In the previous tutorial, I explained Serenity BDD with Cucumber for Web Application. In this tutorial, I will explain the Integration of Serenity with JUnit4. This tutorial gives an idea of how to set up a new project where we like to use Serenity as BDD Framework and JUnit as a Testing framework.
Table of Contents
Prerequisite
- Java 17 installed
- Maven installed
- Eclipse or IntelliJ installed
Dependency List:
- Java 17
- Maven – 3.9.9
- Serenity – 4.0.30
- JUnit – 4.13.2
- Maven Surefire Plugin – 3.2.3
- Maven Failsafe Plugin – 3.2.3
- Maven Compiler Plugin – 3.12.1
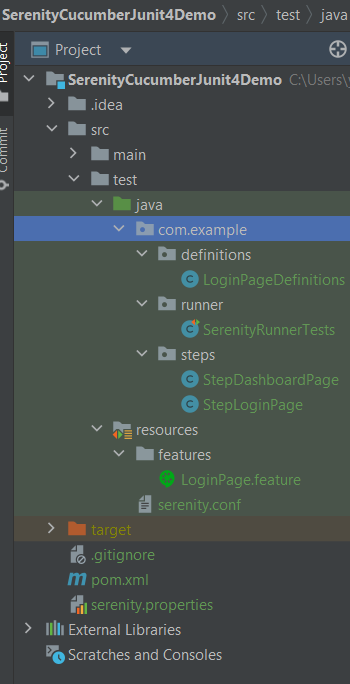
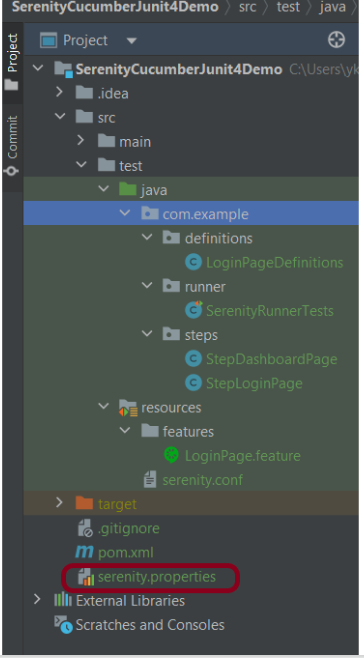
Project Structure

This project consists of various classes – ApplicationLoginTests (This is the Test Class which is going to contain all the tests). NavigationActions is the Action class that is used to open the webpage or application. StepLoginPage, StepDashboardPage, and StepForgotPasswordPage are the Page Object classes that contain multiple functionalities of that page and that help to keep the code clean.

Implementation Steps
Step 1 – Update the Properties section
Update the Properties section in Maven pom.xml, in case of Maven project.
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<serenity.version>4.0.30</serenity.version>
<junit.version>4.13.2</junit.version>
<maven.compiler.plugin.version>3.12.1</maven.compiler.plugin.version>
<maven.surefire.plugin.version>3.2.3</maven.surefire.plugin.version>
<maven.failsafe.plugin.version>3.2.3</maven.failsafe.plugin.version>
<maven.compiler.source.version>17</maven.compiler.source.version>
<maven.compiler.target.version>17</maven.compiler.target.version>
<tags></tags>
<parallel.tests></parallel.tests>
<webdriver.base.url></webdriver.base.url>
</properties>
Step 2 – Add dependencies to POM.xml
Add Serenity and JUnit4 dependencies to POM.xml.
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.serenity-bdd</groupId>
<artifactId>serenity-core</artifactId>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.serenity-bdd</groupId>
<artifactId>serenity-junit</artifactId>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.serenity-bdd</groupId>
<artifactId>serenity-screenplay</artifactId>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.serenity-bdd</groupId>
<artifactId>serenity-screenplay-webdriver</artifactId>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>${junit.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Step 3 – Update the Build Section of pom.xml
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.surefire.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<skip>true</skip>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-failsafe-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.failsafe.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<includes>
<include>**/*.java</include>
</includes>
<parallel>methods</parallel>
<useUnlimitedThreads>true</useUnlimitedThreads>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>integration-test</goal>
<goal>verify</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.compiler.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<source>${maven.compiler.source}</source>
<target>${maven.compiler.target}</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>net.serenity-bdd.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>serenity-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.serenity-bdd</groupId>
<artifactId>serenity-single-page-report</artifactId>
<version>${serenity.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<configuration>
<tags>${tags}</tags>
<reports>single-page-html</reports>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>serenity-reports</id>
<phase>post-integration-test</phase>
<goals>
<goal>aggregate</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Step 4 – Create the Test Class
The Test Class – ApplicationLoginTests is created under src/test/java directory.
