Last Updated On
Sending a JSON file as a payload from an external source using Playwright requires you to read the file from the local filesystem. You then include its contents in the HTTP request. In this tutorial, I will explain to pass a JSON file as a payload to the request. This is needed when the payload is static or there is minimal change in the request payload.
Table of Contents
- System Requirement
- Setup Your Playwright Testing Environment
- Update playwright.config.ts
- Writing the API Test
- Execute the tests through Test Explorer View
- Execute the tests through Command Line
- Evaluate Test Results
System Requirement
- Node.js version 18 or higher and npm (comes with Node.js)
- Windows 10+, macOS 12+, or Ubuntu 20.04+
- Visual Studio for Code is already installed.
- Playwright is already installed
Below is the sample JSON payload used in the request.

Here’s how you can handle them in Playwright:
1. Setup Your Playwright Testing Environment:
Verify that the Playwright installed in your project. If you haven’t yet installed it, you can use:
npm install playwright
2. Update playwright.config.ts
Playwright Test comes with a few built-in reporters for different needs and ability to provide custom reporters. We will add detail in playwright.config.ts to generate the html report, once the test execution is finished.
import { defineConfig } from '@playwright/test';
export default defineConfig({
reporter: 'html',
});
3. Writing the API Test
First, ensure your JSON file is well-structured and readable.
import { test, expect } from '@playwright/test';
const fs = require('fs');
test('Send JSON file as payload', async ({ request }) => {
try {
// Read and parse JSON file directly into a JavaScript object
const jsonPayload = JSON.parse(fs.readFileSync('tests/payloads/jsonpayload.json', 'utf8'));
console.log('JSON data parsed successfully:', jsonPayload);
// Perform a POST request
const postResponse = await request.post('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users', {
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
data: JSON.stringify(jsonPayload)
});
// Check the response status code - expecting 201 if the resource creation is successful
expect(postResponse.status()).toBe(201);
// Parse the response data
const postResponseBody = await postResponse.json();
console.log('RESPONSE:', postResponseBody);
// Validate the response properties - adapt as needed
expect(postResponseBody).toHaveProperty('title', 'Architect');
expect(postResponseBody).toHaveProperty('body', 'DW-BI');
expect(postResponseBody).toHaveProperty('userId', 5);
} catch (error) {
if (error instanceof Error) {
console.error('Error message:', error.message);
} else {
console.error('An unknown error occurred:', error);
}
}
});
Explanation:
1. Imports
This line imports the test and expect functions from Playwright’s testing library. These functions provide a structure for writing tests and asserting conditions within them.
import { test, expect } from '@playwright/test';
2. Test Definition
This defines an asynchronous test case named “Send JSON file as payload”. The test receives a request object as a parameter, which is used to perform HTTP requests.
test('Send JSON file as payload', async ({ request })
3. Read the JSON File
First, you need to read the JSON file into your script. This is typically done using the `fs` module in Node.js.
const fs = require('fs');
4. Read and Parse JSON File
The script attempts to read a JSON file located at ‘tests/payloads/jsonpayload.json’ using fs.readFileSync.
The JSON content is parsed into a JavaScript object using JSON.parse.
// Read and parse JSON file directly into a JavaScript object
const jsonPayload = JSON.parse(fs.readFileSync('tests/payloads/jsonpayload.json', 'utf8'));
console.log('JSON data parsed successfully:', jsonPayload);
5. Performing a POST Request
Sends a POST request to the specified URL. The headers include ‘Content-Type’: ‘application/json’, denoting the request body data format. The request body is the stringified version of the JSON payload.
// Perform a POST request
const postResponse = await request.post('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users', {
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
data: JSON.stringify(jsonPayload)
});
6. Checking the Response Status Code
Retrieve HTTP status code for response validation.
expect(postResponse.status()).toBe(201);
7. Parsing the Response Data
Parse response data into JSON format
// Parse the response data
const postResponseBody = await postResponse.json();
8. Logging the Response
This outputs the response body to the console, allowing you to see the returned JSON data.
console.log(postResponseBody);
9. Perform assertions on the response
The assertions verify that the response contains expected data. expect assertions validate certain properties in the response
- The property `title` should be ‘Architect’.
- The property `body` should be ‘DW-BI’.
- The property `userId` should be 5.
// Validate the response properties - adapt as needed
expect(postResponseBody).toHaveProperty('title', 'Architect');
expect(postResponseBody).toHaveProperty('body', 'DW-BI');
expect(postResponseBody).toHaveProperty('userId', 5);
10. Error Handling
There’s a `try-catch` block capturing errors during file reading, request making, and response handling. The `catch` block checks if the error is an instance of `Error` to log its message.
