In this tutorial, I will explain how to Integrate Allure Report 3 with Playwright, Java and TestNG.
What is an Allure Report?
Allure Framework is a flexible, lightweight, multi-language test report tool. It shows a very concise representation of what has been tested in a neat web report form. It also allows everyone participating in the development process to extract maximum useful information from the everyday execution of tests.
Refer to this tutorial to install allure – What is Allure Report?.
In this tutorial, we are using Allure Report 3.
Table of Contents
- What is an Allure Report?
- System requirements
- Dependency List
- High-Level Execution Flow
- Implementation Steps
- Set Up the Environment
- Project Structure for Maintainability
- Creating Page Object Classes in src/test/java
- Create the utility package in src/test/java
- Write the Test Scripts
- Create testng.xml for the project
- Specifying Allure Results location
- Run the Tests and Generate Allure Report
- How to Generate an Allure Report
- How to View a Report
System requirements
- Java 17 installed
- Maven installed
- Eclipse or IntelliJ installed
- Allure installed
- Browsers on which tests need to be run, like Chrome, Firefox, etc.
Dependency List
- Playwright – 1.57.0
- Java 17
- Maven – 3.9.6
- Allure Report – 2.32.0
- Aspectj – 1.9.25
- Maven Compiler Plugin – 3.13.0
- Maven Surefire Plugin – 3.5.4
High-Level Execution Flow
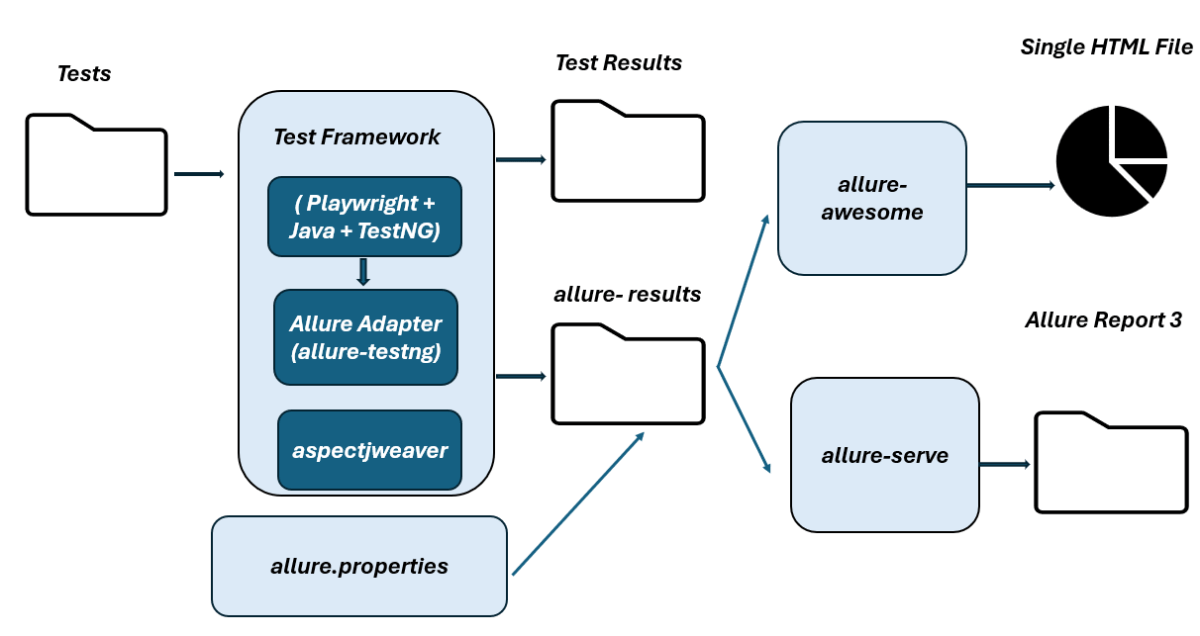
Implementation Steps
1. Set Up the Environment
Step 1 – Update the Properties section in Maven pom.xml
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<playwright.version>1.57.0</playwright.version>
<testng.version>7.11.0</testng.version>
<allure.version>2.32.0</allure.version>
<aspectj.version>1.9.25</aspectj.version>
<maven.compiler.plugin.version>3.13.0</maven.compiler.plugin.version>
<maven.compiler.source.version>17</maven.compiler.source.version>
<maven.compiler.target.version>17</maven.compiler.target.version>
<maven.surefire.plugin.version>3.5.4</maven.surefire.plugin.version>
</properties>
Step 2 – Add dependencies to pom.xml
Add Playwright, TestNG, and Allure-TestNG dependencies to pom.xml (Maven Project).
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.qameta.allure</groupId>
<artifactId>allure-bom</artifactId>
<version>${allure.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<!-- Playwright -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.microsoft.playwright</groupId>
<artifactId>playwright</artifactId>
<version>${playwright.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- TestNG -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.testng</groupId>
<artifactId>testng</artifactId>
<version>${testng.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Allure-TestNG -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.qameta.allure</groupId>
<artifactId>allure-testng</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Step 3 – Update the Build Section of pom.xml in the Allure Report Project
Allure leverages AspectJ for the functionality of @Step and @Attachment annotations.
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.compiler.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<source>${maven.compiler.source.version}</source>
<target>${maven.compiler.target.version}</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.surefire.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<suiteXmlFiles>
<suiteXmlFile>testng.xml</suiteXmlFile>
</suiteXmlFiles>
<argLine>
-javaagent:"${settings.localRepository}/org/aspectj/aspectjweaver/${aspectj.version}/aspectjweaver-${aspectj.version}.jar"
</argLine>
</configuration>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>${aspectj.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
The entire pom.xml is
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>Playwright_PageObjectModel</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>Playwright_PageObjectModel</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<playwright.version>1.57.0</playwright.version>
<testng.version>7.11.0</testng.version>
<allure.version>2.32.0</allure.version>
<aspectj.version>1.9.25</aspectj.version>
<maven.compiler.plugin.version>3.13.0</maven.compiler.plugin.version>
<maven.compiler.source.version>17</maven.compiler.source.version>
<maven.compiler.target.version>17</maven.compiler.target.version>
<maven.surefire.plugin.version>3.5.4</maven.surefire.plugin.version>
</properties>
<!-- Add allure-bom to dependency management to ensure correct versions of all the dependencies are used -->
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.qameta.allure</groupId>
<artifactId>allure-bom</artifactId>
<version>${allure.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<!-- Playwright -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.microsoft.playwright</groupId>
<artifactId>playwright</artifactId>
<version>${playwright.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- TestNG -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.testng</groupId>
<artifactId>testng</artifactId>
<version>${testng.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Allure-TestNG -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.qameta.allure</groupId>
<artifactId>allure-testng</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.compiler.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<source>${maven.compiler.source.version}</source>
<target>${maven.compiler.target.version}</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.surefire.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<suiteXmlFiles>
<suiteXmlFile>testng.xml</suiteXmlFile>
</suiteXmlFiles>
<argLine>
-javaagent:"${settings.localRepository}/org/aspectj/aspectjweaver/${aspectj.version}/aspectjweaver-${aspectj.version}.jar"
</argLine>
</configuration>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>${aspectj.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
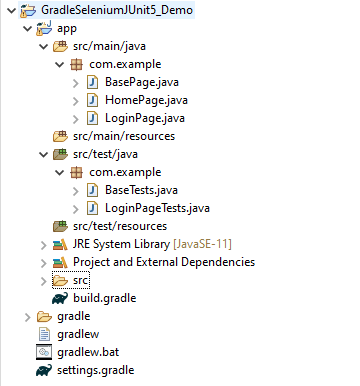
2. Project Structure for Maintainability
Creating a well-organized project structure is crucial for maintaining a scalable and efficient automation framework.
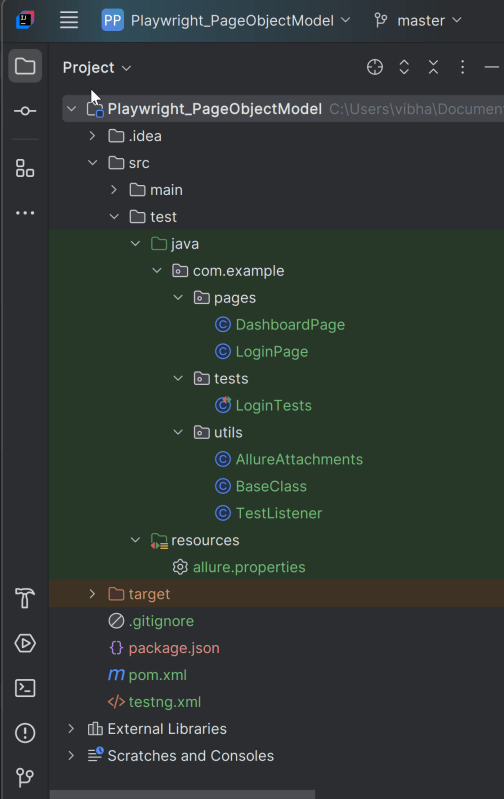
3. Creating Page Object Classes in src/test/java
Please refer to – Mastering Page Object Model for Playwright with Java and TestNG to know more about the Page Object Classes and the respective code.
4. Create the utility package in src/test/java
AllureAttachment class is created to attach binary data (the screenshot) to the currently running test in the Allure lifecycle. This gives a central attachment library for the framework.
package com.example.utils;
import io.qameta.allure.Attachment;
public abstract class AllureAttachments {
@Attachment(value = "Failure Screenshot", type = "image/png")
public static byte[] attachScreenshot(byte[] screenshot) {
return screenshot;
}
}
BaseClass
This class contains the common variables and methods used throughout the project, like setup and teardown methods.
package com.example.utils;
import com.microsoft.playwright.*;
import org.testng.annotations.*;
public class BaseClass {
// Shared between all tests in this class.
Playwright playwright;
Browser browser = null;
// New instance for each test method.
BrowserContext context;
public Page page;
public Page getPage() {
return page;
}
@BeforeClass
public void launchBrowser() {
playwright = Playwright.create();
browser = playwright.chromium().launch(new BrowserType.LaunchOptions().setHeadless(false));
}
@BeforeMethod
public void createContextAndPage() {
context = browser.newContext();
page = context.newPage();
page.navigate("https://opensource-demo.orangehrmlive.com/web/index.php/auth/login");
}
@AfterMethod
public void closeContext() {
context.close();
}
@AfterClass
public void closeBrowser() {
playwright.close();
}
}
TestListener
This class is a TestNG failure hook. Its job is to automatically capture a Playwright screenshot when a test fails. The screenshot is then attached to the Allure report.
By implementing ITestListener, we are plugging into the TestNG test lifecycle. That means this class gets called automatically whenever a test fails.
package com.example.utils;
import com.microsoft.playwright.Page;
import org.testng.ITestListener;
import org.testng.ITestResult;
public class TestListener implements ITestListener {
@Override
public void onTestFailure(ITestResult result) {
System.out.println("❌ onTestFailure triggered");
Page page = BaseClass.getPage();
if (page != null) {
byte[] screenshot = page.screenshot();
AllureAttachments.attachScreenshot(screenshot);
}
}
}
5. Write the Test Scripts
Create a Test files under src/test/java. Use these page classes in your test scripts to perform end-to-end scenarios. This will keep your tests clean and focused on logic rather than details about the UI elements.
We will be automating the following test scenario using Playwright Java and run them in Chromium.
- Verify the invalid username generates error message “Invalid credentials”
- Verify that the user is able to login to the application successfully.
- Verify the missing username generates error message “Required1”. This test will fail
Creating a Login Page Test Class:
package com.example.tests;
import com.example.pages.DashboardPage;
import com.example.pages.LoginPage;
import com.example.utils.BaseClass;
import com.example.utils.TestListener;
import io.qameta.allure.Description;
import io.qameta.allure.Owner;
import io.qameta.allure.Severity;
import org.testng.Assert;
import org.testng.annotations.Listeners;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import static io.qameta.allure.SeverityLevel.*;
public class LoginTests extends BaseClass {
@Test
@Description("This test attempts to log into the website using a invalid login and a password that result in error")
@Severity(NORMAL)
@Owner("Vibha Singh")
public void unsuccessfulLogin() {
LoginPage loginPage = new LoginPage(page);
loginPage.login("abc","abc");
String actualErrorMessage = loginPage.getErrorMessage();
Assert.assertEquals(actualErrorMessage, "Invalid credentials");
}
@Test
@Description("This test attempts to log into the website using a valid login and a password")
@Severity(CRITICAL)
@Owner("Vibha Singh")
public void successfulLogin() {
LoginPage loginPage = new LoginPage(page);
loginPage.login("Admin","admin123");
DashboardPage dashboardPage = new DashboardPage(page);
String actualHeading = dashboardPage.getDashboardPageHeading();
Assert.assertEquals(actualHeading, "Dashboard");
}
@Test
@Description("This test attempts to log into the website using a blank login and a password that result in error")
@Severity(MINOR)
@Owner("Vibha Singh")
public void missingUsername() {
LoginPage loginPage = new LoginPage(page);
loginPage.login("","admin123");
String actualErrorMessage = loginPage.getMissingUsernameErrorMessage();
Assert.assertEquals(actualErrorMessage, "Required1");
}
}
Use the @Description() annotation to set a description statically or use the description() method to set it dynamically in runtime.
