An XML file contains data between the tags. This makes it complex to read compared to other file formats like docx and txt. There are two types of parsers which parse an XML file:
In this article, we will discuss how to parse XML using Java DOM parser.
Table of Contents
What is Java DOM Parser?
DOM stands for Document Object Model. The DOM API provides the classes to read and write an XML file. DOM reads an entire document. It is useful when reading small to medium size XML files. It is a tree-based parser. It is a little slow when compared to SAX. It occupies more space when loaded into memory. We can insert and delete nodes using the DOM API.
How to retrieve tag name from XML?
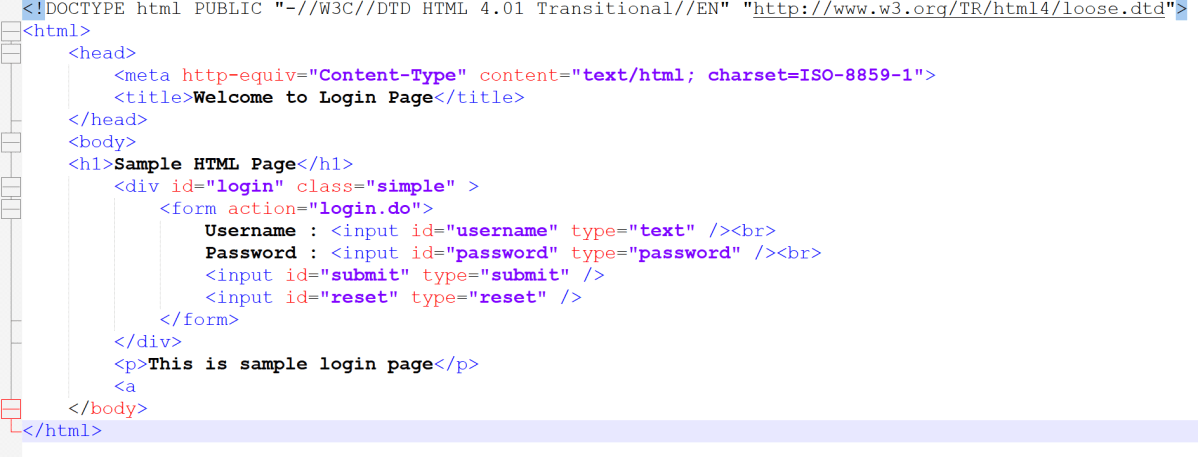
Below is the sample JSON which is used as an example . I have saved this file in resources/Payloads as SimpleXML.xml.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<employees>
<employee id="1">
<name>John William</name>
<position>Software Engineer</position>
</employee>
<employee id="2">
<name>Jane Smith</name>
<position>Project Manager</position>
</employee>
<employee id="3">
<name>Lilly Smith</name>
<position>Product Owner</position>
</employee>
</employees>
The complete program looks like as shown below:
package XML.DOM;
import org.w3c.dom.Document;
import org.w3c.dom.Element;
import org.w3c.dom.NodeList;
import org.xml.sax.SAXException;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;
import javax.xml.parsers.ParserConfigurationException;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class XMLParserTagNameExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// Create a DocumentBuilderFactory
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
// Obtain a DocumentBuilder from the factory
DocumentBuilder builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder();
// Parse the XML file into a Document
Document document = builder.parse(new File("src/test/resources/Payloads/SimpleXML.xml"));
// Normalize XML structure
document.getDocumentElement().normalize();
// Get the root element
Element root = document.getDocumentElement();
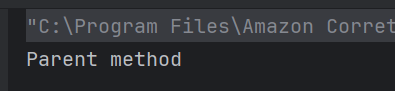
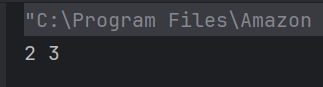
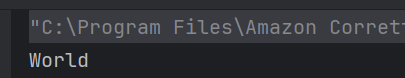
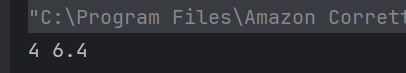
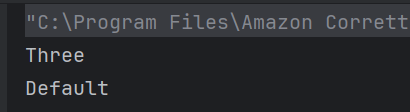
System.out.println("Root Element: " + root.getNodeName());
System.out.println("-----------------------");
// Retrieve the first employee element for extracting tag names
NodeList nodeList = document.getElementsByTagName("employee");
if (nodeList.getLength() > 0) {
// If there is at least one employee, use it to print the element and attribute names
Element employee = (Element) nodeList.item(0);
// Print the tag names
System.out.println("Employee ID Attribute Name: id");
System.out.println("Name Tag: " + employee.getElementsByTagName("name").item(0).getNodeName());
System.out.println("Position Tag: " + employee.getElementsByTagName("position").item(0).getNodeName());
System.out.println("-----------------------");
}
} catch (ParserConfigurationException e) {
System.out.println("Parser configuration error occurred: " + e.getMessage());
} catch (SAXException e) {
System.out.println("SAX parsing error occurred: " + e.getMessage());
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("IO error when loading XML file: " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
System.out.println("XML parsing operation completed.");
