MCQ
Java – Multiple Choice Questions and Answers – Method, Overloading, Overriding
Welcome to the Java Quiz! This blog post features 25 multiple-choice questions that explore concepts of Methods, Method Overloading and Method Overriding in Java.
1. Which method can be defined only once in a program?
a) main method
b) finalize method
c) static method
d) private method
Answer 1
a) main method
main() method can be defined only once in a program. Program execution begins from the main() method by java runtime system.
2. What is the return type of a method that does not return any value?
a) int
b) float
c) void
d) double
Answer 2
c) void
Return type of a method must be made void if it is not returning any value.
3. What will be the output of the following Java code?
class box
{
int width;
int height;
int length;
int volume;
void volume(int height, int length, int width)
{
volume = width*height*length;
}
}
class Prameterized_method
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
box obj = new box();
obj.height = 1;
obj.length = 5;
obj.width = 5;
obj.volume(3,2,1);
System.out.println(obj.volume);
}
}
Choose one option
a) 0
b) 1
c) 6
d) 25
Answer 3
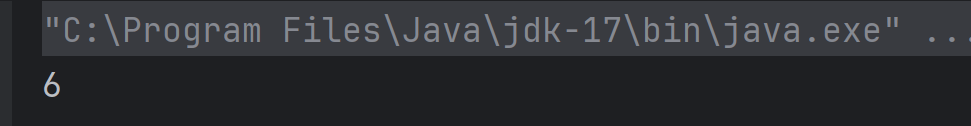
c) 6
The volume() method calculates the product of the parameters passed to it (3, 2, 1) and assigns it to the object’s volume field. Hence, the output is 3 * 2 * 1 = 6.
4. What will be the output of the following Java program?
class equality
{
int x;
int y;
boolean isequal()
{
return(x == y);
}
}
class Output
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
equality obj = new equality();
obj.x = 5;
obj.y = 5;
System.out.println(obj.isequal());
}
}
Choose one option
a) true
b) Runtime error
c) false
d) 0
Answer 4
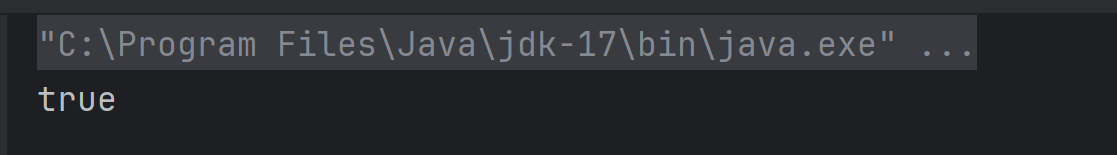
a) true
The method isequal() compares x and y using ==. Since both are set to 5, the condition x == y is true, so the method returns true, which gets printed.
5. Which of the following is a method having same name as that of it’s class?
a) finalize
b) delete
c) class
d) constructor
Answer 5
d) constructor
A constructor is a method that initializes an object immediately upon creation. It has the same name as that of class in which it resides.
6. What will be the output of the following Java program?
class overload
{
int x;
int y;
void add(int a)
{
x = a + 1;
}
void add(int a, int b)
{
x = a + 2;
}
}
class Overload_methods
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
overload obj = new overload();
int a = 0;
obj.add(6);
System.out.println(obj.x);
}
}
Choose one option
a) 5
b) 6
c) 7
d) Runtime error
Answer 6
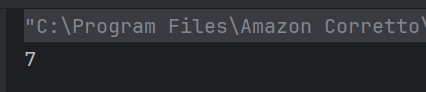
c) 7
Due to method overloading when the add() method is called with a single argument the value of x is set to argument passed i.e. 6 + 1 is returned. Hence the result is 7.
7. What will be the output of the following Java program?
class overload
{
int x;
int y;
void add(int a)
{
x = a + 1;
}
void add(int a , int b)
{
x = a + 2;
}
}
class Overload_methods
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
overload obj = new overload();
int a = 0;
obj.add(6, 7);
System.out.println(obj.x);
}
}
Choose one option
a) 6
b) 7
c) 8
d) 9
Answer 7
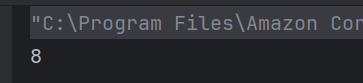
c) 8
Due to method overloading when the add() method is called with two arguments the value of x is set to the first argument passed i.e. 6 + 2 is returned. Hence the result is 8.
8. What will be the output?
class overload
{
int x;
double y;
void add(int a , int b)
{
x = a + b;
}
void add(double c , double d)
{
y = c + d;
}
overload()
{
this.x = 0;
this.y = 0;
}
}
class Overload_methods
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
overload obj = new overload();
int a = 2;
double b = 3.2;
obj.add(a, a);
obj.add(b, b);
System.out.println(obj.x + " " + obj.y);
}
}
Choose one option
a) 6 6
b) 6.4 6.4
c) 6.4 6
d) 4 6.4
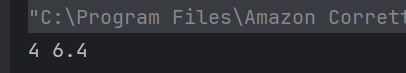
Answer 8
d) 4 6.4
For obj.add(a,a); ,the function in line number 4 gets executed and value of x is 4. For the next function call, the function in line number 7 gets executed and value of y is 6.4.
9. Which of the following best defines method overloading in Java?
a) Redefining a method with the same name and same parameters in child class.
b) Defining multiple methods with the same name but different parameter lists in the same class.
c) Using a method of the parent class in the child class.
d) Declaring a method as static multiple times.
Answer 9
b) Defining multiple methods with the same name but different parameter lists in the same class.
Overloading occurs when methods have the same name but different parameter lists (number or type).
10. Which of the following is NOT a valid way to overload methods in Java?
a) Different number of parameters.
b) Different types of parameters.
c) Different return types only.
d) Different order of parameters.
Answer 10
c) Different return types only
Overloading cannot be achieved by changing only the return type
11. What will be the output?
class area
{
int width;
int length;
int volume;
area()
{
width=5;
length=6;
}
void volume()
{
volume = width*length*height;
}
}
class cons_method
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
area obj = new area();
obj.volume();
System.out.println(obj.volume);
}
}
Choose one option
a) 0
b) 30
c) 1
d) error
Answer 11
d) error
Variable height is not defined

12. Which of the following allows method overriding?
Choose one option
a) Same method name and parameter list in subclass.
b) Same method name but different parameters in subclass.
c) Same method name but different return type in subclass.
d) Static methods in subclass.
Answer 12
a) Same method name and parameter list in subclass
Overriding requires the same method signature (name + parameters) in superclass and subclass
13. What is the default return type of a method in Java if not specified?
Choose one option
a) int
b) void
c) Object
d) Compilation error
Answer 13
d) Compilation error
Java requires an explicit return type. If omitted, it results in a compilation error.
14. What will be the output of the following code?
class test
{
int a;
int b;
test(int i, int j)
{
a = i;
b = j;
}
void meth(test o)
{
o.a *= 2;
o.b /= 2;
}
}
class Output
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
test obj = new test(10 , 20);
obj.meth(obj);
System.out.println(obj.a + " " + obj.b);
}
}
Choose one option
a) 20 10
b) 10 20
c) 20 40
d) 40 20
Answer 14
a) 20 10
Class objects are always passed by reference, therefore changes done are reflected back on original arguments. obj.meth(obj) sends object obj as parameter whose variables a & b are multiplied and divided by 2 respectively by meth() function of class test. a & b becomes 20 & 10 respectively.
15. What will be the result of this expression?
class Output {
public static int sum(int... x) {
int total = 0;
for (int num : x) {
total += num;
}
return total;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println(sum(10));
System.out.println(sum(10, 20));
System.out.println(sum(10, 20, 30));
System.out.println(sum(10, 20, 30, 40));
}
}
Choose one option
a) only sum(10)
b) only sum(10,20)
c) only sum(10) & sum(10,20)
d) all of the mentioned
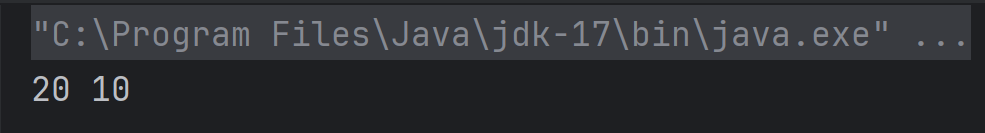
Answer 15
d) all of the mentioned
sum is a variable argument method and hence it can take any number as an argument.
16. What is the result of the following code snippet?
class Test
{
public void m1 (int i,float f)
{
System.out.println(" int float method");
}
public void m1(float f,int i)
{
System.out.println("float int method");
}
public static void main(String[]args)
{
Test test =new Test();
test.m1(20,20);
}
}
Choose one option
a) int float method
b) float int method
c) compile time error
d) run time error
Answer 16
c) compile time error
While resolving overloaded method, compiler automatically promotes if exact match is not found. But in this case, which one to promote is an ambiguity.