package org.example.tests;
import net.serenitybdd.annotations.Pending;
import net.serenitybdd.annotations.Steps;
import net.serenitybdd.annotations.Title;
import net.serenitybdd.core.Serenity;
import net.serenitybdd.junit.runners.SerenityRunner;
import org.example.steps.StepDashBoardPage;
import org.example.steps.StepForgotPasswordPage;
import org.example.steps.StepLoginPage;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertTrue;
@RunWith(SerenityRunner.class)
public class ApplicationLoginTests {
@Steps
NavigateActions navigate;
@Steps
StepLoginPage loginPage;
@Steps
StepDashBoardPage dashboardPage;
@Steps
StepForgotPasswordPage forgetPasswordPage;
@Test
@Title("Login to application with invalid credential generates error message")
public void invalidCredentials() {
// Given
navigate.toTheHomePage();
// When
loginPage.inputUserName("Admin");
loginPage.inputPassword("admin");
loginPage.clickLogin();
// Then
Serenity.reportThat("Passing invalid credentials generates error message",
() -> assertTrue(loginPage.errorMessage().equalsIgnoreCase("Invalid Credentials")));
}
@Test
@Title("Login to application with valid credentials navigates to DashBoard page")
public void successfulLogin() {
navigate.toTheHomePage();
// loginPage.open();
// When
loginPage.inputUserName("Admin");
loginPage.inputPassword("admin123");
loginPage.clickLogin();
// Then
Serenity.reportThat("Passing valid credentials navigates to DashBoard page",
() -> assertTrue(dashboardPage.getHeading().equalsIgnoreCase("DashBoard")));
}
@Test
@Pending
@Title("Verify Forgot your password link")
public void clickForgetPasswordLink() {
// Given
navigate.toTheHomePage();
// When
loginPage.clickForgetPasswordLink();
// Then
Serenity.reportThat("Open Forget Password Page after clicking forget password link",
() -> assertTrue(forgetPasswordPage.getHeadingForgetPasswordPage().equalsIgnoreCase("Reset Password")));
}
}
- The tests run using the Serenity test runner – @RunWith(SerenityRunner.class).
- The @Steps annotation marks a Serenity step library.
- Create the test following the Given/When/Then pattern and using step methods from the step library.
- The @Title annotation lets you provide your own title for this test in the test reports.
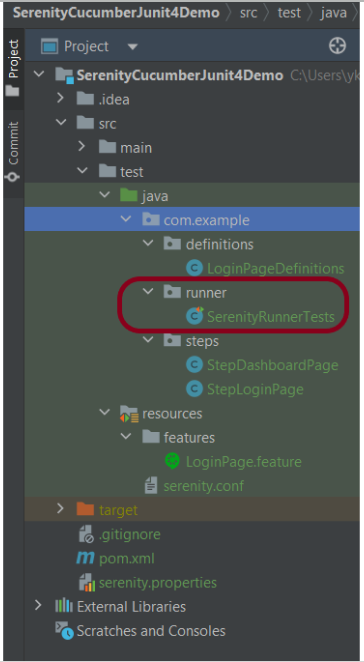
Step 5 – Create the Action class
Create NavigateActions class under src/test/java. This class is used to open a web browser with the URL specified. This class is extended from UIInteractionSteps.
