In this tutorial, we will discuss the Pytest Framework.
Table of Contents
What is Pytest Framework?
PyTest is a popular testing framework for Python. It is widely used for writing and executing unit tests, functional tests, and even complex functional testing scenarios.
pytest requires: Python 3.7+ or PyPy3.
Key features of PyTest include:
1. Fixture Support: pytest supports fixtures, which are functions that can set up and tear down resources needed for testing. This makes it easy to share setup code among multiple tests.
2. Powerful Test Discovery: pytest automatically discovers and runs test functions based on naming conventions. We don’t need to explicitly list your tests; instead, the framework discovers and executes them.
3. Parameterized Testing: We can easily perform parameterized testing using pytest, allowing us to run the same test logic with multiple sets of input data.
4. Integration with Other Tools: pytest integrates well with other tools and libraries, such as Selenium for web testing, Django for web application testing, integrate report generation and more.
5. Assertions: pytest allows us to use the standard Python assert for verifying expectations and values in Python tests.
6. Advanced Test Execution: pytest provides rich features for executing tests, including parallel test execution, selective test execution, and rerunning failed tests.
How to install PyTest?
We need to make sure that Python is already installed. If not, then please refer to this tutorial - How to Install Python on Windows 11.
If you need help in installing PyCharms, please refer to this tutorial – How to install PyCharms on Windows 11.
To install pytest, use the below command:
pip install pytest
Create a PyTest test
Create a new project folder and open it in PyCharm.
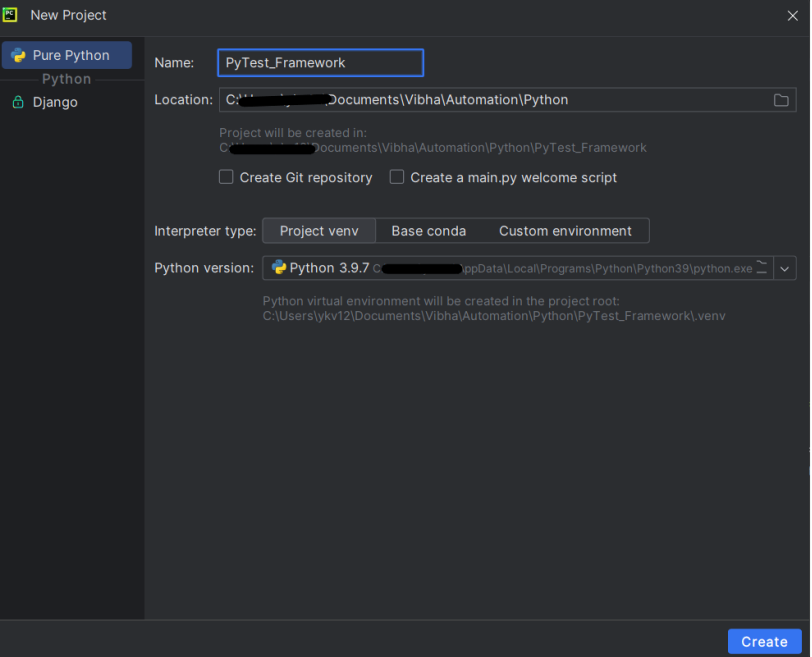
Go to the project folder and Create a new Python file, name it “sample_test.py”.
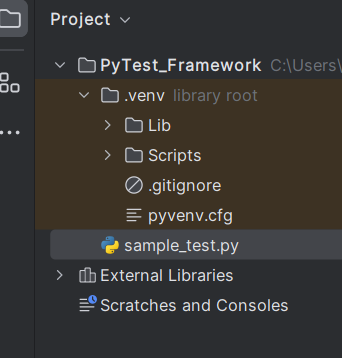
Create tests in the Python file.
def test_addition():
a = 6
b = 5
c = 11
assert a + b == 11, "Sum is not 11"
assert a + b == c, "Sum of a and b is not equal to c"
def test_subtraction():
x = 15
y = 4
z = 18
assert x - y == z, "Subtract y from x is equal to z"
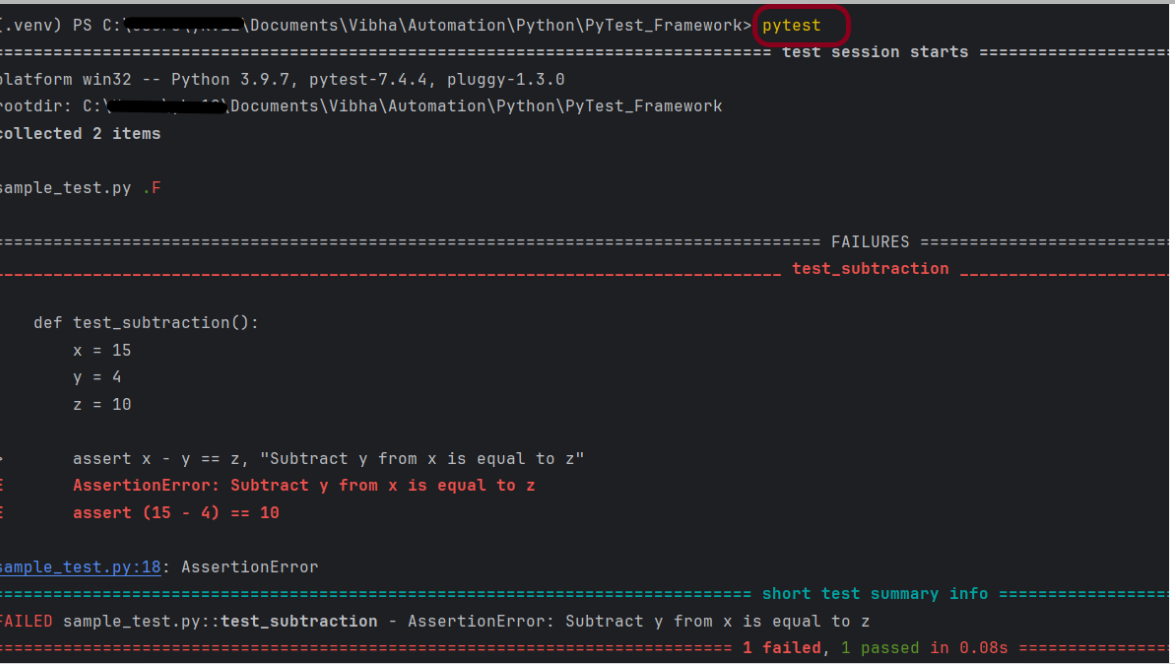
To run the tests, use the below command:
pytest
This command will run all the test file which has *test* in its name. Here, we have 1 Python file named as Sample_test.py. This file has 2 test, one of the test passes and another one fails. In the failures section, we can see the failed method(s) and the line of failure. Here x-y=z means 15-4=10 which is false.
The output of the above execution is
How PyTest Identifies the Test Files and Test Methods
By default pytest only identifies the file names starting with test_ or ending with _test as the test files. We can explicitly mention other filenames though (explained later). Pytest requires the test method names to start with “test.” All other method names will be ignored even if we explicitly ask to run those methods.
See some examples of valid and invalid pytest file names
test_sample - valid
sample_test - valid
sample_tests - invalid
testsample - invalid
sampletest - invalid
We can explicitly ask pytest to pick sample_tests.py, testsample.py and sampletest.py.