17. What will be printed?
class Test {
void show(int a) {
System.out.println("int method: " + a);
}
void show(double a) {
System.out.println("double method: " + a);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test obj = new Test();
obj.show(10); // Line 1
obj.show(10.5); // Line 2
obj.show('A'); // Line 3
}
}
Choose one option
a) int method: 10
double method: 10.5
int method: 65
b) int method: 10
double method: 10.5
double method: 65.0
c) Compilation error
d) Runtime error
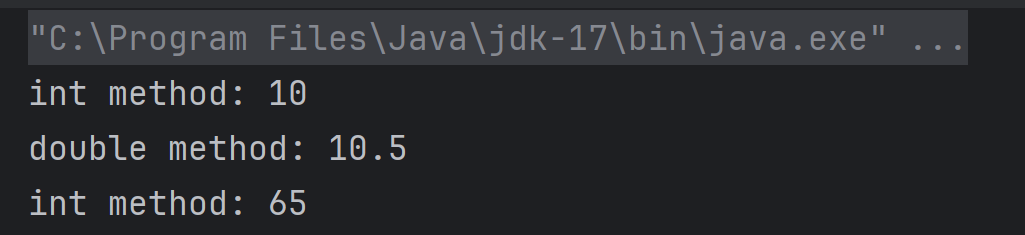
Answer 17
a) int method: 10
double method: 10.5
int method: 65
obj.show('A') → 'A' is a char (ASCII 65). Char can be promoted to int, so it calls show(int) and prints 65.
18. Which principle of OOP is demonstrated by method overriding?
a) Encapsulation
b) Abstraction
c) Polymorphism
d) Inheritance only
Answer 18
c) Polymorphism
19. If a class has two methods: void add(int a, int b) and int add(int x, int y), what happens?
a) Valid overloading
b) Compile-time error
c) Runtime error
d) Both methods are executed
Answer 19
b) Compile-time error
Same parameter list but different return type only results in compile-time error
20. What is the output of the following code?
class Derived
{
public void getDetails()
{
System.out.printf("Derived class ");
}
}
public class Test extends Derived
{
public void getDetails()
{
System.out.printf("Test class ");
super.getDetails();
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Derived obj = new Test();
obj.getDetails();
}
}
Choose one option
a) Test class Derived class
b) Derived class Test class
c) Runtime error
d) Compilation error
Answer 20
a) Test class Derived class
Since getDetails() is overridden in the Test class and super.getDetails() is called inside it, both methods are executed in order.
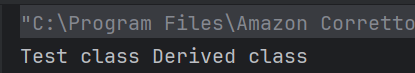
21. What is the output of this switch statement?
import java.io.IOException;
class Derived {
public void getDetails() throws IOException { // Line 4
System.out.println("Derived class");
}
}
public class Test extends Derived {
public void getDetails() throws Exception { // Line 10
System.out.println("Test class");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // Line 14
Derived obj = new Test();
obj.getDetails();
}
}
a) Compilation error due to line 4
b) Compilation error due to line 10
c) Compilation error due to line 14
d) All the above
Answer 21
b) Compilation error due to line 10
The exception thrown by the overriding method should not be new or more broader checked exception.

22. What will be the output of this while loop?
class Derived
{
protected final void getDetails()
{
System.out.println("Derived class");
}
}
public class Test extends Derived
{
protected final void getDetails()
{
System.out.println("Test class");
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Derived obj = new Derived();
obj.getDetails();
}
}
a) Derived class
b) Test class
c) Runtime error
d) Compilation error
Answer 22
d) Compilation error
Final and static methods cannot be overridden.

23. What is the output of the following if-else block?
public class Test
{
public int getData(String temp) throws IOException
{
return 0;
}
public int getData(String temp) throws Exception
{
return 1;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Test obj = new Test();
System.out.println(obj.getData("Happy"));
}
}
a) 0
b) 1
c) Compilation error
d) Runtime error
Answer 23
c) Compilation error
Methods that throws different exceptions are not overloaded as their signature are still the same.

24. Can constructors be overridden in Java?
a) Yes
b) No
c) Only in abstract classes
d) Only for default constructors
Answer 24
b) No
Constructors cannot be inherited, hence cannot be overridden.
25. Which of these statements is correct?
a) Overloading is runtime polymorphism, overriding is compile-time.
b) Overloading is compile-time polymorphism, overriding is runtime.
c) Both overloading and overriding are compile-time polymorphism.
d) Both are runtime polymorphism.
Answer 25
b) Overloading is compile-time polymorphism, overriding is runtime.
We would love to hear from you! Please leave your comments and share your scores in the section below
Java – Multiple Choice Questions and Answers – Basic Java
Last Updated On
Welcome to the Java Quiz! This blog post features 25 multiple-choice questions that explore basic concepts of Java.
1. Which statement is true about Java?
a) Java is a sequence-dependent programming language
b) Java is a code dependent programming language
c) Java is a platform-dependent programming language
d) Java is a platform-independent programming language
Answer 1
d) Java is a platform-independent programming language
2. Which component is used to compile, debug and execute the java programs?
a) JRE
b) JIT
c) JDK
d) JVM
Answer 2
c) JDK
JDK is a core component of Java Environment and provides all the tools, executables and binaries required to compile, debug and execute a Java Program.
3. What will be the output of the following Java code?
class increment {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int g = 3;
System.out.print(++g * 8);
}
}
Choose one option
a) 32
b) 33
c) 24
d) 25
Answer 3
a) 32
Operator ++ has more preference than *, thus g becomes 4 and when multiplied by 8 gives 32.
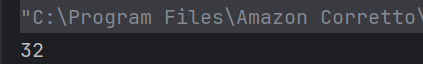
4. What will be the output of the following Java program?
class variable_scope
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int x;
x = 5;
{
int y = 6;
System.out.print(x + " " + y);
}
System.out.println(x + " " + y);
}
}
Choose one option
a) Compilation error
b) Runtime error
c) 5 6 5 6
d) 5 6 5
Answer 4
a) Compilation error
Second print statement doesn’t have access to y , scope y was limited to the block defined after initialization of x.
5. How do you insert COMMENTS in Java code?
a) /* This is a comment
b) # This is a comment
c) // This is a comment
d) None
Answer 5
c) // This is a comment
6. What will be the output of the following Java program?
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 5;
System.out.println(x++);
}
}
Choose one option
a) 5
b) 6
c) Compilation error
d) Runtime error
Answer 6
a) 5
x++ is a post-increment operator, so the current value of x (5) is printed first, and then x is incremented.
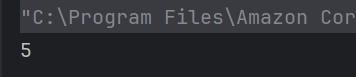
7. What will be the output of the following Java program?
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "Java";
String s2 = new String("Java");
System.out.println(s1 == s2);
}
}
Choose one option
a) true
b) false
c) Compilation error
d) Runtime error
Answer 7
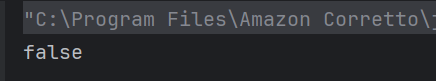
b) false
== compares references, and s1 and s2 refer to different objects. Use .equals() to compare string contents.
8. What will be the output?
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(10 + 20 + "30");
}
}
Choose one option
a) 3030
b) 102030
c) 30
d) None
Answer 8
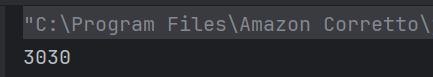
a) 3030
10 + 20 is 30 (integer addition), then 30 + “30” converts 30 to string and concatenates to “30”, resulting in “3030”.
9. Which of the following data types is NOT primitive in Java?
a) int
b) boolean
c) String
d) char
Answer 9
c) String
String is an object, not a primitive type.
10. What is the default value of a boolean variable in Java?
a) true
b) false
c) null
d) 0
Answer 10
b) false
Default value of boolean is false
11. What will be the output?
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
System.out.println(a > b ? a : b);
}
}
Choose one option
a) 10
b) 20
c) true
d) false
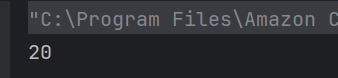
Answer 11
b) 20
Ternary operator returns a if a > b else returns b.
12. What does the % operator do in Java
Choose one option
a) Division
b) Modulus – gives remainder
c) Multiplication
d) Raises to power
Answer 12
b) Modulus – gives remainder
% returns the remainder after division.
13. Which operator has the highest precedence in Java?
Choose one option
a) +
b) *
c) =
d) ()
Answer 13
d) ()
Parentheses have the highest precedence to control evaluation order.
14. What will be the output of the following code?
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 5;
System.out.println(a + b * 2);
}
}
Choose one option
a) 30
b) 20
c) 25
d) 15
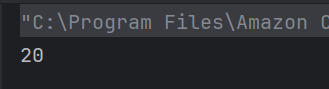
Answer 14
b) 20
According to operator precedence, multiplication is done before addition: 5 * 2 = 10, then 10 + 10 = 20.