openPageNamed() method opens an environment-specific page defined in the serenity.conf file under the pages section. The value of loginForm is derived from serenity.config:
package org.example.tests;
import net.serenitybdd.annotations.Step;
import net.serenitybdd.core.steps.UIInteractionSteps;
public class NavigateActions extends UIInteractionSteps {
@Step
public void toTheHomePage() {
// openUrl("https://opensource-demo.orangehrmlive.com/");
openPageNamed("loginForm");
}
}
serenity.conf (partial config file)
pages{
loginForm = "https://opensource-demo.orangehrmlive.com/"
}
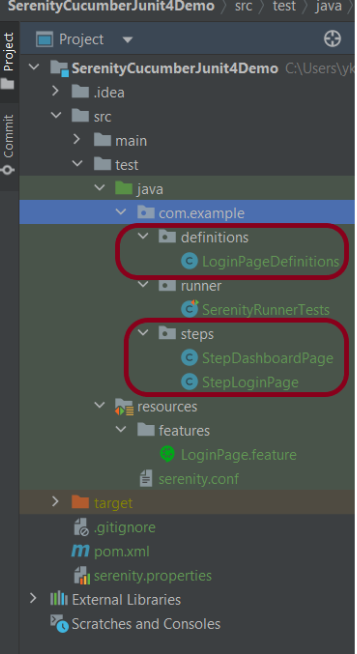
Step 6 – Create the Page Object Classes
The page object classes are created in the src/test/java directory.
StepLoginPage
package org.example.steps;
import net.serenitybdd.annotations.Step;
import net.serenitybdd.core.pages.PageObject;
import net.serenitybdd.core.pages.WebElementFacade;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.FindBy;
public class StepLoginPage extends PageObject {
@FindBy(name = "username")
WebElementFacade username;
@FindBy(name = "password")
WebElementFacade password;
@FindBy(xpath = "//*[@class='oxd-form']/div[3]/button")
WebElementFacade submitButton;
@FindBy(xpath = "//*[@class='orangehrm-login-error']/div/div/p")
WebElementFacade errorMessage;
@FindBy(xpath = "//*[@class='orangehrm-login-forgot']/p")
WebElementFacade linkText;
@Step("Enter Username")
public void inputUserName(String userName) {
username.sendKeys(userName);
}
@Step("Enter Password")
public void inputPassword(String passWord) {
password.sendKeys(passWord);
}
@Step("Click Submit Button")
public void clickLogin() {
submitButton.click();
}
@Step("Error Message on unsuccessful login")
public String errorMessage() {
String actualErrorMessage = errorMessage.getText();
return actualErrorMessage;
}
@Step("Click Forget Password Link")
public void clickForgetPasswordLink() {
linkText.click();
System.out.println("Clicked on Forgot Password Link");
}
}
StepDashBoardPage
package org.example.steps;
import net.serenitybdd.annotations.Step;
import net.serenitybdd.core.pages.PageObject;
import net.serenitybdd.core.pages.WebElementFacade;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.FindBy;
public class StepDashBoardPage extends PageObject {
@FindBy(xpath = "//*[@class='oxd-topbar-header-breadcrumb']/h6")
WebElementFacade dashboardPageTitle;
@Step("Heading of DashBoard Page")
public String getHeading() {
return dashboardPageTitle.getText();
}
}
StepForgetPasswordPage
package org.example.steps;
import net.serenitybdd.annotations.Step;
import net.serenitybdd.core.pages.PageObject;
import net.serenitybdd.core.pages.WebElementFacade;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.FindBy;
public class StepForgotPasswordPage extends PageObject {
@FindBy(xpath = "//*[@class='oxd-form']/h6")
WebElementFacade forgetLink;
@Step("Verify Forget Password Page ")
public String getHeadingForgetPasswordPage() {
return forgetLink.getText();
}
}
Keep in mind to use @FindBy annotation from:
import org.openqa.selenium.support.FindBy;
PageObject class is imported from:
import net.thucydides.core.pages.PageObject;
The JUnit Serenity integration provides some special support for Serenity Page Objects. In particular, Serenity will automatically instantiate any PageObject fields in the JUnit test. When a field of type StepLoginPage is declared in the test, Serenity instantiates it for you. The page is automatically instantiated and ready to be used.
@Managed
WebDriver driver;
@Managed declares a WebDriver instance that will be managed by Serenity. The WebDriver instance will be initialized automatically.