4. Execute the tests through Test Explorer View
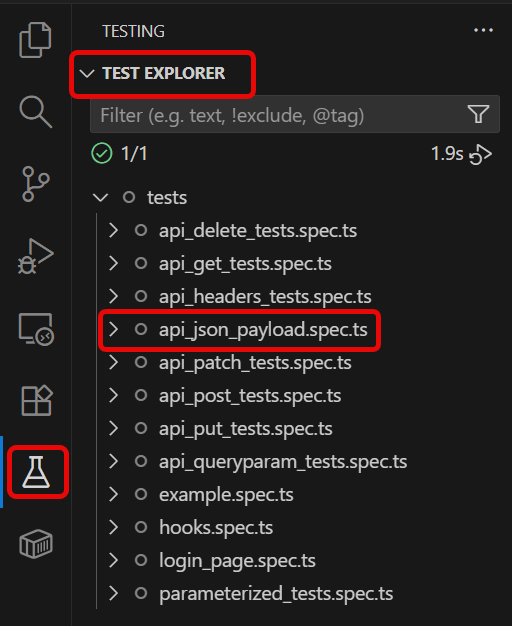
Go to the funnel shape icon called “Testing” or “Test Explorer View”. You can run the tests from the test Explorer view too now. You can run all of the tests in all of the test specs in this directory.
You can also come in and run all of the tests in a particular specification file. Alternatively, run individual tests within a specification file. Here, I want to run the tests of api_json_payload_tests.spec.ts file.
The output of the above program is
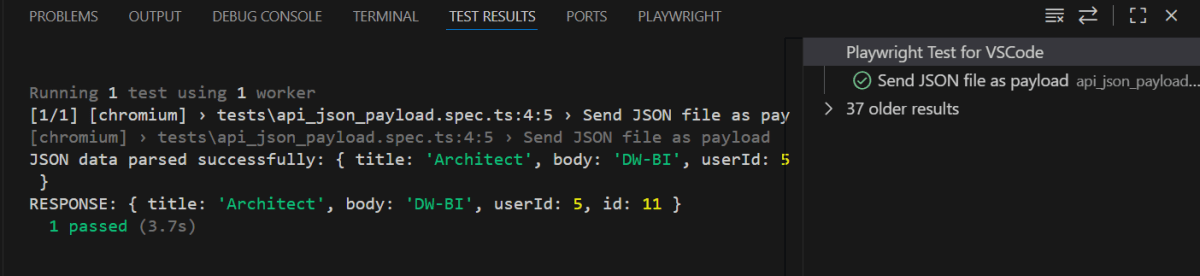
5. Execute the tests through Command Line
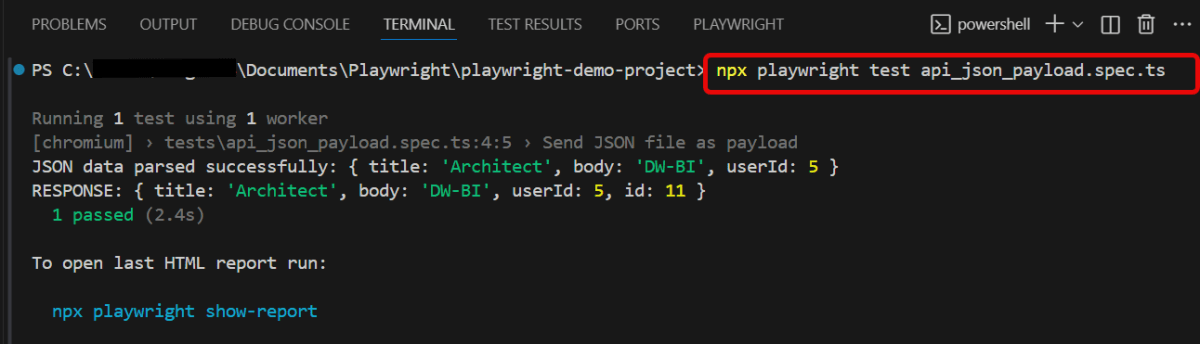
You can also run the tests through the command line. Go to the terminal and use the below command:-
npx playwright test api_json_payload.spec.ts
This command runs all the tests present in this file.
6. Evaluate Test Results
Analyze console outputs and assertions to validate the response data, ensuring that your API endpoints are functioning as designed.