@Description("This test attempts to log into the website using a invalid login and a password that result in error")
6. Create testng.xml for the project
Mention the listener in the testng.xml. This is used for all the test classes.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE suite SYSTEM "http://testng.org/testng-1.0.dtd">
<suite name="Playwright test suite">
<listeners>
<listener class-name="com.example.utils.TestListener"/>
</listeners>
<test name="Integration of Playwright Java with TestNG">
<classes>
<class name="com.example.tests.LoginTests">
</class>
</classes>
</test>
</suite>
7. Specifying Allure Results location
Allure, by default, saves test results in the project’s root directory. However, it is recommended to store your test results in the build output directory.
To configure this, create an allure.properties file and place it in the test resources directory of your project, which is typically located at src/test/resources:
#allure.properties
allure.results.directory=target/allure-results
8. Run the Tests and Generate Allure Report
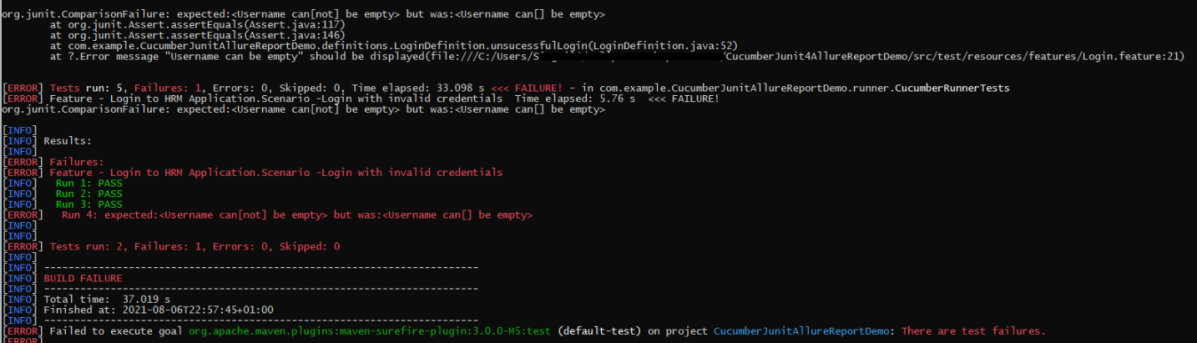
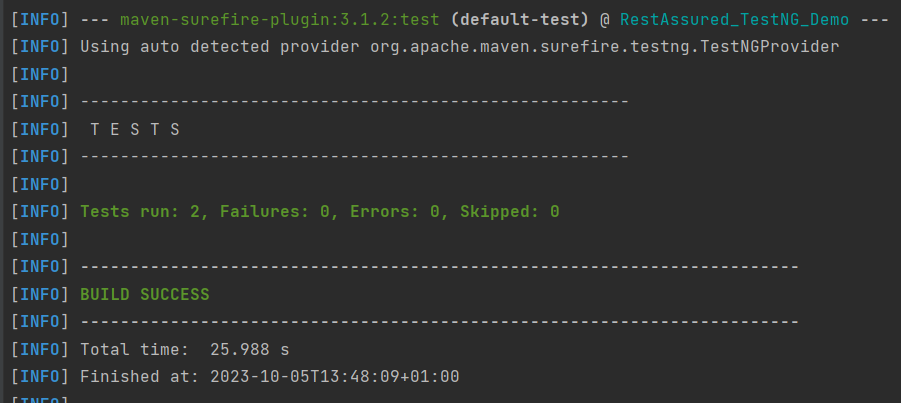
To run the tests, use the below command
mvn clean test
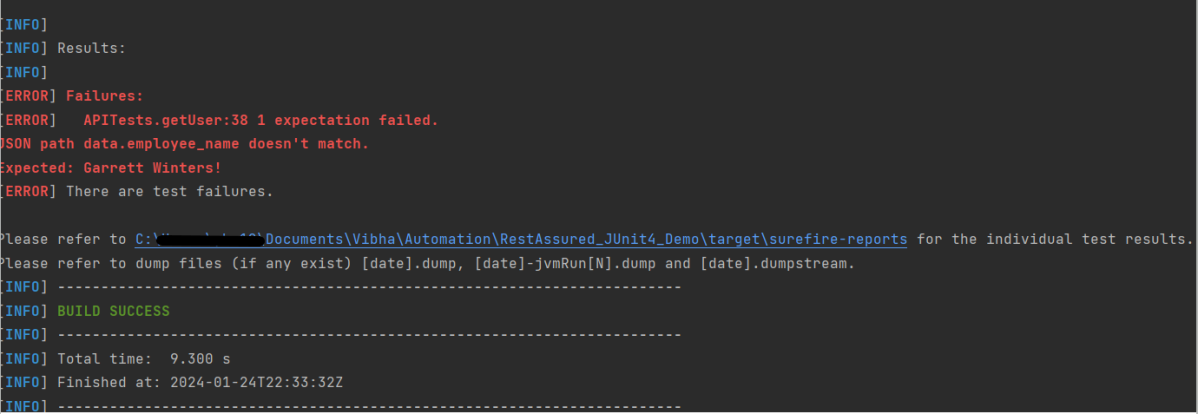
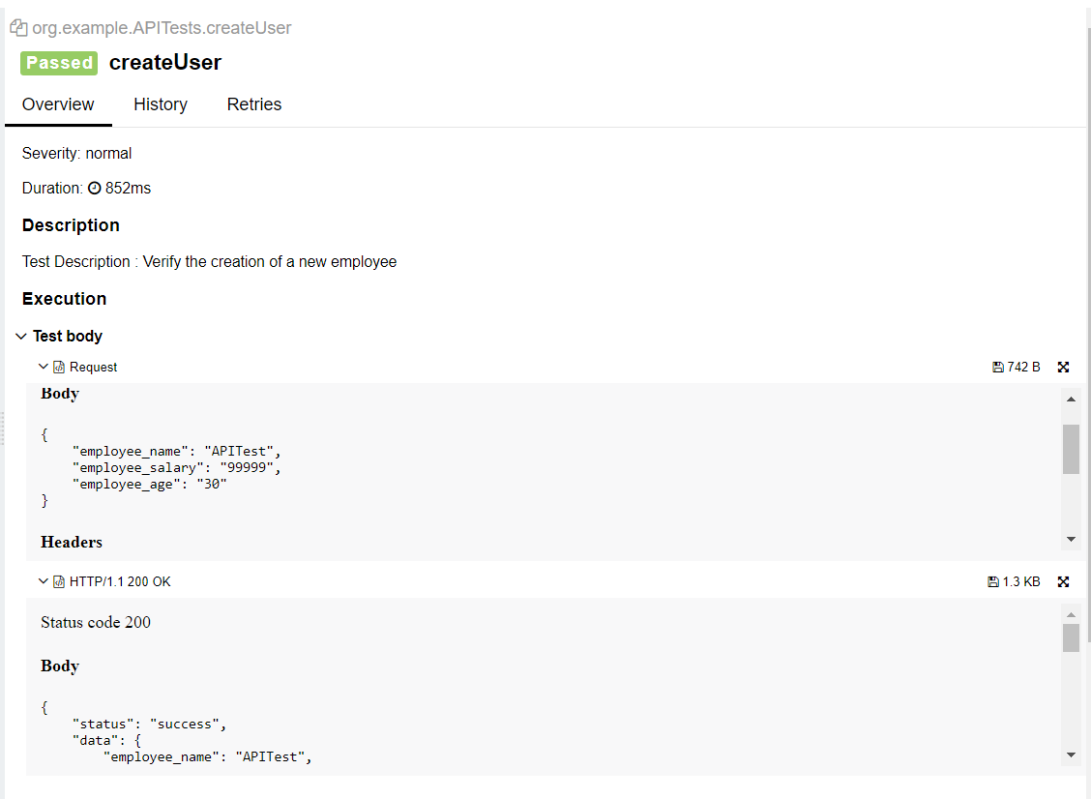
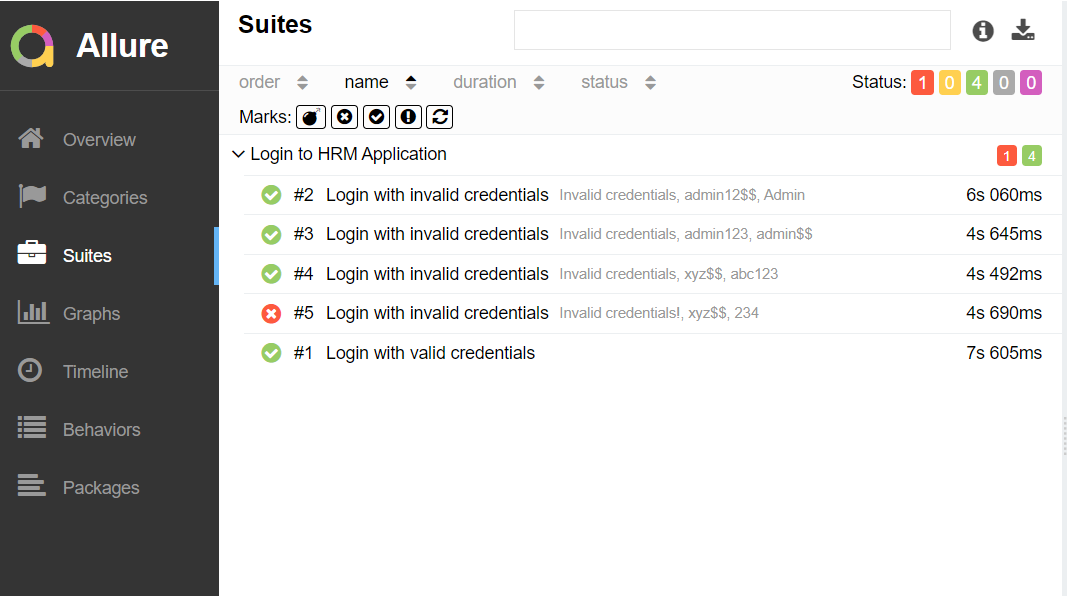
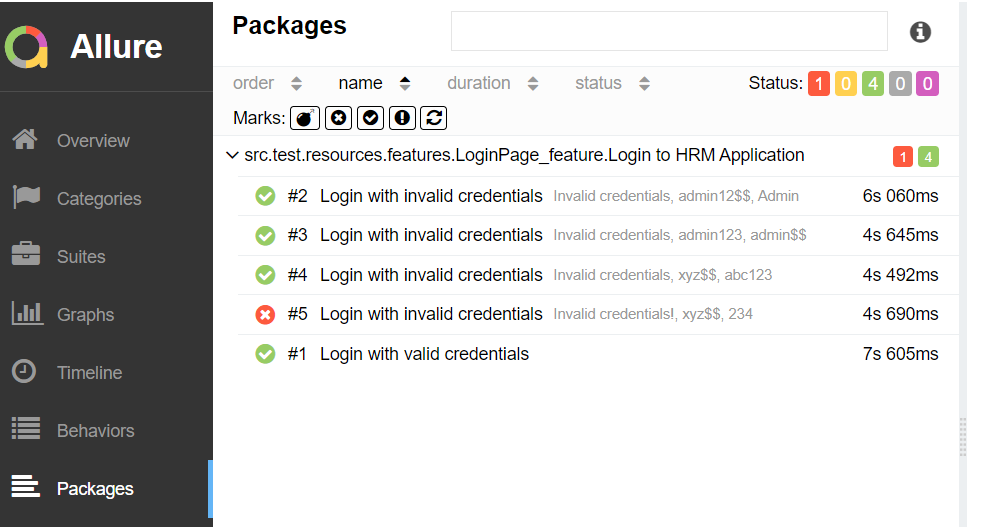
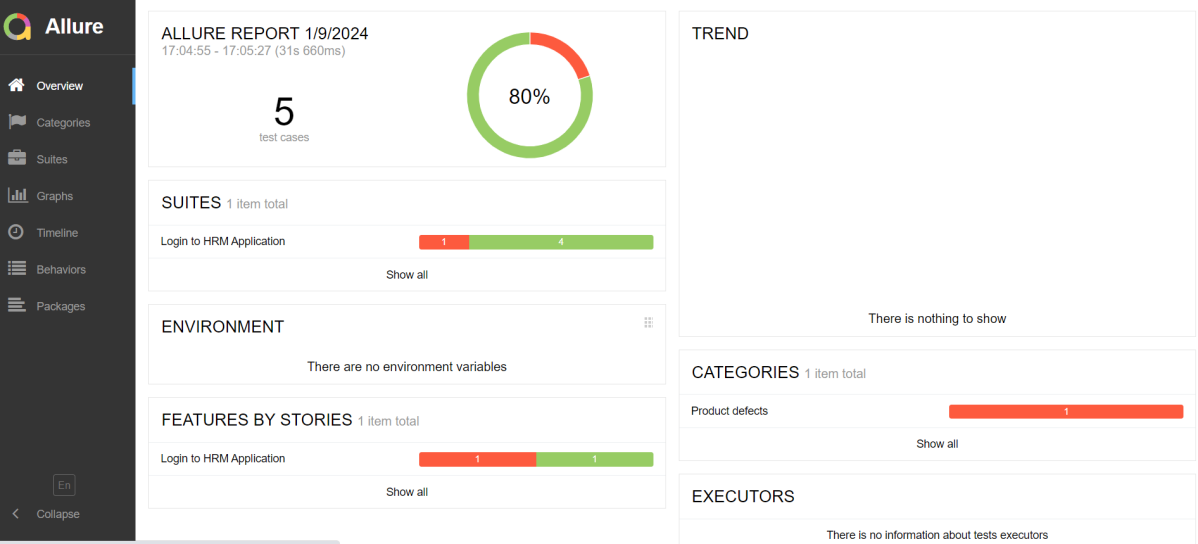
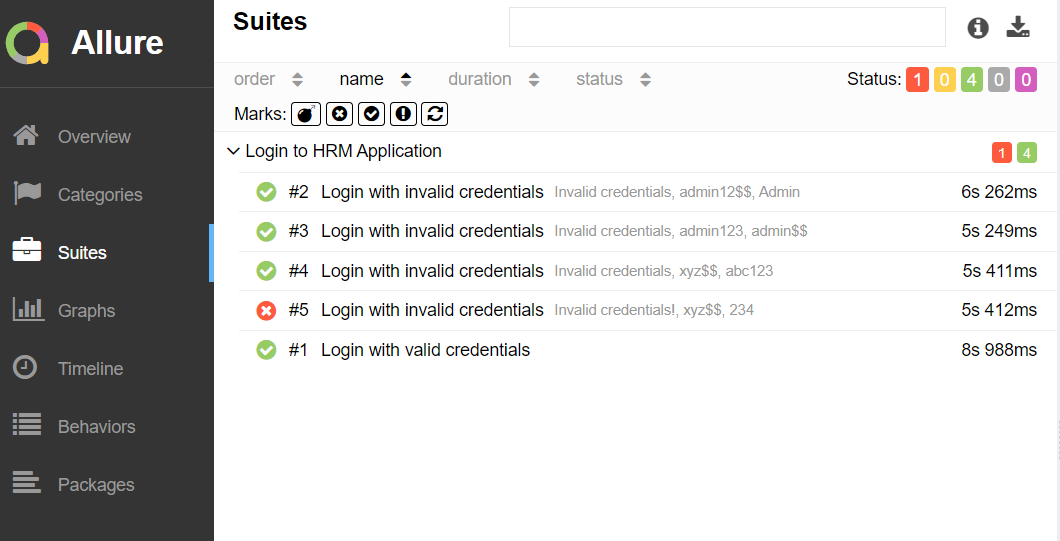
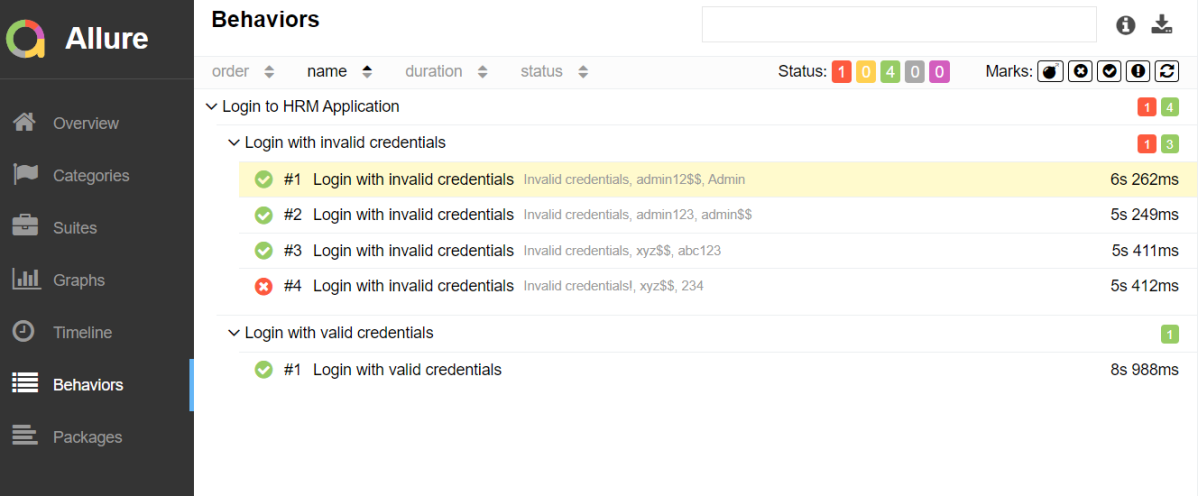
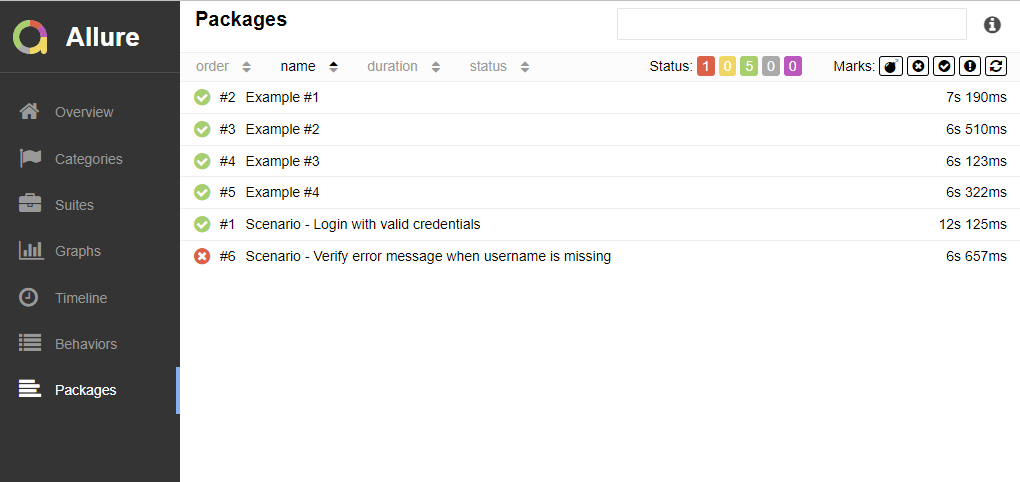
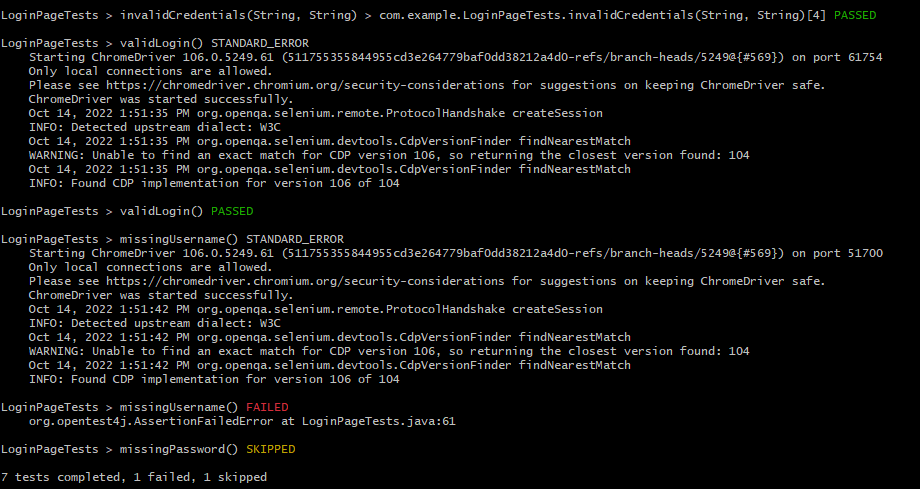
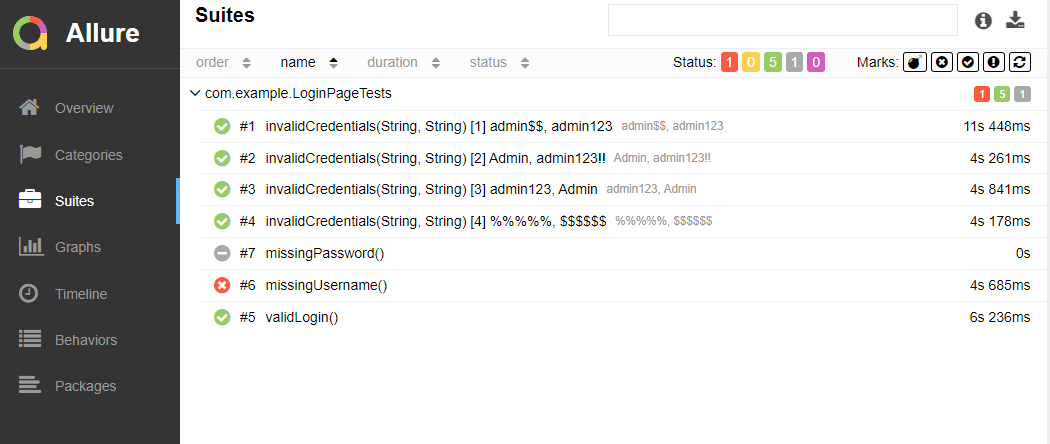
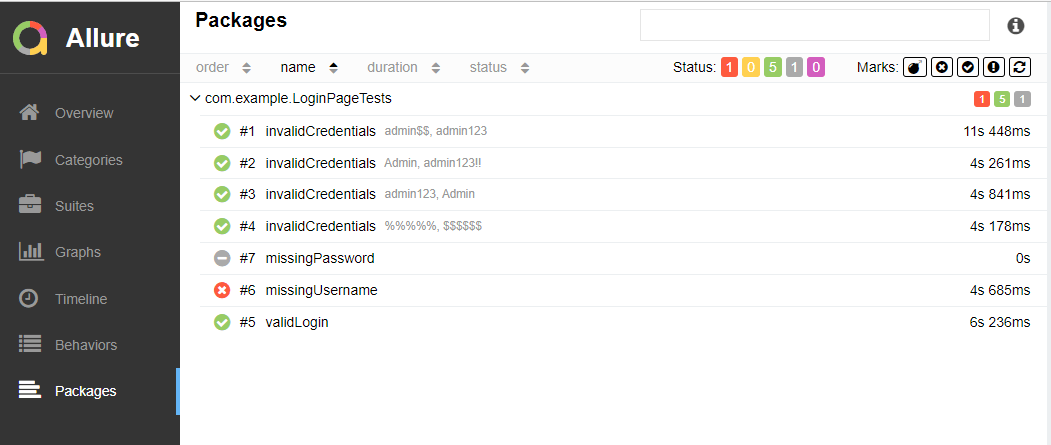
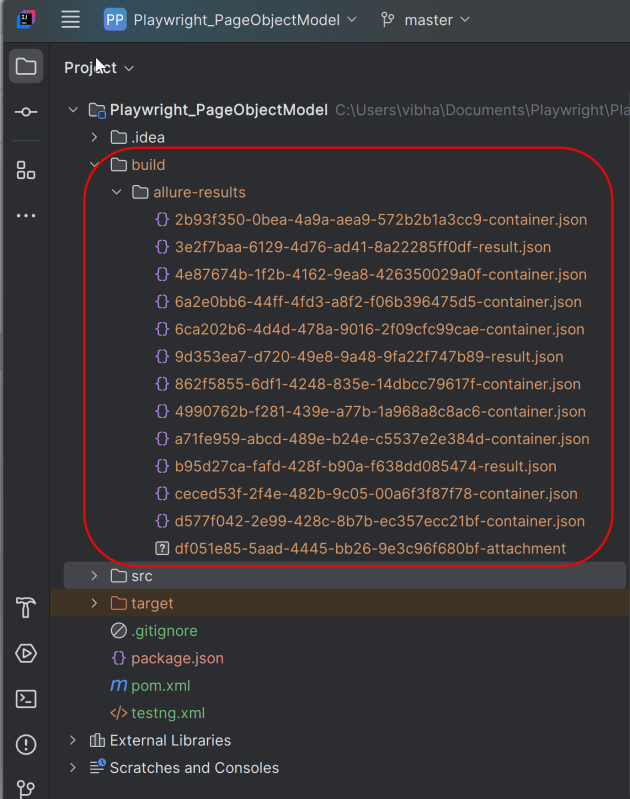
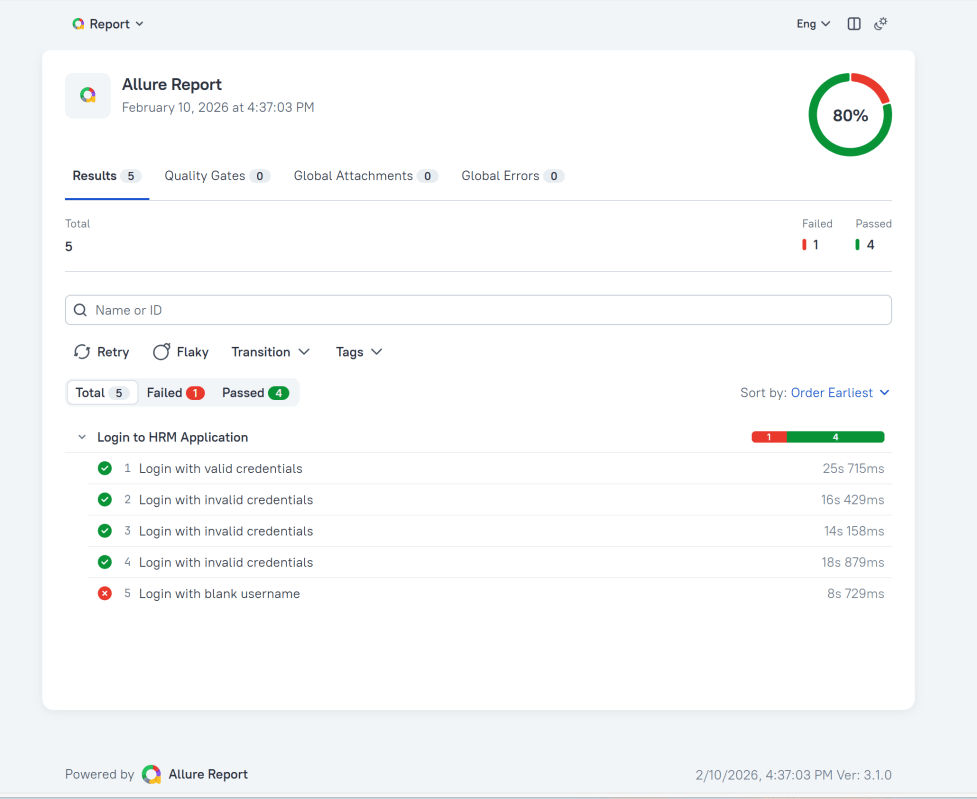
In the image below, we can see that one test failed and four passed out of three tests.