15. What will be the result of this expression?
int x = 10;
int y = 3;
System.out.println(x / y);
Choose one option
a) 3.333
b) 3
c) 4
d) Compilation error
Answer 15
b) 3
Integer division truncates the decimal part. So 10 / 3 = 3.
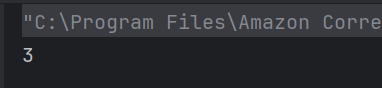
16. What is the result of the following code snippet?
int a = 5;
System.out.println(a++);
System.out.println(a);
Choose one option
a) 5 5
b) 5 6
c) 6 5
d) 6 6
Answer 16
b) 5 6
a++ prints 5 (post-increment), then a becomes 6.
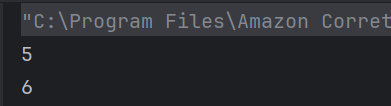
17. What will be printed?
int x = 4;
System.out.println((x > 3) || (x < 2));
Choose one option
a) true
b) false
c) Compilation error
d) Runtime error
Answer 17
a) true
x > 3 is true, so || (logical OR) returns true without checking the second condition (short-circuiting).
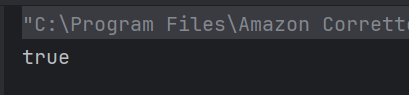
18. Which keyword is used to import a package from the Java API library?
a) import
b) package
c) getlib
d) lib
Answer 18
a) import
19. Which of these is the correct way to declare a method that returns an integer?
a) public void method() {}
b) public int method() { return 1; }
c) public int method() {}
d) public method() { return 1; }
Answer 19
b) public int method() { return 1; }
Method declared to return int must return an int value.
20. What is the output of the following code?
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 5;
if (x < 5)
System.out.println("Less");
else if (x == 5)
System.out.println("Equal");
else
System.out.println("More");
}
}
Choose one option
a) Less
b) Equal
c) More
d) Compilation error
Answer 20
b) Equal
x == 5, so the second condition matches and “Equal” is printed.
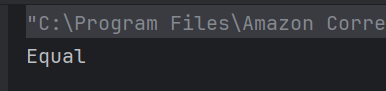
21. What is the output of this switch statement?
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 2;
switch(num + 1) {
case 1: System.out.println("One");
case 2: System.out.println("Two");
case 3: System.out.println("Three");
default: System.out.println("Default");
}
}
}
Choose one option
a) Three
b) Three Default
c) Two Default
d) Two Three Default
Answer 21
b) Three Default
switch(3) matches case 3, no break used, so it also executes default.
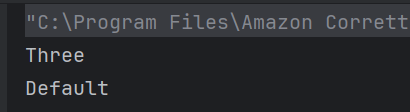
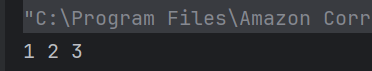
22. What will be the output of this while loop?
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 1;
while (i <= 3) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
i++;
}
}
}
Choose one option
a) 1 2 3
b) 1 2 3 4
c) Infinite loop
d) 1 2
Answer 22
a) 1 2 3
Loop runs while i <= 3, printing 1 to 3
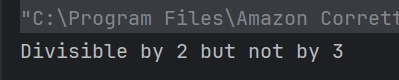
23. What is the output of the following if-else block?
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 4;
if (x % 2 == 0)
if (x % 3 == 0)
System.out.println("Divisible by 6");
else
System.out.println("Divisible by 2 but not by 3");
}
}
Choose one option
a) Divisible by 6
b) Divisible by 3
c) Divisible by 2 but not by 3
d) Compilation error
Answer 23
c) Divisible by 2 but not by 3
4 is divisible by 2 but not by 3
24. Which statement is used to stop a loop?
a) break
b) return
c) exit
d) stop
Answer 24
a) break
25. Which of these are selection statements in Java?
a) break
b) continue
c) for()
d) if()
Answer 25
d) if()
Continue and break are jump statements, and for is a looping statement.
We would love to hear from you! Please leave your comments and share your scores in the section below
SpringBoot – Multiple Choice Questions and Answers – MCQ1
Last Updated On
Welcome to the SpringBoot Quiz! This blog post features 25 multiple-choice questions that explore the concepts of SpringBoot.
1. What is the primary feature of Spring Boot?
a) Simplifies data access
b) Automates code generation
c) Simplifies project setup
d) Enhances UI design
Answer 1
c) Simplifies project setup
Spring Boot simplifies the development of new Spring applications through convention over configuration and automatic setup.
2. Which annotation is used to mark a Spring Boot application entry point?
a) @Configuration
b) @SpringBootApplication
c) @Component
d) @RestController
Answer 2
b) @SpringBootApplication
The @SpringBootApplication annotation is used to mark the main class of a Spring Boot application.
3. The @SpringBootApplication annotation is used to mark the main class of a Spring Boot application.
a) @Component
b) @EnableConfiguration
c) @Configuration
d) @EnableAutoConfiguration
Answer 3
d) @EnableAutoConfiguration
4. What does @SpringBootApplication annotation include?
a) @ComponentScan
b) @EnableAutoConfiguration
c) @SpringBootConfiguration
d) All of the above
Answer 4
d) All of the above
5. Which starter is used for Spring Boot Rest API applications?
a) spring-boot-starter-jdbc
b) spring-boot-starter-web
c) spring-boot-starter-data-jpa
d) spring-boot-starter-security
Answer 5
b) spring-boot-starter-web
The `spring-boot-starter-web` starter includes the necessary dependencies for developing web applications using Spring MVC. It provides essential features for building RESTful APIs, such as HTTP request handling, JSON serialization and deserialization, and web server capabilities.
6. Which starter is used for Spring Boot web applications?
a) spring-boot-starter-jdbc
b) spring-boot-starter-web
c) spring-boot-starter-data-jpa
d) spring-boot-starter-security
Answer 6
b) spring-boot-starter-web
This starter provides the necessary dependencies to develop web applications using Spring MVC.
7. What is auto-configuration in Spring Boot?
a) Automatic setup of the JVM
b) Automatic import of all Java libraries c) Automatic configuration of beans based on classpath settings
d) Automatic update of Spring Boot versions
Answer 7
c) Automatic configuration of beans based on classpath settings
Auto-configuration refers to Spring Boot’s ability to automatically set up application context based on dependencies available in the classpath.
8. What does the following code snippet achieve?
@Bean
public MyService myService() {
return new MyServiceImpl();
}
a) It creates a prototype bean.
b) It registers a singleton bean.
c) It enables caching.
d) It defines a configuration class.
Answer 8
b) It registers a singleton bean.
The @Bean annotation registers a singleton bean in the Spring application context.
9. Which configuration file is commonly used to define properties in a Spring Boot application?
a) application.yml
b) config.properties
c) spring-config.xml
d) web.xml
Answer 9
a) application.yml
The application.yml file is commonly used for defining configuration properties in a Spring Boot application.
10. What is the purpose of the `spring-boot-starter-test` dependency?
a) To start the application faster
b) To provide a built-in testing framework for JUnit, Mockito, etc.
c) To run performance benchmarks
d) To manage database migrations
Answer 10
b) To provide a built-in testing framework for JUnit, Mockito, etc.
This starter provides testing libraries and frameworks for unit tests and mocking, making testing seamless in Spring Boot applications.
11. Which of the following is the correct ?
@RestController
public class ArticleController {
@GetMapping("/articles")
public List<Article> getAllArticles() {
return articleService.findAll();
}
}
Choose one option
a) The method returns a JSON representation of all articles.
b) The method does not return anything.
c) The endpoint is configured for POST requests.
d) The controller does not require a service.
Answer 11
a) The method returns a JSON representation of all articles.
The @GetMapping annotation defines a GET endpoint that returns a JSON representation of all articles.
12. What does the @Value annotation do in the following code?
@Value("${my.api.key}")
private String apiKey;
Choose one option
a) It injects a bean
b) It maps an environment variable
c) It retrieves a property value from application.properties
d) It initializes a method
Answer 12
c) It retrieves a property value from application.properties
The @Value annotation is used to inject a property value from the application.properties file into a field.
13. What will happen if you try to access a bean that is defined with a prototype scope?
@Bean
@Scope("prototype")
public Article article() {
return new Article();
}
Choose one option
a) The same instance is returned every time
b) A new instance is created for each request
c) An exception is thrown
d) The application will not start
Answer 13
b) A new instance is created for each request
A prototype-scoped bean creates a new instance every time it is requested from the application context
14. Which embedded server does Spring Boot use by default for web applications?
Choose one option
a) JBoss
b) WebLogic
c) Tomcat
d) Jetty
Answer 14
c) Tomcat
Spring Boot initially sets Tomcat as its default embedded server, which you can switch to other options like Jetty or Undertow if needed.
15. Which annotation is used to handle exceptions globally in a Spring Boot application?
Choose one option
a) @Controller
b) @RestControllerAdvice
c) @ExceptionHandler
d) @Service
Answer 15
b) @RestControllerAdvice
The @RestControllerAdvice annotation is used to define global exception handling for REST controllers.