}
}
}
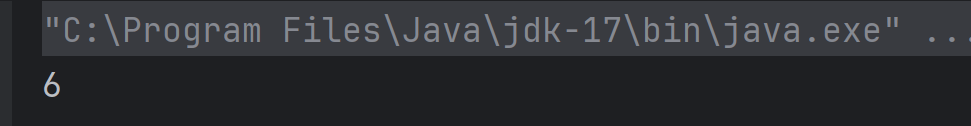
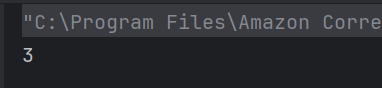
The output of the above program is
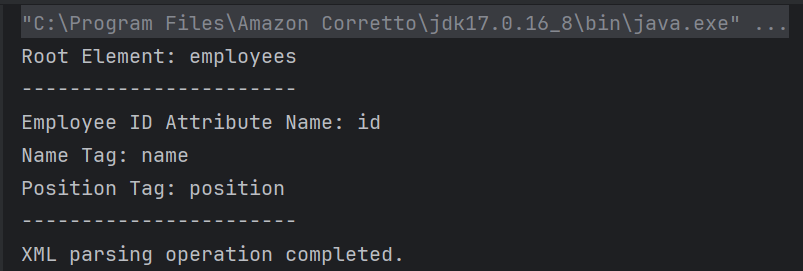
Explanation
1. Creating a DocumentBuilder Object
It has ‘newDocumentBuilder()’ method that creates an instance of the class ‘DocumentBuilder’. This DocumentBuilder class is used to get input in the form of streams, files, URLs and SAX InputSources.
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
DocumentBuilder builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder();
2. Parse the XML file into a Document
DocumentBuilder created in above steps is used to parse the input XML file. It contains a method named parse() which accepts a file or input stream as a parameter and returns a DOM Document object. If the given file or input stream is NULL, this method throws an IllegalArgumentException.
Document document = builder.parse(new File("src/test/resources/Payloads/SimpleXML.xml"));
3. Normalize XML structure
The `normalize` method is called on the document’s root element. This step ensures that the XML structure is uniform, often by merging adjacent text nodes and removing empty ones.
document.getDocumentElement().normalize();
4. Get root node
We can use getDocumentElement() to get the root node and the element of the XML file.
Element root = document.getDocumentElement();
System.out.println("Root Element: " + root.getNodeName());
System.out.println("-----------------------");
5. Retrieving Root Element Name
A `NodeList` containing all elements with the tag name `employee` is obtained using `getElementsByTagName`. This list can be used to iterate over all employee entries in the XML.
NodeList nodeList = document.getElementsByTagName("employee");
if (nodeList.getLength() > 0) {
// If there is at least one employee, use it to print the element and attribute names
Element employee = (Element) nodeList.item(0);
// Print the tag names
System.out.println("Employee ID Attribute Name: id");
System.out.println("Name Tag: " + employee.getElementsByTagName("name").item(0).getNodeName());
System.out.println("Position Tag: " + employee.getElementsByTagName("position").item(0).getNodeName());
System.out.println("-----------------------");
}
}
getTagName() returns the name of the root element in the form of a string. Retrieve the first employee element for extracting tag names and print the tag names.
getNodeName() is used to get the name of the node. It returns the node name in the form of a string.
6. Implement Exception Handling
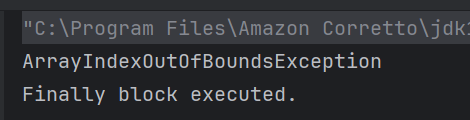
The program catches `ParserConfigurationException`, `SAXException`, and `IOException`, addressing specific issues that might occur during parsing. Each exception type is followed by a custom message that explains the nature of the error. At the end, a message is printed to confirm the completion of the XML parsing operation by using finally block.
catch (ParserConfigurationException e) {
System.out.println("Parser configuration error occurred: " + e.getMessage());
} catch (SAXException e) {
System.out.println("SAX parsing error occurred: " + e.getMessage());
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("IO error when loading XML file: " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
System.out.println("XML parsing operation completed.");
}
Parsing Attributes in XML
Below is the program that parses the attributes in the XML.
