In this tutorial, I will test a SOAP Service using Rest Assured. I will verify the status code, line of Status, and content of the Response. To set up a basic Rest Assured Maven Project, click here and Gradle project, click here.
Add the below-mentioned dependencies to the pom.xml.
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.rest-assured</groupId>
<artifactId>rest-assured</artifactId>
<version>5.3.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
What is the SOAP WebService?
SOAP is an XML-based protocol for accessing web services over HTTP. It has some specifications that could be used across all applications.
SOAP messages are XML documents that are comprised of the following three basic building blocks:
- The SOAP Envelope encapsulates all the data in a message and identifies the XML document as a SOAP message.
- The Header element contains additional information about the SOAP message. This information could be authentication credentials, for example, which are used by the calling application.
- The Body element includes the details of the actual message that needs to be sent from the web service to the calling application. This data includes call and response information.
Implementation Steps:
Step 1 – I have created an XML file for the soap request body in the project resource folder. “Number.xml” is the name of the file.
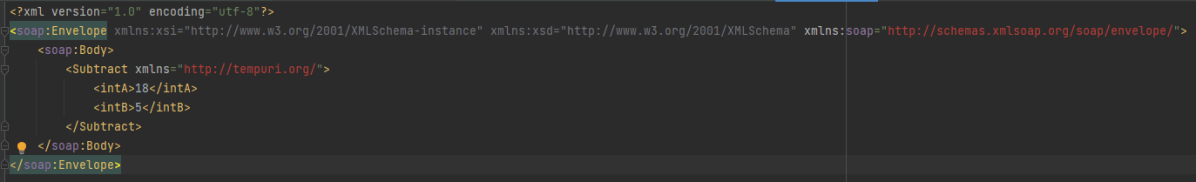
Step 2 – Specify the base URL to the RESTful web service using the RestAssured class.
RestAssured.baseURI = "http://www.dneonline.com";
Step 3 – The response to a request made by REST Assured.
Response response = given()
Response is imported from package:
import io.restassured.response.Response;
Step 4 – Set the content type to specify the format in which the request payload will be sent to the server. Here, the Content-Type is “text/xml; charset=utf-8”.
.header("Content-Type", "text/xml; charset=utf-8")
Step 5 – Pass Request Body.
.body(requestBody)
A Request Body is created by using the below snippet:
requestBody = new File(getClass().getClassLoader().getResource("Number.xml").getFile());
Step 6 – Send the POST request to the server and receive the response of the request made by REST Assured. This response contains every detail returned by hitting request i.e. response body, response headers, status code, status lines, cookies, etc. The response is imported from package:
import io.restassured.response.Response;
Step 7 – To validate a response like status code or value, we have used the below code
Assert.assertEquals(200, response.statusCode());
Assert.assertEquals(13, result);
PrettyPrint() – It prints the response body if possible and returns it as a string. Pretty printing is possible for content types JSON, XML, and HTML.
System.out.println(response.prettyPrint());
Below is an example of testing a SOAP Web Service request using the Rest Assured.
import io.restassured.response.Response;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.File;
import static io.restassured.RestAssured.given;
public class RestAssured_SOAPDemo {
File requestBody;
Response response;
@Test
public void test() {
requestBody = new File(getClass().getClassLoader().getResource("Number.xml").getFile());
response = given()
.baseUri("http://www.dneonline.com")
.basePath("/calculator.asmx")
.header("Content-Type", "text/xml; charset=utf-8")
.body(requestBody)
.post();
System.out.println(response.prettyPrint());
var xPathResult = response.xmlPath().get("//SubtractResult/text()");
var result = Integer.parseInt(String.valueOf(xPathResult));
System.out.println("xPathResult :" + xPathResult);
System.out.println("result :" + result);
Assert.assertEquals(200, response.statusCode());
Assert.assertEquals(13, result);
}
}
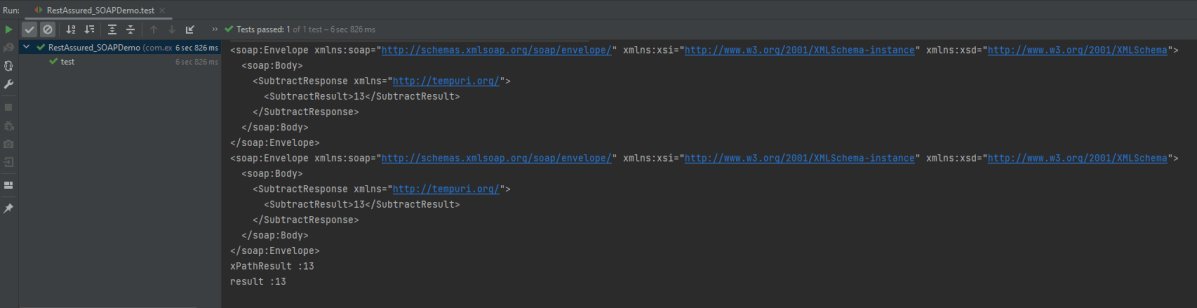
The below image shows the test result of the above test.
Congratulations on making it through this tutorial and hope you found it useful! Happy Learning!! Cheers!!