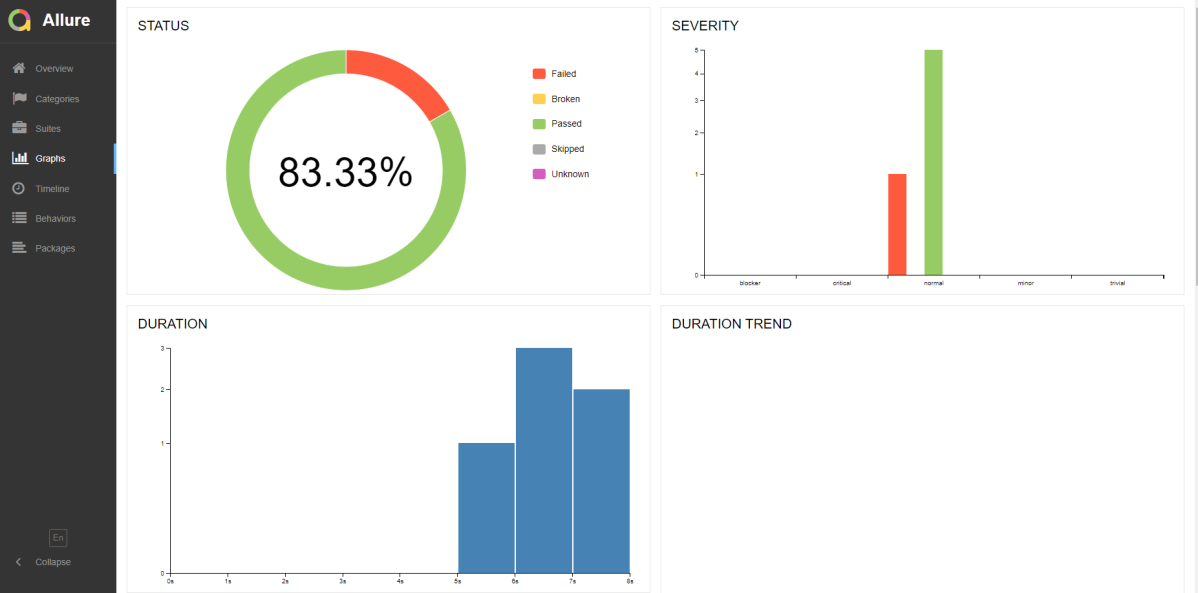
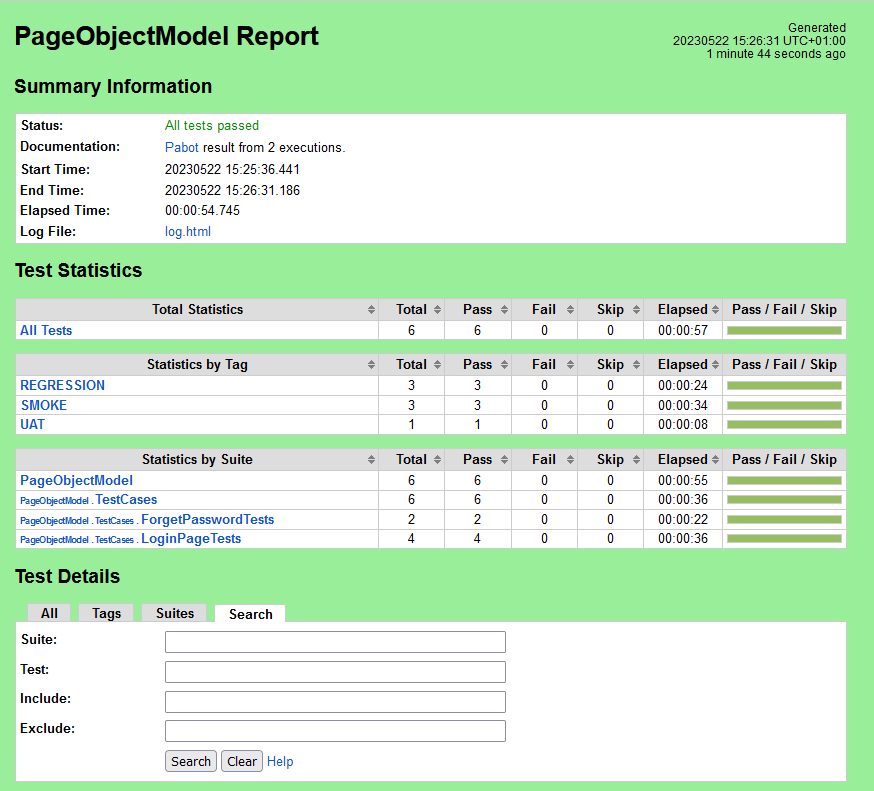
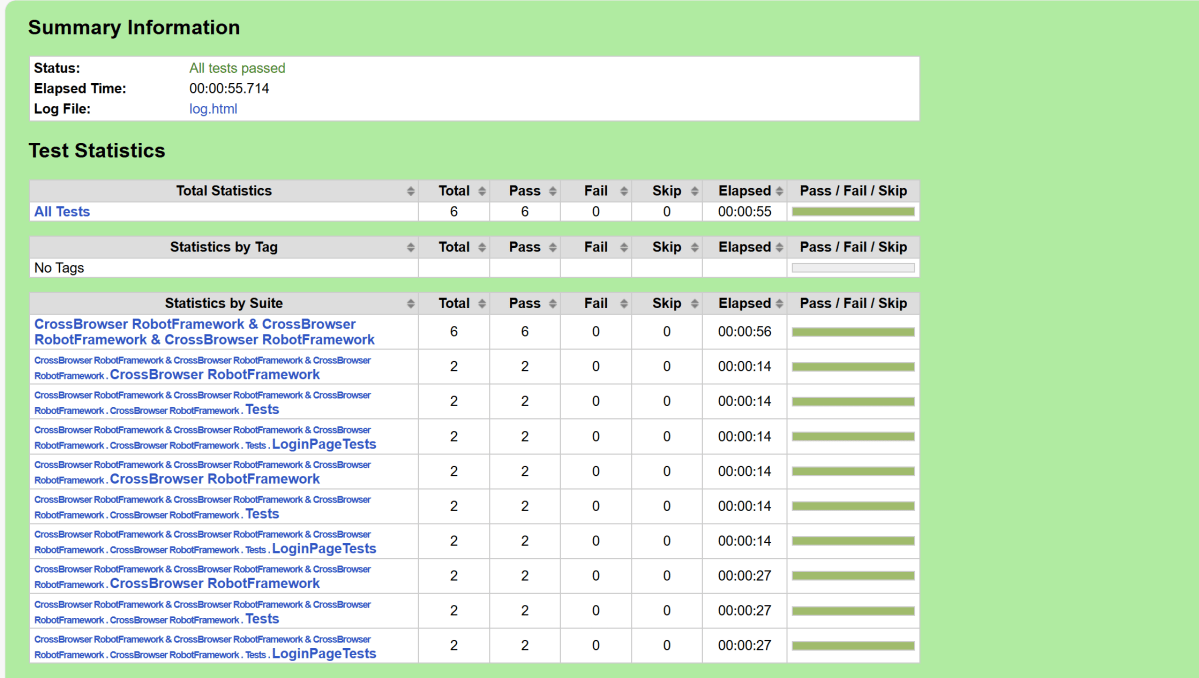