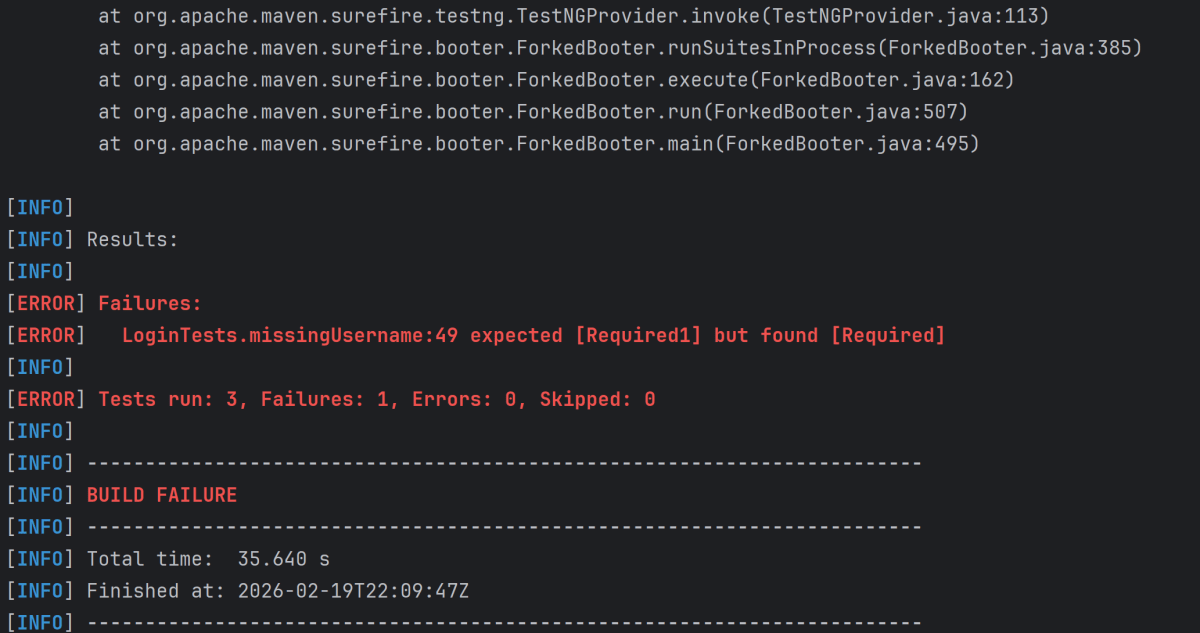
This will create the allure-results folder with all the test reports within build folder. These files will be used to generate Allure Report.
9. How to Generate an Allure Report
allure generate processes the test results and saves an HTML report into the allure-report directory. To view the report, use the allure open command.
allure serve creates the same report as allure generate, then automatically opens the main page of the report in a web browser.
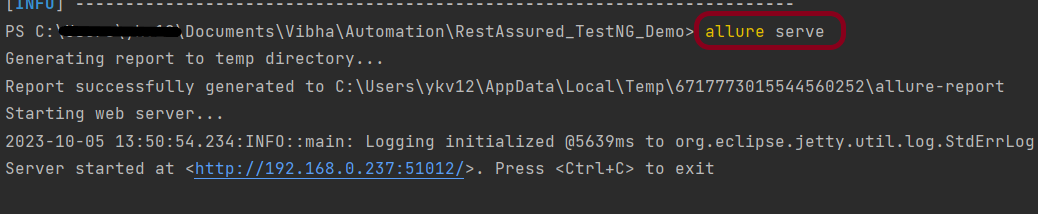
Use the command below to generate the Allure Report
allure serve build/allure-results

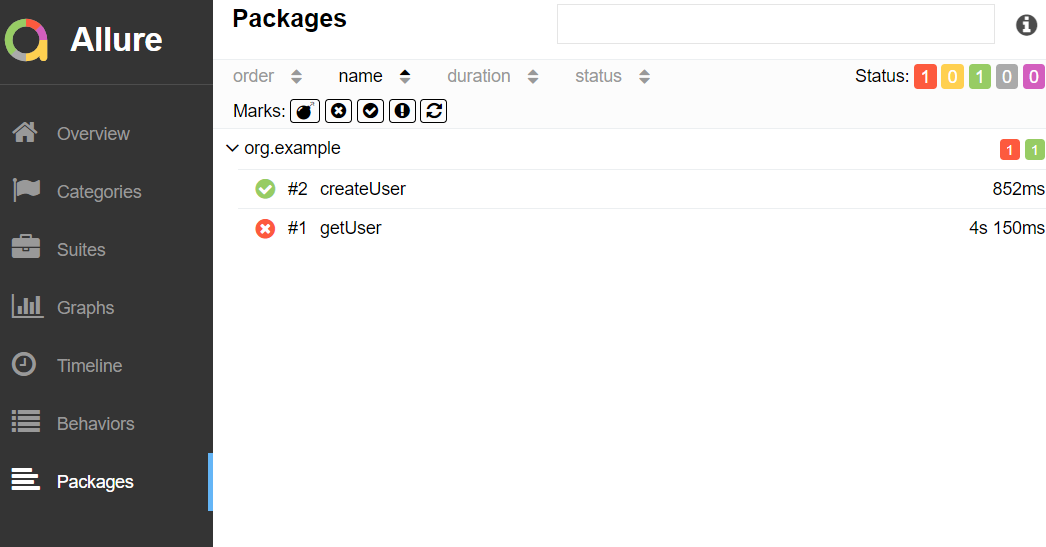
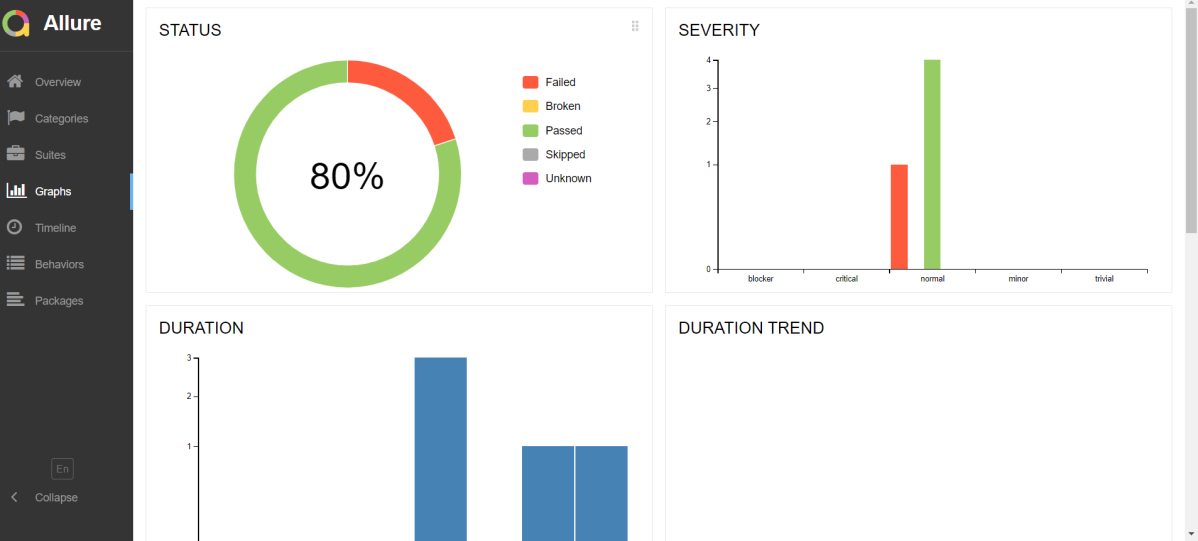
