Last Updated On
Welcome to the SQL Quiz! This blog post features 25 multiple-choice questions that explore JOINS concept of SQL.
1. Which SQL JOIN returns only the rows that have matching values in both tables?
a) LEFT JOIN
b) RIGHT JOIN
c) INNER JOIN
d) FULL OUTER JOIN
Answer 1
c) INNER JOIN
INNER JOIN matches records in both tables based on the join condition.
2. What does the following SQL query return?
SELECT products.product_name, orders.order_date
FROM products
INNER JOIN orders ON products.product_id = orders.product_id;
a) Only products that have been ordered
b) All products, ordered and non-ordered
c) All orders, regardless of the products
d) None of the above
Answer 2
a) Only products that have been ordered
The INNER JOIN retrieves only products that have corresponding order records.
3. If you want all rows from the left table and only the matching rows from the right table, which join will you use?
a) INNER JOIN
b) RIGHT JOIN
c) LEFT JOIN
d) FULL JOIN
Answer 3
c) LEFT JOIN
LEFT JOIN keeps all rows from the left table and adds NULLs for non-matching right table rows.
4. Which join type would you use to include all students and their respective grades, whether or not the grades are recorded?
SELECT students.student_name, grades.grade
FROM students
__________ JOIN grades ON students.student_id = grades.student_id;
a) INNER JOIN
b) RIGHT JOIN
c) LEFT JOIN
d) FULL JOIN
Answer 4
c) LEFT JOIN
A LEFT JOIN includes all students and their grades, with NULL for students without recorded grades.
5. Which JOIN includes all records from both tables, filling NULLs where there are no matches?
a) INNER JOIN
b) CROSS JOIN
c) FULL OUTER JOIN
d) SELF JOIN
Answer 5
c) FULL OUTER JOIN
FULL OUTER JOIN returns all rows from both tables with NULLs where no match exists.
6. What result does the following query produce?
SELECT a.name, b.address
FROM customers a
FULL OUTER JOIN orders b ON a.customer_id = b.customer_id;
a) Only matching customers and orders
b) All customers and orders with matches and non-matches
c) Customers without orders
d) Orders without customers
Answer 6
b) All customers and orders with matches and non-matches
A FULL OUTER JOIN returns all records when there is a match in either table A or table B.
7. What does a CROSS JOIN do?
a) Matches only the common records
b) Returns Cartesian product of two tables
c) Returns only distinct records
d) Works only on primary keys
Answer 7
b) Returns Cartesian product of two tables
CROSS JOIN multiplies all rows from one table with all rows of another.
8. What does the following SQL query do?
SELECT e.employee_id, e.name, d.department_name
FROM employees e
CROSS JOIN departments d;
a) Joins each employee with all departments
b) Returns only matched employees and departments
c) Lists employees without departments
d) Lists departments without employees
Answer 8
a) Joins each employee with all departments
A CROSS JOIN creates a Cartesian product of both tables.
9. Which JOIN is used to join a table with itself?
a) CROSS JOIN
b) SELF JOIN
c) FULL OUTER JOIN
d) NATURAL JOIN
Answer 9
b) SELF JOIN
SELF JOIN is useful for hierarchical or recursive relationships.
10. What is a primary use case for a self join in SQL?
a) To join two unrelated databases
b) To compare rows within the same table
c) To join tables with similar schemas
d) To execute subqueries
Answer 10
b) To compare rows within the same table
SELECT a.employee_id, a.name, b.manager_id
FROM employees a
JOIN employees b ON a.manager_id = b.employee_id;
In the provided query, the employees table is joined with itself to find employees and their respective managers by matching employee IDs with manager IDs.
11. In a self join scenario, how would you distinguish between the different roles of the table being joined to itself?
Choose one option
a) Use different database instances
b) Use table aliases
c) Create a temporary table
d) Use a different SQL dialect
Answer 11
b) Use table aliases
SELECT e1.name AS Employee, e2.name AS Manager
FROM employees e1
JOIN employees e2 ON e1.manager_id = e2.employee_id;
In a self join, table aliases are employed to differentiate between the roles of the same table. Here, `e1` represents employees, and `e2` represents managers, allowing us to fetch the employee names along with their corresponding managers.
12. To avoid a Cartesian product, always include a valid join condition in a WHERE clause.
Choose one option
a) True
b) False
Answer 12
a) True
If we don’t use WHERE clause in a join, it will do a cartesian product.