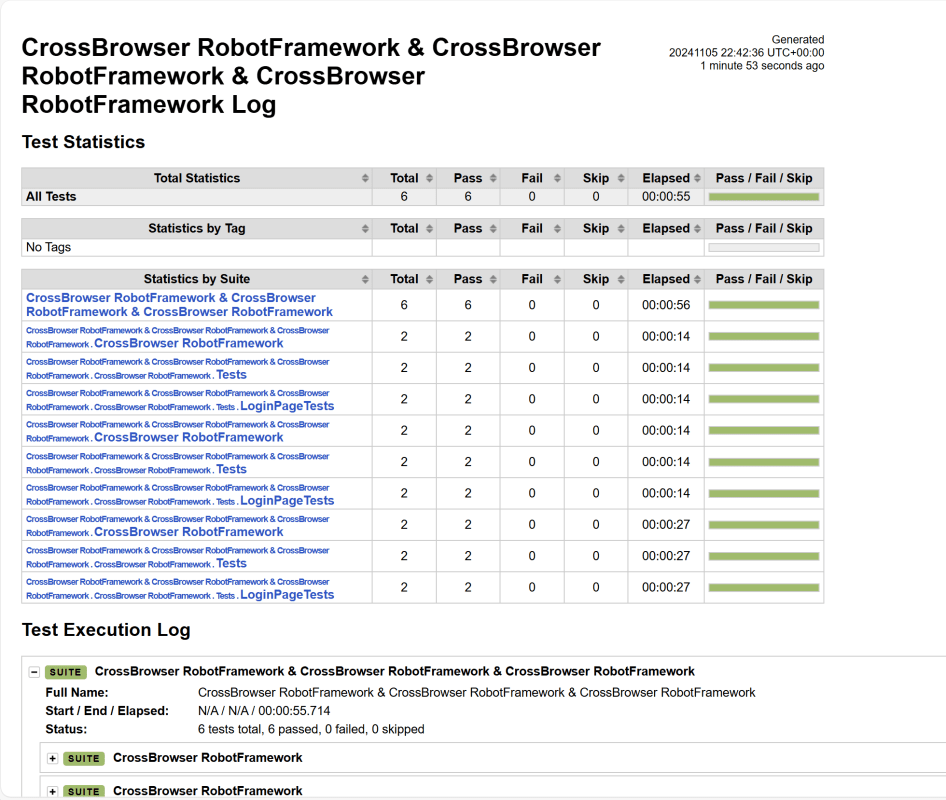
We have total 6 test cases passed (2 test case for each browser).
Let us now see the report and log details.
