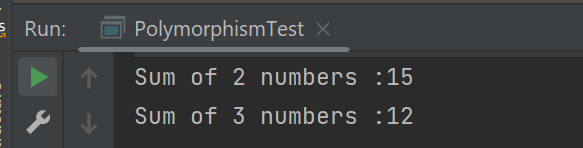
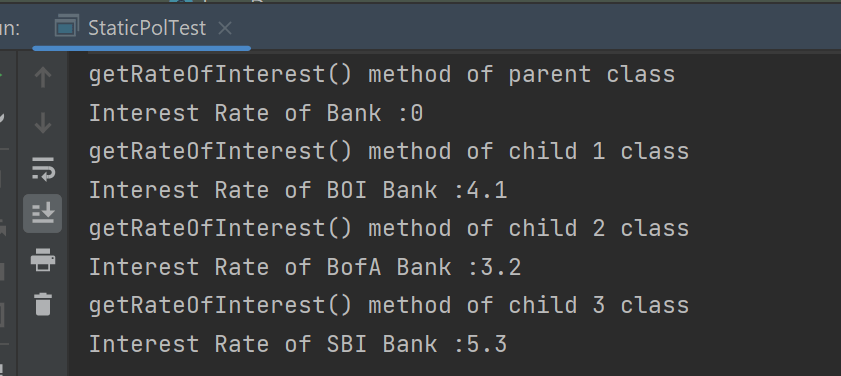
Welcome to the Java Quiz! This blog post features 25 multiple-choice questions that explore the concepts of Inheritance & Polymorphism in Java.
1. What is inheritance in Java?
a) A mechanism where one class acquires the properties of another
b) A way to allow multiple classes to have the same method names
c) A class that implements an interface
d) None of the above
Answer 1
a) A mechanism where one class acquires the properties of another
2. Which keyword is used for inheritance in Java?
a) implements
b) extends
c) inherits
d) uses
Answer 2
b) extends
The extends keyword is used to indicate that a class is inheriting from another class.
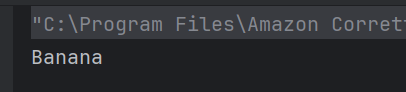
3. What will be the output of the following Java code?
class Apple {
public void print() { System.out.println("Apple"); }
}
class Banana extends Apple {
public void print() { System.out.println("Banana"); }
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Apple apple = new Banana();
apple.print();
}
}
Choose one option
a) Apple
b) Banana
c) No Output
d) Compilation Error
Answer 3
b) Banana
This is an example of dynamic method dispatch (polymorphism). The type of the object, not the reference type, determines which method is called.
4. If a class extends another class, which of the following members are inherited?
Choose one option
a) Only public methods
b) Public and protected members
c) Private methods
d) All members including private
Answer 4
b) Public and protected members
A subclass can inherit public and protected members of the superclass but not private members.
5. Which of these is correct way of inheriting class A by class B?
a) class B + class A {}
b) class B inherits class A {}
c) class B extends A {}
d) class B extends class A {}
Answer 5
c) class B extends A {}
The correct syntax for inheritance in Java is class B extends A {}. The extends keyword is used, and we refer to the superclass by name, not with the keyword class.
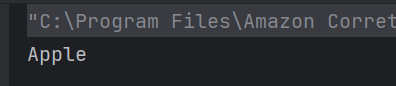
6. What will be the output of the following Java program?
class Apple {
public void print() { System.out.println("Apple"); }
}
class Banana extends Apple {
public void print() { System.out.println("Banana"); }
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Apple apple = new Apple();
apple.print();
}
}
Choose one option
a) Apple
b) Banana
c) No Output
d) Compilation Error
Answer 6
a) Apple
7. What will be the output of the following Java program?
class A {
A(int x) { }
}
class B extends A {
B(int x) {
System.out.println("Constructor B");
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
B obj = new B(10);
}
}
Choose one option
a) It compiles without error.
b) It causes a compilation error.
c) It throws a runtime error.
d) It prints “Constructor B”
Answer 7
b) It causes a compilation error.
The constructor in B needs to explicitly call the constructor of A using super(x). This is required because A doesn’t have a no-argument constructor.

