HOME
1. What are the different types of locators in Selenium?
Locator is the unique address of any web element on web page. Locating elements in WebDriver is done by using the method “findElement(By.locator())”.
Here, the locator() part will be replaced with locator names, like
driver.findElement(By.id("email"))
Types of Locators in Selenium
- ID
- ClassName
- Name
- TagName
- LinkText
- PartialLinkText
- Xpath – Absolute Path & Relative Path
- CSS Selector
For more details, click here.
2. What is an XPath?
XPath is used to locate a web element based on its XML path. The fundamental behind locating elements using XPath is the traversing between various elements across the entire page and thus enabling a user to find an element with the reference of another element.
Various functions used in XPath are:-
1) text()
2) contains()
3) last()
4) AND , OR
5) position()
6) following()
7) preceding()
For more details, click here
3. What is the difference between “/” and “//” in XPath?
Single Slash “/” – A single slash is used to create an XPath with an absolute path i.e. the XPath would be created to start selection from the document node/start node. For example, if we have an XML document with a root element called “form,” each form is represented by a component called “content.” The XPath expression “/form/content” would select all the immediate child elements called “content” of the “form” element. An example is given below
driver.findElement(By.xpath("/html/body/form/content"));
Double Slash “//” – Double slash is used to create an XPath with a relative path i.e. the XPath would be created to start selection from anywhere within the document. For example, the below example will select any element in the document which has an attribute named “id” with the specified value “email”.
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//*[@id = 'email']")
For more details, click here
4. How do we can launch the browser using WebDriver?
Firstly, we should instantiate a Chrome/Chromium session by doing the following
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeOptions;
ChromeOptions options = new ChromeOptions();
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver(options);
The chromedriver is implemented as a WebDriver remote server that instructs the browser what to do by exposing Chrome’s internal automation proxy interface.
Firefox
Similarly, we can launch other browsers too like Firefox, InternetExplorer, Edge
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.Firefox.FirefoxDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.firefox.FirefoxOptions;
FirefoxOptions firefoxOptions = new FirefoxOptions();
WebDriver driver = new FirefoxDriver(firefoxOptions);
MicroSoftEdge
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.edge.EdgeDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.edge.EdgeOptions;
EdgeOptions options = new EdgeOptions();
WebDriver driver = new EdgeDriver(options);
For more details, click here
5. What are the different types of Drivers available in WebDriver?
The different drivers available in WebDriver are
- FirefoxDriver
- InternetExplorerDriver
- ChromeDriver
- SafariDriver
- OperaDriver
- AndroidDriver
- IPhoneDriver
- HtmlUnitDriver
6. Explain the different exceptions in Selenium WebDriver
Exceptions in Selenium are similar to exceptions in other programming languages. The most common exceptions in Selenium are:
1. TimeoutException: This exception is thrown when a command performing an operation does not complete in the expected time.
2. NoSuchElementException: This exception is thrown when an element with given attributes is not found on the web page. Suppose webdriver is trying to click on XPath – “//*[@id=’yDmH0d’]/div/div[2]/div[2]/form/content” which doesn’t exist on that particular web page, then the below exception is displayed – org.openqa.selenium.NoSuchElementException.
3. ElementNotVisibleException: This exception is thrown when the element is present in DOM (Document Object Model), but not visible on the web page.
4. StaleElementException: This exception is thrown when the element is either deleted or no longer attached to the DOM. This exception occurs, when Selenium navigates to a different page, comes back to the same old page, and performs operations on the old page. Technically, it occurs when the element defined in the Selenium code is not found in the cache memory and the Selenium code is trying to locate it.
5. NoSuchFrameException: iframe is the HTML web page inside another HTML web page. In order to work with the Web Elements on any iframe, we have to first switch to the iframe in Selenium and then locate the respective web elements inside the iframe. NoSuchFrameException WebDriver Exception occurs when the driver in the code is unable to find the frame on the web page to switch. i.e. when the driver is switching to an invalid or non-existing iframe.