The driver parameter lets you define what WebDriver driver you want to run these tests in. Possible values include Firefox, chrome, iexplorer, phantomjs, appium, safari, edge, and htmlunit. The default browser in Serenity is Firefox. There are multiple ways to configure webDriver. One of the ways is to mention with @Managed as shown below:
@Managed(driver="chrome")
Step 7 – Create the serenity.conf file
Serenity.conf file is used to specify various features like the type of webdriver used, various test environments, run test in headless mode, and many more options. Serenity.conf can also contain settings like start size, disable sandbox, disable gpu, and others that need to be added to chrome.switches setting. Create serenity.conf file under src/test/resources.
headless.mode = false
pages{
loginForm ="https://opensource-demo.orangehrmlive.com/"
}
webdriver {
driver = chrome
capabilities {
browserName = "chrome"
acceptInsecureCerts = true
"goog:chromeOptions" {
args = ["remote-allow-origins=*","test-type", "no-sandbox", "ignore-certificate-errors", "--window-size=1920,1080",
"incognito", "disable-infobars", "disable-gpu", "disable-default-apps", "disable-popup-blocking",
"disable-dev-shm-usage", "disable-extensions", "disable-web-security", "disable-translate", "disable-logging"]
}
}
}
Step 8 – Create a serenity.properties file
The serenity.properties file is created at the root of the project.
serenity.project.name = Serenity and Junit4 Demo
Step 9 – Run the tests through the command
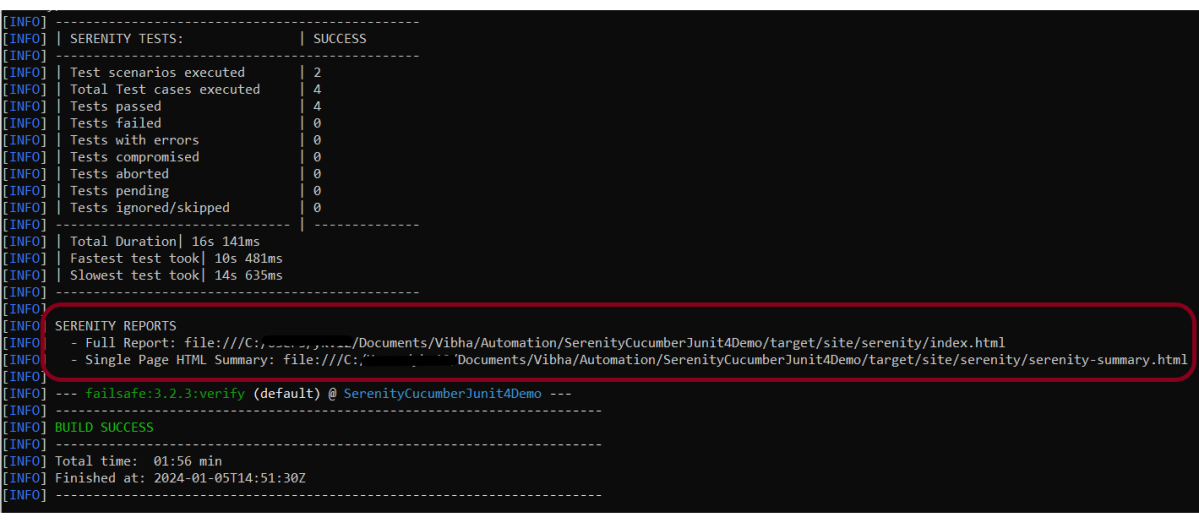
