In Python, the requests library is commonly employed for retrieving content from a specific resource URI. When a request is made to a designated URI using Python, it yields a response object. This response object is then utilized to access various attributes, including content and headers. This article focuses on demonstrating how to examine the response.elapsed attribute within a response object.
Prerequisite:
- Python is installed on the machine
- PIP is installed on the machine
- PyCharm or other Python Editor is installed on the machine
If you need help in installing Python, please refer to this tutorial – How to Install Python on Windows 11.
If you need help in installing PyCharms, please refer to this tutorial – How to install PyCharms on Windows 11.
In Python, response.elapsed is an attribute of the Response object from the requests library, which is commonly used for making HTTP requests. The elapsed attribute represents the time elapsed between sending the request and receiving the response.
Below is the example of response.elapsed.
import requests
endpoint = 'https://reqres.in/api/users'
def test_response():
payload = {
"name": "Vibha",
"Job": "CEO"
}
response = requests.post(endpoint, payload)
response_body = response.json()
print("Response :", response_body)
assert response.status_code == 201
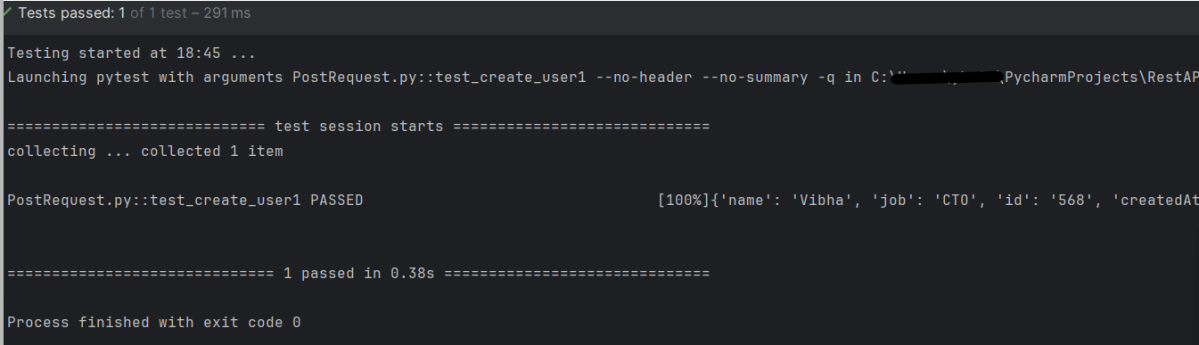
print("Elapsed Time :", response.elapsed.total_seconds())
Save above file as ResponseTime_test.py and run using the below command:
pytest ResponseTime_test.py -s
Note: -s is shortcut for –capture=no
The output of the above program is

We are done! Congratulations on making it through this tutorial and hope you found it useful! Happy Learning!