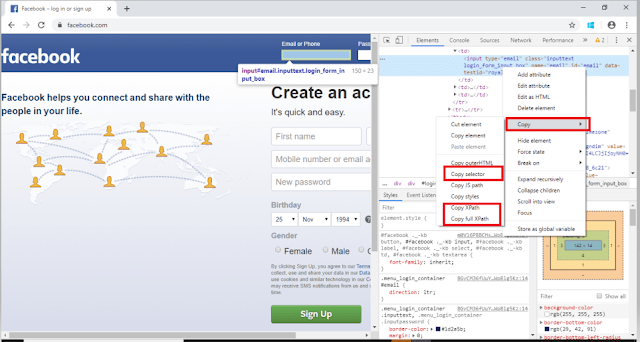
CSS Selectors are string patterns used to identify an element based on a combination of HTML tag, id, class, and attributes. Locating by CSS Selector is more complicated than the previous methods like by Id, class, XPath, but it is the most common locating strategy of advanced Selenium users because it can access even those elements that have no ID or name.
CSS is preferred way of locating element as it is faster than Xpath.
Table of Contents
- Located by ID
- Located by Class
- Located by Attribute
- Located by ID/Class and attribute
- Located by Sub String Matches
- Locating child element
1) Located by ID
Syntax
(By.cssSelector("input#email"))
(By.cssSelector("#email"))
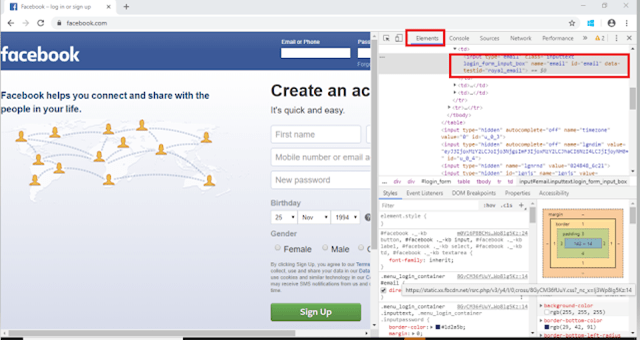
- HTML tag – HTML tag of the element being accessed
- # – The hash sign is use to symbolize ID attribute. It is mandatory to use hash sign if ID attribute is use to create CSS Selector.
- Value of ID attribute – It is the value of an ID attribute that access. A hash sign always precedes the value of ID.

If two or more web elements have the same HTML tag and attribute value, the first element marked in the page source will identify.
2) Located by Class
Syntax
(By.cssSelector("input.inputtext"))
- HTML tag = HTML tag of the element being accessed
- . = the dot sign should always be present when using CSS with class
- class = class of the element being accessed

3) Located by Attribute
Syntax
(By.cssSelector("input[type='email']"))
- HTML tag = HTML tag of the element being accessed
- [ and ] = square brackets within which a specific attribute and its corresponding value will be placed
- attribute = attribute to be used, preferable unique to the element
- value = corresponding value of the chosen attribute.

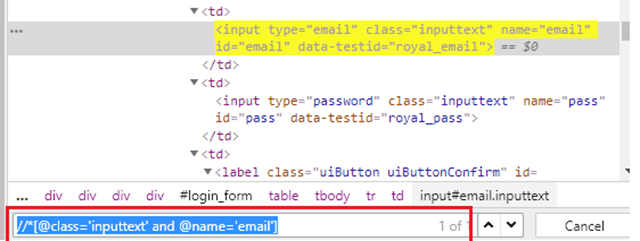
4) Located by ID/Class and attribute
Syntax
(By.cssSelector("input.inputtext[name='email']")
- HTML tag = HTML tag of the element being accessed
- . = the dot sign should always be present when using a CSS with class
- class = class of the element being accessed
- [ and ] = square brackets within which a specific attribute and its corresponding value will be placed
- attribute = attribute to be used, preferable unique to the element
- value = corresponding value of the chosen attribute.