6. NoAlertPresentException: In order to work with Alert pop-ups, we have to first switch to Alert and then perform operations on Alert like reading the messages on the Alerts or Accepting the alert by pressing ‘OK’ button on the alert, etc. NoAlertPresentException WebDriver Exception occurs when the web driver is unable to find the Alert on the web page to switch. i.e. when the driver is switching to an invalid or non-existing Alert pop-up.
7. NoSuchWindowException: In order to work with the Web Elements on any Browser Pop-up Window, we have to first switch to the pop-up in Selenium and then locate the respective web elements inside the pop-up window. NoSuchWindowException WebDriver Exception occurs when the web driver is unable to find the pop-up window on the web page to switch. i.e. when the driver is switching to an invalid or non-existing pop-up window.
8. ElementNotSelectableException: This exception comes under the InvalidElementStateException class The ElementNotSelectableException indicates that the web element is present on the web page but cannot be selected.
9. SessionNotFoundException: This Exception will occur when the driver is trying to perform operations on the Web Application after the Browser is closed.
7. What are the different types of waits available in WebDriver?
How do you achieve synchronization in WebDriver?
There are three types of wait in Selenium WebDriver
1. Implicit Wait – The implicit wait will tell to the web driver to wait for a certain amount of time before it throws a “NoSuchElementException“. The default setting is 0. Once we set the time, the web driver will wait for that time before throwing an exception. Implicit waits are used to provide a default waiting time (say 30 seconds) between each consecutive test step/command across the entire test script.
We need to import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit to use ImplicitWait.
driver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(Duration.ofSeconds(2));
2. Explicit Wait – An explicit wait is a code you define to wait for a certain condition to occur before proceeding further in the code. The explicit wait will tell the web driver to wait for certain conditions like visibilityOfElementLocated and the maximum amount of time before throwing the NoSuchElementException exception. Unlike Implicit waits, explicit waits are applied for a particular instance only.
Wait<WebDriver> wait = new WebDriverWait(driver, Duration.ofSeconds(2));
wait.until(d -> revealed.isDisplayed());
3. Fluent Wait – Fluent Wait instance defines the maximum amount of time to wait for a condition, as well as the frequency with which to check the condition.
Users may configure the wait to ignore specific types of exceptions whilst waiting, such as NoSuchElementException when searching for an element on the page.
Fluent Wait commands are mainly used when the web elements which sometimes visible in a few seconds and sometimes take more time than usual. Mainly in Ajax applications. We could set the default pooling period based on the requirement.
Wait<WebDriver> wait =
new FluentWait<>(driver)
.withTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(2))
.pollingEvery(Duration.ofMillis(300))
.ignoring(ElementNotInteractableException.class);
wait.until(
d -> {
revealed.sendKeys("Displayed");
return true;
});
For more details, click here
8. How to set the size of the Window in Selenium WebDriver?
First, fetch the size of the browser window in pixels by the below code Dimension
//Access each dimension individually
int width = driver.manage().window().getSize().getWidth();
int height = driver.manage().window().getSize().getHeight();
//Or store the dimensions and query them later
Dimension size = driver.manage().window().getSize();
int width1 = size.getWidth();
int height1 = size.getHeight();
Now, change the size of the window by using
driver.manage().window().setSize(new Dimension(1024, 768));
9. How to set the position of Window in Selenium?
First fetch the coordinates of the top left coordinate of the browser window by
// Store the dimensions and query them later
Point position = driver.manage().window().getPosition();
int x1 = position.getX();
int y1 = position.getY();
// Access each dimension individually
int x = driver.manage().window().getPosition().getX();
int y = driver.manage().window().getPosition().getY();
The window can be moved to the chosen position by
// Move the window to the top left of the primary monitor
driver.manage().window().setPosition(new Point(0, 0));
10. What is the difference between driver.findElement() and driver.findElements() commands?
FindElement – This method locates the first web element on the current web page matching the criteria mentioned as the parameter.