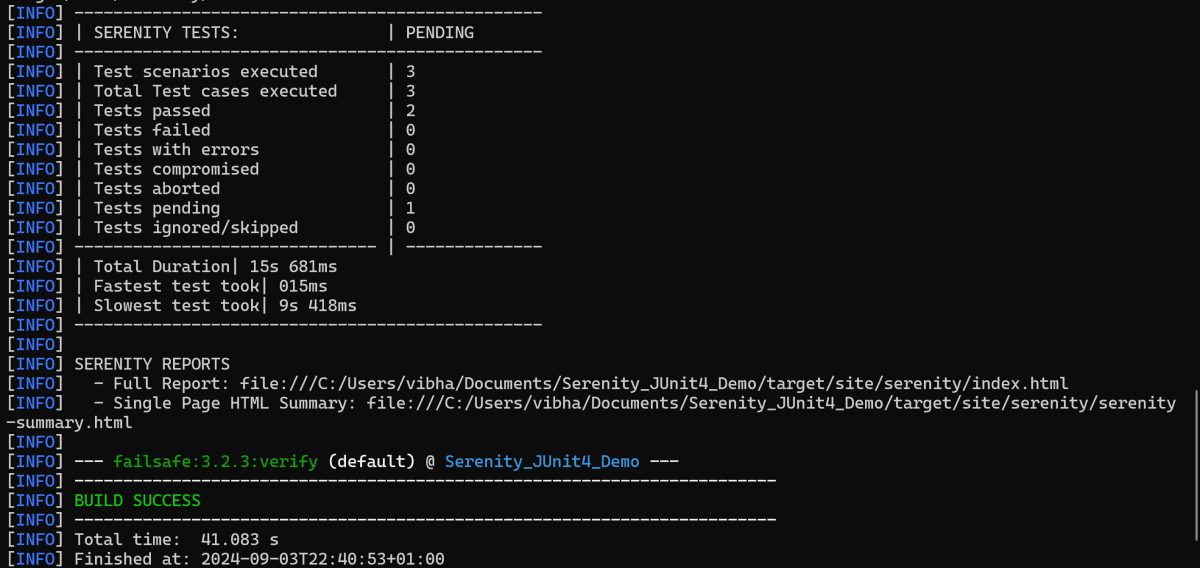
Open the command line and go to the location where the pom.xml of the project is present and type the below command.
mvn clean verify
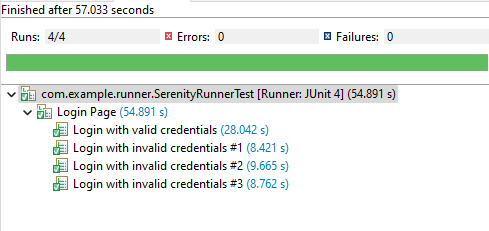
Below is the execution status.
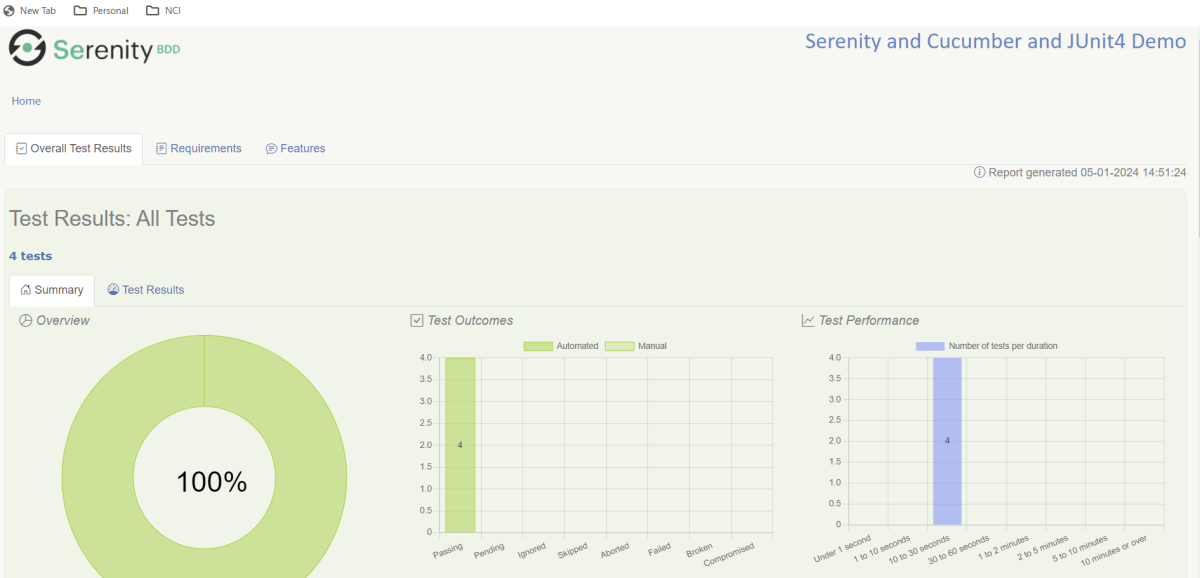
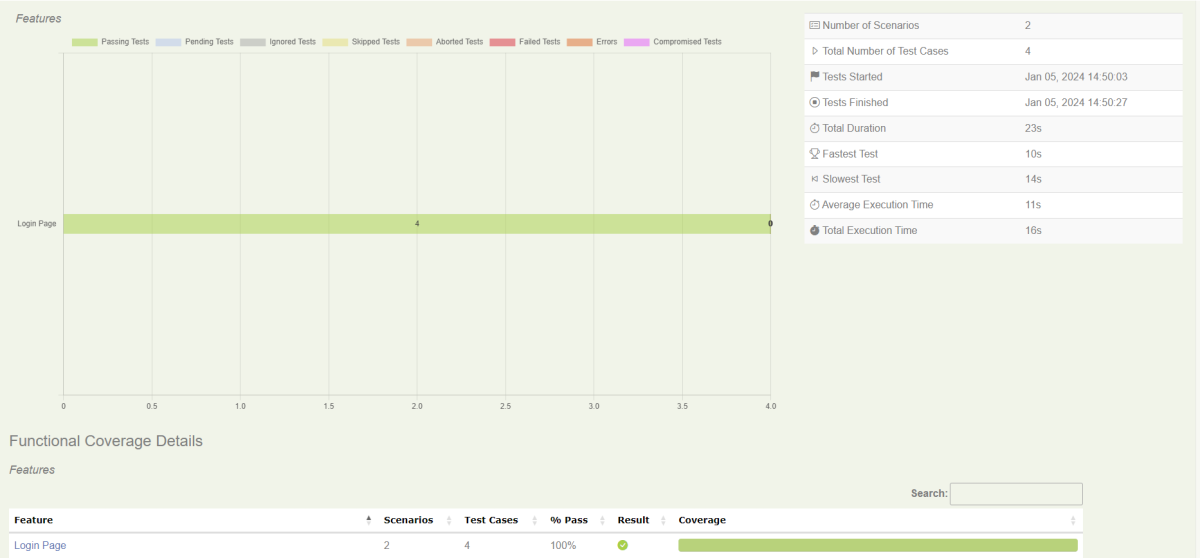
Step 10 – View the Serenity Reports
There are 2 types of reports are generated – Index.html and Serenity-Summary.html.
Index.html

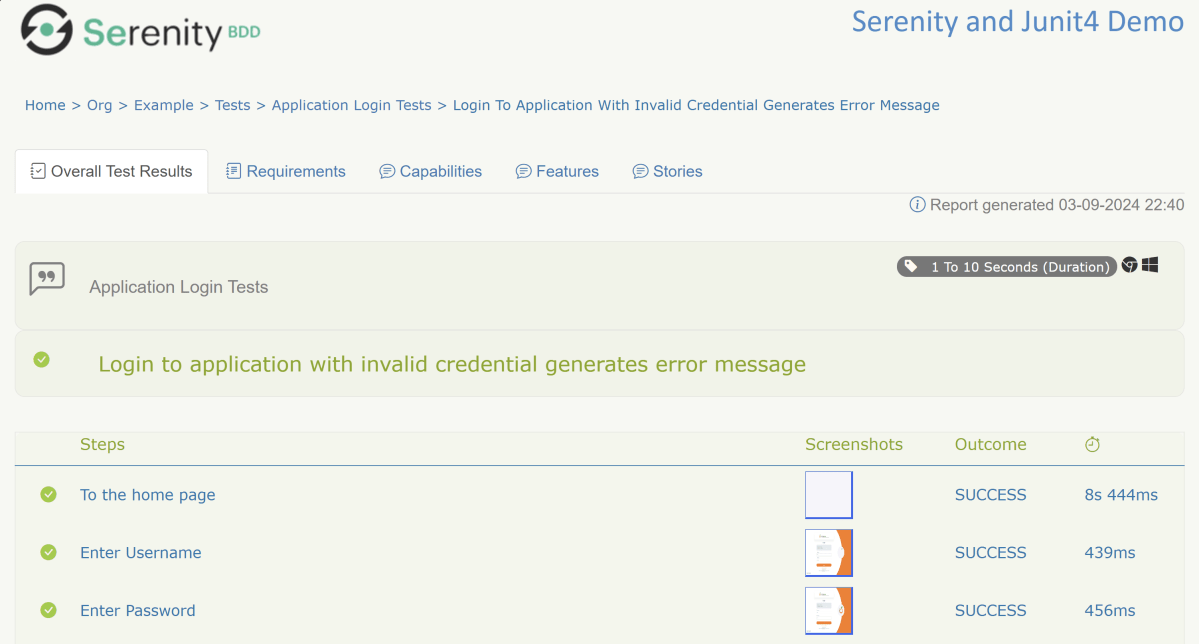
We can see the value of the @Title annotation, ‘Login to the application with valid credentials navigates to DashBoard page’, added as the heading. The value of @Step annotation, ‘Enter Username’, and ‘Enter Password’ is added to the Report as various steps.