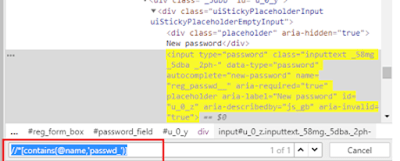
5) Located by Sub String Matches
CSS in Selenium has an interesting feature of allowing partial string matches using ^, $, and *.
a) Starts with (^): To select the element, we would use ^ which means ‘starts with’.
Syntax
(By.cssSelector("input[name^='em']"))
- ^– Symbolic notation to match a string using prefix.
Prefix – It is the string based on which match operation is performed. The likely string is expected to start with the specified string

b) Ends with ($): To select the element, we would use $ which means ‘ends with’.
Syntax
(By.cssSelector("input[name$='il']"))
- $ – Symbolic notation to match a string using suffix.
- The suffix – It is the string based on which match operation is perform. The likely string is expect to ends with the specified string.

c) Contains (*): To select the element, we would use * which means ‘sub-string’.
Syntax
(By.cssSelector("input[name*='rst']"))
(By.cssSelector("input:contains('rst')")
* – This is used to match the sub-string

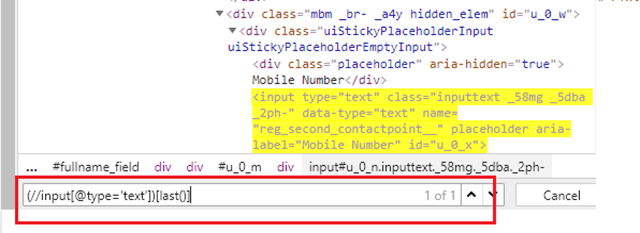
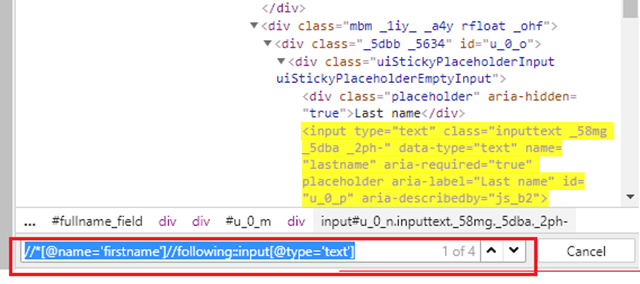
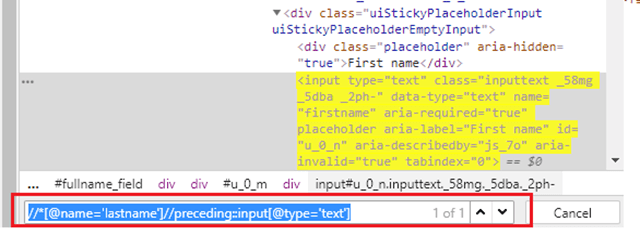
6) Locating child element
Here, id =”content” is the parent locator. It will go to first div as child or sub child, then again div as child or sub child, and third div as child or sub child. Then it will go to div class _4bl7 _m-_ which further go to div class _ihd _3ma mbs _6n _6s _6v.
Syntax
(By.cssSelector("#content>div>div>div>div._4bl7._m-_>div._ihd._3ma.mbs._6n._6s._6v"))

Locating nth Child:
To locate the element with text ‘Female’, we use nth type css.
Syntax
(By.cssSelector("#u_0_13 > span:nth-child(1) > label"))

To select the last child element, i.e. ‘Male’, we can use.
Syntax
(By.cssSelector("#u_0_13 > span:last-child> label"))

Now, let’s write a small program to show the use of CSS Selectors. This program is it we have done for XPath , the only difference is the use of CSS Selectors to identify the web elements.
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeOptions;
import java.time.Duration;
public class Selenium_Demo {
protected static WebDriver driver;
public static void main(String[] args) {
ChromeOptions options = new ChromeOptions();
options.addArguments("--start-maximized");
driver = new ChromeDriver(options);
driver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(Duration.ofSeconds(2));
driver.get("https://opensource-demo.orangehrmlive.com/");
driver.manage().window().maximize();
//CSS Selectors for TextBox
driver.findElement(By.cssSelector("input.oxd-input[name='username'")).sendKeys("Admin");
driver.findElement(By.cssSelector("input.oxd-input[name='password'")).sendKeys("admin123");
driver.findElement(By.cssSelector("button[type='submit'")).click();
driver.close();
}
}
That’s it! Congratulations on making it through this tutorial and hope you found it useful! Happy Learning!!