A HashMap stores items in “key/value” pairs, and you can access them by an index of another type (e.g. a String).
One object is used as a key (index) to another object (value). It can store different types: String keys and Integer values, or the same type, like String keys and String values. We need to import java.util.HashMap or its superclass in order to use the HashMap class and methods.
It is not an ordered collection, which means it does not return the keys and values in the same order in which they have been inserted into the HashMap.
Table of Contents
- Add Items
- Access an Item
- Remove an Item
- Checking whether HashMap is empty or not
- Check if a particular key exists in HashMap
- Check if a particular value exists in HashMap
Create a HashMap object as shown below from:-
import java.util.HashMap;
Syntax of HashMap
HashMap<String, String> employeeDetail = new HashMap<String, String>();
HashMap<String, String> employeeDetail = new HashMap<>();
HashMap<String, Integer> employeeDetail = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
Add Items
Below is an example where we are adding items to HashMap by using put() method.
import java.util.HashMap;
public class HashMap_Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* This is how to declare HashMap of key and Value as String */
HashMap<String, String> employeeDetail = new HashMap<String, String>();
// Add keys and values (Name, Designation)
employeeDetail.put("Tim", "DBA");
employeeDetail.put("Dong", "SDET");
employeeDetail.put("Nisha", "BA");
employeeDetail.put("Ulana", "Dev");
System.out.println("Detail of Employees :" + employeeDetail);
}
}
The output of the above program is

Below is an example where we are adding items to HashMap by using put() method.
Here, the key is String, and the Value is Integer.
import java.util.HashMap;
public class HashMap_Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Combination of String(key) and Integer(value)
HashMap<String, Integer> employeeAge = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
// Add keys and values (Name, Age)
employeeAge.put("Tim", 25);
employeeAge.put("Dong", 26);
employeeAge.put("Nisha", 29);
employeeAge.put("Ulana", 34);
System.out.println("Age of Employees :" + employeeAge);
}
}
The output of the above program is
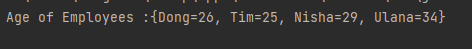
Access an Item
To access a value in the HashMap, use the get() method and refer to its key:-
import java.util.HashMap;
public class HashMap_Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Combination of String(key) and Integer(value)
HashMap<String, Integer> employeeAge = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
// Add keys and values (Name, Age)
employeeAge.put("Tim", 25);
employeeAge.put("Dong", 26);
employeeAge.put("Nisha", 29);
employeeAge.put("Ulana", 34);
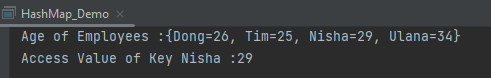
System.out.println("Age of Employees :"+ employeeAge);
// Access a value
System.out.println("Access Value of Key Nisha :" + employeeAge.get("Nisha"));
}
}
The output of the above program is
Remove an Item
To remove an item, use the remove() method and refer to the key:
import java.util.HashMap;
public class HashMap_Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Combination of String(key) and Integer(value)
HashMap<String, Integer> employeeAge = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
// Add keys and values (Name, Age)
employeeAge.put("Tim", 25);
employeeAge.put("Dong", 26);
employeeAge.put("Nisha", 29);
employeeAge.put("Ulana", 34);
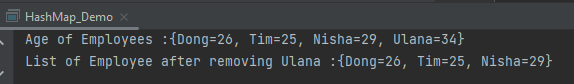
System.out.println("Age of Employees :" + employeeAge);
// To remove an item, use the remove() method and refer to the key
employeeAge.remove("Ulana");
System.out.println("List of Employee after removing Ulana :" + employeeAge);
}
}
The output of the above program is
To remove all items, use the clear() method:-
import java.util.HashMap;
public class HashMap_Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Combination of String(key) and Integer(value)
HashMap<String, Integer> employeeAge = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
// Add keys and values (Name, Age)
employeeAge.put("Tim", 25);
employeeAge.put("Dong", 26);
employeeAge.put("Nisha", 29);
employeeAge.put("Ulana", 34);
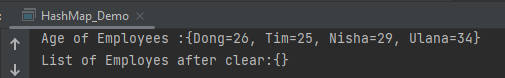
System.out.println("Age of Employees :" + employeeAge);
// To remove all items, use the clear() method:
employeeAge.clear();
System.out.println("List of Employes after clear:" + employeeAge);
}
}
The output of the above program is
Checking whether HashMap is empty or not
We are using isEmpty() method of the HashMap class to perform this check.
import java.util.HashMap;
public class HashMap_Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* This is how to declare HashMap */
HashMap<String, String> employeeDetail = new HashMap<String, String>();
// Add keys and values (Name, Designation)
employeeDetail.put("Tim", "DBA");
employeeDetail.put("Dong", "SDET");
employeeDetail.put("Nisha", "BA");
employeeDetail.put("Ulana", "Dev");
System.out.println("Detail of Employees :" + employeeDetail);
// Checking whether HashMap is empty or not
System.out.println("Is HashMap Empty? " + employeeDetail.isEmpty());
// Delete all items from HasMap
employeeDetail.clear();
System.out.println("Is HashMap Empty now? " + employeeDetail.isEmpty());
}
}
The output of the above program is

Check if a particular key exists in HashMap
We will be using containsKey() method of the HashMap class to perform this check. This method returns a boolean value.
import java.util.HashMap;
public class HashMap_Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* This is how to declare HashMap */
HashMap<String, String> employeeDetail = new HashMap<String, String>();
// Add keys and values (Name, Designation)
employeeDetail.put("Tim", "DBA");
employeeDetail.put("Dong", "SDET");
employeeDetail.put("Nisha", "BA");
employeeDetail.put("Ulana", "Dev");
System.out.println("Detail of Employees :" + employeeDetail);
// Check if a particular key exists in HashMap
boolean flag = employeeDetail.containsKey("Nisha");
System.out.println("Key Nisha exists in HashMap? : " + flag);
boolean flag1 = employeeDetail.containsKey("Shawn");
System.out.println("Key Shawn exists in HashMap? : " + flag1);
}
}
The output of the above program is

Check if a particular value exists in HashMap
We will be using containsValue() method of the HashMap class to perform this check.
import java.util.HashMap;
public class HashMap_Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* This is how to declare HashMap */
HashMap<String, String> employeeDetail = new HashMap<String, String>();
// Add keys and values (Name, Designation)
employeeDetail.put("Tim", "DBA");
employeeDetail.put("Dong", "SDET");
employeeDetail.put("Nisha", "BA");
employeeDetail.put("Ulana", "Dev");
System.out.println("Detail of Employees :" + employeeDetail);
// Check if a particular value exists in HashMap
boolean valueExists = employeeDetail.containsValue("Dev");
System.out.println("String Dev exists in HashMap? : " + valueExists);
boolean valueNotExists = employeeDetail.containsValue("Test");
System.out.println("String Test exists in HashMap? : " + valueNotExists);
}
}
The output of the above program is

We are done! Congratulations on making it through this tutorial and hope you found it useful! Happy Learning!!