Last Updated On
Welcome to the Java Quiz! This blog post features 25 multiple-choice questions that explore the concepts of Strings in Java.
1. What is the primary characteristic of strings in Java?
a) Mutable
b) Immutable
c) Dynamic
d) External
Answer 1
b) Immutable
Strings in Java are immutable, meaning their values cannot be changed once created.
2. What is the correct way to declare a String in Java?
a) String str = ‘Hello’;
b) String str = new String(“Hello”);
c) String str = String(“Hello”);
d) String str = Hello;
Answer 2
b) String str = new String(“Hello”);
Strings in Java are declared using String str = new String(“Hello”); or simply String str = “Hello”;.
3. What is the default value of an element in an int array in Java?
Choose one option
a) 1
b) 0
c) null
d) Undefined
Answer 3
b) 0
In Java, arrays of primitive types like int are initialized to their default values. The default value for int is 0
4. What will be the output of the following Java program?
class Test
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int array_variable [] = new int[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
{
array_variable[i] = i;
System.out.print(array_variable[i] + " ");
i++;
}
}
}
Choose one option
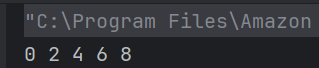
a) 0 2 4 6 8
b) 1 3 5 7 9
c) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
d) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Answer 4
a) 0 2 4 6 8
When an array is declared using new operator then all of its elements are initialized to 0 automatically. for loop body is executed 5 times as whenever controls comes in the loop i value is incremented twice, first by i++ in body of loop then by ++i in increment condition of for loop.
5. Why are Strings immutable in Java?
a) To improve performance
b) To allow modifications in-place
c) To ensure thread safety and security
d) Because Java does not support mutable objects
Answer 5
c) To ensure thread safety and security
String immutability ensures that once created, a String cannot be modified, making it thread-safe and secure.
6. What will be the output of the following Java program?
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String obj = "I" + "like" + "Java";
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
Choose one option
a) I
b) like
c) Java
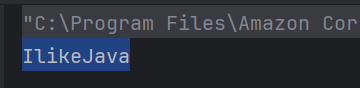
d) IlikeJava
Answer 6
d) IlikeJava
Java defines an operator +, it is used to concatenate strings.
7. What will be the output of the following Java program?
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String obj = "I LIKE JAVA";
System.out.println(obj.charAt(3));
}
}
Choose one option
a) I
b) L
c) K
d) E
Answer 7
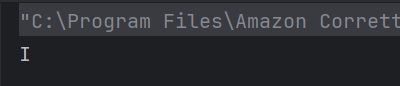
a) I
charAt() is a method of class String which gives the character specified by the index. obj.charAt(3) gives 4th character
8. What will be the output of the following Java program?
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String obj = "I LIKE JAVA";
System.out.println(obj.length());
}
}
Choose one option
a) 9
b) 10
c) 11
d) 12
Answer 8
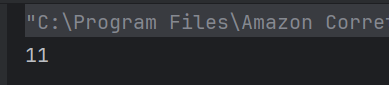
c) 11
The string “I LIKE JAVA” contains 11 characters, including the spaces. The length() method returns the total number of characters in the string. So, the output is 11.
9. What will be the output of the following Java program?
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String obj = "hello";
String obj1 = "world";
String obj2 = obj;
obj2 = " world";
System.out.println(obj + " " + obj2);
}
}
a) hello hello
b) world world
c) hello world
d) world hello
Answer 9
c) hello world
This is the standard way of declaring an array of strings in Java.
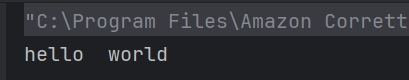
10. Which of the following is a valid declaration and initialization of String array in Java
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String obj = "hello";
String obj1 = "world";
String obj2 = "hello";
System.out.println(obj.equals(obj1) + " " + obj.equals(obj2));
}
}
a) false false
b) true true
b) true false
d) false true
Answer 10
d) false true
equals() is method of class String, it is used to check equality of two String objects, if they are equal, true is retuned else false.
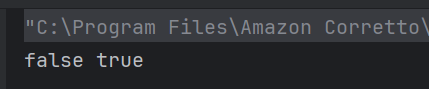
11. What will be the output?
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("Hello World".indexOf('W'));
}
}
Choose one option
a) 0
b) 5
c) 6
d) -1
Answer 11
c) 6
The indexOf() method returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified character.