13. Which type of JOIN is used to select all records from the right table and the matched records from the left table?
Choose one option
a) OUTER JOIN
b) SELF JOIN
c) RIGHT JOIN
d) NATURAL JOIN
Answer 13
c) RIGHT JOIN
A RIGHT JOIN returns all records from the right table and the matched records from the left table. Unmatched left table records receive NULLs.
14. Given the tables employees and departments, which query will list all department names even if they have no employees?
Choose one option
a) LEFT JOIN
b) SELF JOIN
c) RIGHT JOIN
d) INNER JOIN
Answer 14
c) RIGHT JOIN
SELECT departments.department_name, employees.name
FROM departments
RIGHT JOIN employees ON departments.id = employees.department_id;
The RIGHT JOIN returns all department names, including those with no associated employees.
15. Can multiple JOIN operations be used in a single SQL query?
Choose one option
a) True
b) False
Answer 15
a) True
Multiple JOIN operations can be utilized in a single query to combine data from more than two tables.
16. In a SQL JOIN, what does the ON keyword do?
Choose one option
a) Specifies the columns for joining
b) Specifies the conditions for joining
c) Specifies the number of rows to return
d) Specifies the order of columns
Answer 16
b) Specifies the conditions for joining
The ON keyword specifies conditions that determine which rows are retrieved in the join operation.
17. To combine data from multiple tables where relationships exist, which SQL feature should be used besides JOINs?
Choose one option
a) Subqueries
b) Cursors
c) Triggers
d) Indexes
Answer 17
a) Subqueries
Subqueries can be used to combine data or perform operations that retrieve data from multiple tables based on conditions.
18. What is a NATURAL JOIN based on?
a) Explicit conditions
b) Common columns automatically determined
c) Primary keys
d) Foreign keys
Answer 18
b) Common columns automatically determined
A NATURAL JOIN automatically joins tables based on columns with matching names and compatible data types.
19. Below two tables (A & B) are given.
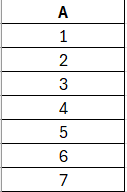
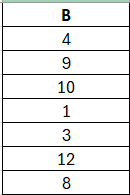
What will be the result of inner join between these tables?
a) 1,3,4
b) 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,12
c) 1,2,3,4,5,6,7
d) 1,3,4,8,9,10,12
Answer 19
a) 1,3,4
20. What will be the result of FULL OUTER JOIN between these tables?
Choose one option
a) 1,3,4
b) 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,12
c) 1,2,3,4,5,6,7
d) 1,3,4,8,9,10,12
Answer 20
b) 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,12
21. Select the correct query/queries for cross join:
a) Select * FROM Table1 T1 CROSS JOIN Table1 T2;
b) Select * FROM Table1 T1 ALL CROSS JOIN Table1 T2;
c) Select * FROM Table1 T1,Table1 T2;
d) Select * FROM Table1 T1 CROSS Table1 T2;
Answer 21
a) Select * FROM Table1 T1 CROSS JOIN Table1 T2;
22. Which clause can be used with a JOIN to filter records?
a) WHERE
b) HAVING
c) GROUP BY
d) ORDER BY
Answer 22
a) WHERE
The WHERE clause can be used to filter records after the JOIN operation, whereas HAVING is typically used with GROUP BY.
23. How can SQL JOINs be optimized for better performance?
a) Using indexes on join columns
b) Avoiding WHERE clauses
c) Using more complex joins
d) Increasing database storage
Answer 23
a) Using indexes on join columns
Optimizing SQL JOIN performance generally involves using indexes on the columns involved in the join conditions.
24. Consider the tables `students` and `enrollments`, both having the column `student_id`. What will the following SQL statement do?
SELECT * FROM students NATURAL JOIN enrollments;
a) Join using all columns that are common between the two tables
b) Require user to specify a join condition
c) Join using columns named `student_id`
d) Join with duplicate column names represented multiple times
Answer 24
c) Join using columns named `student_id`
The NATURAL JOIN will operate on all columns with the same name, joining on `student_id` as it’s the common column between `students` and `enrollments`.
25. What is a potential disadvantage of using NATURAL JOIN?
a) It is only available in a few SQL dialects
b) Can join tables that have no related columns
c) Lacks explicit control over join conditions
d) Always results in Cartesian product of the tables
Answer 25
c) Lacks explicit control over join conditions
NATURAL JOIN does not allow you to specify which common columns to use for joining, which can lead to unforeseen results if multiple columns share the same name across tables.
We would love to hear from you! Please leave your comments and share your scores in the section below