If the web element is not found, it will throw an exception – NoSuchElementException.
driver.findElement(By.xpath("Xpath location"));
FindElements – This method locates all the web elements on the current web page matching the criteria mentioned as parameters.
If not found any WebElement on the current page as per the given element locator mechanism, it will return the empty list.
findElements (By arg0):List<WebElement
For more details, click here
11. How to type in a textbox using Selenium?
The user can use sendKeys(“String to be entered”) to enter the string in the textbox. The sendKeys type a key sequence in the DOM element even if a modifier key sequence is encountered.
Syntax - sendKeys(CharSequence… keysToSend ) : void
Command – driver.findElement(By.xpath("//*[@name = 'email']")).sendKeys("abc123@gmail.com")
For more details, click here
12. How can we get a text of a web element?
The get command is used to retrieve the inner text of the specified web element. The command doesn’t require any parameter but returns a string value. It is also one of the extensively used commands for verification of messages, labels, errors, etc displayed on the web pages.
String Text = driver.findElement(By.id(“Text”)).getText();
13. How to input text in the text box without calling the sendKeys()?
We can execute JavaScript directly to set the value of the text box.
//Creating the JavascriptExecutor interface object by Type casting JavascriptExecutor js = (JavascriptExecutor)driver;
//Launching the Site
driver.get("https://www.google.com/");
js.executeScript("document.getElementsByName('q')[0].value = 'Selenium Introduction';");
The Actions class can simulate typing without sendKeys().
Actions actions = new Actions(driver);
actions.moveToElement(element).click().sendKeys("Selenium Introduction").build().perform();
For more details, click here
14. How to read a JavaScript variable in Selenium WebDriver?
You can execute JavaScript and retrieve the variable’s value using the executeScript method. This executes JavaScript in the browser context and retrieves the value of the variable.
//To initialize the JS object
JavascriptExecutor JS = (JavascriptExecutor) webdriver;
//To get the site title
String title = (String)JS.executeScript("return document.title");
System.out.println("Title of the webpage : " + title);
For more details, click here
15. What is JavaScriptExecutor and in which cases JavaScriptExecutor will help in Selenium automation?
There are some conditions where we cannot handle problems with only WebDriver. Web controls don’t react well to selenium commands. In this kind of situation, we use Javascript. It is useful for custom synchronizations, hiding or showing web elements, changing values, testing flash/HTML5, and so on.
To do these, we can use Selenium’s JavascriptExecutor interface which executes JavaScript through Selenium driver.
It provides “executescript” & “executeAsyncScript“ methods, to run JavaScript in the context of the currently selected frame or window.
JavascriptExecutor js = (JavascriptExecutor) driver;
js.executeScript(Script,Arguments);
Script – This is the JavaScript that needs to be executed.
Arguments – It is the arguments to the script. It’s optional
Let’s see some scenarios we could handle using this Interface:
1. To type Text in Selenium WebDriver without using sendKeys() method 2. To click a Button in Selenium WebDriver using JavaScript
