In this tutorial we’re going to talk about parameterizing the REST Assured tests.
What is Parameterization?
Parameterization refers to the process of passing different set of data to the same code. This allows you to verify that the code behaves as expected for various inputs without writing multiple test cases. It enhances the coverage of the test suite by testing the functionality with different data sets and helps identify edge cases or potential bugs that could occur with different input values.
We are using junit4-dataprovider dependency here.
<!-- Data Provider -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.tngtech.junit.dataprovider</groupId>
<artifactId>junit4-dataprovider</artifactId>
<version>${junit.dataprovider.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
Add the necessary dependencies to the project.
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>Parameterized_APITests</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>Parameterized_APITests</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<properties>
<rest-assured.version>5.4.0</rest-assured.version>
<junit.version>4.13.2</junit.version>
<junit.dataprovider.version>2.10</junit.dataprovider.version>
<maven.compiler.plugin.version>3.12.1</maven.compiler.plugin.version>
<maven.surefire.plugin.version>3.2.3</maven.surefire.plugin.version>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- Rest-Assured Dependency -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.rest-assured</groupId>
<artifactId>rest-assured</artifactId>
<version>${rest-assured.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- JUnit4 Dependency -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>${junit.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Data Provider -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.tngtech.junit.dataprovider</groupId>
<artifactId>junit4-dataprovider</artifactId>
<version>${junit.dataprovider.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.compiler.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<source>${maven.compiler.source}</source>
<target>${maven.compiler.target}</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.surefire.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<testFailureIgnore>true</testFailureIgnore>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Create a test data collection
The first step is to create a test data collection, which is a collection of input and expected outcome values that we want to feed to our test.
@RunWith(DataProviderRunner.class): This annotation tells JUnit to run the tests in this class using the DataProviderRunner, which allows the use of the @DataProvider annotation for parameterized tests
@RunWith(DataProviderRunner.class)
@DataProvider: This annotation marks the method responseData as a provider of test data. The method returns a 2D array of objects (Object[][]), where each inner array represents a set of parameters for a single test run.
The responseData method provides four sets of parameters: an ID, a first name, and a last name.
@DataProvider
public static Object[][] responseData() {
return new Object[][] {
{ "1", "George", "Bluth" },
{ "2", "Janet", "Weaver" },
{ "3", "Emma", "Wong" },
{ "4", "Eve", "Holt" }
};
}
Create the Test using the parameterized data
import com.tngtech.java.junit.dataprovider.DataProvider;
import com.tngtech.java.junit.dataprovider.DataProviderRunner;
import com.tngtech.java.junit.dataprovider.UseDataProvider;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import static io.restassured.RestAssured.given;
import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
@RunWith(DataProviderRunner.class)
public class ParameterizedTets {
@DataProvider
public static Object[][] responseData() {
return new Object[][] {
{ "1", "George", "Bluth" },
{ "2", "Janet", "Weaver" },
{ "3", "Emma", "Wong" },
{ "4", "Eve", "Holt" }
};
}
@Test
@UseDataProvider("responseData")
public void verifyResponse(String id, String expectedFirstName, String expectedLastName)
{
given().
when().
pathParam("id", id).
get("https://reqres.in/api/users/{id}").
then().
assertThat().
statusCode(200).
body("data.first_name", equalTo(expectedFirstName)).
body("data.last_name", equalTo(expectedLastName));
}
}
This code defines a parameterized test that verifies the first name and last name of users returned by the API https://reqres.in/api/users/{id} for given user IDs. The test runs multiple times, once for each set of parameters provided by the responseData method. The RestAssured library is used to perform the API requests and assertions.
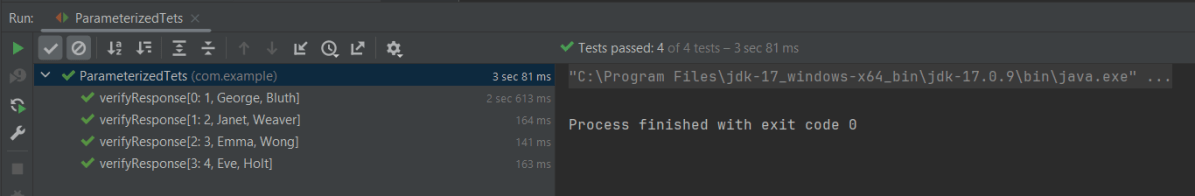
The output of the above program is
Congratulations on making it through this tutorial and hope you found it useful! Happy Learning!! Cheers!!