REST Assured provides a convenient way to retrieve and assert response time. Rest Assured provides a method to get response time in milliseconds by default or the time unit we want. We can also validate if the response time is less than, greater than, or in between the expected values as well.
Interface ResponseOptions
This interface contains four methods:-
- getTime() – The response time in milliseconds (or -1 if no response time could be measured)
- getTimeIn(TimeUnit timeunit) – The response time in the given time unit (or -1 if no response time could be measured)
- time() – The response time in milliseconds (or -1 if no response time could be measured)
- timeIn( TimeUnit timeunit ) – The response time in the given time unit (or -1 if no response time could be measured)
Technically, getTime() and time() both are the same, and getTimeIn() and timeIn() both are the same.
Below is an example.
import io.restassured.RestAssured;
import io.restassured.response.Response;
import io.restassured.specification.RequestSpecification;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class ResponseTime {
@Test
public void getResponseTime() {
RequestSpecification requestSpecification = RestAssured.given();
// Calling GET method
Response response = requestSpecification.get("https://reqres.in/api/users/2");
// Let's print response body.
String resString = response.prettyPrint();
System.out.println("Response Details : " + resString);
//Get Response Time
System.out.println("Response Time in milliseconds: " + response.getTime());
System.out.println("Response Time in seconds: " + response.getTimeIn(TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println("Response Time in milliseconds: " + response.time());
System.out.println("Response Time in seconds: " + response.timeIn(TimeUnit.SECONDS));
}
}
The output of the above program is

Interface ValidatableResponseOptions
This interface has overloaded time() methods that accept Matcher.
- time(Matcher matcher) – Validate that the response time (in milliseconds) matches the supplied matcher.
- time(Matcher macther, TimeUnit timeunit) – Validate that the response time matches the supplied matcher and time unit.
Below is an example.
import org.hamcrest.Matchers;
import org.junit.Test;
import static io.restassured.RestAssured.given;
public class ResponseTime {
@Test
public void verifyResponseTime() {
// Given
given()
// When
.when()
.get("https://reqres.in/api/users/2")
// Then
.then()
.statusCode(200).statusLine("HTTP/1.1 200 OK")
// Asserting response time is less than 2000 milliseconds
.time(Matchers.lessThan(3000L));
}
}
The output of the above program is
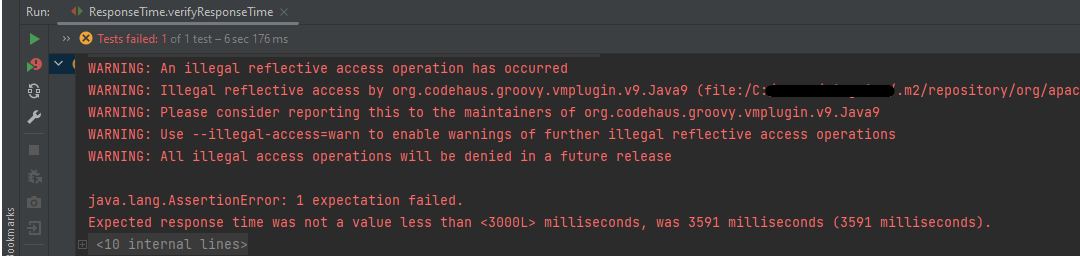
In the above example, we can see that the time taken by the request to provide the response is 3591 ms, which is greater than 3000 ms, so the test failed.
Similarly, we can use greaterthan() method too.
@Test
public void verifyGreaterResponseTime() {
// Given
given()
// When
.when()
.get("https://reqres.in/api/users/2")
// Then
.then()
.statusCode(200).statusLine("HTTP/1.1 200 OK")
// Asserting response time is greater than 3000 milliseconds
.time(Matchers.greaterThan(2000L));
}
The output of the above program is

If you want to verify the time range, it can also be done using the Matchers. Below is an example of the same.
@Test
public void verifyResponseTimeRange() {
// Given
given()
// When
.when()
.get("https://reqres.in/api/users/2")
// Then
.then()
.statusCode(200).statusLine("HTTP/1.1 200 OK")
// Asserting response time is greater than 1000 milliseconds and less than 2000 milliseconds
.time(Matchers.both(Matchers.greaterThanOrEqualTo(1000L)).and(Matchers.lessThanOrEqualTo(2000L)));
}
The output of the above program is

In the above example, the response time is 2550 ms, which does not fall in the range of 1000-2000 ms. So, the test is failed.
We are done! Congratulations on making it through this tutorial and hope you found it useful! Happy Learning!!