In this tutorial, will get to know the Exceptions in JAVA.
Table of Contents
- What are Exceptions?
- Category of Exceptions
- Types of Exceptions
- ArithmeticException
- ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
- StringIndexOutOfBoundsException
- NullPointerException
- NumberFormatException
- FileNotFoundException
- ClassNotFoundException
- IOException
- NoSuchMethodException
- InterruptedException
- NoSuchFieldException
- RuntimeException
- SQLException
- IllegalArgumentException
What are Exceptions?
Exceptions in Java are events that disrupt the normal flow of the program’s instructions during runtime. When an exceptional event occurs, an exception object is created, which the runtime system then throws. This exception object contains information about the error, including its type and the state of the program when the error occurred.
Category of Exceptions
Java defines two categories of exceptions – Built-in Exceptions and User-Defined Exception.
Built-in Exceptions
These exceptions are available in Java libraries. There are various types of exceptions which are suitable to specific type of exception situations. Built-in Exceptions are divided into Checked and Unchecked Exceptions.
Checked Exceptions
- These are exceptions that are checked at compile-time.
- They must be either handled using a try-catch block or declared in the method signature using the `throws` keyword.
- Examples include IOException, SQLException, and FileNotFoundException.
UnChecked Exceptions
- These are exceptions that are not checked at compile-time but are instead checked at runtime.
- Unchecked exceptions are subclasses of RuntimeException. They do not need to be declared or handled explicitly.
- Examples include NullPointerException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException, and ArithmeticException.
User-defined or Custom Exceptions
There are several conditions where built-in exceptions in Java is unable to handle certain situations. In such cases, user can create a custom or user defined exception.
In this tutorial, I’ll explain about built-in exceptions.
Types of Exceptions
1. ArithmeticException
It is thrown when an exception has occurred in an arithmetic operation. Below is an example of this exception.
public class ArithmeticExceptionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
{
try {
int a = 30, b = 0;
int c = a / b; // cannot divide by zero
System.out.println("Result = " + c);
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("Can't divide a number by 0");
}
}
}
}
The output of the above program is
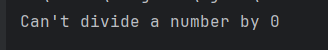
2. ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
It is thrown when an array has been accessed with an illegal index. The index is either negative or greater than or equal to the size of the array.
public class ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsExceptionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
{
try {
// Create an array of size 5
int a[] = new int[5];
// Access 11th element from array of size 5
a[10] = 9;
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("Array Index is Out Of Bounds");
}
}
}
}
The output of the above program is
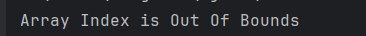
3. StringIndexOutOfBoundsException
It is thrown by String class methods to indicate that an index is either negative or greater than the size of the string.
public class StringOutOfBoundDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
{
try {
String a = "This is testing"; // length is 15
System.out.println("Length of String :" + a.length());
char b = a.charAt(20); // accessing 20th element
System.out.println(b);
} catch (StringIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("StringIndexOutOfBoundsException");
}
}
}
}
The output of the above program is
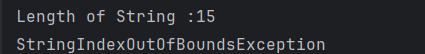
4. NullPointerException
This exception is thrown when referring to the members of a null object.
public class NullPointerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
{
try {
String a = null; // null value
System.out.println(a.length());
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println("NullPointerException");
}
}
}
}
The output of the above program is

5. NumberFormatException
This exception is thrown when a method can not convert a string into a numeric format.
public class NumberFormatDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// "java" is not a number
int num = Integer.parseInt("java");
System.out.println(num);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("Number format exception");
}
}
}
The output of the above program is
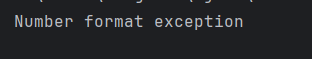
6. FileNotFoundException
This Exception is thrown when a file is not accessible or does not open.
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
public class FileNotFoundDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// Following file does not exist
File file = new File("C://demofile.txt");
FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("File does not exist");
}
}
}
The output of the above program is

7. ClassNotFoundException
This Exception is raised when we try to access a class whose definition is not found.
package JavaDemo;
public class ClassNotFoundExceptionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Class temp = Class.forName("gfg");
// Calling the clas gfg which is not present in the
// current class temp instance of calling class it
// will throw ClassNotFoundException;
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// block executes when mention exception occur
System.out.println("Class does not exist check the name of the class");
}
}
}
The output of the above program is

8. IOException
It is thrown when an input-output operation failed or interrupted.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class IOExceptionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filepath = "C:\\Users\\Desktop\\IOTest1.txt";
BufferedReader br1 = null;
String curline;
try {
br1 = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filepath));
while ((curline = br1.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(curline);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("IOException found :" + e.getMessage());
} finally {
try {
if (br1 != null)
br1.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
The output of the above program is

9. NoSuchMethodException
It is thrown when accessing a method which is not found.
10. InterruptedException
It is thrown when a thread is waiting , sleeping , or doing some processing , and it is interrupted.
11. NoSuchFieldException
It is thrown when a class does not contain the field (or variable) specified.
12. RuntimeException
This represents any exception which occurs during runtime. They are ignored during compilation time. Such as logical bugs.
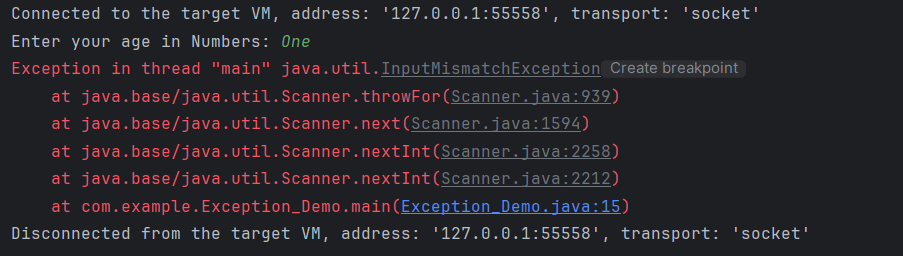
import java.util.Scanner;
public class RunTimeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Reading user input
Scanner input_dev = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter your age in Numbers: ");
int age1 = input_dev.nextInt();
if (age1 > 20) {
System.out.println("You can view the page");
} else {
System.out.println("You cannot view the page");
}
}
}
The output of the above program is
13. SQLException
This type of exception occurs while executing queries on a database related to the SQL syntax.
14. IllegalArgumentException
It is thrown when an inappropriate and incorrect argument is passed to the method. Suppose, a method does not allow null, but we are providing null as the parametr, then this exception is thrown.