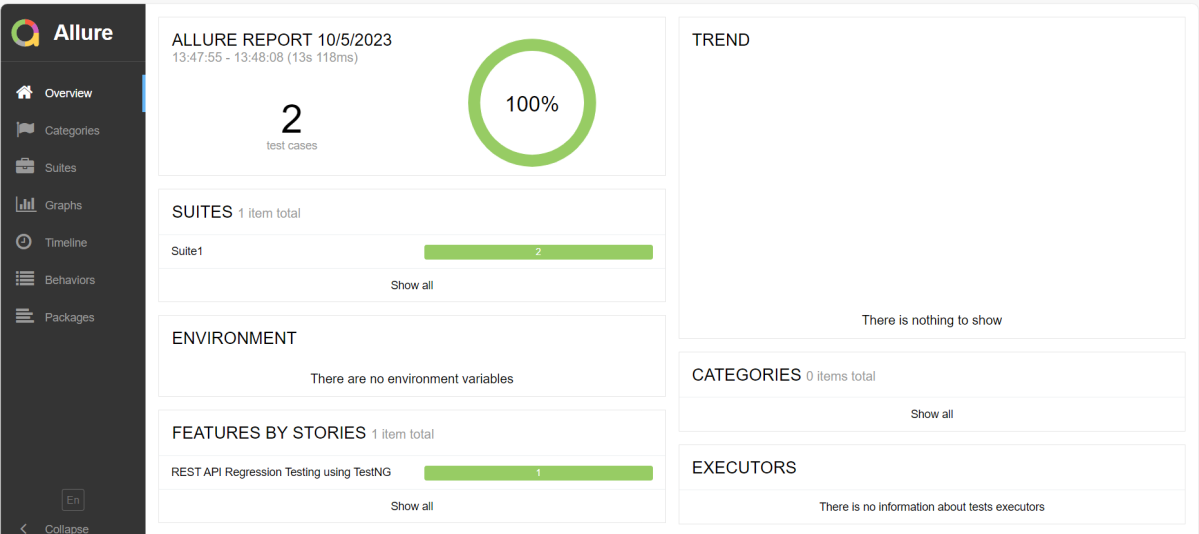
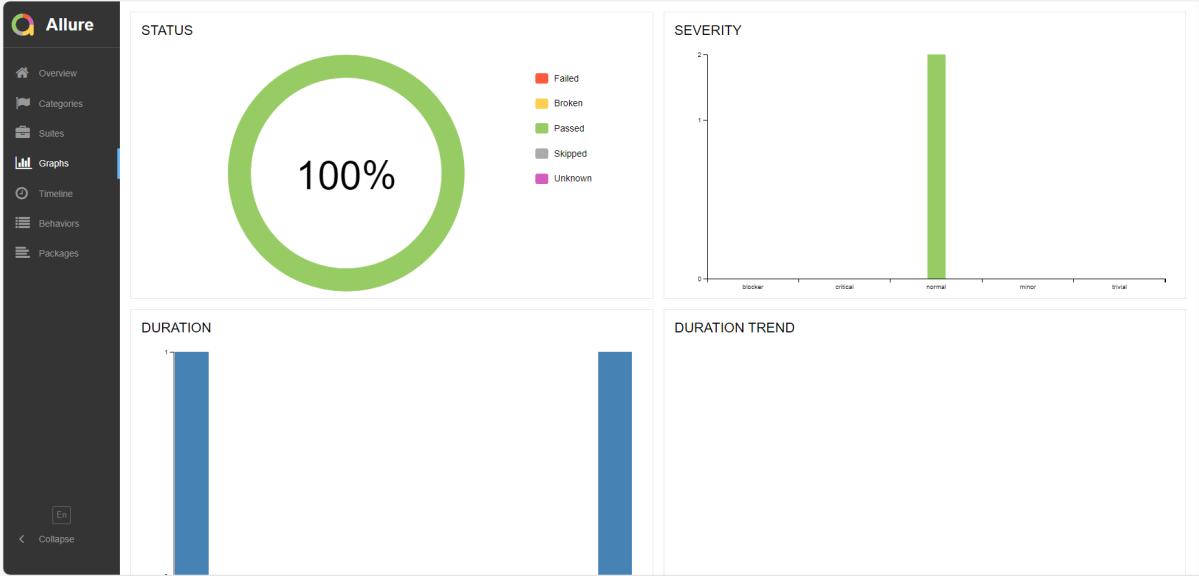
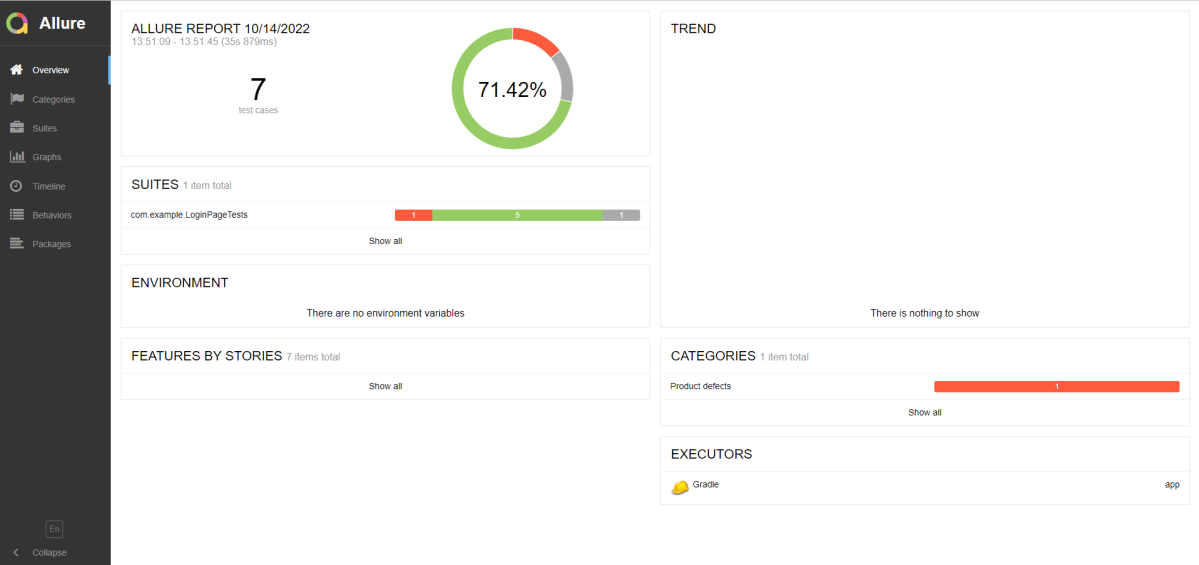
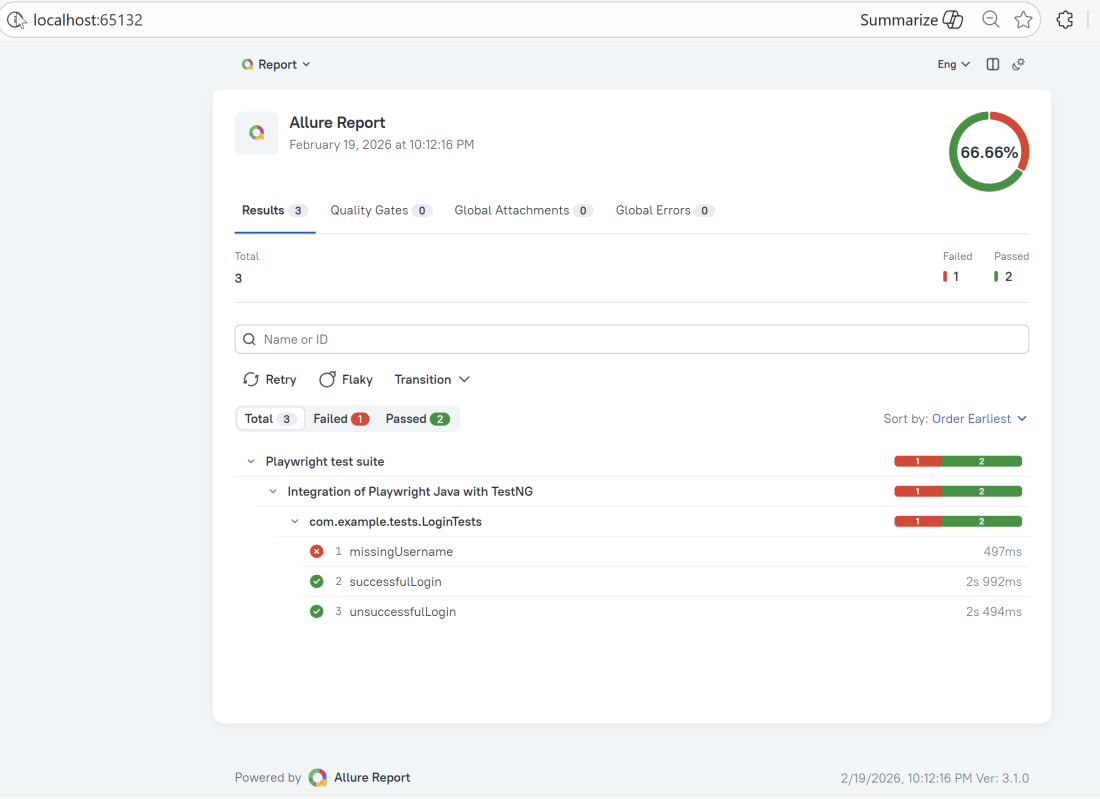
This will generate the beautiful Allure Test Report as shown below.
10. How to View a Report
Test reports generated with Allure Report are basically small HTML websites intended to be viewed in a web browser.
Title
A human-readable title of the test. If not provided, the function name is used instead.
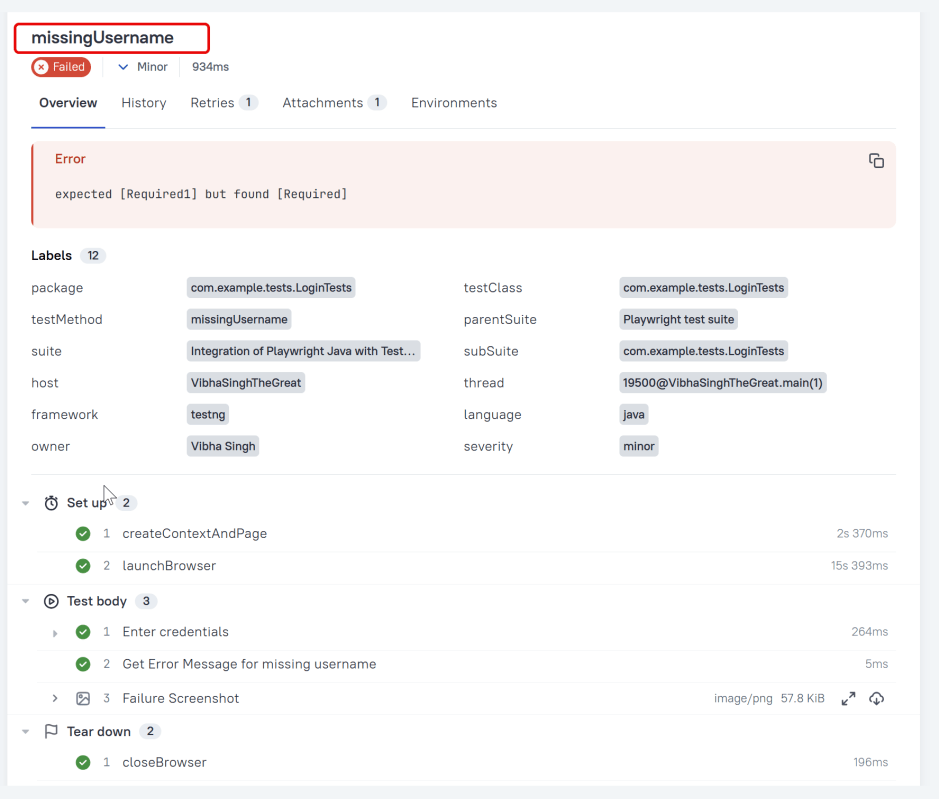
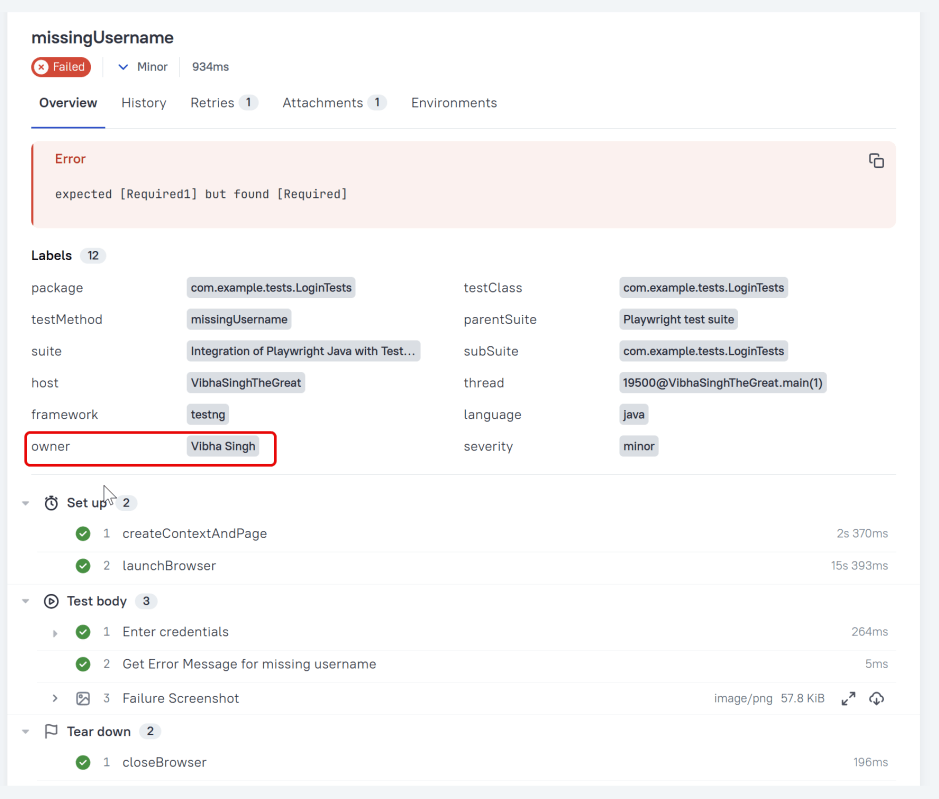
Owner
The team member who is responsible for the test’s stability. For example, this can be the test’s author, the leading developer of the feature being tested, etc.