This report contains a screenshot of each step also.
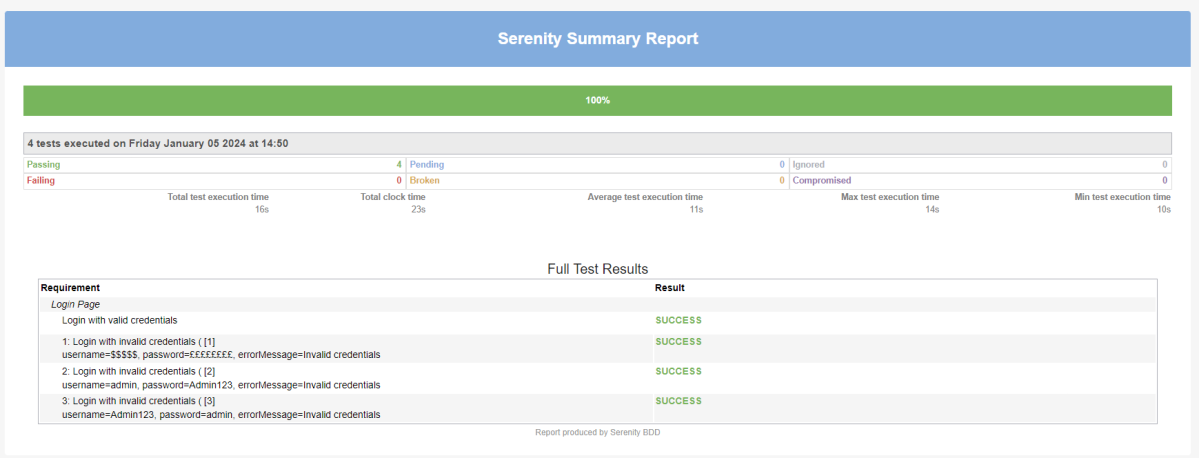
Emailable Report (Serenity-Summary.html)
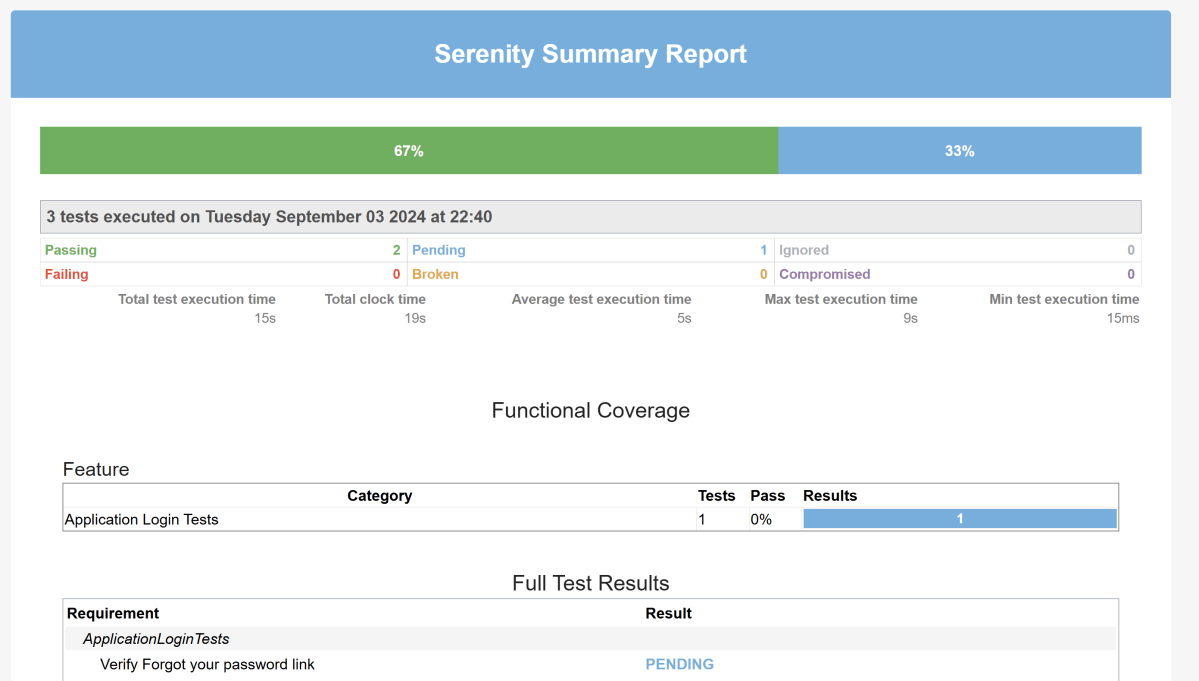
These reports are present under /target/site/serenity.
