What is Apache JMeter?
The Apache JMeter™ application is open-source software, a 100% pure Java application designed to load test functional behaviour and measure performance. JMeter is mainly used for testing Web applications or FTP applications but currently, it is applicable in functional testing, JDBC database connections, Web services, generic TCP connections, and OS native processes. You can perform various testing activities like Performance, Load, Stress, Regression, and Functional testing, in order to get accurate performance metrics against your web server.
JMeter is not a browser, it works at the protocol level. As far as web services and remote services are concerned, JMeter looks like a browser (or rather, multiple browsers); however, JMeter does not perform all the actions supported by browsers. In particular, JMeter does not execute the JavaScript found in HTML pages. Nor does it render the HTML pages as a browser does (it’s possible to view the response as HTML etc., but the timings are not included in any samples, and only one sample in one thread is ever displayed at a time). More detail about JMeter can be found here.
Apache JMeter features include:
- Open Source – JMeter is a 100% pure Java desktop application
- Platform independent -JMeter is written and developed using Java, so it can run on any environment/workstation that accepts a Java virtual machine, for example – Windows, Linux, Mac, etc.
- Supports cross platform –JMeter has unlimited testing capabilities allowing you to work both with local and server-based instances. The only thing you need to get started is Java (JRE) installed on the host.
- Simulation – JMeter can simulate multiple users by using virtual users or unique users in order to generate a heavy load against the web application under test.
- Supports Concurrency – Full multi-threading framework allows concurrent sampling by many threads and simultaneous sampling of different functions by separate thread groups.
- Easy to Use – On Linux/Unix, JMeter can be invoked by clicking on JMeter shell script. On Windows, it can be invoked by starting the jmeter.bat file.
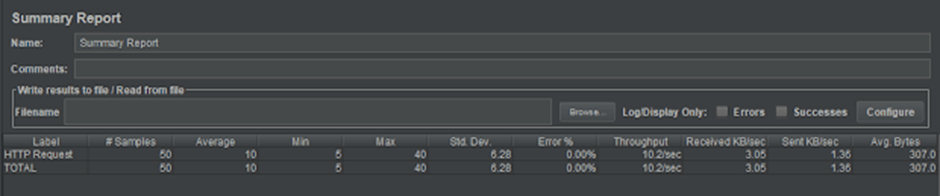
- Test Result Visualization – JMeter has a set of tools for collecting and displaying results, like table, graph, tree, and reports. The results can be saved in CSV, XML, HTML etc.
- Support various server types – JMeter is highly extensible and capable to load the performance test in different server types: HTTP, HTTPS, SOAP, JDBC, LDAP, JMS, POP3
- Works great even without UI – Test cases are executable in the command line which allows for their full integration into CI tools’ cases.
JMeter Workflow
JMeter sends requests to a target server by simulating a group of users. Server process the requests. Subsequently, data is collected to calculate statistics and display performance metrics of the target server through various formats.

Congratulations on making it through this tutorial and hope you found it useful! Happy Learning!! Cheers!!
Additional Tutorials