Severity
A value indicating how important the test is. This may give the future reader an idea of how to prioritize the investigations of different test failures.
Allowed values are: “trivial”, “minor”, “normal”, “critical”, and “blocker”.
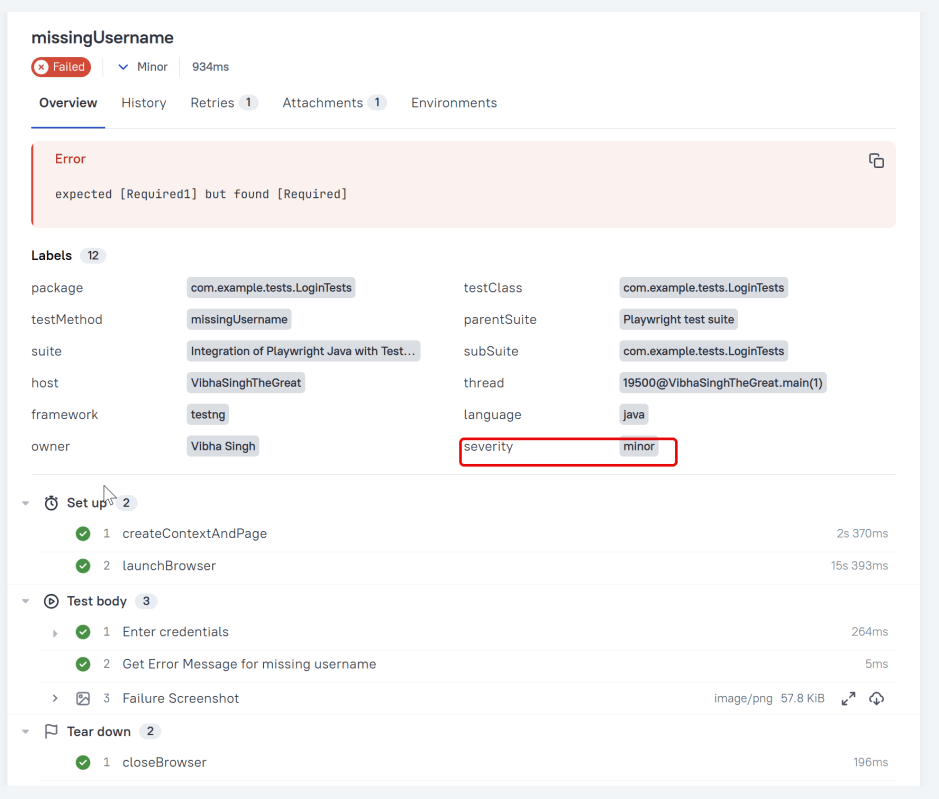
Steps
Allure TestNG provides three ways of creating steps and sub-steps: “annotated steps”, “lambda steps” and “no-op steps”. Define a test step with the given name.
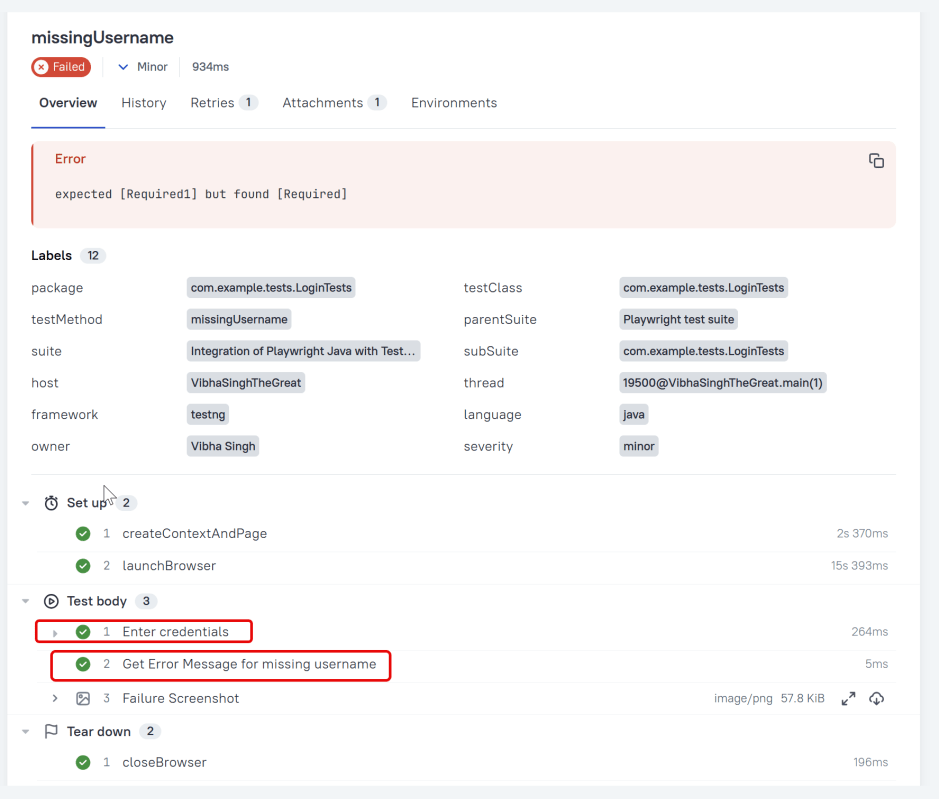
Attachment
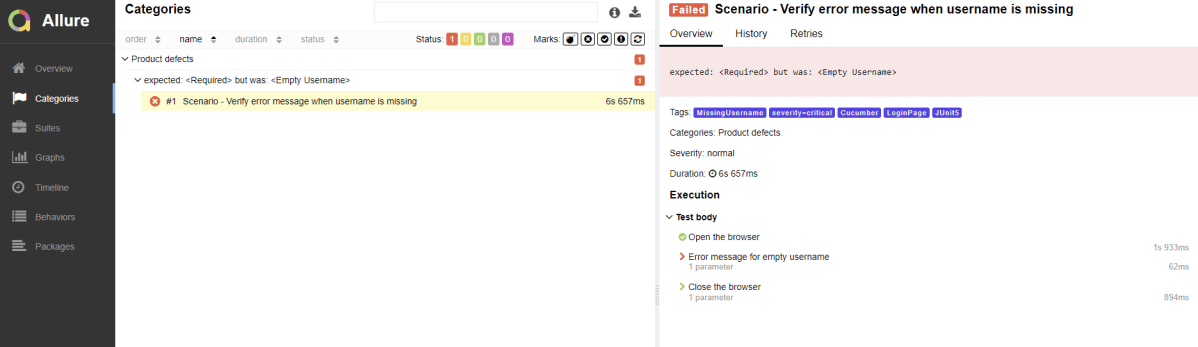
We can attach any sorts of files to your Allure report. Allure TestNG provides various ways to create an