Skipping the tests
In Serenity, you use the @Pending annotation, either for a test or for a @Step-annotated method, to indicate that the scenario is still being implemented and that the results are not available yet. These tests appear as ‘Pending’ (shown in blue) in the test reports.
@Test
@Pending
@Title("Verify Forgot your password link")
public void clickForgetPasswordLink() {
// Given
loginPage.open();
// When
loginPage.clickForgetPasswordLink();
// Then
Assert.assertTrue(forgetpasswordPage.ForgetPasswordPage());
}
The output of the above program is
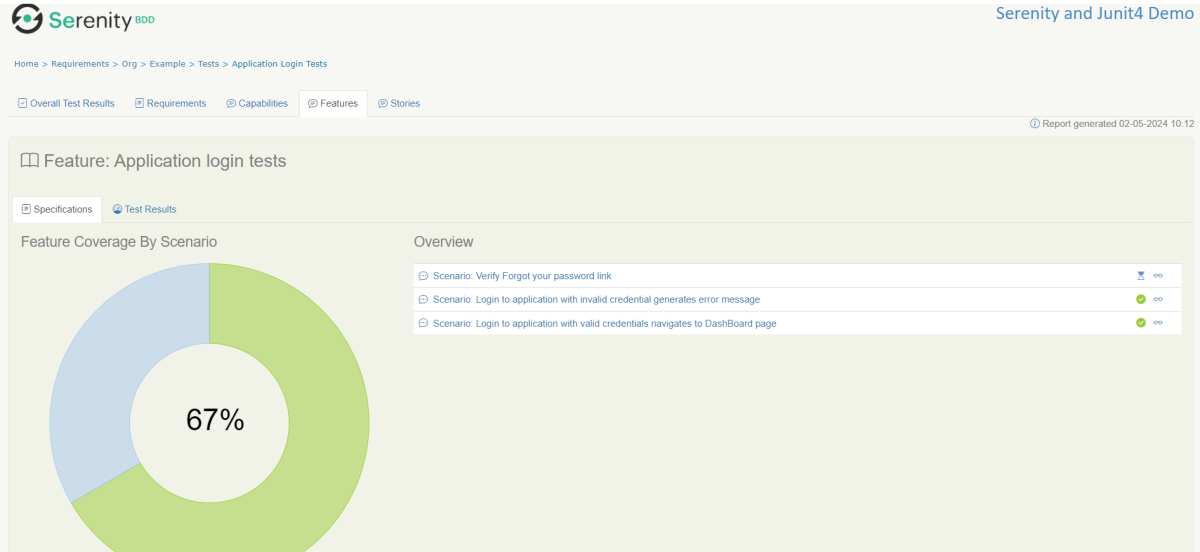

Tests marked with @Ignore will appear as ‘Ignored’ (from JUnit) and appears as grey in the test reports.
We are done! Congratulations on making it through this tutorial and hope you found it useful! Happy Learning!!
Please find the complete code here – https://github.com/vibssingh/Serenity_JUnit4_Demo.