16. Given the following configuration, what is the purpose of the @Profile annotation?
@Profile("dev")
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
return new H2DataSource();
}
Choose one option
a) It marks a bean as singleton
b) It specifies that the bean should only be loaded in the ‘dev’ profile
c) It creates a prototype bean
d) It initializes the application context
Answer 16
b) It specifies that the bean should only be loaded in the ‘dev’ profile
The @Profile annotation indicates that the dataSource bean should only be instantiated when the ‘dev’ profile is active.
17. What does the ‘@RestController’ annotation do?
Choose one option
a) Enables automatic logging Configurator
b) Combines @Controller and @ResponseBody annotations
c) Configures a package
d) Sets the application port
Answer 17
b) Combines @Controller and @ResponseBody annotations
The @RestController annotation is used in Spring MVC applications to handle RESTful web services, simplifying the controller implementation.
18. What dependency is required for embedding an H2 database in a Spring Boot application?
a) spring-boot-starter-data-mongo
b) spring-boot-starter-jdbc
c) spring-boot-starter-data-jpa
d) h2
Answer 18
d) h2
The H2 database is an in-memory database, and its dependency needs to be included in the pom.xml or build.gradle file to be used.
19. What is the function of ‘spring-boot-starter-parent’ in a Maven-based Spring Boot project?
a) To hold all project dependencies
b) To provide default project structure
c) To provide default configuration settings and inherit dependency management
d) To define the project version
Answer 19
c) To provide default configuration settings and inherit dependency management
spring-boot-starter-parent provides default configurations and helps manage dependencies, versions, and default plugins for the project.
20. How can you define a scheduled task in a Spring Boot application?
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 2000)
public void reportCurrentTime() {
System.out.println("Current time: " + new Date());
}
Choose one option
a) It runs every 2 seconds
b) It is triggered by an event
c) It executes only once
d) It runs at application startup only
Answer 20
a) It runs every 2 seconds
21. Which of the following layers is not part of a typical Spring Boot application?
a) DAO layer
b) Logger layer
c) Service layer
d) Controller layer
Answer 21
b) Logger layer
Common layers in a Spring Boot application include the DAO, Service, and Controller layers; logging is a cross-cutting concern, not a separate layer.
22. What is the default package used in a Spring Boot project if none is specified?
a) main.java
b) default.package
c) org.springframework.boot
d) The root package specified in the @SpringBootApplication class
Answer 22
d) The root package specified in the @SpringBootApplication class
The @SpringBootApplication annotation triggers auto-configuration only within its package and sub-packages, so it acts as the root package if not specified.
23. How can you disable the default web server in a Spring Boot application? build process?
a) Set server.enabled: false in application.properties
b) Set server.port: 0 in application.properties
c) Use the @DisableWebServer annotation
d) Use a command-line argument to set the server port to 0
Answer 23
b) Set server.port: 0 in application.properties
Setting the server port to 0 effectively disables the embedded web server.
24. How can you switch from using the default Tomcat server to Jetty in a Spring Boot application?
a) Modify server.xml
b) Change the server property in application.properties
c) Exclude Tomcat and include Jetty dependencies in pom.xml
d) Use @EnableJetty annotation
Answer 24
c) Exclude Tomcat and include Jetty dependencies in pom.xml
Tomcat is included by default, so you must exclude it and add Jetty’s dependencies to switch the server.
25. What is Actuator in Spring Boot?
a) A tool to monitor and manage applications
b) A GUI design tool
c) A security framework
d) A configuration tool
Answer 25
a) A tool to monitor and manage applications
Spring Boot Actuator provides various endpoints for monitoring and managing the application, such as health checks and metrics.
We would love to hear from you! Please leave your comments and share your scores in the section below
Docker – Advance Level – Multiple Choice Questions and Answers – MCQ1
Last Updated On
Welcome to the Docker Quiz! This blog post features 25 multiple-choice questions that explore advance concepts of Docker.
1. How do Docker containers achieve process isolation on the host system?
a) Virtual Machines
b) Hypervisors
c) Namespaces and cgroups
d) Dedicated resources
Answer 1
c) Namespaces and cgroups
Namespaces are a feature of the Linux kernel that provide isolation for resources such as process IDs, network, user IDs, and file systems.
Docker uses cgroups to allocate resources efficiently among containers running on the same host, preventing one container from consuming excessive resources and impacting others.
2. What is the purpose of a Dockerfile?
a) To create virtual machines
b) To optimize application code
c) To store environment variables
d) To define and build Docker images
Answer 2
d) To define and build Docker images
A Dockerfile contains a set of instructions to define and build a Docker image, specifying dependencies, configuration, and application code.
3. What does the Dockerfile contain?
a) Compiled source code
b) Docker images
c) Binary data
d) Instructions for building a Docker image
Answer 3
Instructions for building a Docker image
A Dockerfile is a text file that contains a set of instructions used to automatically build a Docker image. These instructions define everything needed to assemble the image, such as: Base Image, Package Installation, Execution Commands, File Operations
4. How many types of volumes are there in Docker?
a) 3
b) 2
c) 4
d) 5
Answer 4
b) 2
There are two types of volumes in docker – Named volumes and Bind Mounts
5. Which of the following volume type allows you to share a directory from the host’s filesystem into the container?
a) Named volumes
b) Bind Mounts
Answer 5
b) Bind Mounts
The bind mount volume type allows you to share a directory from the host’s filesystem into the container.
6. In which of the following volume type docker chooses the host location?
a) Named volumes
b) Bind Mounts
Answer 6
a) Named volumes
In the Named volume type docker chooses the host location, whereas you decide the host location in the bind mount type of volume.
7. Which command is used to remove unused Docker objects, such as containers and images?
a) docker prune
b) docker clean
c) docker system prune
d) docker remove
Answer 7
c) docker system prune
8. To list all the networks linked with Docker on the host, the ____ command is used.
a) docker network list
b) docker network ls
c) docker ls
d) network ls
Answer 8
b) docker network ls
To list all the networks linked with Docker on the host, the docker network ls command is used.
9. What is port binding in Docker?
a) Binding environment variables
b) Assigning internal ports to external ones
c) Binding memory resources
d) Binding IP addresses to containers
Answer 9
b) Assigning internal ports to external ones
Port binding in Docker refers to the process of linking internal ports within a Docker container to external ports on the host system. This allows applications running inside the container to communicate with external networks or systems
10. Which of the following is a tool that was built to assist define and distribute multi-container applications?
a) Docker setup
b) Docker compose
c) Docker notify
Answer 10
b) Docker compose
Docker Compose is a tool that was built to assist define and distribute multi-container applications.
11. Which of the following command is used to display the statistics of a running container?
Choose one option
a) Docker statistics
b) Stats
c) Docker statics
d) Docker stats
Answer 11
d) Docker stats
The stats command is used to display the statistics of a running container.
12. Which command is used to view the logs of a running container?
Choose one option
a) docker view [container ID]
b) docker logs [container ID]
c) docker inspect [container ID]
d) docker output [container ID]
Answer 12
b) docker logs [container ID]
13. What is the default Docker network mode?
Choose one option
a) host
b) none
c) bridge
d) overlay
Answer 13
c) bridge
14. After making changes to a running container, how can you save those changes into an image?
Choose one option
a) docker save
b) docker commit
c) docker store
d) docker snapshot
Answer 14
b) docker commit
15. What does the `ENTRYPOINT` directive do in a Dockerfile?
a) Sets an environment variable
b) Specifies the command that will run on container start
c) Exposes a port
d) Confirms the image build
Answer 15
b) Specifies the command that will run on container start
16. What is the function of the `Dockerfile` directive `COPY`?
Choose one option
a) Copies files and directories from localhost to the image
b) Moves data between volumes
c) Copies data between containers
d) Duplicates Docker images
Answer 16
a) Copies files and directories from localhost to the image
17. What is the syntax used to specify base image in a Dockerfile?
Choose one option
a) FROM [image name]
b) BASE [image name]
c) SOURCE [image name]
d) INITIAL [image name]
Answer 17
a) FROM [image name]
18. What is the primary function of the .dockerignore file?
Choose one option
a) To list all images to be pulled from the Docker Hub
b) To specify commands to run inside a container
c) To prevent certain files and directories from being copied into an image
d) To provide metadata about a Docker image
Answer 18
c) To prevent certain files and directories from being copied into an image
The .dockerignore file allows users to exclude files and directories from being copied to the image during the build process, much like .gitignore does for git repositories.
19. In a docker-compose.yml file, what is the function of the depends_on key?
a) Specifies the base images for services
b) Specifies the build context for services
c) Specifies the order in which services are started
d) Specifies the network links between services
Answer 19
c) Specifies the order in which services are started
In a docker-compose.yml file, the depends_on key indicates the order in which services should be started. A service with a depends_on key will not start until the services it depends on have been started.