attachment, both from existing files or generated dynamically. To create an attachment using the Annotations API, define a method that returns some data and annotate it with @Attachment. Call the method at any point during your test.
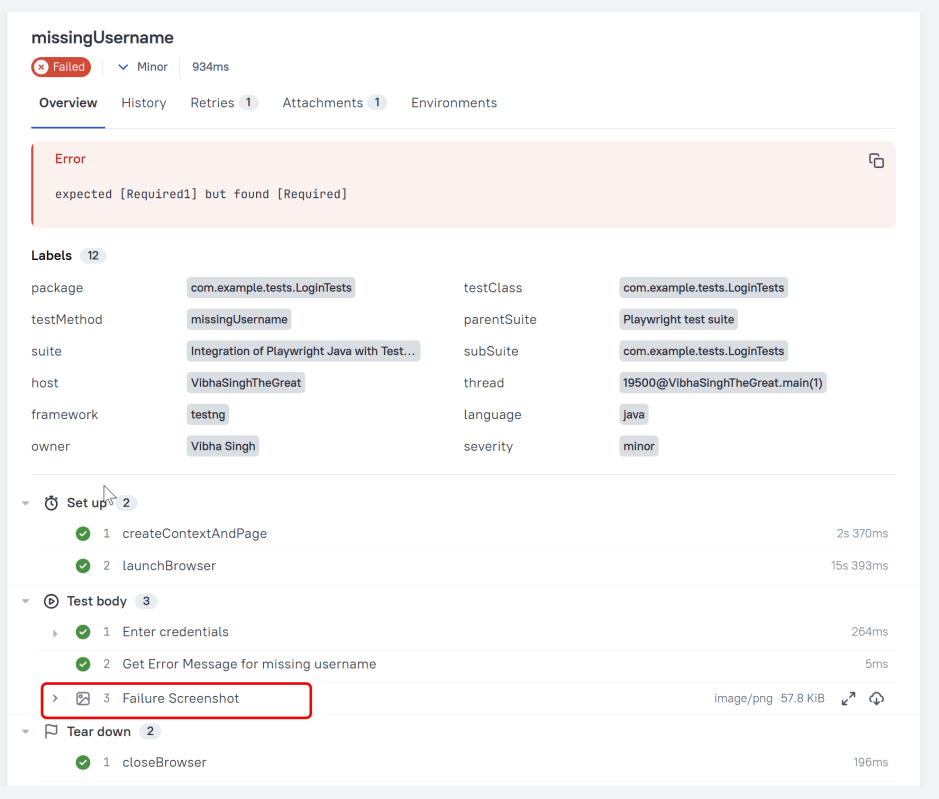
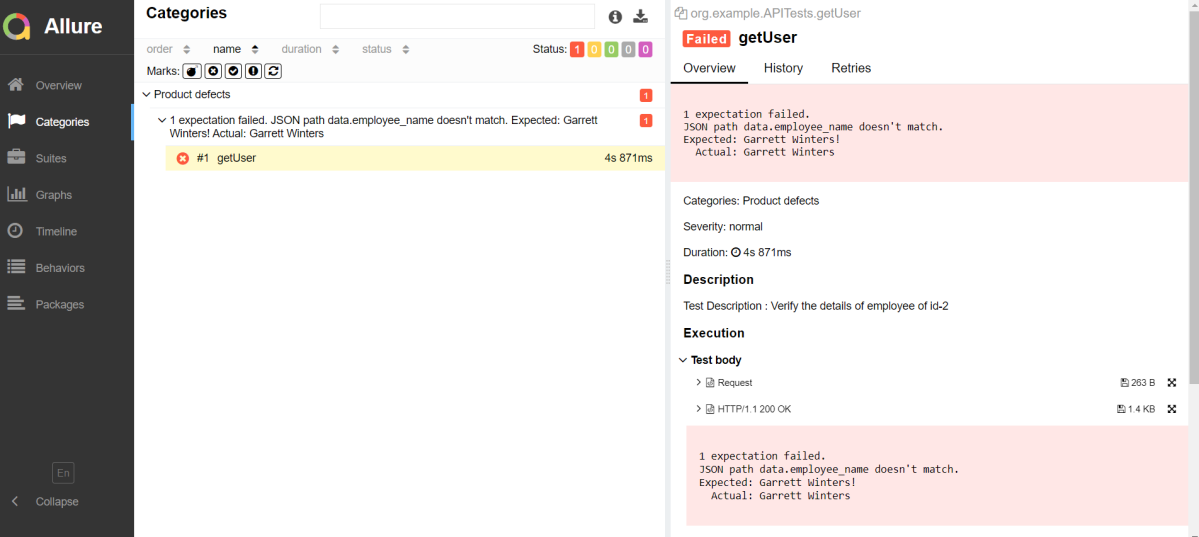
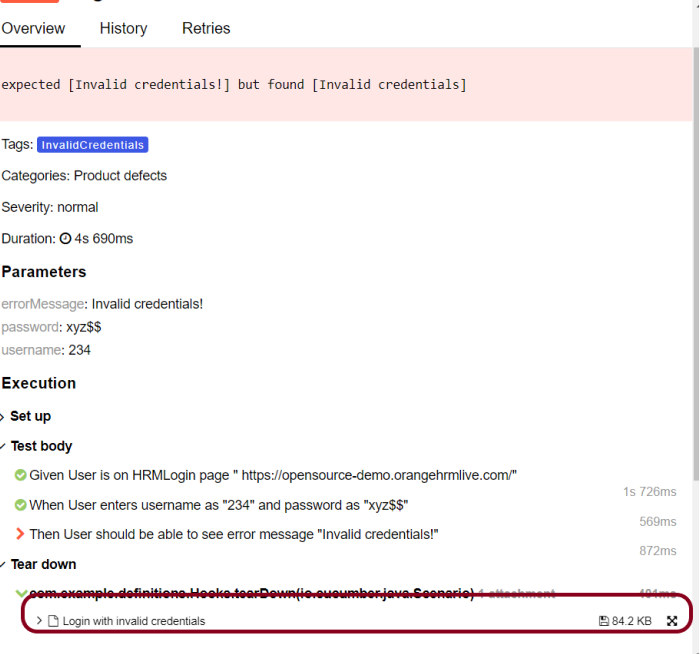
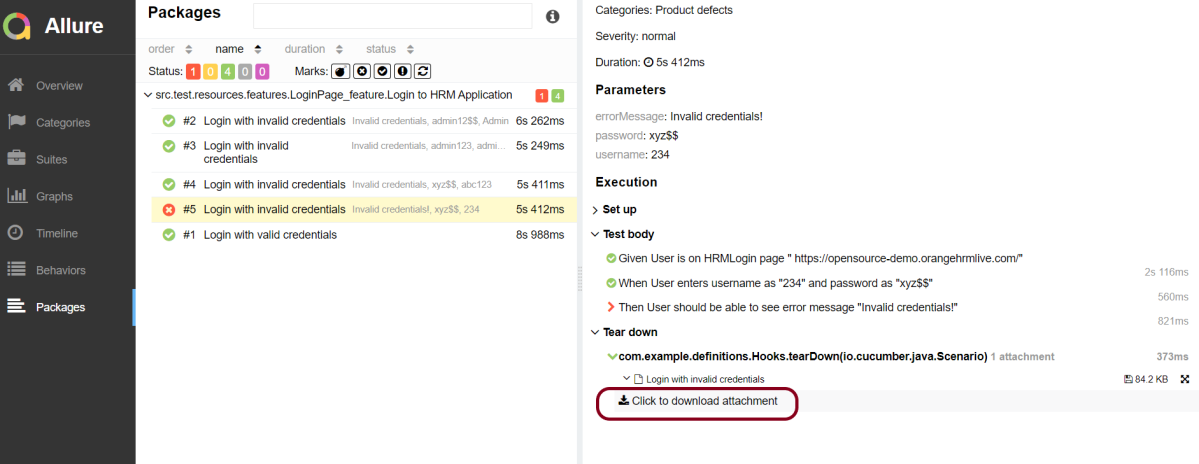
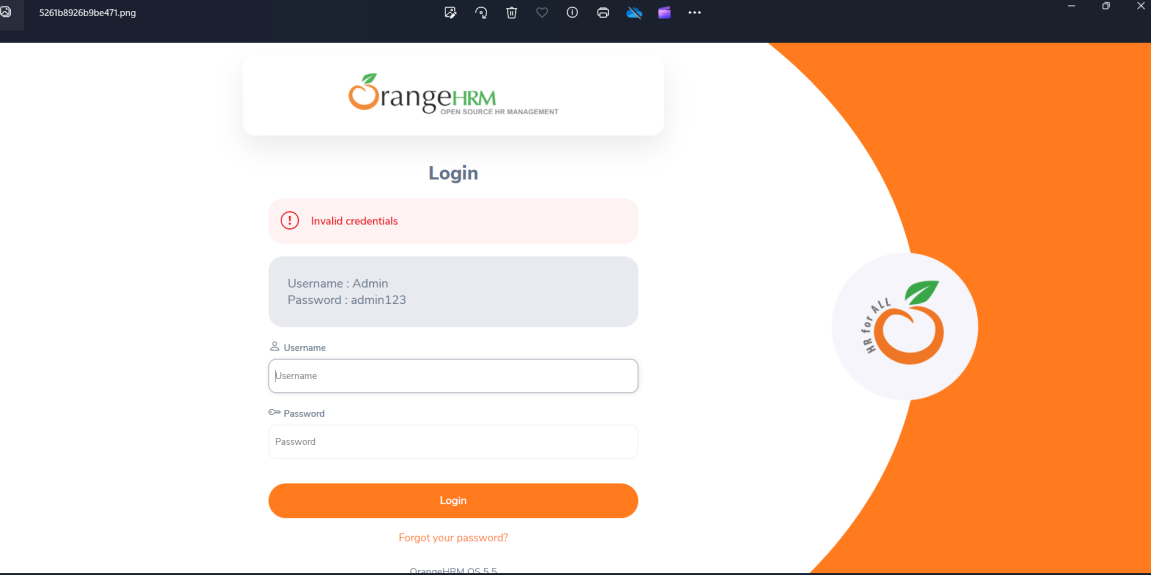
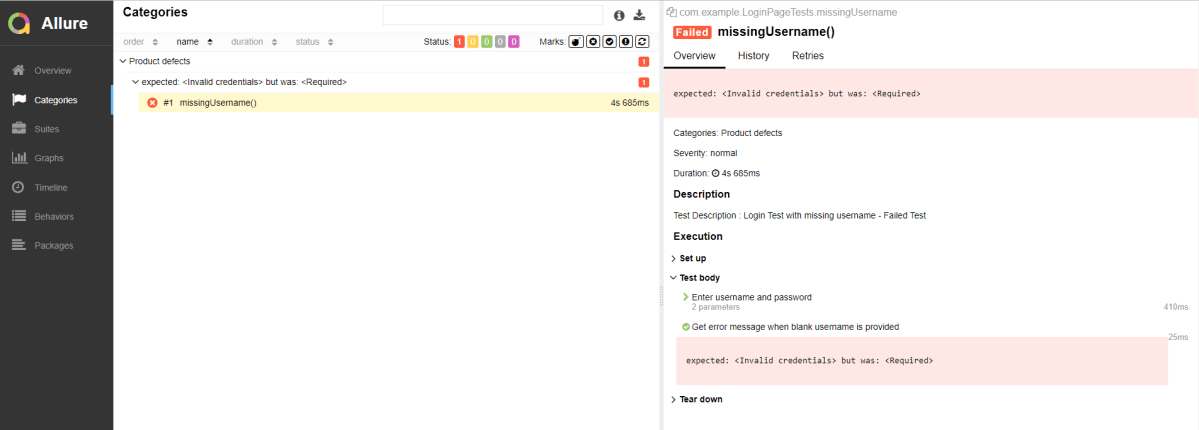
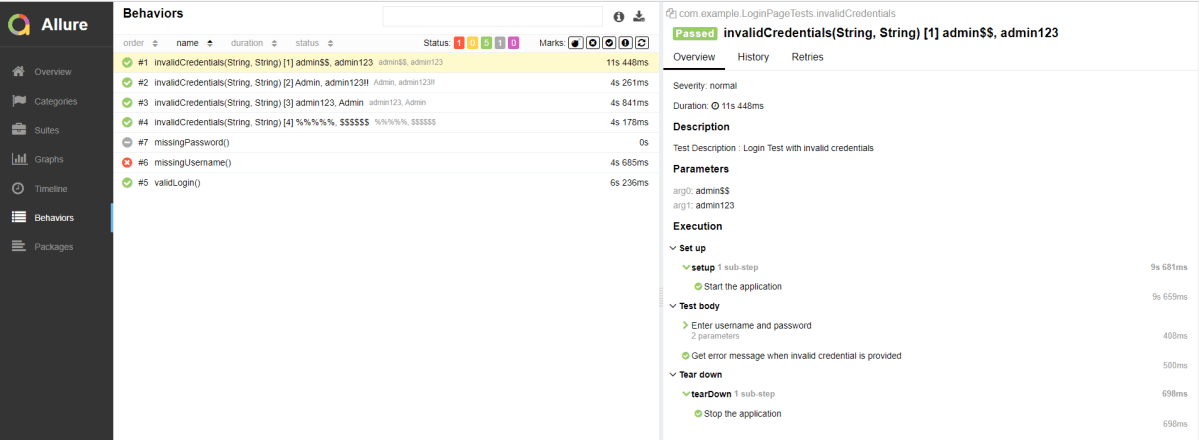
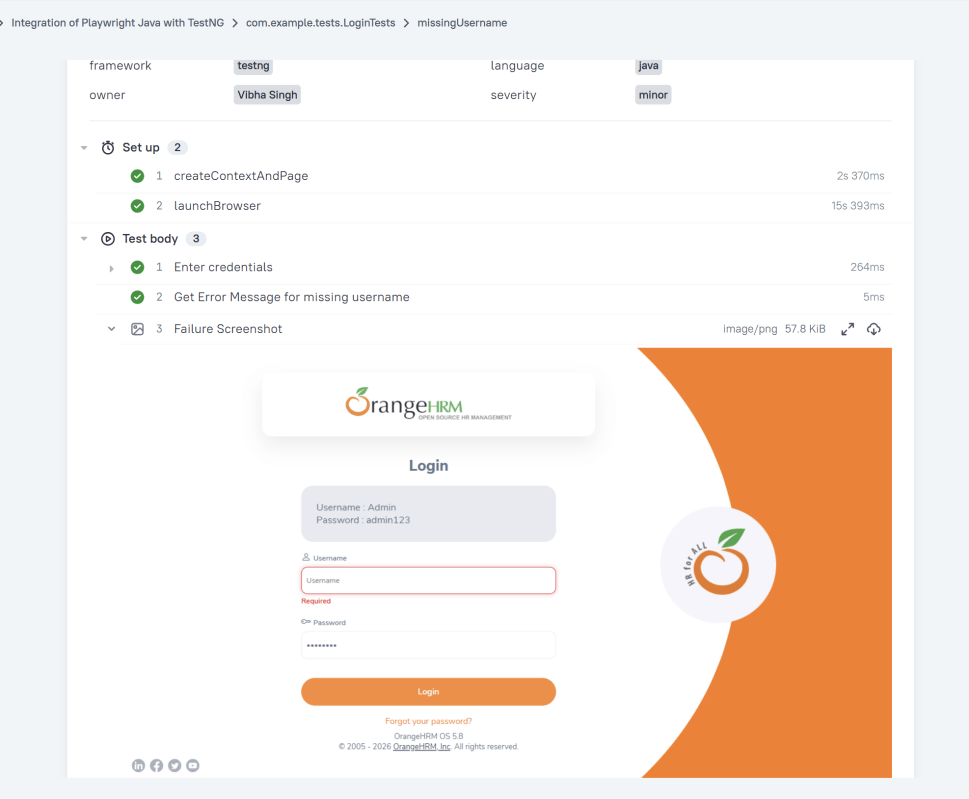
Click on the highlighted portion and we can see the screenshot of the failed test.
