Cucumber is not an API automation tool, but it works well with other API automation tools.
There are 2 most commonly used Automation Tools for JVM to test API – Rest-Assured and Karate. In this tutorial, I will use RestAssured with Cucumber and JUnit4 for API Testing.
Table of Contents
- What is Rest Assured?
- What is Cucumber?
- Project Structure
- Implementation Steps
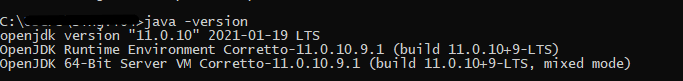
- Download and Install Java
- Download and setup Eclipse IDE on the system
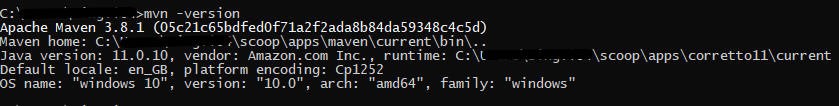
- Setup Maven
- Create a new Maven Project
- Install the Cucumber Eclipse plugin for the Eclipse project
- Create source folder src/test/resources
- Add Rest-Assured and Cucumber dependencies to the project
- Add Maven Compiler Plugin
- Create a feature file under src/test/resources
- Create the Step Definition class or Glue Code for the Test Scenario
- Create a JUnit Cucumber Runner class
- Run the tests from JUnit
- Run the tests from the Command Line
- Cucumber Report Generation
What is Rest Assured?
REST Assured is a Java library that provides a domain-specific language (DSL) for writing powerful, maintainable tests for RESTful APIs. REST Assured can be used easily in combination with existing unit testing frameworks, such as JUnit and TestNG. Rest assured, no matter how complex the JSON structures are, Rest Assured has methods to retrieve data from almost every part of the request and response.
What is Cucumber?
Cucumber is one such open-source tool, which supports Behaviour Driven Development(BDD). In simple words, Cucumber can be defined as a testing framework, driven by plain English. It serves as documentation, automated tests, and development aid – all in one.
Each scenario is a set of steps that the Cucumber must complete. Cucumber validates the software’s compliance with the specification and generates a report indicating success or failure for each scenario.
The cucumber must adhere to some basic syntax rules known as Gherkin in order to comprehend the scenarios.
In this tutorial, I will explain creating a framework for the testing of Rest API in Cucumber BDD.
This framework consists of:
- Cucumber – 7.18.0
- Java 17
- JUnit – 4.13.2
- Maven – 3.9.6
- Rest Assured – 5.4.0
- Maven Compiler – 3.13.0