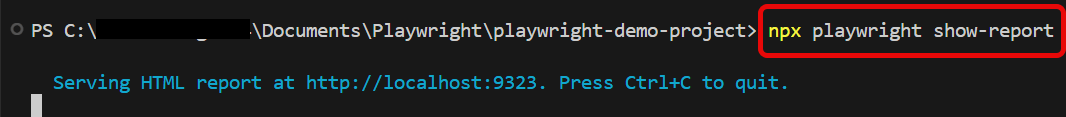
Playwright generates a test report after the execution of the tests. This test report can be viewed by using the below command:
npx playwright show-report
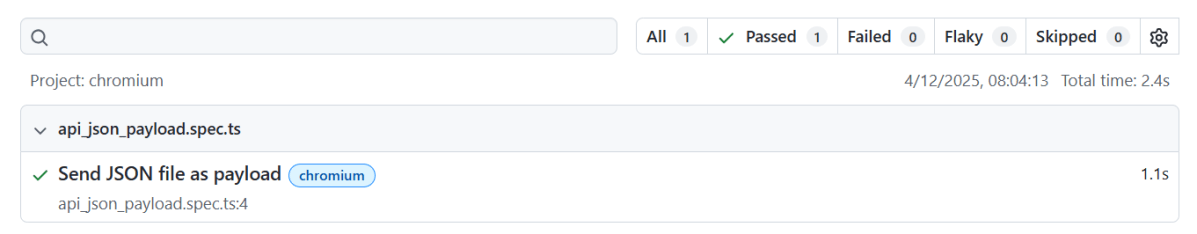
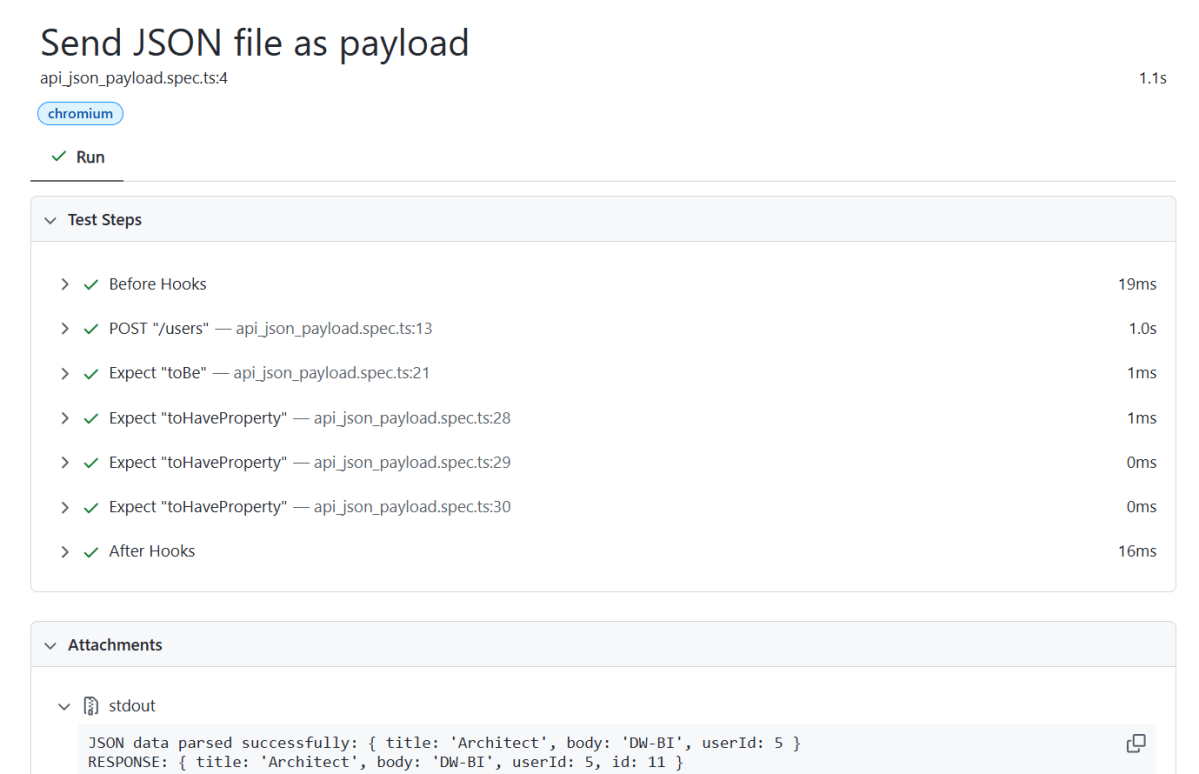
The output of the above command is
The Index.html report is shown below:
Summary:
File Paths: The file paths are correctly specified relative to the execution directory or use absolute paths.
Content-Type Headers: The `Content-Type` header should match the format of the data being sent (`application/json` for JSON).
Network Configuration: The target endpoint should support POST requests and accept data in the given formats.
To know more about Playwright UI mode, please refer to this website – https://playwright.dev/docs.