3. To handle Checkbox
4. To generate an Alert Pop window in Selenium
5. To refresh the browser window using Javascript
6. To get inner text of the entire webpage in Selenium
7. To get the Title of our webpage
8. To get the domain
9. To get the URL of a webpage
10. To perform Scroll on an application using Selenium
For more details, click here
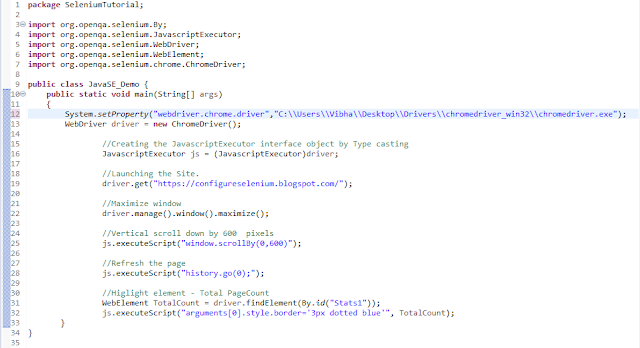
16. How To Highlight Element Using Selenium WebDriver?
By using the JavascriptExecutor interface, we could highlight the specified element
//Create the JavascriptExecutor interface object by Type casting
JavascriptExecutor js = (JavascriptExecutor)driver;
//Higlight element - Total PageCount
WebElement TotalCount = driver.findElement(By.id("Stats1"));
js.executeScript("arguments[0].style.border='3px dotted blue'", TotalCount);
For more details, click here
17. List some scenarios that we cannot automate using Selenium WebDriver?
- Bitmap comparison is not possible using Selenium WebDriver.
- Automating Captcha is not possible using Selenium WebDriver.
- We can not read bar code using Selenium WebDriver.
- Selenium lacks built-in capabilities for image recognition or visual testing.
- Selenium WebDriver is not designed for mobile app automation.
- Selenium does not provide network-level control or inspection.
- Selenium is not suitable for load or performance testing.
- Selenium cannot interact with or verify multimedia content.
- Selenium cannot handle scenarios that require advanced security testing, such as Multi-factor authentication (MFA), Token-based authentication.
18. How can you find if an element is displayed on the screen?
WebDriver facilitates the user with the following methods to check the visibility of the web elements. These web elements can be buttons, drop boxes, checkboxes, radio buttons, labels, etc.
- isDisplayed()
- isSelected()
- isEnabled()
isDisplayed():
boolean elePresent = driver.findElement(By.xpath("xpath")).isDisplayed();
isSelected():
boolean eleSelected= driver.findElement(By.xpath("xpath")).isSelected();
isEnabled():
boolean eleEnabled= driver.findElement(By.xpath("xpath")).isEnabled();
19. Explain how you can switch back from a frame?
To switch back from a frame use the method defaultContent().
driver.switchTo().defaultContent();
20. What is the difference between getWindowhandles() and getwindowhandle() ?
getwindowhandles(): It is used to get the address of all the open browser and its return type is Set<String>
getwindowhandle(): It is used to get the address of the current browser where the control is and return type is string.
For more details, click here
21. How to select the value in a dropdown?
To perform any operation on DropDown, we need to do 2 things:-
1) Import package org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.Select
2) Create a new Select object of the class Select
Select oSelect = new Select());
Different Select Commands
1. selectByValue
Select yselect = new Select(driver.findElement(By.id("year")));
yselect.selectByValue("1988");
2. selectByVisibleText
Select mselect = new Select(driver.findElement(By.id("month")));
mselect.selectByVisibleText("Apr");
3. selectByIndex
Select bselect = new Select(driver.findElement(By.name("birthday_day")));
bselect.selectByIndex(8);
For more details, click here
22. How to switch to a new window (new tab) that opens up after you click on a link?
If you click on a link in a web page and it opens a new window, but WebDriver will not know which window the Operating system consider active. To change the WebDriver’s focus/ reference to the new window we need to use the switchTo() command. driver.switchTo().window();
Here, ‘windowName’ is the name of the window you want to switch your reference to.
In case you do not know the name of the window, then you can use the driver.getWindowHandle() command to get the name of all the windows that were initiated by the WebDriver. Note that it will not return the window names of browser windows which are not initiated by your WebDriver.
Once you have the name of the window, then you can use an enhanced for loop to switch to that window. Look at the piece of code below.
String handle= driver.getWindowHandle();
for (String handle : driver.getWindowHandles())
{
driver.switchTo().window(handle);
}
//Store the ID of the original window
String originalWindow = driver.getWindowHandle();
//Check we don't have other windows open already
assert driver.getWindowHandles().size() == 1;
//Click the link which opens in a new window
driver.findElement(By.linkText("new window")).click();
//Wait for the new window or tab
wait.until(numberOfWindowsToBe(2));
//Loop through until we find a new window handle
for (String windowHandle : driver.getWindowHandles()) {
if(!originalWindow.contentEquals(windowHandle)) {
driver.switchTo().window(windowHandle);
break;
}
}
//Wait for the new tab to finish loading content
wait.until(titleIs("Selenium documentation"));
For more details, click here
23. How to handle browser (chrome) notifications in Selenium?
In Chrome, we can use ChromeOptions as shown below.
