Last Updated On
In this article, we will discuss how to pass the Authentication Token in the header. We will focus on its implementation in Robot Framework.
What is an authorization token?
An authorization token is often referred to as an access token. It is a piece of data or credential. This token is used to authenticate. It authorizes access to protected resources or operations in a system.
Below is an example of passing authorization token in Postman.

Table of Contents
Prerequisite:
- Install Python
- Install PIP
- Install Robot Framework
- Install Robot framework Selenium Library
- Install PyCharm IDE
Please refer to this tutorial to install Robot Framework – How to install and setup Robot Framework for Python.
What is RequestLibrary?
RequestLibrary is a Robot Framework library aimed to provide HTTP API testing functionalities by wrapping the well-known Python Requests Library.
Implementation Steps:
Step 1 – Create a new project
Step 1.1 – Open PyCharm and create a new project. Go to File and select New Project from the main menu.
Step 1.2 – Choose the project location. Click the “Browse” button next to the Location field and specify the directory for your project.
Deselect the Create a main.py welcome script checkbox because you will create a new Python file for this tutorial.
Click on the “Create” Button.
Step 1.3 – A new dialog appears asking to open the project using any one of the given options. I have selected New Window as I like to have separate windows for each project.
Below is the image of the new project created in PyCharms.
Step 2 – Install RequestLibrary
To install RequestLibrary, you need to use the below command:
pip install robotframework-requests
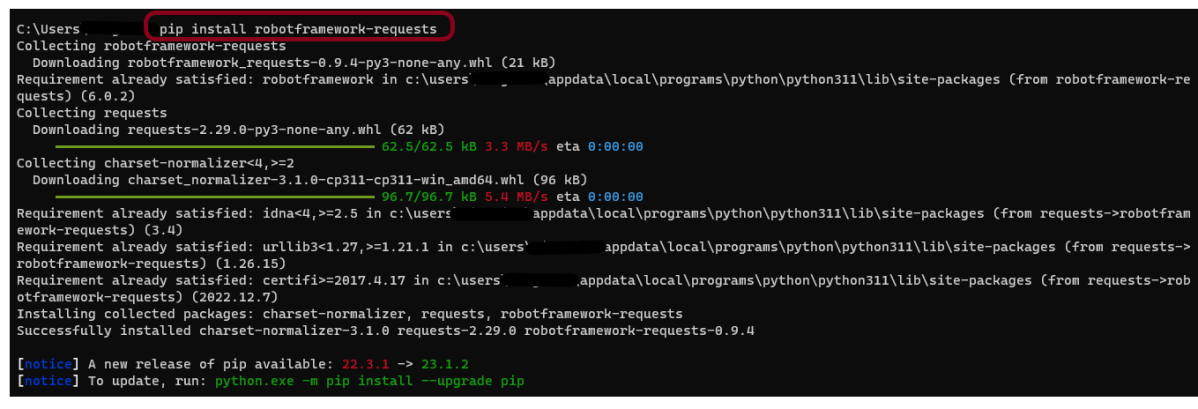
Step 3 – Add robotframework-requests package to the PyCharms
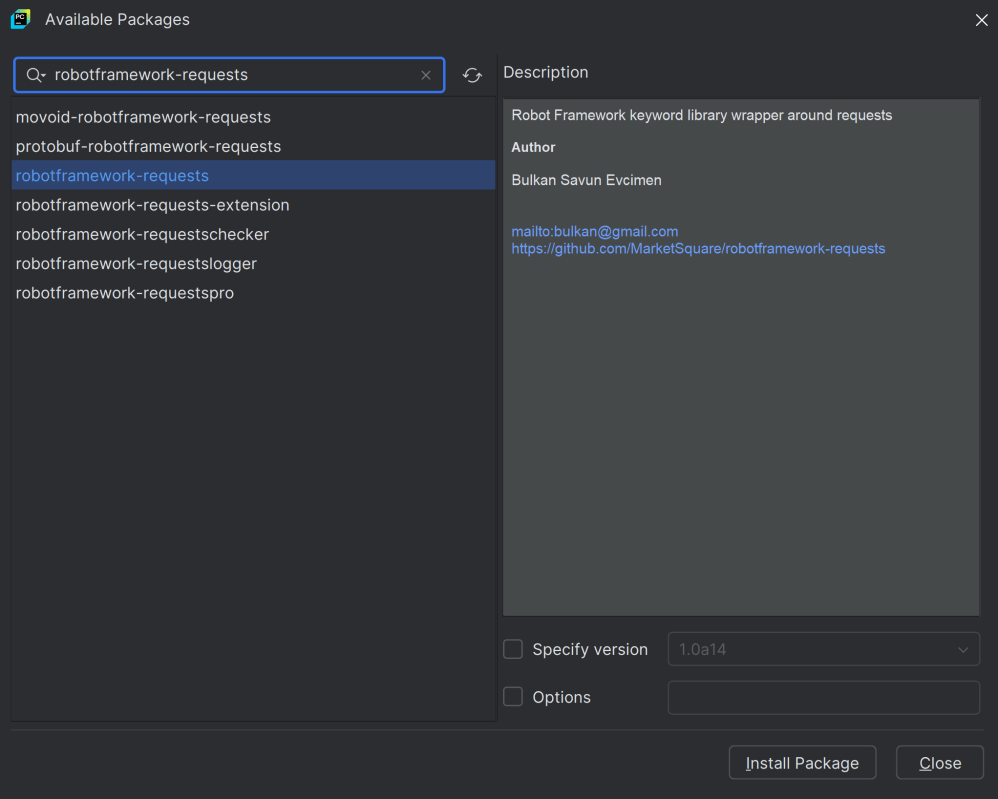
Go to File->Settings ->Project:API_RobotFramework ->Python Interpreter.
Click on the “+” sign and enter robotframework-requests in the search bar. It will show a list of packages. Select the “robotframework-requests” package and click on the “Install Package”.
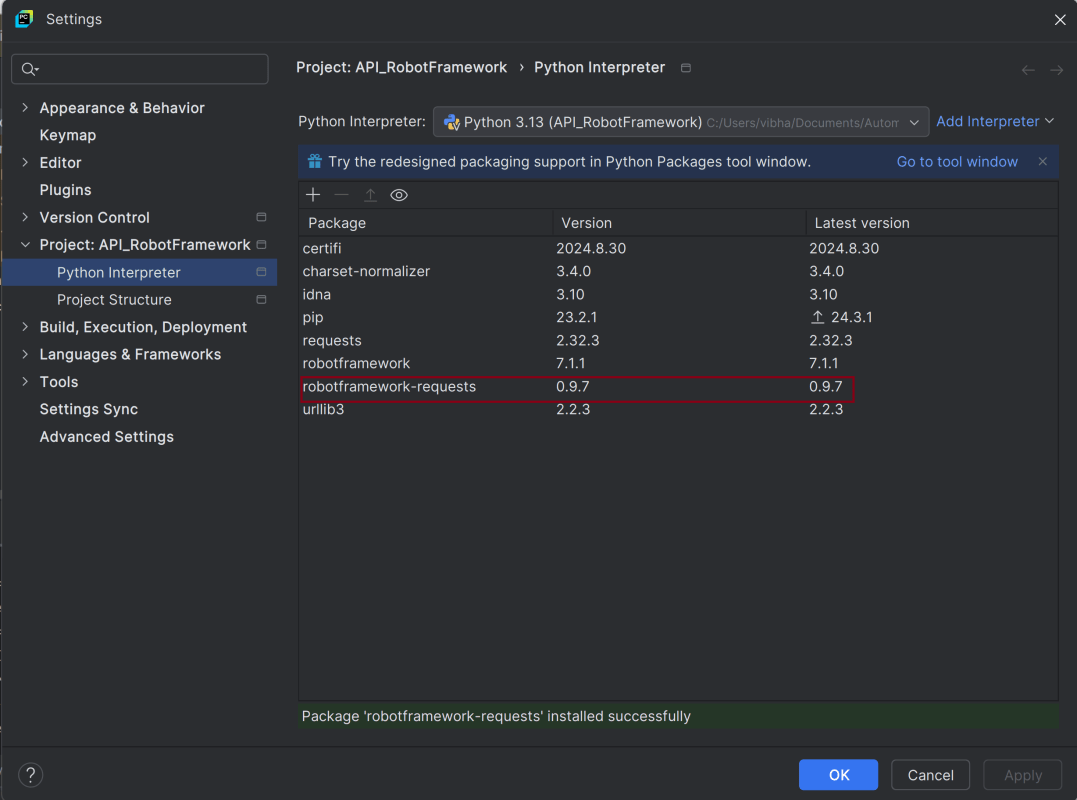
Once the package is installed, we will see the message that the package is installed successfully.