20. What is the primary purpose of Docker Swarm?
a) Image version management
b) Multi-host container orchestration
c) Container storage optimization
d) Automated container build pipeline
Answer 20
b) Multi-host container orchestration
Docker Swarm is a native clustering and orchestration tool for Docker. It allows you to create and manage a swarm of Docker nodes and orchestrate services across multiple hosts.
21. What command initializes a node as a Docker Swarm manager?
a) docker swarm init
b) docker swarm start
c) docker swarm create
d) docker swarm manager
Answer 21
a) docker swarm init
The docker swarm init command initializes the current node as a Docker Swarm manager, which manages the infrastructure of a swarm.
22. How can you inspect the details of a Docker network?
a) docker network view NETWORK_NAME
b) docker network show NETWORK_NAME
c) docker network detail NETWORK_NAME
d) docker network inspect NETWORK_NAME
Answer 22
d) docker network inspect NETWORK_NAME
The docker network inspect command is used to display detailed information about a network.
23. Which command creates a Docker volume?
a) docker storage create
b) docker add volume
c) docker volume create
d) docker create
Answer 23
c) docker volume create
The docker volume create command creates a new Docker volume for persistent storage.
24. Why is Docker commonly integrated with CI/CD pipelines?
a) Consistent environments across testing and production
b) Easier dependency management
c) Faster build and deployment times
d) All of the mentioned
Answer 24
d) All of the mentioned
Docker integration with CI/CD ensures faster deployments, dependency management, and environment consistency.
25. Why is Kubernetes often paired with Docker?
a) For debugging local machines
b) For virtualizing operating systems
c) For orchestrating large-scale container deployments
d) For building individual containers
Answer 25
c) For orchestrating large-scale container deployments
Kubernetes orchestrates, deploys, and manages containers at scale, complementing Docker’s container creation capabilities.
We would love to hear from you! Please leave your comments and share your scores in the section below
Docker – Basic Level – Multiple Choice Questions and Answers – MCQ1
Last Updated On
Welcome to the Docker Quiz! This blog post features 25 multiple-choice questions that explore basic concepts of Docker.
1. What is Docker?
a) A Hypervisor
b) An Operating System
c) A Virtual Machine
d) A Containerization platform
Answer 1
d) A Containerization platform
Docker is a containerization platform that allows developers to package and distribute applications and their dependencies in isolated containers.
2. Which of the following is the core component of Docker?
a) Docker CLI
b) Docker Engine
c) Docker Server
d) Docker Hypervisor
Answer 2
b) Docker Engine
Docker Engine is the core component of Docker. It is responsible for creating, managing, and running Docker containers.
3. Which command is used to check the version of Docker?
a) docker details
b) docker info
c) docker version
d) docker –version
Answer 3
d) docker –version
4. What is a Docker Container?
a) A network service
b) A lightweight executable package
c) An Operating System kernel
d) A Virtual Machine
Answer 4
b) A lightweight executable package
A Docker container is a lightweight, standalone executable package containing everything needed to run a piece of software, including code, runtime, libraries, and system tools.
5. Which command creates and starts a new container?
a) docker create
b) docker start
c) docker run
d) docker build
Answer 5
c) docker run
The command docker run creates and starts a new container from a specified Docker image. It combines the functions of the docker create and docker start commands into a single step, allowing the user to instantiate and execute a container immediately.
6. Which of the following command you will use to list your containers?
a) docker list
b) docker show
c) docker ps
d) docker display
Answer 6
c) docker ps
The docker ps command lists all running Docker containers, along with various details like container ID, image name, creation time, and so on.
7. Which of the following statement is correct?
a) To remove a container, you first need to stop it
b) You can directly remove a container, without stopping it.
Answer 7
a) To remove a container, you first need to stop it
To remove a container, you first need to stop it. Once it has stopped, you can remove it.
8. How do you stop a running Docker container?
a) docker pause
b) docker terminate
c) docker end
d) docker stop
Answer 8
d) docker stop
The docker stop command stops a running container, gracefully terminating its processes.
9. What is a Docker Image?
a) A running container
b) A snapshot of an application and its dependencies
c) A configuration file
d) A virtual hard drive
Answer 9
b) A snapshot of an application and its dependencies
A Docker Image contains all the necessary components to run an application, including code, libraries, dependencies, and runtime.
10. Which command is used to create a new Docker image?
a) docker build
b) docker pull
c) docker run
d) docker commit
Answer 10
a) docker build
The docker build command is used to build a new image from a Dockerfile and a “context”. The context is the set of files in a specified directory or URLs that the image is built from.
11. Which command pulls an image from Docker Hub?
Choose one option
a) docker get
b) docker fetch
c) docker pull
d) docker download
Answer 11
c) docker pull
The docker pull command is used to pull or download a Docker image from a registry like Docker Hub.
12. How can you remove a Docker image?
Choose one option
a) docker remove
b) docker delete
c) docker rm
d) docker rmi
Answer 12
d) docker rmi
The docker rmi command is used to remove a Docker image from the system.
13. How can you run a command inside an existing Docker container?
Choose one option
a) docker exec
b) docker attach
c) docker run
d) docker enter
Answer 13
a) docker exec
The docker exec command allows you to run commands inside an existing container. For example, docker exec -it container_id /bin/bash would open a bash shell inside the container with ID container_id.
14. What is Docker Compose?
Choose one option
a) A scripting language for Docker
b) A continuous integration tool for Docker
c) A tool for defining and running multi-container Docker applications
d) A Docker CLI plugin
Answer 14
c) A tool for defining and running multi-container Docker applications
Docker Compose is a tool for defining and running multi-container Docker applications. With Compose, you define the services, networks, and volumes in a single docker-compose.yml file and then use docker-compose up to start the entire application stack.
15. What is the difference between a Docker Container and a Virtual Machine?
Choose one option
a) Containers are slower than VMs
b) VMs run on hardware, while containers do not
c) Containers share the host OS kernel, while VMs have their own kernel
d) Containers are heavier than VMs
Answer 15
c) Containers share the host OS kernel, while VMs have their own kernel
Containers share the host OS kernel, whereas VMs have their own OS kernel, making containers more lightweight and efficient.
16. Which of the following is the default registry used by Docker?
Choose one option
a) Kubernetes Hub
b) Container Store
c) Docker Hub
d) Image Hub
Answer 16
c) Docker Hub
Docker Hub is the default public registry where Docker images are stored and shared. You can pull and push images from and to Docker Hub.
17. What are the key components of Docker architecture?
Choose one option
a) Docker Manager, Docker Processor, Docker Configurator
b) Docker Master, Docker Node, Docker Registry
c) Docker Engine, Docker CLI, Docker Daemon
d) Docker Kernel, Docker Service, Docker Network
Answer 17
c) Docker Engine, Docker CLI, Docker Daemon
18. What is the role of the Docker Daemon?
a) It stores operating system data
b) It manages containers, images, and networks
c) It interacts with the user interface
d) It only handles logs
Answer 18
b) It manages containers, images, and networks
19. What is a Docker Registry?
a) A network router
b) A local storage system
c) A virtual machine host
d) A repository for storing and sharing Docker images
Answer 19
d) A repository for storing and sharing Docker images
A Docker Registry is a storage system where you can store, share, and retrieve Docker images. Docker Hub is a popular example.
20. What is the primary purpose of the Docker Engine?
Choose one option
a) To provide a graphical visualization of containers
b) To build and run containers
c) To manage databases inside containers
d) To interface with Kubernetes
Answer 20
b) To build and run containers
21. Which of the following commands logs you into Docker Hub from the CLI?
a) docker login
b) docker auth
c) docker sign-in
d) docker connect
Answer 21
a) docker login
The docker login command allows users to log into Docker Hub or any other Docker registry from the command-line interface.
22. What does the -d flag do in the docker run command?
a) Deletes the container
b) Displays detailed information
c) Detaches the container (runs in the background)
d) Downloads the latest image
Answer 22
c) Detaches the container (runs in the background)
23. How do you specify a Dockerfile other than the default “Dockerfile” during the build process?
a) Use –filename option
b) Use –source option
c) Use –file option
d) Use –dockerfile option
Answer 23
c) Use –file option
The –file or -f option allows users to specify a different Dockerfile than the default one. For example, docker build –f MyDockerfile .
24. Which CLI command shows detailed information about a container?
a) docker inspect
b) docker show
c) docker details
d) docker info
Answer 24
a) docker inspect
docker inspect provides detailed information about containers, including network configurations, status, and metadata.
25. Once the container has stopped, which of the following command you will use to remove a container?
a) Docker remove
b) Docker Destroy
c) Docker rm
d) Docker del
Answer 25
c) Docker rm
When the container has stopped, use the docker rm command to remove it.
We would love to hear from you! Please leave your comments and share your scores in the section below
JUnit – Multiple Choice Questions and Answers – MCQ1
Welcome to the JUnit Quiz! This blog post features 25 multiple-choice questions that explore concepts of JUnit.