ChromeOptions options = new ChromeOptions();
options.addArguments("disable-infobars");
WebDriver player = new ChromeDriver(options);
24. How to delete Browser Cookies with Selenium Web Driver?
To clear all cookies from the browser:
driver.Manage().Cookies.DeleteAllCookies();
To delete a specific cookie, you need to retrieve it by its name and then delete it:
driver.manage().deleteCookieNamed("cookie_name");
If you already have the cookie object, you can delete it directly:
// Get the cookie
Cookie cookie = driver.manage().getCookieNamed("cookie_name");
// Delete the specific cookie
driver.manage().deleteCookie(cookie);
25. What are the different types of navigation commands?
- driver.navigate().forward(); – to navigate to the next web page with reference to the browser’s history.
- driver.navigate().back(); – takes back to the previous webpage with reference to the browser’s history.
- driver.navigate().refresh(); – to refresh the current web page thereby reloading all the web elements.
- driver.navigate().to(“url”); – to launch a new web browser window and navigate to the specified URL.
For more details, click here
26. How can we handle Web-based Pop-ups or Alerts in Selenium?
To handle Web-based alerts or popups, we need to do switch to the alert window and call Selenium WebDriver Alert API methods.
- dismiss(): To click on Cancel button.
- accept(): To Click on OK button.
- getText(): To get the text which is present on the Alert.
- sendKeys(): To enter the text into the alert box.
For more details, click here
27. What are the ways to refresh a browser using Selenium WebDriver?
1. Using driver.navigate().refresh() command.
2. Using driver.get(“URL”) on the current URL or using driver.getCurrentUrl()
3. Using driver.navigate().to(“URL”) on the current URL or driver.navigate().to(driver.getCurrentUrl());
4. Using sendKeys(Keys.F5) on any textbox on the webpage.
28. What are the different mouse actions that can be performed?
The different mouse events supported in selenium are
1. click(WebElement element)
2. doubleClick(WebElement element)
3. contextClick(WebElement element)
4. mouseDown(WebElement element)
5. mouseUp(WebElement element)
6. mouseMove(WebElement element)
7. mouseMove(WebElement element, long xOffset, long yOffset)
For more details, click here
29. Write the code to double-click an element in selenium?
To double-click an element in Selenium, you can use the Actions class, which provides the doubleClick() method. The code to double-click an element in selenium is mentioned below
driver.get("https://www.selenium.dev/selenium/web/mouse_interaction.html");
WebElement clickable = driver.findElement(By.id("clickable"));
new Actions(driver)
.doubleClick(clickable)
.perform();
30. Write the code to right-click an element in selenium?
To right-click an element in Selenium, you can use the Actions class, which provides the contextClick() method for performing a right-click action. Below is an example:
driver.get("https://www.selenium.dev/selenium/web/mouse_interaction.html");
WebElement clickable = driver.findElement(By.id("clickable"));
new Actions(driver)
.contextClick(clickable)
.perform();
31. How to mouse hover an element in selenium?
Code to mouse hover over an element in selenium is mentioned below:-
// Launch the URL
driver.get("https://www.selenium.dev/selenium/web/mouse_interaction.html");
WebElement hoverable = driver.findElement(By.id("hover"));
new Actions(driver)
.moveToElement(hoverable)
.perform();
32. How to do drag and drop in Selenium?
Using the Action class, drag and drop can be performed in selenium.