8. What will be the output?
class Parent {
void method() {
System.out.println("Parent method");
}
}
class Child extends Parent {
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Child obj = new Child();
obj.method();
}
}
Choose one option
a) Parent method
b) Child method
c) Compilation Error
d) Runtime Error
Answer 8
a) Parent method
Child doesn’t override method(), it inherits method() from Parent.
9. Which of the following statements about inheritance is false?
a) Java supports single inheritance.
b) Java allows multiple class inheritance using extends.
c) Interfaces can be used to achieve multiple inheritance.
d) The super keyword can be used to invoke the parent class constructor.
Answer 9
b) Java allows multiple class inheritance using extends.
Java does not allow multiple class inheritance using extends to avoid ambiguity issues. Instead, interfaces provide an alternative for multiple inheritance.
10. Which type of inheritance is demonstrated when a class inherits from a class that already inherits from another class?
a) Single inheritance
b) Multiple inheritance
c) Multilevel inheritance
d) Hierarchical inheritance
Answer 10
c) Multilevel inheritance
The type of inheritance demonstrated when a class inherits from a class that already inherits from another class is called multilevel inheritance. In this type of inheritance, a class is derived from a derived class, effectively creating a hierarchy of classes.
11. What is the keyword used in Java to prevent a class from being inherited?
Choose one option
a) abstract
b) final
c) static
d) private
Answer 11
b) final
The final
keyword in Java is used to prevent a class from being inherited. When a class is declared as final, it cannot be extended by any other class.
12. What is the purpose of using the `super` keyword in Java?
Choose one option
a) To create a new object instance
b) To call a constructor of the subclass
c) To refer to the current object’s superclass
d) To hide inherited methods
Answer 12
c) To refer to the current object’s superclass
The super keyword is used to access the superclass’s constructor or methods and can be used to invoke the superclass version of an overridden method.
13. Which of the following statements about the super keyword in Java is true?
Choose one option
a) The super keyword is used to call the parent class constructor.
b) The super keyword is used to access the methods and properties of the parent class.
c) The super keyword is used to create an instance of a child class.
d) The super keyword is not supported in Java.
Answer 13
b) The super keyword is used to access the methods and properties of the parent class.
The super keyword in Java is used to access the methods and properties of the parent class. It is often used to invoke the overridden methods of the parent class in the child class.
14. What will be the output of the following code?
class Parent {
public void print() {
System.out.println("Parent");
}
}
class Child extends Parent {
public void print() {
System.out.println("Child");
super.print();
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Child child = new Child();
child.print();
}
}
Choose one option
a) Parent
Child
b) Child
Parent
c) Parent
d) Child
Answer 14
b) Child
Parent
This exception is thrown when a program attempts to use an object reference that has not been properly initialized.
15. What will be the result of the following code?
package pack1;
public class A {
public void display() {
System.out.println("Hello from A");
}
}
package pack2;
import pack1.A;
public class B {
public static void main(String args[]) {
A obj = new A();
obj.display();
}
}
Choose one option
a) No output
b) Hello from A
c) Compiler error
d) Runtime error
Answer 15
b) Hello from A
Since class A is public and properly imported in pack2, there is no issue accessing it.
16. What is the result of the following code snippet?
class A
{
int i;
void display()
{
System.out.println(i);
}
}
class B extends A
{
int j;
void display()
{
System.out.println(j);
}
}
class Test
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
B obj = new B();
obj.i=1;
obj.j=2;
obj.display();
}
}
Choose one option
a) 0
b) 1
c) 2
d) Compilation Error
Answer 16
c) 2
Class A & class B both contain display() method, class B inherits class A, when display() method is called by object of class B, display() method of class B is executed rather than that of Class A.
