What is a Properties File in Java?
In Java, a properties file is a simple text-based file used to store configuration or settings in key-value pairs. It provides a convenient way to externalize application-specific parameters that can be easily modified without modifying the source code.
Properties File always stores information about the configuration parameters such as project configuration data such as URL, username, password, and project settings config like browser name, environment, and so on.
Properties files have a “.properties” extension.
How to modify specific value in a Properties File without overwriting all the existing values
Imagine we want to update the value of a particular key in the existing properties file.
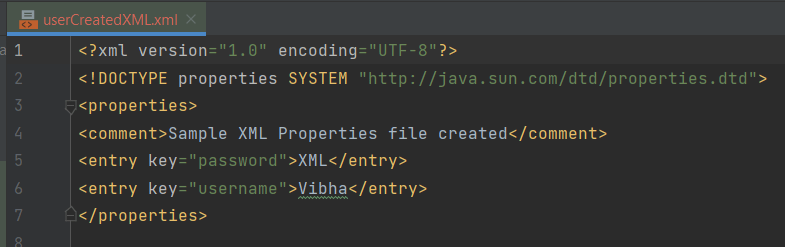
Below is an example of userCreated.properties.

We want to replace the password from Admin to Admin123.
Java API has java.util.Properties class, and it has utility stores() methods to store properties in Text format.
You can write properties to a properties file using the Properties class. Create a Properties object and use the load() method to load the existing properties from the file.
Properties properties = new Properties();
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("src/test/resources/userCreated.properties");
properties.load(fileInputStream);
Modify the specific value by using the “setProperty()” method to update the key-value pair in the “Properties” object.
properties.setProperty("password", "Admin123");
Save the changes back to the file. Create a “FileOutputStream” object and specify the same file path. Use the “store()” method to save the modified properties back to the file.
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("src/test/resources/userCreated.properties");
// store() method is used to write the properties into properties file
properties.store(fileOutputStream, "File is modified");
Below is a complete example:
package org.example;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class ModifyPropertiesExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// Creating properties files from Java program
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("src/test/resources/userCreated.properties");
properties.load(fileInputStream);
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
properties.setProperty("password", "Admin123");
try {
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("src/test/resources/userCreated.properties");
// store() method is used to write the properties into properties file
properties.store(fileOutputStream, "File is modified");
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
The updated userCreated.properties file is shown below:

Thank you for completing this tutorial! I’m glad you found it helpful. Happy learning and cheers to your success!