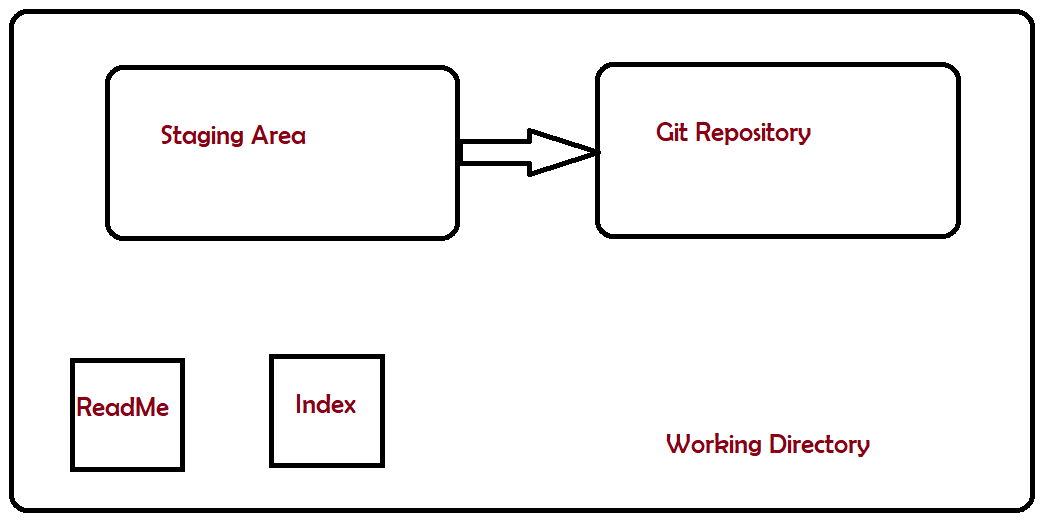
The previous example has explained the staging of new files to the staging area.
What is git rm?
This command removes the file from the staging area. The files from the working directory will remain intact. This means that you’ll still have a copy of the file locally. The file will be removed from the index tracking of Git project.
Let us explain this with the help of an example.
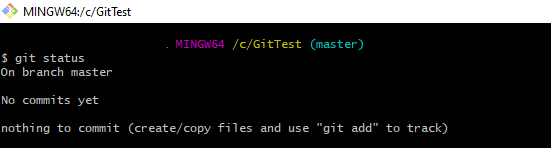
- Create an empty Git Repository – GitTest
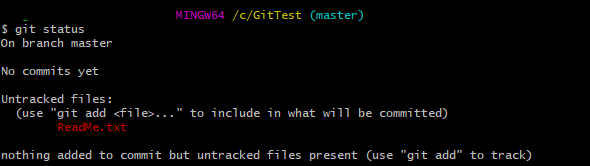
- Create a new file – ReadMe.txt and add the file to staging area.
- Create another file – Index.html
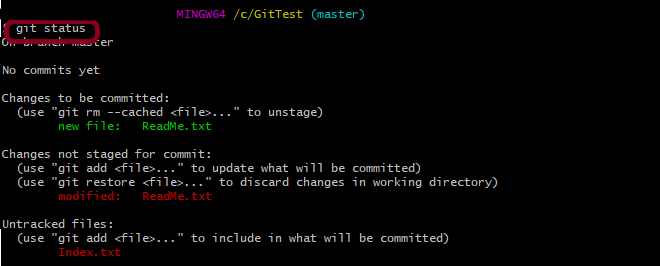
- Update the first file – ReadMe.txt which is already staged.
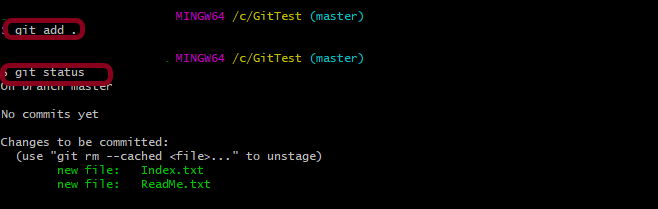
- Use “git add .” to stage both the files.

Later, we realized that we don’t want to commit both the files. We try to commit the logically same files, like files created or changed to fix a particular bug. So, if in the future we want to track back the changes, it is easy to figure out which all files are changed or impacted.
We want to unstage the “Index.txt” file.
Use the below command to reset the changes from the staging area to the working directory.
git rm --cached Index.txt
The “cached” option specifies that the removal should happen only on the staging index.

I have used “git status” command and it shows that “ReadMe.txt” can either be unstage or commit. Whereas “Index.txt” is unstage. So, if we want to commit “Index.txt“, first we need to stage this file using “git add“ command.
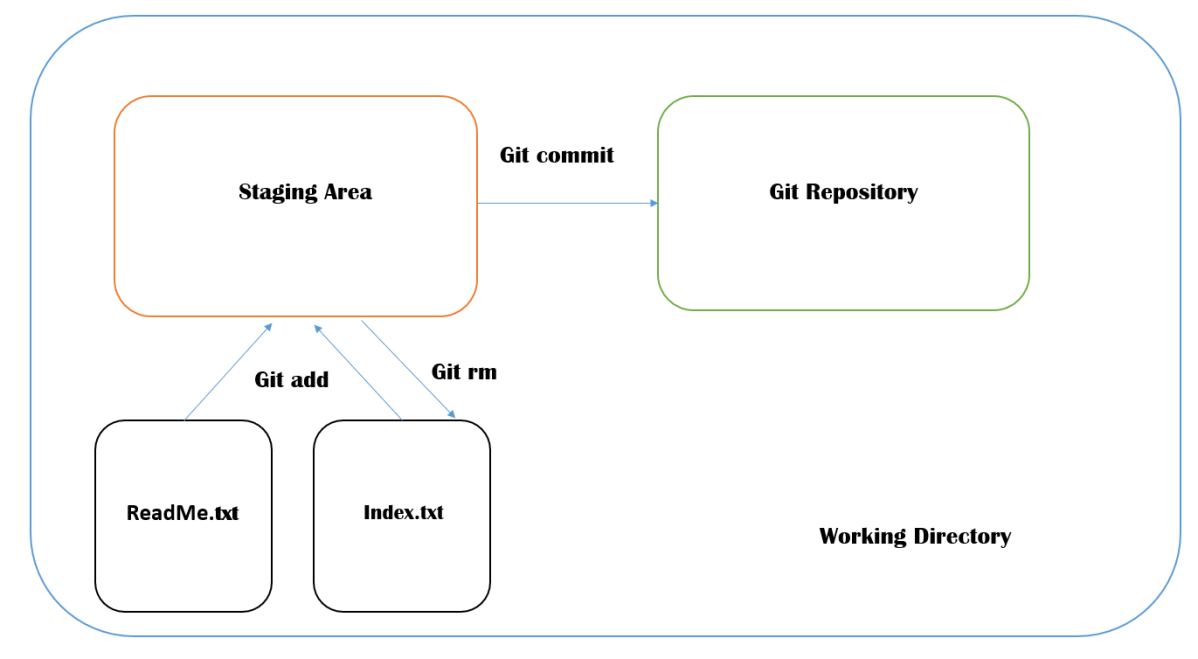
This image shows that git rm moves the staged file from Staging Area to back to working Directory.
I hope this tutorial has helped you to understand git rm command.