17. What will be printed?
class A
{
int i;
}
class B extends A
{
int j;
void display()
{
super.i = j + 1;
System.out.println(j + " " + i);
}
}
class Test
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
B obj = new B();
obj.i=1;
obj.j=2;
obj.display();
}
}
Choose one option
a) Hello
a) 2 2
b) 3 3
c) 2 3
d) 3 2
Answer 17
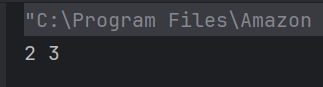
c) 2 3
Class A and Class B both contain a display() method. Class B inherits Class A. When the display() method is called by an object of Class B, the display() method of Class B is executed rather than that of Class A. The value of i is updated in the display() method using the super keyword.
18. What is polymorphism in Java?
a) A feature that allows a class to be abstract
b) A feature that allows one interface to be used for a general class of actions
c) A type of inheritance in Java
d) A way to modularize the code
Answer 18
b) A feature that allows one interface to be used for a general class of actions
Polymorphism allows methods to do different things based on the object it is acting upon, using a general interface for different underlying forms (data types).
19. How can you achieve polymorphism in Java?
a) By method overloading only
b) By method overriding only
c) By both method overloading and overriding
d) By using final classes
Answer 19
c) By both method overloading and overriding
Polymorphism can be achieved through method overloading (compile-time polymorphism) and method overriding (run-time polymorphism).
20. Which of the following statements about multiple inheritance of interfaces is true?
Choose one option
a) It is allowed in Java
b) It is not allowed in Java
c) It leads to ambiguity
d) Only one interface can be inherited
Answer 20
a) It is allowed in Java
Java allows a class to implement multiple interfaces, enabling multiple inheritance of method signatures.
21. What is the output of the below program?
public class Parent {
void m1(String x) {
System.out.println("One");
}
}
public class Derived extends Parent{
public void m1(String x) {
System.out.println("Two");
super.m1(null);
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
Parent obj = new Derived();
obj.m1(null);
}
}
a) Two, One
b) One, Two
c) Compiler error
d) Runtime error
Answer 21
a) Two, One
The m1 method of Derived is executed first because Derived overrides m1. It prints “Two”. Then, super.m1(null) is executed within the m1 method of Derived, which calls the m1 method of the Parent class, printing “One”.
22. What will be the output of this program?
public class Test{
void m1(String x){
System.out.println("One");
}
protected void m1(String x, String y){
System.out.println("Two");
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Test obj = new Test();
obj.m1("ABC");
obj.m1("PQR", "XYZ");
}
}
a) Two One
b) One Two
c) Compile time error
d) Runtime error
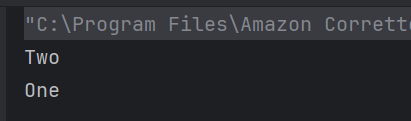
Answer 22
b) One Two

23. What is the output of the following program?
public class PolymorphismDemoClass {
void add(int x, int y){
System.out.println("1. Addition is: " +(x+y));
}
void add(int y, int x){
System.out.println("2. Addition is: " +(x+y));
}
public static void main(String[] args){
PolymorphismDemoClass obj = new PolymorphismDemoClass();
obj.add(20, 30);
}
}
a) Prints 2. Addition of two numbers: 50
b) Prints 1. Addition of two numbers: 50
c) Compile time error
d) Runtime error
Answer 23
c) Compile time error

24. What is the key difference between compile-time and runtime polymorphism in Java?
a) Compile-time polymorphism is implemented using method overriding, while runtime polymorphism is implemented using method overloading.
b) Compile-time polymorphism is determined during compilation, while runtime polymorphism is resolved at runtime.
c) Runtime polymorphism is faster than compile-time polymorphism.
d) Compile-time polymorphism is achieved using interfaces.
Answer 24
b) Compile-time polymorphism is determined during compilation, while runtime polymorphism is resolved at runtime.
Compile-time polymorphism (method overloading) is resolved at compile-time, while runtime polymorphism (method overriding) is determined during execution via dynamic method dispatch.
25. What will happen if two classes in different packages have the same name and are imported in a Java file?
a) Compilation error due to ambiguity.
b) The last imported class is used.
c) The first imported class is used.
d) Java automatically renames one class.
Answer 25
a) Compilation error due to ambiguity.
Java does not allow ambiguity in class names across packages. Fully qualified names must be used in such cases.
We would love to hear from you! Please leave your comments and share your scores in the section below