In the previous tutorial, I explained about the Testing of SpringBoot POST Method. In this tutorial, I will discuss the Testing of Exceptions in the SpringBoot application.
Table of Contents
- Response Statuses for Errors
- Default Exception Handling with Spring Boot
- Customizing Exception Handling with Spring Boot
- What is ExceptionHandler?
- What is ControllerAdvice?
- Customizing Error Response Structure
- How to execute a Get Request Method with an Invalid URL using Postman
- Test Code to test the above scenario (StepDefinition file)
Response Statuses for Errors
The most commonly used error codes in SpringBoot Application are:-
- 404 – RESOURCE NOT FOUND
- 400 – BAD REQUEST
- 401 – UNAUTHORIZED
- 415 – UNSUPPORTED TYPE – Representation not supported for the resource
- 500 – SERVER ERROR
Default Exception Handling with Spring Boot
Spring Boot provides a good default implementation for exception handling for RESTful Services.
This is the response when you try getting details of a non-existing student. You can see that the response status is 500 – Internal Server Error.

Customizing Exception Handling with Spring Boot
There are 2 most commonly used annotations used in Error Handling – @ExceptionHandler and @ControllerAdvice.
What is ExceptionHandler?
The @ExceptionHandler is an annotation used to handle the specific exceptions and send the custom responses to the client.
@ExceptionHandler(StudentNotFoundException.class)
What is ControllerAdvice?
A controller advice allows you to use exactly the same exception-handling techniques but apply them across the whole application, not just to an individual controller.
A combination of Spring and Spring Boot provides multiple options to customize responses for errors.
@ControllerAdvice
@RestController
public class CustomizedResponseEntityExceptionHandler extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler {
You can specify the Response Status for a specific exception along with the definition of the Exception with the ‘@ResponseStatus’ annotation.
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)
I have defined the StudentNotFoundExceptionclass. This Exception will be thrown by the controller when no resource i.e. Student to be returned in our case is found with HTTP Status of NOT_FOUND (404).
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)
public class StudentNotFoundException extends RuntimeException {
public StudentNotFoundException(String exception) {
super(exception);
}
}
Now the response will be 404 – Not Found
{
"timestamp": "2021-02-22T15:56:59.494+00:00",
"status": 404,
"error": "Not Found",
"trace": "StudentNotFoundException: id-100,
"message": "id-100",
"path": "/students/100"
}
Customizing Error Response Structure
The default error response provided by Spring Boot contains all the details that are typically needed.
However, you might want to create a framework-independent response structure for your organization. In that case, you can define a specific error response structure.
import java.util.Date;
public class ExceptionResponse {
private Date timestamp;
private String message;
private String details;
public ExceptionResponse(Date timestamp, String message, String details) {
super();
this.timestamp = timestamp;
this.message = message;
this.details = details;
}
public Date getTimestamp() {
return timestamp;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public String getDetails() {
return details;
}
}
To use ExceptionResponse to return the error response, let’s define a ControllerAdvice as shown below.
@ControllerAdvice
@RestController
public class CustomizedResponseEntityExceptionHandler extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(StudentNotFoundException.class)
public final ResponseEntity<Object> handleUserNotFoundException(StudentNotFoundException ex, WebRequest request) {
ExceptionResponse exceptionResponse = new ExceptionResponse(new Date(), ex.getMessage(),
request.getDescription(false));
return new ResponseEntity(exceptionResponse, HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
Scenario 1- How to execute a Get Request Method with an Invalid URL using Postman
The below picture shows how we can execute a Get Request Method with an Invalid URL using Postman.
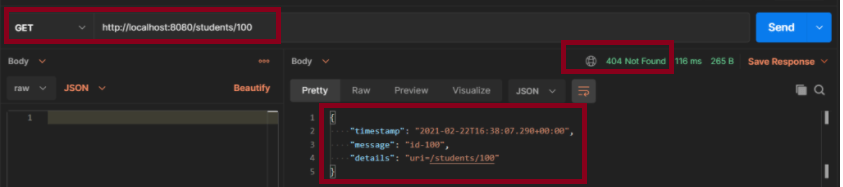
The above scenario can be tested in the below way.
Feature: Student Exception
@InvalidURL
Scenario: Send a valid Request to create a student
Given I send a request to the invalid URL "/students/100" to get a student details
Then the response will return status of 404 and message "id-100"
Test Code to test the above scenario (StepDefinition file)
@SpringBootTest(classes = SpringBootRestServiceApplication.class, webEnvironment = WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
public class CustomizedErrorsDefinition {
private final static String BASE_URI = "http://localhost";
@LocalServerPort
private int port;
private ValidatableResponse validatableResponse;
private void configureRestAssured() {
RestAssured.baseURI = BASE_URI;
RestAssured.port = port;
}
protected RequestSpecification getAnonymousRequest() throws NoSuchAlgorithmException {
configureRestAssured();
return given();
}
@Given("^I send a request to the invalid URL \"([^\"]*)\" to get a student details$")
public void iSendARequest(String endpoint) throws Throwable {
validatableResponse = getAnonymousRequest().contentType(ContentType.JSON).when().get(endpoint).then();
}
@Then("^the response will return status of (\\d+) and message \"([^\"]*)\"$")
public void extractResponse(int status, String message) { validatableResponse.assertThat().statusCode(equalTo(status)).body("message", equalTo(message));
}
}
The output of the above program is
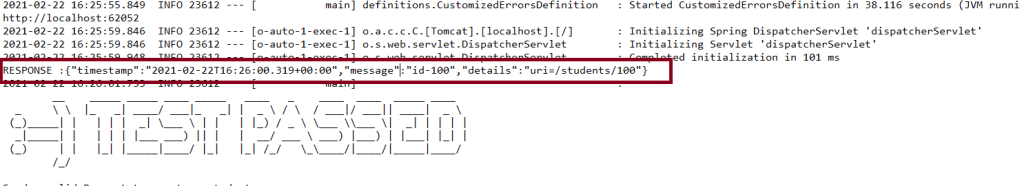
To know more about SpringBootTest, refer to the tutorial on Integration Testing of SpringBoot.
@SpringBootTest(classes = SpringBootRestServiceApplication.class, webEnvironment = WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
To know about all the dependencies we need to add to pom.xml to run the SpringBoot Test, refer to the tutorial about Testing of SpringBoot REST Application using Serenity BDD and Rest Assured for GET Method.
To know how you can test a SpringBoot Application in BDD format using Serenity, refer to the tutorial related to Serenity BDD with Cucumber for SpringBoot application.
The next tutorial explains the Testing of SpringBoot Validation for RESTful Services.