The previous tutorials have explained the conversion of Java Object to JSON using Gson API. This tutorial explains the process of reading the JSON Payload from a file using Gson API.
Gson is a Java library that can be used to convert Java Objects into their JSON representation. It can also be used to convert a JSON string to an equivalent Java object. Gson can work with arbitrary Java objects, including pre-existing objects for those you do not have source code.
- Provide simple toJson() and fromJson() methods to convert Java objects to JSON and vice versa.
Add the below dependency to POM.xml to use Gson API.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.code.gson</groupId>
<artifactId>gson</artifactId>
<version>2.10.1</version>
</dependency>
Let us take an example of a JSON.
{
"firstName": "Vibha",
"lastName": "Singh",
"age": 30,
"salary": {
"2023": 74000,
"2022": 62000,
"2021": 50000
},
"designation": "Manager",
"contactNumber": "+919999988822",
"emailId": "abc@test.com"
}
Let us create a table named Employee which contains the data members same as node names in the above JSON payload and their corresponding getter and setter methods.
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.Map;
public class Employee {
// private data members of POJO class
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private int age;
private Map<String, BigDecimal> salary;
private String designation;
private String contactNumber;
private String emailId;
// Getter and setter methods
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Map<String, BigDecimal> getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(Map<String, BigDecimal> salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public String getDesignation() {
return designation;
}
public void setDesignation(String designation) {
this.designation = designation;
}
public String getContactNumber() {
return contactNumber;
}
public void setContactNumber(String contactNumber) {
this.contactNumber = contactNumber;
}
public String getEmailId() {
return emailId;
}
public void setEmailId(String emailId) {
this.emailId = emailId;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "(firstName: " + firstName + "," +
"lastName: " + lastName + "," +
"age: " + age + ", " +
"salary: " + salary + "," +
"designation: " + designation + ", " +
"contactNumber: " + contactNumber + ", " +
"emailId: " + emailId + ")";
}
}
We will convert a JSON Object to a Java Object.
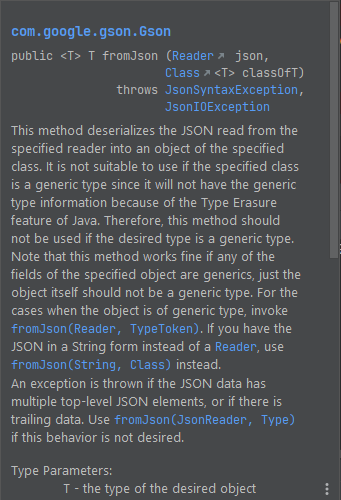
The JSON file – Employee.json is present in src/test/resources.
Below is the image of JSON.
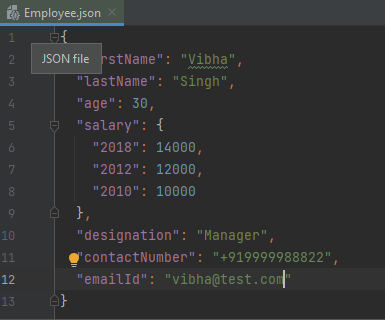
You can create a Gson instance by invoking a new Gson() if the default configuration is all you need, as shown in the below example.
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
public class GsonReadFromFile {
@Test
public void readJsonFromFile() throws FileNotFoundException {
String userDir = System.getProperty("user.dir");
File jsonFilePath = new File(userDir + "\\src\\test\\resources\\Employee.json");
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(jsonFilePath);
Gson gson = new Gson();
Employee employee = gson.fromJson(fileReader, Employee.class);
System.out.println(employee.toString());
System.out.println("FirstName :" + employee.getFirstName());
System.out.println("LastName :" + employee.getLastName());
System.out.println("Age :" + employee.getAge());
System.out.println("Salary :" + employee.getSalary());
System.out.println("Designation :" + employee.getDesignation());
System.out.println("ContactNumber :" + employee.getContactNumber());
System.out.println("EmailId :" + employee.getEmailId());
}
}
The execution message is shown below.
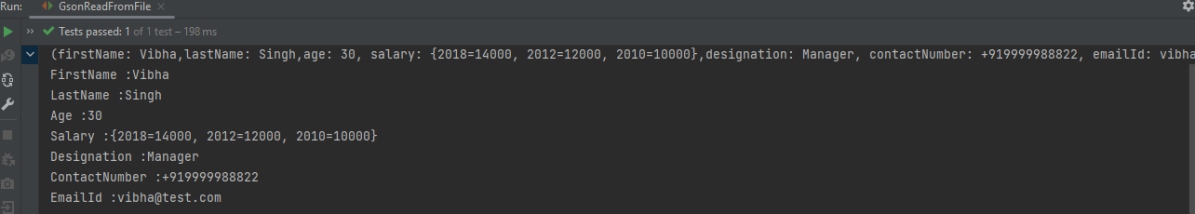
We are done! Congratulations on making it through this tutorial and hope you found it useful! Happy Learning!!