package XML.DOM;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;
import javax.xml.parsers.ParserConfigurationException;
import org.w3c.dom.Document;
import org.w3c.dom.Element;
import org.w3c.dom.Node;
import org.w3c.dom.NodeList;
import org.xml.sax.SAXException;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class SimpleXMLParserExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// Create a DocumentBuilderFactory
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
// Obtain a DocumentBuilder from the factory
DocumentBuilder builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder();
// Parse the XML file into a Document
Document document = builder.parse(new File("src/test/resources/Payloads/SimpleXML.xml"));
// Normalize XML structure
document.getDocumentElement().normalize();
// Get the root element
Element root = document.getDocumentElement();
System.out.println("Root Element: " + root.getNodeName());
System.out.println("-----------------------");
// Retrieve all employee nodes
NodeList nodeList = document.getElementsByTagName("employee");
// Iterate over the employee nodes
for (int i = 0; i < nodeList.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nodeList.item(i);
if (node.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) {
Element employee = (Element) node;
// Get the attribute and text content
String id = employee.getAttribute("id");
String name = employee.getElementsByTagName("name").item(0).getTextContent();
String position = employee.getElementsByTagName("position").item(0).getTextContent();
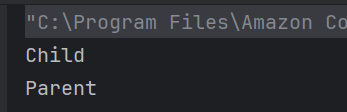
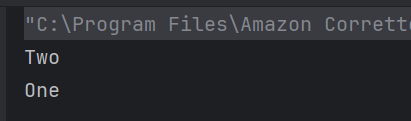
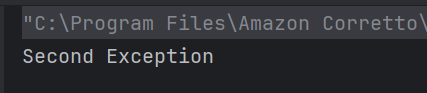
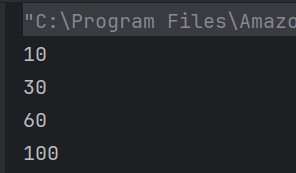
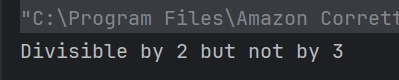
System.out.println("Employee ID: " + id);
System.out.println("Name: " + name);
System.out.println("Position: " + position);
System.out.println("-----------------------");
}
}
} catch (ParserConfigurationException e) {
System.out.println("Parser configuration error occurred: " + e.getMessage());
} catch (SAXException e) {
System.out.println("SAX parsing error occurred: " + e.getMessage());
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("IO error when loading XML file: " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
System.out.println("XML parsing operation completed.");
}
}
}
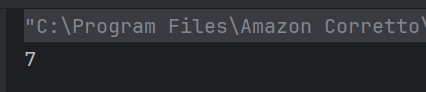
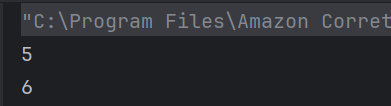
The output of the above program is
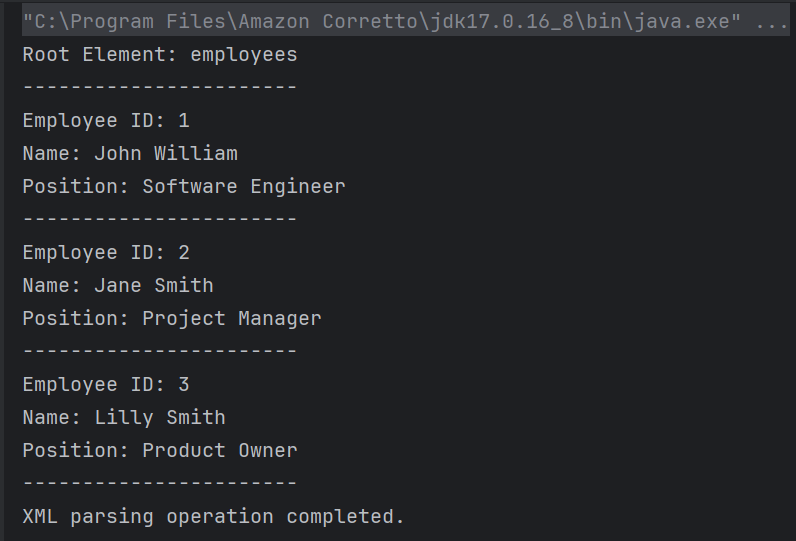
Explanation
1. Step 1, 2, 3 and 4 are same as the above program
5. Retrieve all employee nodes
The method `getElementsByTagName(“employee”)` returns a `NodeList` containing all elements in the document with the tag name “employee”.
NodeList nodeList = document.getElementsByTagName("employee");
6. Iterate Over Employee Nodes
The program loops through each node in the `NodeList`. Each node is checked if it is an `ELEMENT_NODE`. For each valid employee element, it extracts:
– Attribute: The `id` attribute value using `getAttribute(“id”)`.
– Text Content: The contents of child elements “name” and “position” using `getElementsByTagName(“name”).item(0).getTextContent()` and similarly for “position”.
for (int i = 0; i < nodeList.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nodeList.item(i);
if (node.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) {
Element employee = (Element) node;
// Get the attribute and text content
String id = employee.getAttribute("id");
String name = employee.getElementsByTagName("name").item(0).getTextContent();
String position = employee.getElementsByTagName("position").item(0).getTextContent();
System.out.println("Employee ID: " + id);
System.out.println("Name: " + name);
System.out.println("Position: " + position);
System.out.println("-----------------------");
}
}
}
getTextContent() is used to get the text content of elements.
7. Implement Exception Handling
This is same as the step 6 of the above program.
We are done! Congratulations on making it through this tutorial and hope you found it useful! Happy Learning!!