1. What is JUnit primarily used for?
Select the best answer
a) Debugging
b) Profiling
c) Unit Testing
d) Continuous Integration
Answer 1
c) Unit Testing
JUnit is a testing framework primarily designed for unit testing in the Java programming language.
2. Which of the following is not correct about JUnit?
Choose one option
a) Junit provides test runners for running test
b) Junit cannot be run automatically
c) Junit is the open-source framework
d) Junit provides an annotation to identify test methods
Answer 2
b) Junit cannot be run automatically
JUnit test can be run automatically and they check their own results and provide immediate feedback.
3. Which annotation is used to indicate a method as a test method in JUnit?
Choose one option
a) @Testify
b) @TestCase
c) @Testing
d) @Test
Answer 3
d) @Test
The @Test annotation is used to mark a method as a test method in JUnit.
4. JUnit test files are written in files with which file extension?
Choose one option
a) .unit
b) .java
c) .test
d) .junit
Answer 4
b) .java
JUnit test files are regular java files with special methods which are referenced via annotations.
5. Which of the following is NOT a core feature of JUnit?
Choose one option
a) Test suites
b) Test runners
c) Test profilers
d) Test listeners
Answer 5
c) Test profilers
While JUnit provides support for suites, runners, and listeners, it does not have an in-built profiler.
6. If a JUnit test method throws an exception, what will be the outcome?
a) Success
b) Compilation error
c) Failure
d) Ignored
Answer 6
c) Failure
If a JUnit test method throws an exception, the test is considered a failure.
7. How do you specify that a particular test method should be ignored during execution?
a) @IgnoreTest
b) @Skip
c) @Ignore
d) @Avoid
Answer 7
c) @Ignore
In JUnit, you can specify that a test method should be ignored during execution by using the `@Ignore` annotation. This annotation tells the JUnit framework to skip the execution of the annotated test method.
8. Which JUnit version introduced the use of annotations?
Choose one option
a) JUnit 3
b) JUnit 4
c) JUnit 5
d) JUnit 2
Answer 8
b) JUnit 4
9. Which of the following annotation causes that method run once before any of the test methods in the class?
Choose one option
a) @Test
b) @Before
c) @BeforeClass
d) @AfterClass
Answer 9
c) @BeforeClass
Annotating a public static void method with @BeforeClass causes it to be run once before any of the test methods in the class.
10. The @Test annotation tells JUnit that the public void method to which it is attached can be run as a test case.
Choose one option
a) True
b) False
Answer 10
a) True
The @Test annotation tells JUnit that the public void method to which it is attached can be run as a test case.
11. What does the @AfterEach annotation signify?
Choose one option
a) It runs after all test methods in the current test class.
b) It runs before each test method.
c) It runs after each test method.
d) It runs before all test methods in the current test class.
Answer 11
c) It runs after each test method.
The @AfterEach annotation is used to denote a method that should be executed after each test method in the current class.
12. Which JUnit annotation allows parameterized tests?
Choose one option
a) @Parameters
b) @ParameterizedTest
c) @TestWithParams
d) @DataDrivenTest
Answer 12
b) @ParameterizedTest
13. Which annotation is used to run a piece of code before each test method?
Choose one option
a) @Before
b) @Setup
c) @Init
d) @PreTest
Answer 13
a) @Before
The @Before annotation allows a specific method to run before each test method, often used to set up test preconditions.
14. What is the purpose of the @After annotation in JUnit?
Choose one option
a) To clean up resources after all tests
b) To execute tests in sequence
c) To run code after each test method
d) To initialize test data
Answer 14
c) To run code after each test method
15. In which version of JUnit was the Jupiter API introduced?
Choose one option
a) JUnit 3
b) JUnit 4
c) JUnit 5
d) JUnit 2
Answer 15
c) JUnit 5
The Jupiter API, which provides a new programming and extension model for writing tests, was introduced in JUnit 5.
16. What is the purpose of the @Test(expected = Exception.class) annotation?
Choose one option
a) To prevent exception throwing
b) To specify an exception that should be thrown
c) To log exceptions
d) To convert exceptions
Answer 16
b) To specify an exception that should be thrown
This indicates that a test is expected to throw a specific exception, validating error handling.
17. In JUnit, what does the fail() method do when encountered in a test case?
Choose one option
a) Automatically succeeds the test
b) Disregards the error and continues
c) Causes the test to fail unconditionally
d) Logs a warning message but passes
Answer 17
c) Causes the test to fail unconditionally
The fail() method immediately triggers a test failure when executed.
18. How are test cases grouped in JUnit?
Choose one option
a) Using suites
b) With collections
c) Through category annotations
d) By file naming conventions
Answer 18
a) Using suites
JUnit facilitates grouping test cases via test suites, enabling batch execution of related tests.
19. What JUnit feature allows us to assume certain preconditions for the execution of a test?
a) Conditional test execution
b) Expectations
c) Assumptions
d) PreTestConditions
Answer 19
c) Assumptions
Assumptions in JUnit, via the Assume class, can determine whether a test should proceed based on certain preconditions.
20. How do you specify a timeout for a test method in JUnit?
Choose one option
a) Using the timeout attribute in the @Test annotation.
b) By calling the setTimeout() method on the test instance.
c) Using a separate @Timeout annotation before the test method.
d) By wrapping the test method inside a TimeLimited block.
Answer 20
a) Using the timeout attribute in the @Test annotation.
21. Which of the following assertions checks that a condition is true?
a) assertThat()
b) assertEquals()
c) assertTrue()
d) assertNotNull()
Answer 21
c) assertTrue()
22. What functionality does the assertNotNull() method offer?
a) Asserts an object is not null
b) Checks object equality
c) Verifies object types
d) Disallows object creation
Answer 22
a) Asserts an object is not null
assertNotNull() ensures that a specific object reference is not null.
23. Which keyword is used to denote a test case should not execute in JUnit?
a) @SkipTest
b) @Disabled
c) @Postpone
d) @Cancel
Answer 23
b) @Disabled
@Disabled annotation can be added to avoid running specific test cases without deletion.
24. Which version of JUnit introduced lambda functions for assertions?
a) JUnit 3
b) JUnit 4
c) JUnit 5
d) JUnit 6
Answer 24
c) JUnit 5
25. Which of the following is NOT a type of assertion provided by JUnit?
a) Timeout assertions
b) Conditional assertions
c) Exception assertions
d) Repetition assertions
Answer 25
d) Repetition assertions
We would love to hear from you! Please leave your comments and share your scores in the section below
PyTest Multiple Choice Questions – MCQ2
Last Updated On
Welcome to the Pytest Framework Quiz! This blog post features 25 multiple-choice questions that explore concepts of Pytest Framework.
1. What is pytest primarily used for?
Select the best answer
a) Web development
b) Data science
c) Testing Python code
d) Network programming
Answer 1
c) Testing Python code
2. How can you configure Pytest to show the output of print statements in test runs?
Choose one option
a) Pytest -s
b) Pytest -v
c) Pytest -x
d) Pytest -k
Answer 2
a) Pytest -s
The `-s` option disables output capturing, allowing print statements to display their output in the terminal.
3. Which pytest plugin is used to measure code coverage of tests?
Choose one option
a) pytest-cov
b) pytest-cover
c) pytest-covplugin
d) pytest-check
Answer 3
a) pytest-cov
You can run Pytest tests with coverage analysis by using the option “–cov”, followed by the name of the module or package to analyze.
4. How can you run a specific test function within a test file using pytest?
Choose one option
a) pytest test_filename::test_function_name
b) pytest -run=test_function_name
c) pytest –function=test_function_name
d) pytest -f test_function_name
Answer 4
a) pytest test_filename::test_function_name
This command allows you to execute only the specified test function within the given test file.
5. What does the `pytest.raises` context manager do?
Choose one option
a) Logs exceptions
b) Retrieves exception details
c) Asserts that a specific exception is raised
d) Avoids exception processing in tests
Answer 5
c) Asserts that a specific exception is raised
Pytest.raises() is used to test if a specific exception is raised during the execution of a Pytest test.
6. How can you generate a JUnit-style XML test report in Pytest?
a) Pytest –junitxml=report.xml
b) Pytest –xml-report=report.xml
c) Pytest –report-junit=report.xml
d) Pytest –junit=report.xml
Answer 6
a) Pytest –junitxml=report.xml
You can generate a JUnit-style XML test report in Pytest by using the option “–junitxml”, followed by the name of the report file.
7. What is the purpose of the assert statement in Pytest tests?
a) To define test fixtures
b) To skip certain tests
c) To define and manage test parameters
d) To check test results and raise an exception if they are not as expected
Answer 7
d) To check test results and raise an exception if they are not as expected
8. What is the purpose of Pytest plugins?
Choose one option
a) To define and manage test fixtures and hooks
b) To extend the functionality of Pytest
c) To skip certain tests
d) To collect and report test results
Answer 8
b) To extend the functionality of Pytest
9. What is the purpose of the Pytest-mock library?
Choose one option
a) To provide mocking functionality for Pytest tests
b) To provide a framework for testing asynchronous code
c) To provide performance testing functionality for Pytest tests
d) To provide load testing functionality for Pytest tests
Answer 9
a) To provide mocking functionality for Pytest tests
The Pytest-mock library is used to provide mocking functionality for Pytest tests.
