Last Updated On
Welcome to the Java Quiz! This blog post features 25 multiple-choice questions that explore basic concepts of Java.
1. Which statement is true about Java?
a) Java is a sequence-dependent programming language
b) Java is a code dependent programming language
c) Java is a platform-dependent programming language
d) Java is a platform-independent programming language
Answer 1
d) Java is a platform-independent programming language
2. Which component is used to compile, debug and execute the java programs?
a) JRE
b) JIT
c) JDK
d) JVM
Answer 2
c) JDK
JDK is a core component of Java Environment and provides all the tools, executables and binaries required to compile, debug and execute a Java Program.
3. What will be the output of the following Java code?
class increment {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int g = 3;
System.out.print(++g * 8);
}
}
Choose one option
a) 32
b) 33
c) 24
d) 25
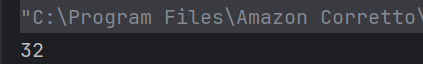
Answer 3
a) 32
Operator ++ has more preference than *, thus g becomes 4 and when multiplied by 8 gives 32.
4. What will be the output of the following Java program?
class variable_scope
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int x;
x = 5;
{
int y = 6;
System.out.print(x + " " + y);
}
System.out.println(x + " " + y);
}
}
Choose one option
a) Compilation error
b) Runtime error
c) 5 6 5 6
d) 5 6 5
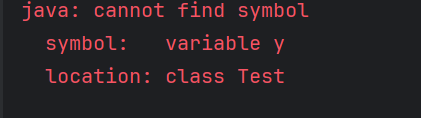
Answer 4
a) Compilation error
Second print statement doesn’t have access to y , scope y was limited to the block defined after initialization of x.
5. How do you insert COMMENTS in Java code?
a) /* This is a comment
b) # This is a comment
c) // This is a comment
d) None
Answer 5
c) // This is a comment
6. What will be the output of the following Java program?
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 5;
System.out.println(x++);
}
}
Choose one option
a) 5
b) 6
c) Compilation error
d) Runtime error
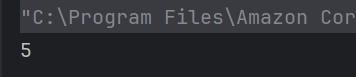
Answer 6
a) 5
x++ is a post-increment operator, so the current value of x (5) is printed first, and then x is incremented.
7. What will be the output of the following Java program?
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "Java";
String s2 = new String("Java");
System.out.println(s1 == s2);
}
}
Choose one option
a) true
b) false
c) Compilation error
d) Runtime error
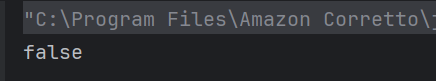
Answer 7
b) false
== compares references, and s1 and s2 refer to different objects. Use .equals() to compare string contents.
8. What will be the output?
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(10 + 20 + "30");
}
}
Choose one option
a) 3030
b) 102030
c) 30
d) None
Answer 8
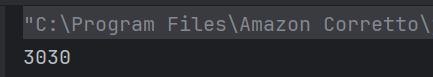
a) 3030
10 + 20 is 30 (integer addition), then 30 + “30” converts 30 to string and concatenates to “30”, resulting in “3030”.
9. Which of the following data types is NOT primitive in Java?
a) int
b) boolean
c) String
d) char
Answer 9
c) String
String is an object, not a primitive type.
10. What is the default value of a boolean variable in Java?
a) true
b) false
c) null
d) 0
Answer 10
b) false
Default value of boolean is false
11. What will be the output?
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
System.out.println(a > b ? a : b);
}
}
Choose one option
a) 10
b) 20
c) true
d) false
Answer 11
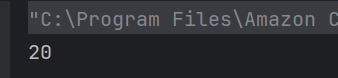
b) 20
Ternary operator returns a if a > b else returns b.
12. What does the % operator do in Java
Choose one option
a) Division
b) Modulus – gives remainder
c) Multiplication
d) Raises to power
Answer 12
b) Modulus – gives remainder
% returns the remainder after division.
13. Which operator has the highest precedence in Java?
Choose one option
a) +
b) *
c) =
d) ()
Answer 13
d) ()
Parentheses have the highest precedence to control evaluation order.