Once the package is installed, it can be seen under the package list as shown below:
Step 4 – Create a new directory in the new project
Right-Click on the project, select New->Directory, and provide the name as Tests
Below is the image of the new directory.
Right-click on the new directory and select New File and provide the name as AuthTokenDemo.robot as shown below:

Step 5 – Create API tests in Robot Framework
The API Test in Robot Framework.
*** Settings ***
Library RequestsLibrary
Library Collections
Library BuiltIn
*** Variables ***
${BASE_URL} https://httpbin.org/basic-auth/user/pass
${AUTH_TOKEN} Basic dXNlcjpwYXNz
*** Test Cases ***
Example API Request with Authorization Header
[Documentation] Example of sending a GET request with an Authorization token in the header
Create Session api ${BASE_URL}
# Create headers dictionary in the test case
${headers}= Create Dictionary Authorization=${AUTH_TOKEN} Content-Type=application/json
${response}= GET On Session api url=${BASE_URL} headers=${headers}
Log To Console Status Code: ${response.status_code}
Log To Console Response Body: ${response.text}
Should Be Equal As Numbers ${response.status_code} 200
Settings Section
RequestsLibrary: Used for making HTTP requests.
Collections: Provides utilities like creating and manipulating dictionaries.
BuiltIn: Provides core Robot Framework keywords (like Log To Console).
Variables Section
${BASE_URL}: The base URL for the HTTP request.
${AUTH_TOKEN}: Authentication Token
Test Case Section:
This test case send an HTTP GET request with an Authorization token in the headers.
1. Initializes an HTTP session named “api” with the specified base URL.
Create Session api ${BASE_URL}
2. Create Headers and includes the predefined token (Basic dXNlcjpwYXNz) for basic authentication.
${headers}= Create Dictionary Authorization=${AUTH_TOKEN} Content-Type=application/json
3. Sends a GET request on the “api” session to the specified URL. This request uses the headers created earlier, which includes the headers (${headers}) for authentication.
${response}= GET On Session api url=${BASE_URL} headers=${headers}
${response}= We are saving the response of the GET operation in the ${response} variable.
4. Asserts that the response status code is 200, indicating a successful request.
Log To Console Status Code: ${response.status_code}
Log To Console Response Body: ${response.text}
Should Be Equal As Numbers ${response.status_code} 200
Step 6 – Execute the tests
We need the below command to run the Robot Framework script.
robot AuthTokenDemo.robot
The output of the above program is

Step 7 – View Report and Log
We have the test case passed. The Robot Framework generates log.html, output.xml, and report.html by default.
Let us now see the report and log details.