10. What is the purpose of the Pytest-bdd library?
Choose one option
a) To provide mocking functionality for Pytest tests
b) To provide a framework for testing asynchronous code
c) To provide performance testing functionality for Pytest tests
d) To provide a behavior-driven development (BDD) testing framework for Pytest tests
Answer 10
d) To provide a behavior-driven development (BDD) testing framework for Pytest tests
The Pytest-bdd library is used to provide a behavior-driven development (BDD) testing framework for Pytest tests.
11. How can you run Pytest tests on multiple Python versions?
Choose one option
a) By using the tox tool
b) By using the Pytest-xdist plugin
c) By using the Pytest-cov plugin
d) By using the Pytest-flake8 plugin
Answer 11
a) By using the tox tool
Tox is a tool specifically designed to automate testing across multiple Python environments, allowing you to define configurations for different Python versions in a `tox.ini` file.
12. What is the purpose of the Pytest-html plugin?
Choose one option
a) To provide mocking functionality for Pytest tests
b) To provide a framework for testing asynchronous code
c) To provide performance testing functionality for Pytest tests
d) To generate HTML reports of Pytest test results
Answer 12
d) To generate HTML reports of Pytest test results
13. What is the purpose of the Pytest-xdist plugin?
Choose one option
a) To provide mocking functionality for Pytest tests
b) To provide a framework for testing asynchronous code
c) To provide performance testing functionality for Pytest tests
d) To distribute Pytest tests across multiple CPUs or machines
Answer 13
d) To distribute Pytest tests across multiple CPUs or machines
The Pytest-xdist plugin is used to distribute Pytest tests across multiple CPUs or machines.
14. What is the purpose of the Pytest-cov plugin?
Choose one option
a) To provide mocking functionality for Pytest tests
b) To provide a framework for testing asynchronous code
c) To provide performance testing functionality for Pytest tests
d) To provide coverage analysis for Pytest tests
Answer 14
d) To provide coverage analysis for Pytest tests
15. How can you mark a Pytest test with a custom label?
Choose one option
a) @Pytest.label
b) @Pytest.tag
c) @Pytest.mark.label
d) @Pytest.mark.tag
Answer 15
d) @Pytest.mark.tag
16. Can we run tests in pytest parallely?
Choose one option
a) Yes
b) No
Answer 16
a) Yes
17. How can you run Pytest tests in parallel?
Choose one option
a) Pytest -n
b) Pytest -x
c) Pytest -k
d) Pytest -p
Answer 17
a) Pytest -n
You can run Pytest tests in parallel by using the option “-n”, followed by the number of workers to use.
18. Which marker in pytest is used to execute tests serially, avoiding parallel execution?
Choose one option
a) @pytest.single
b) @pytest.serial
c) @pytest.mark.no_parallel
d) @pytest.mark.run
Answer 18
c) @pytest.mark.no_parallel
19. How do you parameterize tests in pytest?
a) Use @pytest.param
b) Use @pytest.mark.variable
c) Use @pytest.mark.parametrize
d) Use @pytest.parameterize
Answer 19
c) Use @pytest.mark.parametrize
20. What is the purpose of pytest’s `-q` option?
a) Run tests quietly with minimal output
b) Enable quick testing mode
c) Execute tests without dependencies
d) Provide a verbose output
Answer 20
a) Run tests quietly with minimal output
21. How do you add an environmental variable before running tests in pytest?
a) Use @env
b) Use pytest.env_var
c) Use the custom fixture setup
d) Directly set the variable in the terminal
Answer 21
d) Directly set the variable in the terminal
Setting environment variables directly in the terminal is a common way to configure the environment before running pytest tests.
22. Which pytest feature allows grouping and organizing test codes logically?
a) Packages
b) Test Suites
c) Collections
d) Test Modules
Answer 22
b) Test Suites
23. What is the function of pytest.ini or tox.ini in the context of pytest?
a) To manage test assertions
b) To configure pytest options and plugins
c) To store test logs
d) To compile test code
Answer 23
b) To configure pytest options and plugins
24. How can test output be redirected to a file in pytest?
a) Use –logfile=file.log
b) pytest –log=file.log
c) Redirect output manually in the terminal
d) pytest test.py > output.log
Answer 24
d) pytest test.py > output.log
The command pytest test.py > output.log is used to execute tests in a file named test.py using pytest, while redirecting the console output to a file named output.log
25. How do you ignore warnings in pytest test outputs?
a) –ignore-warnings
b) –restrict-warnings
c) –disable-warnings
d) pytest does not support ignoring warnings
Answer 25
c) –disable-warnings
You can use the --disable-warnings command-line option to suppress the warning summary entirely from the test run output.
We would love to hear from you! Please leave your comments and share your scores in the section below
GitHub – Multiple Choice Questions and Answers – MCQ1
Welcome to the GitHub Quiz! This blog post features 25 multiple-choice questions that explore concepts of GitHub.
1. What is GitHub?
Select the best answer
a) A software to draw diagrams
b) A web-based platform for version control and collaboration
c) A mobile app for photo editing
d) A music player
Answer 1
b) A web-based platform for version control and collaboration
GitHub is a web-based platform used for hosting Git repositories. It enables collaboration by providing tools for version control, issue tracking, and project management, making it easier for teams to work together.
2. What is the primary purpose of GitHub?
Choose one option
a) To host Git repositories
b) To write code
c) To debug programs
d) To compile code
Answer 2
a) To host Git repositories
3. GitHub is based on which version control system?
Choose one option
a) Mercurial
b) SVN
c) Git
d) CVS
Answer 3
c) Git
4. Which of these is NOT a feature of GitHub?
Choose one option
a) Repository hosting
b) Issue tracking
c) Video streaming
d) Pull requests
Answer 4
c) Video streaming
5. Which icon is used to “star” a repository?
Choose one option
a) 🛠️
b) ⭐
c) 💬
d) 🔒
Answer 5
b) ⭐
6. What is the purpose of a GitHub repository’s README.md file?
a) To describe the project and provide instructions
b) To store sensitive information
c) To commit code changes
d) To manage branches
Answer 6
a) To describe the project and provide instructions.
The README.md file in a GitHub repository serves as the main documentation for the project. It typically contains a description of the project. It provides instructions on how to install and use it. The README also includes information on how to contribute.
7. What is the purpose of the Issues tab in a repository?
a) Chat with followers
b) Log bugs, tasks, or feature requests
c) Share files
d) View stars
Answer 7
b) Log bugs, tasks, or feature requests
The Issues tab in a repository is used for logging and tracking bugs, tasks, or feature requests. It serves as a project management tool, allowing contributors to identify, discuss, and resolve various issues related to the project.
8. What does the “Fork” button do?
Choose one option
a) Merges two branches
b) Creates a duplicate copy of a repository under your account
c) Deletes the repository
d) Creates a zip file
Answer 8
b) Creates a duplicate copy of a repository under your account
The “Fork” button on platforms like GitHub or GitLab creates a copy of a repository under your own account.
9. What is GitHub Pages used for?
Choose one option
a) Database hosting
b) Deploying static websites
c) Messaging
d) Cloud computing
Answer 9
b) Deploying static websites
GitHub Pages is a feature provided by GitHub that allows users to host static websites directly from their repositories. It is an ideal platform for creating projects, documentation, or personal websites. It leverages static files such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. There is no need for server-side processing.
10. Which GitHub feature allows you to manage bugs and tasks?
Choose one option
a) Projects
b) Issues
c) Actions
d) Forks
Answer 10
b) Issues
GitHub Issues is a feature that allows the tracking and management of bugs, tasks, and enhancements within a repository.
11. What does “watching” a repository mean?
Choose one option
a) Getting updates
b) Downloading
c) Editing
d) Sharing
Answer 11
a) Getting updates
“Watching” a repository on platforms like GitHub means subscribing to notifications and updates related to the repository. When you watch a repository, you receive notifications about new releases, pull requests, issues, and any discussions or changes made within that repository.
12. What does a green check mark in a pull request indicate?
Choose one option
a) Merged
b) Pending
c) Failed tests
d) Passed checks
Answer 12
d) Passed checks
In the context of a pull request on platforms like GitHub, a green check mark typically indicates that all checks have passed successfully. This can include automated tests, linting, and other CI/CD pipeline checks that are set to run on the code changes within the pull request.
13. What is the default branch name in a new GitHub repository (as of 2020+)?
Choose one option
a) master
b) default
c) main
d) dev
Answer 13
c) main
Starting from late 2020, GitHub changed the default branch name for new repositories from “master” to “main”. This change was part of a broader effort to make inclusive naming the default across software projects and platforms.