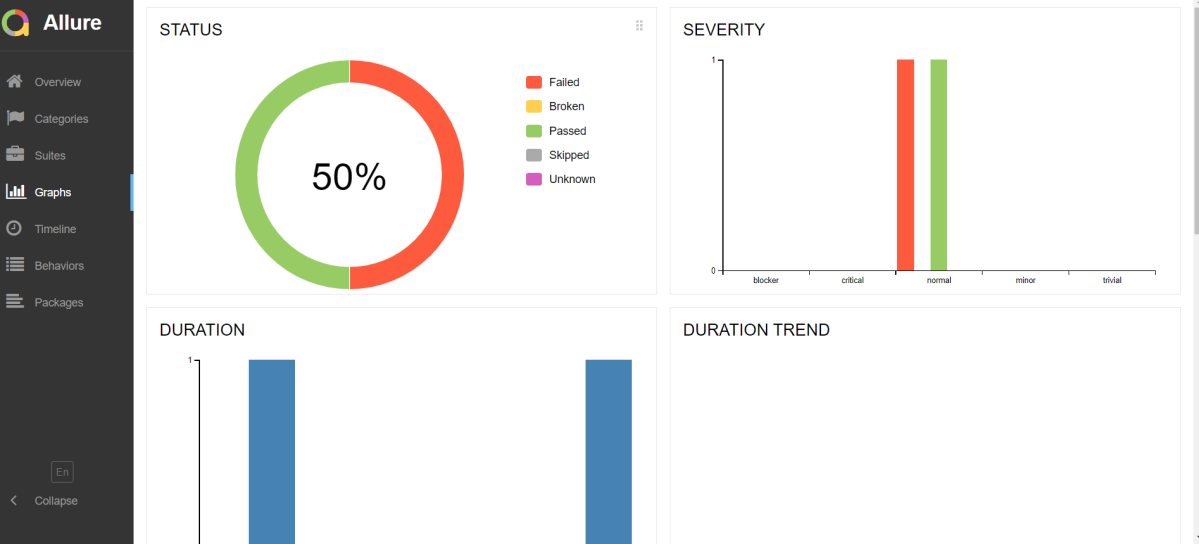
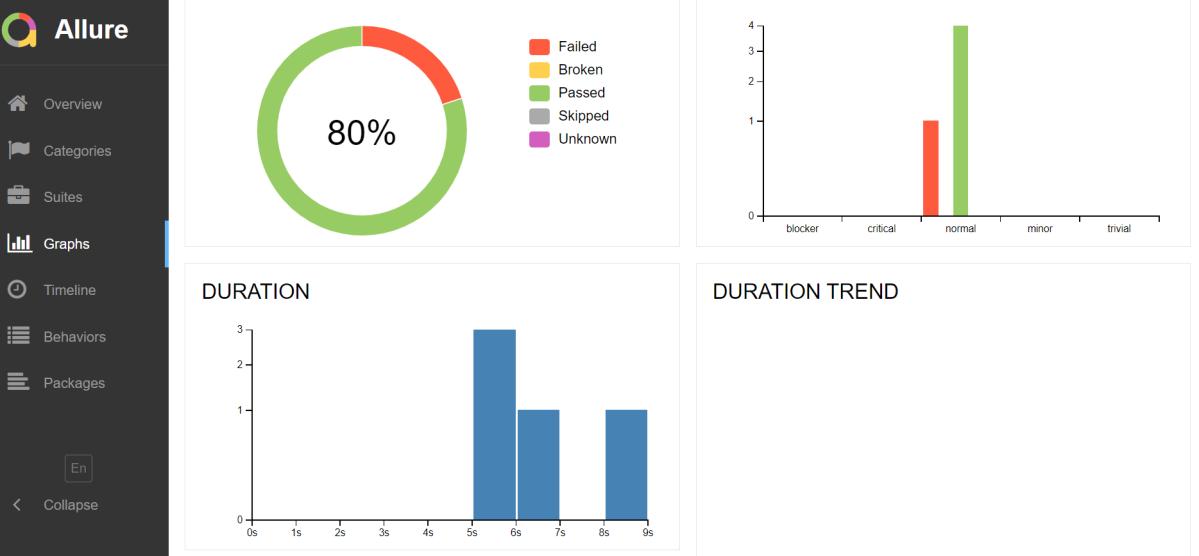
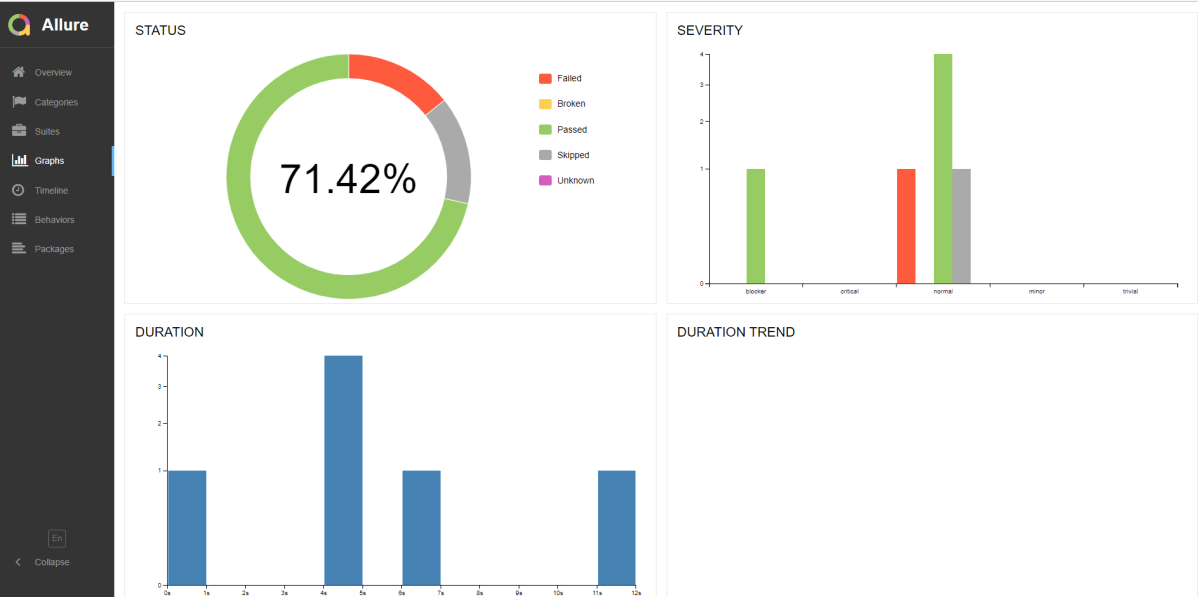
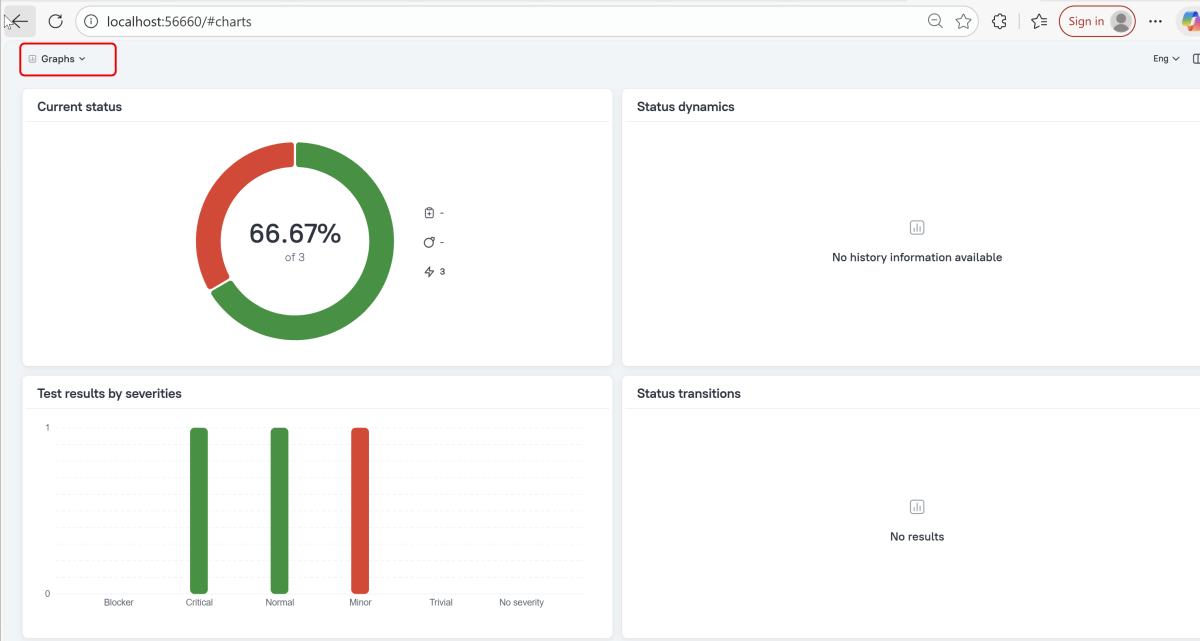
Graphs in Allure Report
Graphs allow you to see different statistics collected from the test data: status breakdown or severity and duration diagrams.
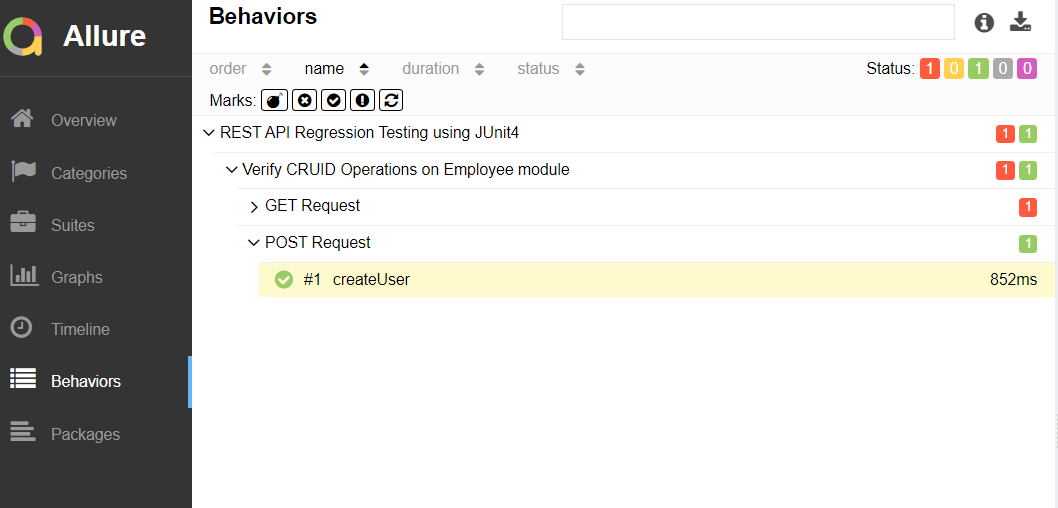
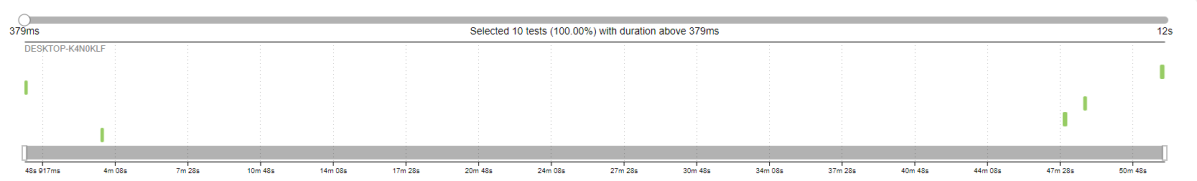
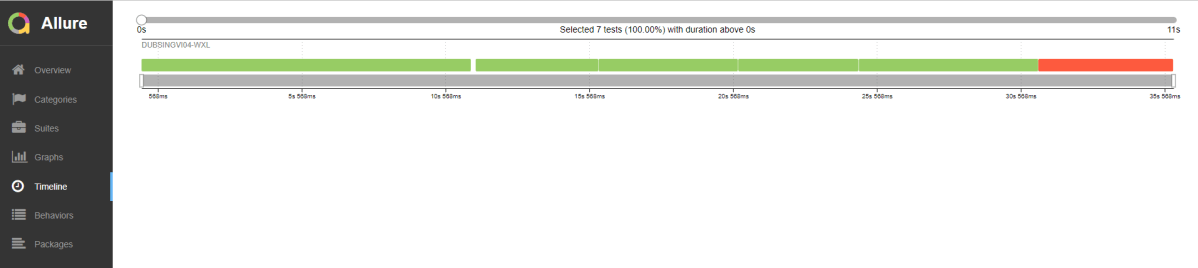
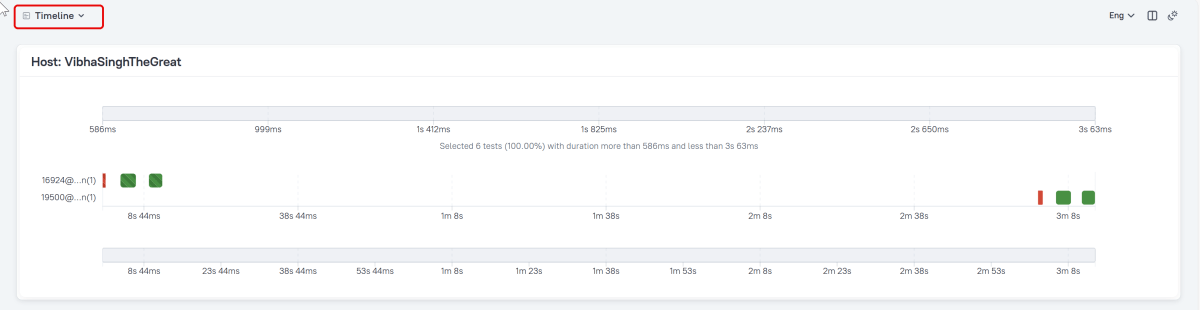
Timeline in Allure Report
The timeline tab visualizes retrospective test execution. Allure adaptors collect precise timings of tests. Here on this tab, they are arranged according to their sequential or parallel timing structure.
Generate Reports with the Allure Awesome Plugin
Allure 3 Report also features an advanced report generator plugin – Allure Awesome. It supports additional configuration options, such as generating the report as a single HTML file, setting the theme, custom branding and language of the generated report, and taking known issues into account.
To manually generate a customized Allure Awesome report, use the awesome command:
allure awesome build/allure-results
Congratulations!! We have integrated an allure report with Cucumber, Selenium, and TestNG. I hope this tutorial is useful to you.
Additional Tutorials on Allure Reports
Integration of Allure Report with Selenium and JUnit4
Integration of Allure Report with Selenium and TestNG
Gradle – Allure Report for Selenium and JUnit4
Gradle – Allure Report for Cucumber, Selenium and TestNG
Integration of Allure Report with Rest Assured and JUnit4