// Launch the URL
driver.get("https://www.selenium.dev/selenium/web/mouse_interaction.html");
WebElement hoverable = driver.findElement(By.id("hover"));
new Actions(driver)
.moveToElement(hoverable)
.perform();
Or
driver.get("https://www.selenium.dev/selenium/web/mouse_interaction.html");
WebElement draggable = driver.findElement(By.id("draggable"));
WebElement droppable = driver.findElement(By.id("droppable"));
new Actions(driver)
.dragAndDrop(draggable, droppable)
.perform();
For more details, click here
33. How can we capture screenshots in selenium?
Using the getScreenshotAs method of the TakesScreenshot interface, we can take the screenshots in selenium.
File scrFile = ((TakesScreenshot)driver).getScreenshotAs(OutputType.FILE);
FileUtils.copyFile(scrFile, new File("D:\\testScreenShot.jpg"));
34. Explain the difference between getText() and getAttribute() in Selenium
getAttribute() method provides the value of a particular HTML attribute and the getText() method provides the visible text of a web element. getAttribute() can be used to access attributes that are not visible on the page or to get specific information like the URL of an anchor tag (<a>).
35. Explain how to handle browser cookies in Selenium WebDriver and some different scenarios it applies to.
A HTTP cookie is comprised of information about the user and their preferences. It stores information using a key-value pair. It is a small piece of data sent from Web Application and stored in Web Browser, while the user is browsing that website.
Handling browser cookies is useful in various scenarios:
Login Sessions: Managing authentication and session cookies to simulate user login/logout scenarios. When automating Online Shopping Application, you many need to automate test scenarios like place order, View Cart, Payment Information, order confirmation, etc. If cookies are not stored, you will need to perform login action every time before you execute above listed test scenarios. This will increase your coding effort and execution time. The solution is to store cookies in a File. Later, retrieve the values of cookie from this file and add to it your current browser session. As a result, you can skip the login steps in every Test Case because your driver session has this information in it.
Remember Me Functionality: Verifying if “remember me” cookies are set and persist across sessions.
User Preferences: Storing and retrieving user-specific preferences stored in cookies.
Tracking and Analytics: Testing tracking and analytics cookies to ensure they are set correctly and track user behavior.
Consent Management: Testing cookie consent banners and verifying if cookies are set according to user consent.
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS): Handling cookies across different domains for testing cross-origin requests.
Return The List of all Cookies
Set<Cookie> cookies = driver.manage().getCookies();
Return specific cookie according to name
driver.manage().getCookieNamed(arg0);
Create and add the cookie
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("cookieName", "cookieValue");
driver.manage().addCookie(cookie);
Delete specific cookie
driver.manage().deleteCookieNamed("cookieName");
Delete all cookies
driver.manage().deleteAllCookies();
To know more, please refer to How to handle browser cookies in Selenium WebDriver.
36. What is the main disadvantage of implicit wait?
Implicit wait adds a fixed delay before each element interaction, even if the element is already available. This can significantly increase the overall test execution time, especially when there are multiple elements involved.
With implicit wait, you cannot specify different timeouts for different elements or actions on a page. It applies globally to all elements, which may not be ideal for scenarios where certain elements require shorter or longer waiting times.
If an element takes longer than expected to appear or interact with during test execution, it can be challenging to identify whether it’s due to a genuine delay or an issue with the application under test.
37. Name some of the commonly used automation testing tools that are used for non-functional automation
1. JMeter – Apache JMeter is a popular open-source tool for load testing, performance testing, and stress testing of web applications.
2. Ready API – ReadyAPI is a comprehensive suite of tools for API testing, functional testing, load testing, and security testing. It is developed by SmartBear Software and provides a unified platform to design, test, and monitor APIs throughout their lifecycle.
3. LoadRunner – LoadRunner by Micro Focus is a comprehensive performance testing tool that supports various protocols and provides in-depth analysis of system behavior under different loads.
4. Locust – Locust is an open-source load-testing framework written in Python that allows you to define user behavior using code, making it highly flexible and customizable.
5. Gatling – Gatling is another open-source load and performance testing tool that is designed to be highly scalable and efficient.
Advanced Selenium Interview Questions and Answers 2026