Report
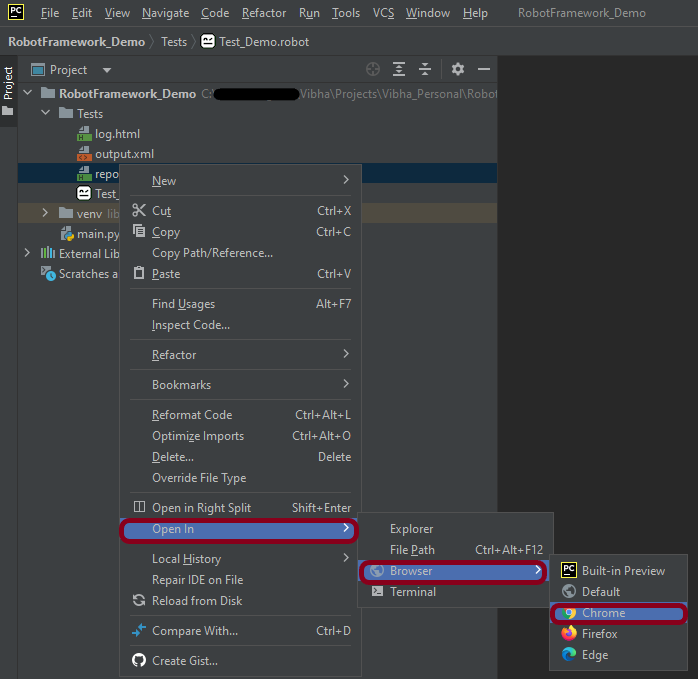
Right-click on report.html. Select Open In->Browser->Chrome(any browser of your wish).
The Report generated by the framework is shown below:
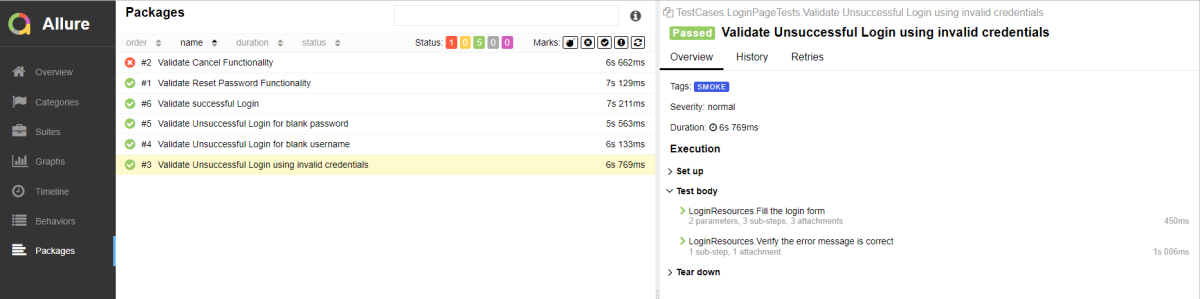
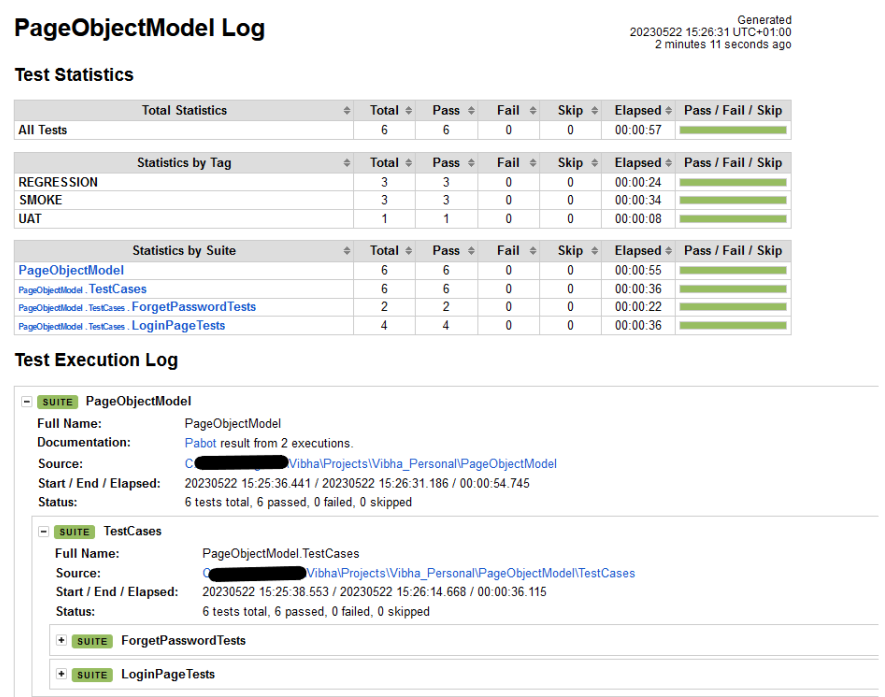
Log
The screenshots will be included in the log.html file under the specific failed test case step. Robot Framework has multiple log levels that control what is shown in the automatically generated log file. The default Robot Framework log level is INFO.
Right-click on log.html. Select Open In->Browser->Chrome(any browser of your wish).
That’s it! Congratulations on making it through this tutorial and hope you found it useful! Happy Learning!!
Additional Tutorials