14. What symbol is used to reference users on GitHub?
Choose one option
a) #
b) $
c) @
d) &
Answer 14
c) @ s
15. How can you open a pull request on GitHub?
Choose one option
a) Through the command line
b) Through the repository page on GitHub
c) Only with admin access
d) By watching the repository
Answer 15
b) Through the repository page on GitHub
To open a pull request on GitHub, you first go to the repository page. This is where you have forked or made changes. From there, you click on the “Pull Requests” tab. Next, click on the “New Pull Request” button to propose your changes.
16. Which tab in a GitHub repo lets you download a ZIP of the project?
Choose one option
a) Code
b) Pull requests
c) Issues
d) Actions
Answer 16
a) Code
17. Can you edit a file directly on GitHub without cloning it?
Choose one option
a) No
b) Yes
c) Only admins can
d) Only with GitHub Pro
Answer 17
b) Yes
18. What do you need to clone a GitHub repo?
Choose one option
a) A password
b) A link to the repository
c) A GitHub invitation
d) An SSH certificate
Answer 18
b) A link to the repository
19. What does the “Insights” tab show?
a) Programming errors
b) Contribution and activity stats
c) File size
d) Email history
Answer 19
b) Contribution and activity stats
20. Where is the “README.md” file displayed?
Choose one option
a) Inside the issues
b) At the top of the repository main page
c) In GitHub Pages
d) Hidden from users
Answer 20
b) At the top of the repository main page.
21. What’s the purpose of a commit message?
a) To delete files
b) To describe what changes were made
c) To reset changes
d) To download the code
Answer 21
b) To describe what changes were made
22. What is required to create a GitHub account?
a) Mobile number
b) GitHub invite code
c) Email address
d) GitHub token
Answer 22
c) Email address
23. What does the green “Code” button do on a repo’s main page?
a) Upload files
b) Share a video
c) Lets you clone or download the repository
d) Edit code online
Answer 23
c) Lets you clone or download the repository
24. Which GitHub feature displays the commit history visually?
a) Timeline
b) Graph
c) Network
d) Feed
Answer 24
c) Network
25. Which GitHub feature can automate workflows?
a) GitHub Pages
b) GitHub Actions
c) GitHub Gist
d) GitHub Sponsors
Answer 25
b) GitHub Actions
We would love to hear from you! Please leave your comments and share your scores in the section below
Robot Framework – Multiple Choice Questions and Answers – MCQ2
Welcome to the Robot Framework Quiz! This blog post features 25 multiple-choice questions that explore concepts of Robot Framework.
1. Which command line tool is used to execute Robot Framework tests?
Select the best answer
a) robot
b) run_rf
c) test_execute
d) execute_robot
Answer 1
a) robot
2. Which configuration is used to define test setup and teardown in Robot Framework?
Choose one option
a) Test Configuration
b) Test Fixture
c) Suite Setup
d) Keyword Setup
Answer 2
c) Suite Setup
*** Settings ***
Documentation Tests to login to Login Page
Library SeleniumLibrary
Test Setup Open the Browser with URL
Test Teardown Close Browser Session
Resource ../Resources/GenericResources.robot
3. Robot Framework is built on top of which programming language?
Choose one option
a) Python
b) JavaScript
c) C#
d) PHP
Answer 3
a) Python
Robot Framework is primarily implemented using Python, and it relies on Python libraries for its functionality. It also allows for creation of test libraries using Python.
4. What is the name of the tool provided by Robot Framework to execute test cases?
Choose one option
a) Test Runner
b) RobotExecutor
c) Pybot
d) RIDE
Answer 4
c) Pybot
5. Which command is used to install Robot Framework using pip?
Choose one option
a) pip install robot
b) pip install robotframework
c) pip install robotframework-core
d) pip install robotframework-tools
Answer 5
pip install robotframework
6. In which format are the test results generated by Robot Framework by default?
a) PDF
b) Excel
c) HTML
d) JSON
Answer 6
c) HTML
7. How do you write a comment in a Robot Framework test case file?
a) // This is a comment
b) # This is a comment
c) % This is a comment
d) Comment This is a comment
Answer 7
b) # This is a comment
8. What is the purpose of the RequestsLibrary in Robot Framework?
Choose one option
a) To provide keywords for database operations
b) To provide keywords for web testing
c) To provide keywords for file operations
d) To provide keywords for REST API testing
Answer 8
d) To provide keywords for REST API testing
The RequestsLibrary in Robot Framework provides keywords for testing REST APIs. It supports making HTTP requests and validating responses using different methods.
9. What is the purpose of the DatabaseLibrary in Robot Framework?
Choose one option
a) To provide keywords for database operations
b) To provide keywords for web testing
c) To provide keywords for file operations
d) To provide keywords for REST API testing
Answer 9
a) To provide keywords for database operations
The DatabaseLibrary in Robot Framework provides keywords for database testing. It supports connecting to different types of databases and executing SQL queries.
10. What is the purpose of the Collections library in Robot Framework?
Choose one option
a) To provide keywords for manipulating collections
b) To provide keywords for web testing
c) To provide keywords for file operations
d) To provide keywords for REST API testing
Answer 10
a) To provide keywords for manipulating collections
The Collections library in Robot Framework provides keywords for manipulating different types of collections like lists, dictionaries, and sets.
11. What is the purpose of the Requests library in Robot Framework?
Choose one option
a) To provide keywords for interacting with HTTP services using the Requests library
b) To provide keywords for web testing
c) To provide keywords for file operations
d) To provide keywords for REST API testing
Answer 11
a) To provide keywords for interacting with HTTP services using the Requests library
The Requests library in Robot Framework provides keywords for interacting with HTTP services using the Requests library. It supports sending HTTP requests and receiving HTTP responses.
12. What is the purpose of the AppiumLibrary in Robot Framework?
Choose one option
a) To provide keywords for mobile app testing using Appium
b) To provide keywords for web testing using Selenium
c) To provide keywords for file operations
d) To provide keywords for REST API testing
Answer 12
a) To provide keywords for mobile app testing using Appium
The AppiumLibrary in Robot Framework provides keywords for mobile app testing using Appium. It supports automating mobile apps on different platforms.
13. What is the purpose of the “Documentation” keyword in Robot Framework test cases?
Choose one option
a) To execute a test case
b) To import a module
c) To provide an explanation of the test case
d) To declare a variable
Answer 13
c) To provide an explanation of the test case
14. Which file generated by Robot Framework provides a high-level overview of the test execution results?
Choose one option
a) Log.html
b) Output.xml
c) Report.html
d) Summary.txt
Answer 14
c) Report.html
15. In Robot Framework, which file contains detailed information about each step of the test execution?
Choose one option
a) Log.html
b) Output.xml
c) Report.html
d) DetailedLog.html
Answer 15
a) Log.html
16. Which of the following assertion levels is captured by default in Robot Framework logs?
Choose one option
a) DEBUG
b) TRACE
c) INFO
d) WARNING
Answer 16
c) INFO
17. What is the command to run a Robot Framework test file named `test.robot` using Python?
Choose one option
a) python -m test.robot
b) python robot.run test.robot
c) robot test.robot
d) python -m robot test.robot
Answer 17
c) robot test.robot
18. Robot Framework supports parallel testing?
Choose one option
a) Yes
b) No
Answer 18
a) Yes
19. Which tool is commonly used to enable parallel execution of Robot Framework test cases?
a) RobotIDE
b) Selenium Grid
c) Pabot
d) Pybot
Answer 19
c) Pabot
Pabot is a parallel test runner for Robot Framework. It can be used to run tests in parallel on a single machine with multiple processes.
20. To run tests in parallel, the test cases in Robot Framework must be:
Choose one option
a) Written in a single file
b) Independent of each other
c) Using only one library
d) Sequentially organized
Answer 20
b) Independent of each other.
21. In Pabot, how can you separate test cases logically for parallel execution?
a) Cluster by keyword usage
b) Group using tags
c) Divide based on file size
d) Merge test data files
Answer 21
b) Group using tags
22. Which command is used to solely convert an `Output.xml` file to a log and report?
a) robot –relog Output.xml
b) rebot –recreate Output.xml
c) rebot Output.xml
d) robot –convert Output.xml
Answer 22
c) rebot Output.xml
23. How can you disable the generation of the report file in Robot Framework?
a) Use the option –no-report
b) Use the option –disable-report
c) Use the option –skip-report
d) Use the option –report NONE
Answer 23
d) Use the option –report NONE
24. What is the purpose of the Faker library in Robot Framework?
a) To generate random test data
b) To provide keywords for web testing using Selenium
c) To provide keywords for file operations
d) To provide keywords for mobile app testing using Appium
Answer 24
a) To generate random test data
25. Can we run Robot Framework tests in CI/CD pipeline?
a) Yes
b) No
Answer 25
a) Yes
We would love to hear from you! Please leave your comments and share your scores in the section below