14. What will be the output of the following code?
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 5;
System.out.println(a + b * 2);
}
}
Choose one option
a) 30
b) 20
c) 25
d) 15
Answer 14
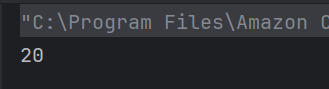
b) 20
According to operator precedence, multiplication is done before addition: 5 * 2 = 10, then 10 + 10 = 20.
15. What will be the result of this expression?
int x = 10;
int y = 3;
System.out.println(x / y);
Choose one option
a) 3.333
b) 3
c) 4
d) Compilation error
Answer 15
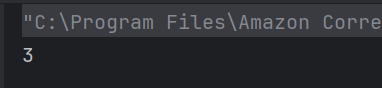
b) 3
Integer division truncates the decimal part. So 10 / 3 = 3.
16. What is the result of the following code snippet?
int a = 5;
System.out.println(a++);
System.out.println(a);
Choose one option
a) 5 5
b) 5 6
c) 6 5
d) 6 6
Answer 16
b) 5 6
a++ prints 5 (post-increment), then a becomes 6.
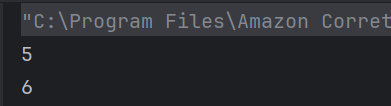
17. What will be printed?
int x = 4;
System.out.println((x > 3) || (x < 2));
Choose one option
a) true
b) false
c) Compilation error
d) Runtime error
Answer 17
a) true
x > 3 is true, so || (logical OR) returns true without checking the second condition (short-circuiting).
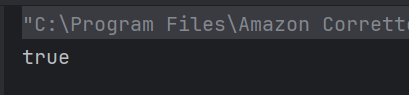
18. Which keyword is used to import a package from the Java API library?
a) import
b) package
c) getlib
d) lib
Answer 18
a) import
19. Which of these is the correct way to declare a method that returns an integer?
a) public void method() {}
b) public int method() { return 1; }
c) public int method() {}
d) public method() { return 1; }
Answer 19
b) public int method() { return 1; }
Method declared to return int must return an int value.
20. What is the output of the following code?
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 5;
if (x < 5)
System.out.println("Less");
else if (x == 5)
System.out.println("Equal");
else
System.out.println("More");
}
}
Choose one option
a) Less
b) Equal
c) More
d) Compilation error
Answer 20
b) Equal
x == 5, so the second condition matches and “Equal” is printed.
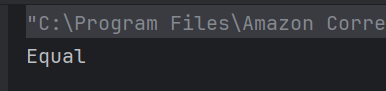
21. What is the output of this switch statement?
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 2;
switch(num + 1) {
case 1: System.out.println("One");
case 2: System.out.println("Two");
case 3: System.out.println("Three");
default: System.out.println("Default");
}
}
}
Choose one option
a) Three
b) Three Default
c) Two Default
d) Two Three Default
Answer 21
b) Three Default
switch(3) matches case 3, no break used, so it also executes default.
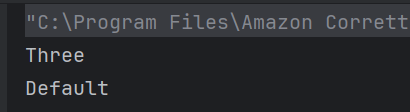
22. What will be the output of this while loop?
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 1;
while (i <= 3) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
i++;
}
}
}
Choose one option
a) 1 2 3
b) 1 2 3 4
c) Infinite loop
d) 1 2
Answer 22
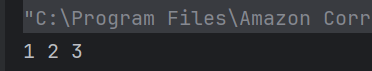
a) 1 2 3
Loop runs while i <= 3, printing 1 to 3
23. What is the output of the following if-else block?
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 4;
if (x % 2 == 0)
if (x % 3 == 0)
System.out.println("Divisible by 6");
else
System.out.println("Divisible by 2 but not by 3");
}
}
Choose one option
a) Divisible by 6
b) Divisible by 3
c) Divisible by 2 but not by 3
d) Compilation error
Answer 23
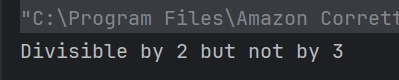
c) Divisible by 2 but not by 3
4 is divisible by 2 but not by 3
24. Which statement is used to stop a loop?
a) break
b) return
c) exit
d) stop
Answer 24
a) break
25. Which of these are selection statements in Java?
a) break
b) continue
c) for()
d) if()
Answer 25
d) if()
Continue and break are jump statements, and for is a looping statement.
We would love to hear from you! Please leave your comments and share your scores in the section below