A method is a block of code that is use to perform certain actions. Method runs when it called. Method allow us to reuse the code. Methods are essentially functions within a class that define the behavior of the class or objects created from that class.
Types of methods in Java
- Standard Library methods
- User defined methods
Standard Library Method
They are built-in Java methods are readily available to use. For example, sqrt() is a Method of Math and returns square root of a number.
User-defined Method
User can define a method inside a class as per his/her wish.
How to create a Method?
modifier returnType nameOfMethod (Parameter List) {
// method body }
Here,
- modifier − It defines the access type of the method like public, protected, default, private
- returnType − Method may return a value or not. Void does not return any value.
- nameOfMethod − This is the method name. The method signature consists of the method name and the parameter list.
- Parameter List − The list of parameters, it is the type, order, and number of parameters of a method. These are optional, method may contain zero parameters.
- method body − The method body defines what the method does with the statements.
public static int methodName(int a, int b) {
// body
}
Below is an example of method.
public class Method_Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Standard Library Method
System.out.println("Square root of 9 is : " + Math.sqrt(9));
//User defined Method
MyMethod();
}
public static void MyMethod()
{
System.out.println("My User defined Method");
}
}
The output of the above program is
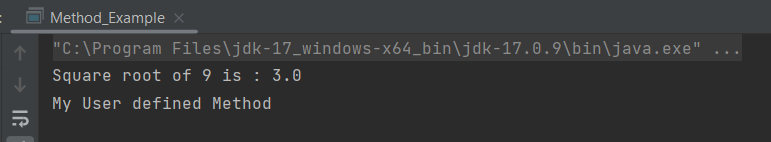
Java Methods with Arguments and Return Value
A Java method can have zero or more parameters, and they may return a value.
public class Min_Method {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 5;
int c = minMethod(a,b);
System.out.println("Minimum value is :" + c);
}
//Define function min_function
public static int minMethod(int x, int y)
{
int min;
if (x>y)
min =y;
else
min = x;
//return value
return min;
}
}
The output of the above program is
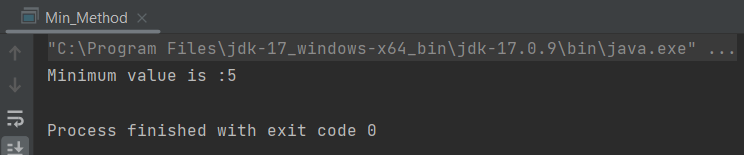
In the above example, minMethod() method is if return type int and returning the value of variable min.
Void Keyword
The void keyword allows us to create methods that do not return a value. When a method’s return type is void, it means that the method performs some operation or task but does not produce any result that needs to be returned to the caller.
public class Min_Method {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 5;
//Call function
minMethod(a,b);
}
//Define function min_function
public static void minMethod(int x, int y)
{
int min;
if(x>y)
min =y;
else
min = x;
System.out.println("Minimum value is :" + min);
}
}
The output of the above program is
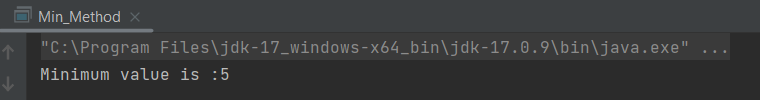
In the above example, minMethod() method is if return type void, so it is not returning any value.
Method Overloading
When a class has two or more methods by the same name but different parameters, it known as method overloading. To know more about method overloading, click here.
public class Overloading_Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a= 10;
int b = 24;
double c = 12.0;
double d = 13.0;
min_function(a, b);
min_function(c,d);
}
public static void min_function(int x, int y)
{
int min;
if(x>y)
min = y;
else
min = x;
System.out.println("Minimum value for integer is :"+ min);
}
public static void min_function(double m, double n)
{
double min;
if(m>n)
min=n;
else
min=m;
System.out.println("Minimum value for integer is :"+ min);
}
}
The output of the above program is
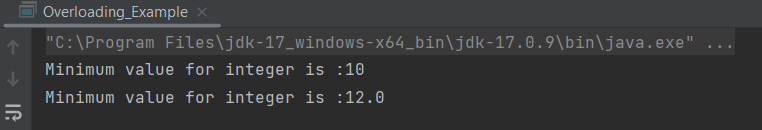
What is main method in Java?
The main()method is the entry point into the application. The signature of the method is always: public static void main(String[] args).
public: The main method is typically declared as public so that it can be accessed from outside the class.
static: The main method is declared as static because it belongs to the class rather than any specific instance of the class.
void: The main method does not return any value.
String[] args: The main method accepts an array of strings as arguments, which can be used to pass command-line arguments to the Java program.