Project Structure

Implementation Steps
Step 1 – Download and Install Java
Cucumber and Rest-Assured need Java to be installed on the system to run the tests. Click here to know How to install Java.
Step 2 – Download and setup Eclipse IDE on the system
The Eclipse IDE (integrated development environment) provides strong support for Java developers. Click here to know How to install Eclipse.
Step 3 – Setup Maven
To build a test framework, we need to add several dependencies to the project. Click here to know How to install Maven.
Step 4 – Create a new Maven Project
File -> New Project-> Maven-> Maven project-> Next -> Enter Group ID & Artifact ID -> Finish
Click here to know How to create a Maven project
Step 5 – Install the Cucumber Eclipse plugin for the Eclipse project (Eclipse Only)
The Cucumber plugin is an Eclipse plugin that allows eclipse to understand the Gherkin syntax. Cucumber Eclipse Plugin highlights the keywords present in Feature File. To install Cucumber Eclipse Plugin, please refer to this tutorial – How to install Cucumber Eclipse Plugin.
Step 6 – Create source folder src/test/resources
Create source folder src/test/resources to create test scenarios in the Feature file.
A new Maven Project is created with 2 folders – src/main/java and src/test/java. To create test scenarios, we need a new source folder called – src/test/resources. To create this folder, right-click on your maven project ->select New ->Java and then Source Folder.
Mention the source folder name as src/test/resources and click the Next button. This will create a source folder under your new Maven project as shown in the below image.
Step 7 – Add Rest-Assured and Cucumber dependencies to the project
You should place rest-assured before the JUnit dependency declaration in your pom.xml / build.gradle to make sure that the correct version of Hamcrest is used.
REST Assured includes JsonPath and XmlPath as transitive dependencies.
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<rest.assured.version>5.4.0</rest.assured.version>
<cucumber.version>7.18.0</cucumber.version>
<junit.version>4.13.2</junit.version>
<maven.compiler.plugin.version>3.13.0</maven.compiler.plugin.version>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- Rest Assured -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.rest-assured</groupId>
<artifactId>rest-assured</artifactId>
<version>${rest.assured.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Cucumber with JUnit4 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.cucumber</groupId>
<artifactId>cucumber-junit</artifactId>
<version>${cucumber.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Cucumber with Java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.cucumber</groupId>
<artifactId>cucumber-java</artifactId>
<version>${cucumber.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- JUnit4 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>${junit.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Step 8 – Add Maven Compiler Plugin
The compiler plugin is used to compile the source code of a Maven project. This plugin has two goals, which are already bound to specific phases of the default lifecycle:
- compile – compile main source files
- testCompile – compile test source files
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.compiler.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<source>${maven.compiler.source}</source>
<target>${maven.compiler.target}</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
The complete POM.xml will look like something below:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>RestAPI_Cucumber_JUnit4_Demo</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>RestAPI_Cucumber_JUnit4_Demo</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<rest.assured.version>5.4.0</rest.assured.version>
<cucumber.version>7.18.0</cucumber.version>
<junit.version>4.13.2</junit.version>
<maven.compiler.plugin.version>3.13.0</maven.compiler.plugin.version>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- Rest Assured -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.rest-assured</groupId>
<artifactId>rest-assured</artifactId>
<version>${rest.assured.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Cucumber with JUnit4 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.cucumber</groupId>
<artifactId>cucumber-junit</artifactId>
<version>${cucumber.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Cucumber with Java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.cucumber</groupId>
<artifactId>cucumber-java</artifactId>
<version>${cucumber.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- JUnit4 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>${junit.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.compiler.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<source>${maven.compiler.source}</source>
<target>${maven.compiler.target}</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Step 9 – Create a feature file under src/test/resources
Create a folder with name features. Now, create the feature file in this folder. The feature file should be saved with extension .feature. This feature file contains the test scenarios created to test the application. The Test Scenarios are written in Gherkins language in the format of Given, When, Then, And, But.
Below is an example of a Test Scenario where we are using the GET method to get the information from the API.
Feature: Validation of get method
@GetUserDetails
Scenario Outline: Send a valid Request to get user details
Given I send a request to the URL to get user details
Then the response will return status <statusCode> and id <id> and email "<employee_email>" and first name "<employee_firstname>" and last name "<employee_lastname>"
Examples:
| statusCode | id | employee_email | employee_firstname | employee_lastname |
| 200 | 2 | janet.weaver@reqres.in | Janet | Weaver |
Step 10 – Create the Step Definition class or Glue Code for the Test Scenario
StepDefinition acts as an intermediate to your runner and feature file. It stores the mapping between each step of the scenario in the Feature file. So when you run the scenario, it will scan the step definition file to check the matched glue or test code.
import io.cucumber.java.en.Given;
import io.cucumber.java.en.Then;
import io.restassured.http.ContentType;
import io.restassured.response.ValidatableResponse;
import static io.restassured.RestAssured.given;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.equalTo;
public class APIDemoDefinitions {
private ValidatableResponse validatableResponse;
private String endpoint = "https://reqres.in/api/users/2";
@Given("I send a request to the URL to get user details")
public void sendRequest(){
validatableResponse = given().contentType(ContentType.JSON)
.when().get(endpoint).then();
System.out.println("Response :"+validatableResponse.extract().asPrettyString());
}
@Then("the response will return status {int} and id {int} and email {string} and first name {string} and last name {string}")
public void verifyStatus(int expectedStatusCode, int expectedId, String expectedEmail, String expectedFirstName, String expectedLastName){
validatableResponse.assertThat().statusCode(expectedStatusCode);
validatableResponse.assertThat().body("data.id",equalTo(expectedId));
validatableResponse.assertThat().body("data.email",equalTo(expectedEmail));
validatableResponse.assertThat().body("data.first_name",equalTo(expectedFirstName));
validatableResponse.assertThat().body("data.last_name",equalTo(expectedLastName));
}
}
In order to use REST assured effectively it’s recommended to statically import methods from the following classes:
io.restassured.RestAssured.*
io.restassured.matcher.RestAssuredMatchers.*
org.hamcrest.Matchers.*
There is another way to perform these assertions. We can use multiple body assertions together.
@Then("the response will return status {int} and id {int} and email {string} and first name {string} and last name {string}")
public void verifyStatus(int expectedStatusCode, int expectedId, String expectedEmail, String expectedFirstName, String expectedLastName){
validatableResponse.assertThat().statusCode(expectedStatusCode).body("data.id",equalTo(expectedId)).and()
.body("data.email",equalTo(expectedEmail)).body("data.first_name",equalTo(expectedFirstName))
.body("data.last_name",equalTo(expectedLastName));
Step 11 – Create a JUnit Cucumber Runner class
A runner will help us to run the feature file and act as an interlink between the feature file and StepDefinition Class.
import io.cucumber.junit.Cucumber;
import io.cucumber.junit.CucumberOptions;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
@RunWith(Cucumber.class)
@CucumberOptions(features= {"src/test/resources"}, glue= {"com.example.stepdefinitions"})
public class CucumberRunnerTests {
}
Note:- The name of the Runner class should end with Test otherwise we can’t run the tests using Command-Line.
Step 12 – Run the tests from JUnit
You can execute the test script by right-clicking on TestRunner class -> Run As JUnit (Eclipse).
You can execute the test script by right-clicking on TestRunner class -> Run CucumberRunnerTests (IntelliJ).

Step 13 – Run the tests from the Command Line
Run the below command in the command prompt to run the tests and to get the test execution report.
mvn clean test
The output of the above program is

Step 14 – Cucumber Report Generation
To get Cucumber Test Reports, add cucumber.properties under src/test/resources and add the below instruction in the file.
cucumber.publish.enabled=true

We are done! Congratulations on making it through this tutorial and hope you found it useful! Happy Learning!!
Additional Tutorials