HOME
What is XML Path? XML Path Language(XPath) is a query language for selecting nodes from an XML document. XPath provides a syntax for navigating through elements and attributes in an XML document. Paths can be absolute or relative:
Absolute paths starts from the root node, using a single slash (/) e.g., “//rootelement”.
Relative paths start from the current context node, using the double slashes (//) e.g., “//element”.
What is XmlPath in Rest Assured? XmlPath is a utility that allows us to parse and query XML responses. XmlPath is analogous to JsonPath, but it is specifically designed for handling the XML data.
Add the below mentioned dependency to the pom.xml.
<dependency>
<groupId>io.rest-assured</groupId>
<artifactId>xml-path</artifactId>
<version>5.5.0</version>
</dependency>
Sample XML File
<shopping>
<category type="groceries">
<item>
<name>Chocolate</name>
<price>10</price>
</item>
<item>
<name>Coffee</name>
<price>20</price>
</item>
</category>
<category type="supplies">
<item>
<name>Paper</name>
<price>5</price>
</item>
<item quantity="4">
<name>Pens</name>
<price>15</price>
</item>
</category>
<category type="present">
<item when="Aug 10">
<name>Kathryn's Birthday</name>
<price>200</price>
</item>
</category>
</shopping>
Below is an example of using the XmlPath.
import io.restassured.path.xml.XmlPath;
import io.restassured.path.xml.element.Node;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.List;
public class XMLPath_Demo {
String body = "<shopping>\n" +
" <category type=\"groceries\">\n" +
" <item>\n" +
" <name>Chocolate</name>\n" +
" <price>10</price>\n" +
" </item>\n" +
" <item>\n" +
" <name>Coffee</name>\n" +
" <price>20</price>\n" +
" </item>\n" +
" </category>\n" +
" <category type=\"supplies\">\n" +
" <item>\n" +
" <name>Paper</name>\n" +
" <price>5</price>\n" +
" </item>\n" +
" <item quantity=\"4\">\n" +
" <name>Pens</name>\n" +
" <price>15</price>\n" +
" </item>\n" +
" </category>\n" +
" <category type=\"present\">\n" +
" <item when=\"Aug 10\">\n" +
" <name>Kathryn's Birthday</name>\n" +
" <price>200</price>\n" +
" </item>\n" +
" </category>\n" +
" </shopping>";
@Test
public void test() {
XmlPath xmlPath = new XmlPath(body);
//Get the name of the first category item:
String name = xmlPath.get("shopping.category.item[0].name");
System.out.println("Item Name: " + name);
// Get the price of the first category price:
String chocolatePrice = xmlPath.get("shopping.category.item[0].price");
System.out.println("chocolatePrice :" + chocolatePrice);
// Get the price of the second category price:
String coffeePrice = xmlPath.get("shopping.category.item[1].price");
System.out.println("coffeePrice :" + coffeePrice);
//To get the number of category items:
int itemSize = xmlPath.get("shopping.category.item.size()");
System.out.println("Item Size: " + itemSize);
// Get a specific category:
Node category = xmlPath.get("shopping.category[0]");
System.out.println("category :" + category);
//To get the number of categories with type attribute equal to 'groceries':
int groceryCount = xmlPath.get("shopping.category.findAll { it.@type == 'groceries' }.size()");
System.out.println("groceryCount :" + groceryCount);
//Get all items with price greater than or equal to 10 and less than or equal to 20:
List<Node> itemsBetweenTenAndTwenty = xmlPath.get("shopping.category.item.findAll { item -> def price = item.price.toFloat(); price >= 10 && price <= 20 }");
System.out.println("itemsBetweenTenAndTwenty :" + itemsBetweenTenAndTwenty);
// Get the chocolate price:
int priceOfChocolate = xmlPath.getInt("**.find { it.name == 'Chocolate' }.price");
System.out.println("priceOfChocolate :" + priceOfChocolate);
}
}
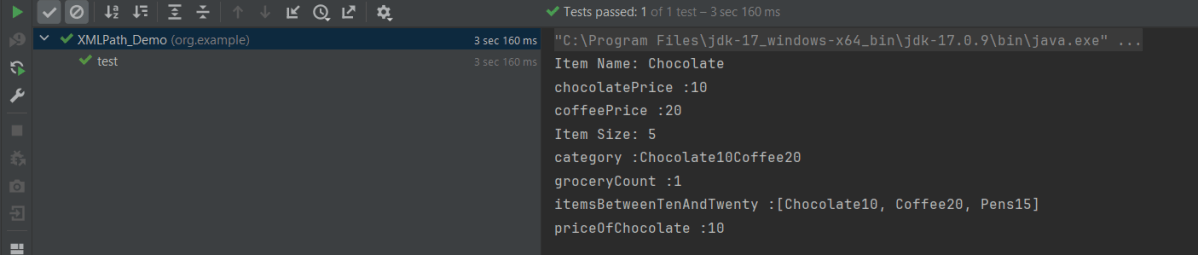
The output of the above program is
That’s it! Congratulations on making it through this tutorial and hope you found it useful! Happy Learning!!