SOAP is a messaging protocol specification for exchanging structured information in the implementation of web services. Its purpose is to induce extensibility, neutrality, and independence. Testing SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) services using JMeter requires setting up a test plan. The test plan simulates requests. It also analyzes responses from the SOAP web service.
Here’s a detailed guide to help you test SOAP services using JMeter:
Table of Contents
- Prerequisite
- Implementation Steps
Prerequisite:
Install JMeter on your system.
Implementation Steps
The sample request and response used in this tutorial are shown below:
Sample Request
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<soap:Envelope xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/">
<soap:Body>
<NumberToWords xmlns="http://www.dataaccess.com/webservicesserver/">
<ubiNum>500</ubiNum>
</NumberToWords>
</soap:Body>
</soap:Envelope>
Sample Response
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<soap:Envelope xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/">
<soap:Body>
<m:NumberToWordsResponse xmlns:m="http://www.dataaccess.com/webservicesserver/">
<m:NumberToWordsResult>five hundred </m:NumberToWordsResult>
</m:NumberToWordsResponse>
</soap:Body>
</soap:Envelope>
1. Create a Test Plan in JMeter
Create a new test plan in JMeter by selecting File > New Test Plan. You can provide name to the test plan (e.g., “SOAP Test Plan”) and click Create. This will create a new test plan with a default thread group.

2. Add Thread Group
- Select Test Plan on the tree
- Add Thread Group
- To add Thread Group: Right-click on the “Test Plan” and add a new thread group: Add -> Threads (Users) -> Thread Group

In the Thread Group control panel, enter Thread Properties as follows:
- Number of Threads: 10 – Number of users connects to the target website
- Loop Count: 5 – The loop count specifies how many times each thread will execute. Given a loop count of 5, each of the 10 threads will run the entire test sequence 5 times. In total, this results in 50 iterations across all threads (10 threads x 5 loops).
- Ramp-Up Period: 5 – It tells JMeter how long to delay before starting the next user. A ramp-up period of 5 seconds means that JMeter will start a new thread every 0.5 seconds (calculated as total ramp-up time divided by number of threads: 5 seconds / 10 threads = 0.5 seconds).

3. Adding JMeter elements
The JMeter element used here is HTTP Request Sampler. In the HTTP Request Control Panel, the Path field indicates which URL request you want to send
Add HTTP Request
To add: Right-click on Thread Group and select: Add -> Sampler -> HTTP Request

The below-mentioned are the values used in HTTP Request to perform the test
- Protocol– https
- Server Name or IP – http://www.dataaccess.com
- Method – POST
- Path – /webservicesserver/NumberConversion.wso
- Body Data – as mentioned above

Add HTTP Head Manager
SOAP requests require specific content-type headers. The Header Manager lets you add or override HTTP request headers like can add Accept-Encoding, Accept, Cache-Control
To add: Right-click on Thread Group and select: Add -> Config Element -> HTTP Read Manager

The below-mentioned are the values used in Http Request to perform the test
Content-type = text/xml

4. Add Response Assertion
Add a “Response Assertion” to check for expected values, tags, or response status codes in the XML response.
To add: Right-click on HTTP Request and select: Add -> Assertions-> Response Assertions

Here, I have selected below options:-
Apply to : Main Sample only
Field to Test: Response Code
Pattern To Test: 200

5. Adding Listeners to Test Plan
Listeners – They show the results of the test execution. They can show results in a different format such as a tree, table, graph, or log file
We are adding the View Result Tree listener & Aggregate Report listener.
View Result Tree
View Result Tree shows the results of the user request in basic HTML format
To add: Right-click on Test Plan, Add -> Listener -> View Result Tree

Aggregate Report
It is almost the same as Summary Report except Aggregate Report gives a few more parameters like, “Median”, “90% Line”, “95% Line” and “99% Line”.
To add: Right Click on Thread Group > Add > Listener > Aggregate Report

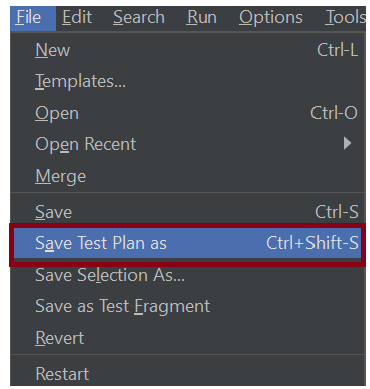
6. Save the Test Plan
To Save: Click File and Select -> Save Test Plan as ->Give the name of the Test Plan. It will be saved in .jmx format.
7. Run the Test Plan
Click on the Green Triangle as shown at the top to run the test.

8. View the Execution Status
Click on View Result Tree to see the status of Run. A successful request will be of a Green colour in the Text Section.
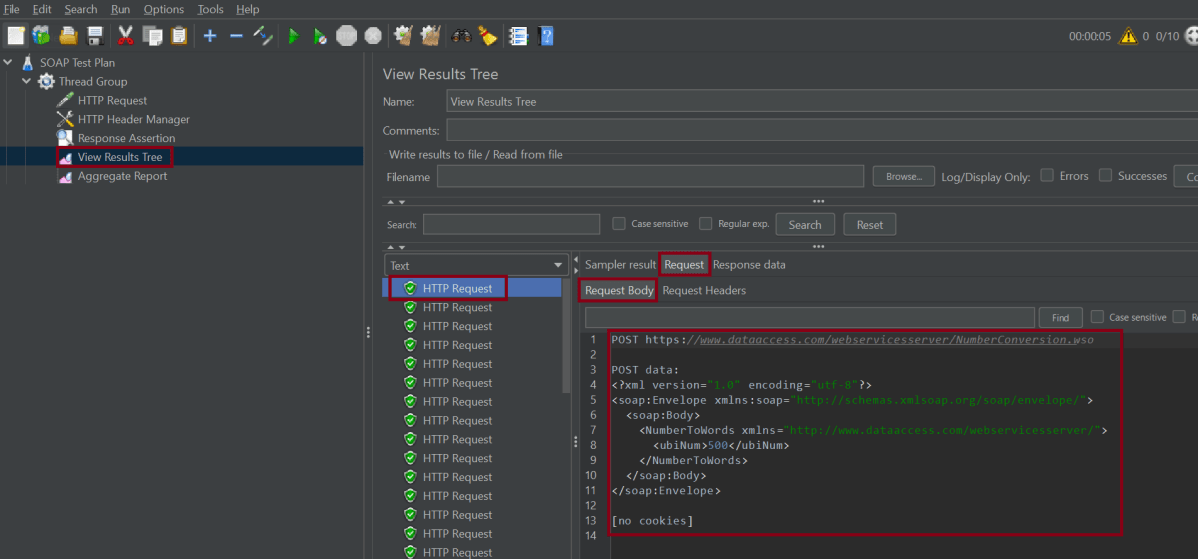
Click on Response data and Response Header to view other information about Response.

Click on Aggregate Report Result to see the aggregated status of Run.

9. Troubleshooting
Incorrect SOAP Request Format
Received server errors due to incorrect SOAP messages. Ensure the SOAP Envelope is correctly formatted according to the Web Service Description Language (WSDL).
Resource Limitations
JMeter runs out of memory or experiences high CPU usage. Run tests in Non-GUI mode to reduce resource consumption.
Handling Dynamic Data
Failing tests due to unexpected dynamic response content. Use PostProcessors like Regular Expression Extractor or JSON Extractor to capture and handle dynamic data effectively.
We are done! Congratulations on making it through this tutorial and hope you found it useful! Happy Learning!!
Additional Tutorials