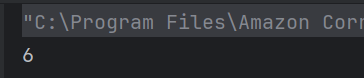
12. How do you compare two strings in Java?
Choose one option
a) ==
b) equals()
c) compareTo()
d) Both b) and c)
Answer 12
d) Both b) and c)
Use equals() for value comparison and compareTo() for lexicographical order.
13. Which of the following will return a substring from a string?
Choose one option
a) str.sub()
b) str.substring()
c) str.slice()
d) str.split()
Answer 13
b) str.substring()
The substring() method extracts a substring from the string.
14. What is printed by the following code snippet?
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("Java".compareTo("Java"));
}
}
Choose one option
a) 0
b) 1
c) -1
d) Compilation error
Answer 14
a) 0
The compareTo() method returns 0 if the two strings are equal.
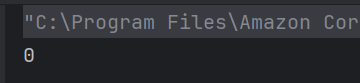
15. What will be the result of this expression?
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("abc".substring(1, 3));
}
}
Choose one option
a) ab
b) abc
c) bc
d) a
Answer 15
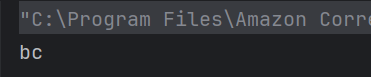
c) bc
The substring(start, end) method returns the substring from start index to end-1.
16. How can you check if a string is empty?
Choose one option
a) str.isEmpty()
b) str.length() == 0
c) Both a) and b)
d) str.equals(“”)
Answer 16
c) Both a) and b)
Both methods can be used to check if a string is empty.
17. What does the StringBuilder class do?
Choose one option
a) It creates immutable strings.
b) It creates mutable strings.
c) It converts strings to numbers.
d) It is not a class in Java.
Answer 17
b) It creates mutable strings.
StringBuilder allows for the creation of mutable strings, which can be modified.
18. Which method would you use to split a string into an array based on a delimiter?
a) split()
b) divide()
c) slice()
d) substring()
Answer 18
a) split()
The split() method splits a string into an array based on a specified delimiter.
19. Which of the following will convert a string to a number?
a) parseInt()
b) valueOf()
c) toNumber()
d) Both a) and b)
Answer 19
d) Both a) and b)
Both parseInt() and valueOf() can convert a string to a number.
20. What is the output of the following code?
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("abc".repeat(3));
}
}
Choose one option
a) abcabcabc
b) abc abc abc
c) abcabc abc
d) Compilation Error
Answer 20
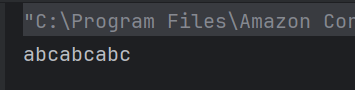
a) abcabcabc
The repeat(int) method returns a string whose value is the concatenation of the specified string repeated the given number of times.
21. What is the output of the following code?
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("Hello".replace('e', 'a'));
}
}
Choose one option
a) Hallo
b) Hello
c) Halla
d) Hella
Answer 21
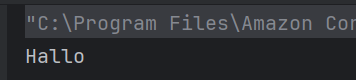
a) Hallo
The replace() method replaces the specified character with another character.
22. What will be the output of the following program
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String s1 = new String("Hello");
String s2 = new String("Hello");
System.out.println(s1 == s2);
}
}
Choose one option
a) true
b) false
c) Compilation error
d) Runtime error
Answer 22
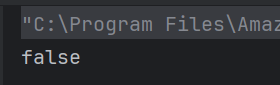
b) false
The == operator compares object references, not values. Since s1 and s2 are two different objects, it returns false.
23. Which of these methods can be used to check if two strings are equal, ignoring case considerations?
Choose one option
a) equals()
b) equalsIgnoreCase()
c) compareTo()
d) compareIgnoreCase()
Answer 23
b) equalsIgnoreCase()
The equalsIgnoreCase() method compares two strings, ignoring case differences.
24. What will be the result if you try to modify an existing string?
a) The string will be changed
b) A new string will be created
c) An exception will be thrown
d) Compilation error
Answer 24
b) A new string will be created
Strings in Java are immutable, so any modification creates a new string.
25. Which method checks if a string starts with a specified prefix?
a) beginsWith()
b) start()
c) startsWith()
d) prefix()
Answer 25
c) startsWith()
The startsWith() method checks if the string begins with the specified prefix.
We would love to hear from you! Please leave your comments and share your scores in the section below