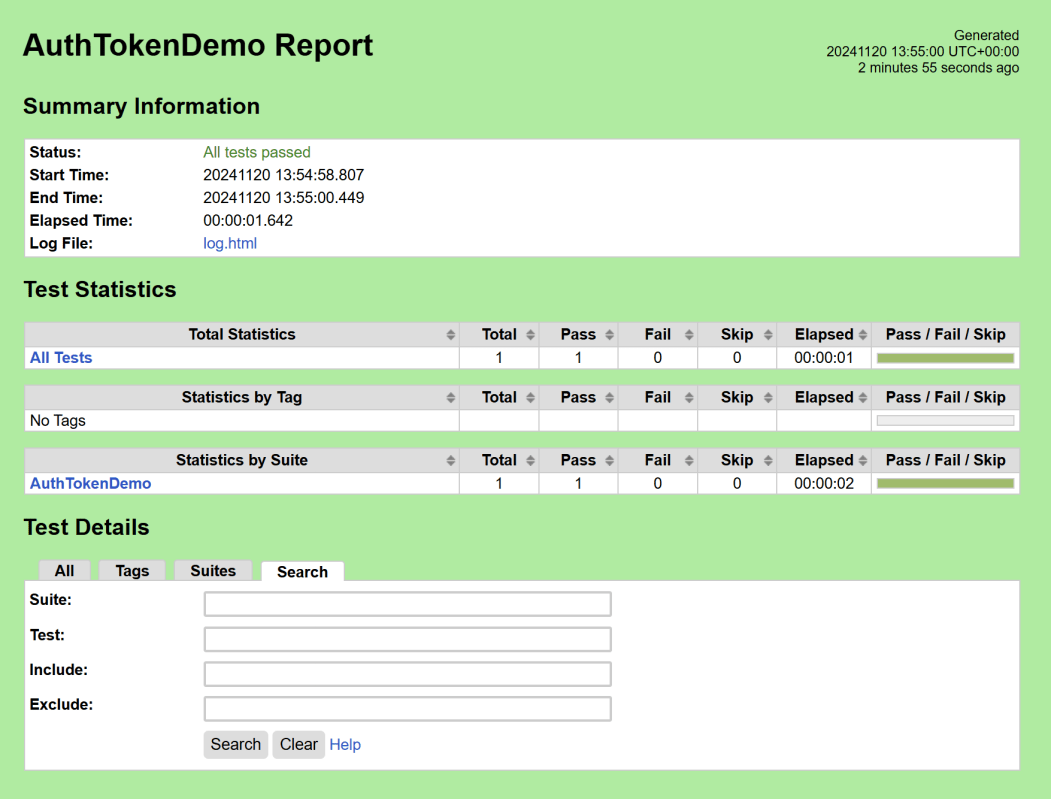
Report
Right-click on report.html. Select Open In->Browser->Chrome(any browser of your wish).
The Report generated by the framework is shown below:
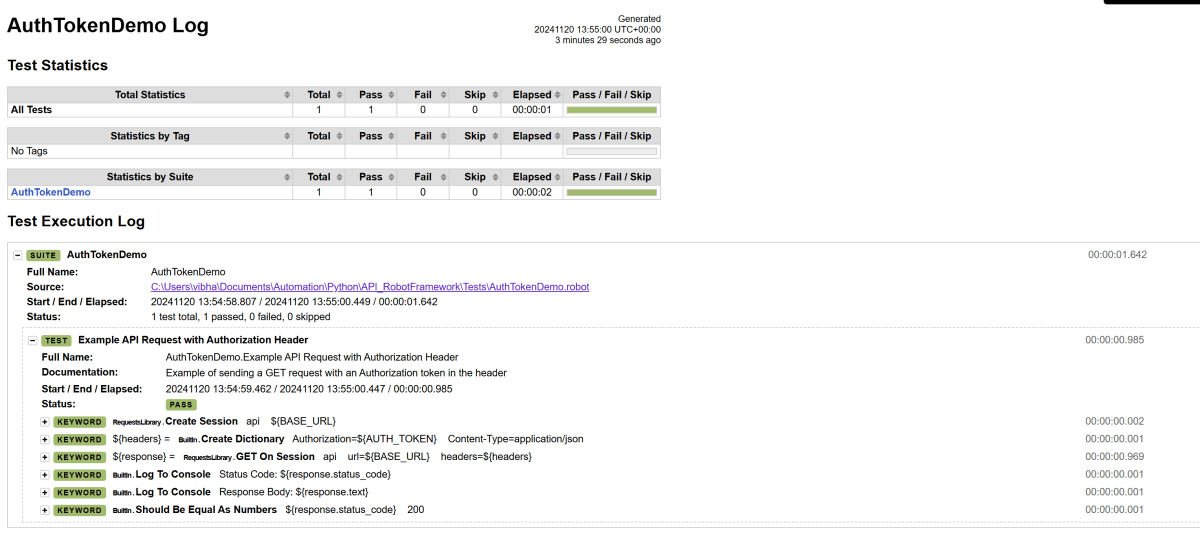
Log
Robot Framework has multiple log levels that control what is shown in the automatically generated log file. The default Robot Framework log level is INFO.
Right-click on log.html. Select Open In->Browser->Chrome(any browser of your wish).
That’s it! Congratulations on making it through this tutorial and hope you found it useful! Happy Learning!!
Additional Tutorials