In this tutorial, we will discuss various types of Assertions present in Hamcrest that are used in Rest Assured.
Table Of Contents
What is Assertion?
An assertion is a way to verify that the expected result and the actual result match or not in the test case. A test is considered successful ONLY if it is completed without throwing any exceptions. If the current value and the expected value match then the assertion passes and when the assertion passes nothing happens. But when an assertion fails, it will fail the test case.
There are various ways to perform assertions in API Testing. For API Testing, we are using Rest Assured, which uses either Hamcrest or JUnit assertions. We are going to discuss Hamcrest Assertions here.
What is Hamcrest?
Hamcrest is a framework for writing matcher objects, allowing ‘match’ rules to be defined declaratively. We do not need to add Hamcrest dependency explicitly as the Rest-Assured 4.3.3 version includes itself. To learn more about Hamcrest, please refer to this link.
We need to add the below dependency to use Hamcrest in the project. Please use the latest version from here
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hamcrest</groupId>
<artifactId>hamcrest</artifactId>
<version>3.0</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
To run all the scenarios mentioned below, please add the below-mentioned dependencies to the POM.xml.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>RestAssured_TestNG_Demo</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<hamcrest.version>3.0</hamcrest.version>
<testng.version>7.8.0</testng.version>
<rest-assured.version>5.3.2</rest-assured.version>
<maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- Hamcrest Dependency -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hamcrest</groupId>
<artifactId>hamcrest</artifactId>
<version>${hamcrest.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- TestNG Dependency -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.testng</groupId>
<artifactId>testng</artifactId>
<version>${testng.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Rest Assured -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.rest-assured</groupId>
<artifactId>rest-assured</artifactId>
<version>${rest-assured.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
Below is an example of a JSON Response. I will perform various assertions on this JSON Response.
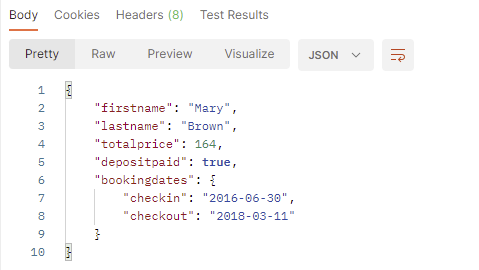
To use hamcrest assertion, please import the Matchers class, static member.
Number related assertions
- equalTo – It checks whether the retrieved number from the response is equal to the expected number.
- greaterThan – checks extracted number is greater than the expected number.
- greaterThanOrEqualTo – checks whether the extracted number is greater than equal to the expected number.
- lessThan – It checks whether the retrieved number from the response is lesser than the expected number.
- lessThanOrEqualTo – It checks whether the retrieved number from the response is lesser than or equal to the expected number.
Below assertions are imported from the package shown below:-
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.equalTo;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.greaterThan;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.greaterThanOrEqualTo;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.lessThanOrEqualTo;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.lessThan;
Below are examples to show the use of number-related assertions.
import io.restassured.RestAssured;
import io.restassured.http.ContentType;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.equalTo;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.greaterThan;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.greaterThanOrEqualTo;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.lessThanOrEqualTo;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.lessThan;
public class HamcrestNumberExample {
public String endpoint = "https://restful-booker.herokuapp.com/booking/1";
@Test
public void numberAssertions() {
RestAssured.given().contentType(ContentType.JSON)
.when().get(endpoint).then()
.body("totalprice", equalTo(164));
RestAssured.given().contentType(ContentType.JSON)
.when().get(endpoint)
.then().body("totalprice",greaterThan(100));
RestAssured.given().contentType(ContentType.JSON)
.when().get(endpoint)
.then().body("totalprice",greaterThanOrEqualTo(50));
RestAssured.given().contentType(ContentType.JSON)
.when().get(endpoint)
.then().body("totalprice",lessThan(1000));
RestAssured.given().contentType(ContentType.JSON)
.when().get(endpoint)
.then().body("totalprice",lessThanOrEqualTo(1000));
}
}
The output of the above program is
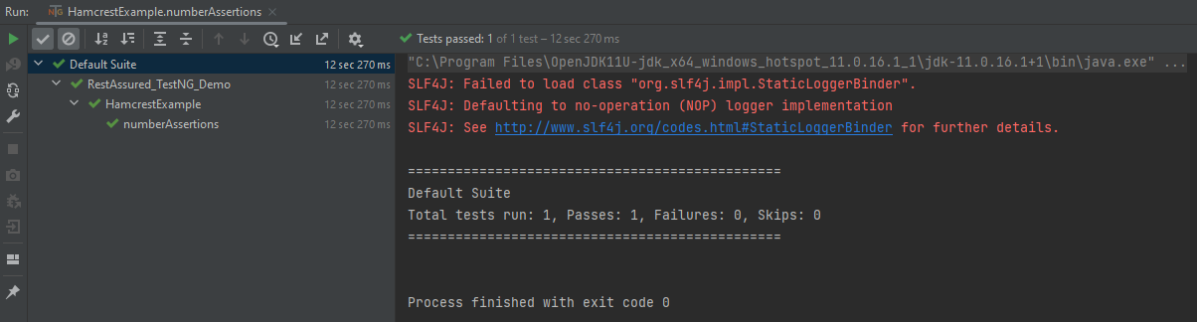
String related Assertions
- equalTo – It checks whether the extracted string from JSON is equal to the expected string.
- equalToIgnoringCase – It checks if the extracted string from JSON matches the expected string. The comparison does not consider case (small or capital).
- equalToIgnoringWhiteSpace – It checks if the extracted string from JSON matches the expected string. It takes into account the white spaces.
- containsString – It checks whether the extracted string from JSON contains the expected string as a substring.
- startsWith – It checks whether the extracted string from JSON is starting with a given string or character.
- endsWith – It checks whether the extracted string from JSON is ending with a given string or character.
Below assertions are imported from the package shown below:-
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.containsString;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.endsWith;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.equalTo;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.equalToIgnoringCase;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.startsWith;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.equalToIgnoringWhiteSpace;
Below are examples to show the use of string-related assertions.
import io.restassured.RestAssured;
import io.restassured.http.ContentType;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.containsString;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.endsWith;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.equalTo;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.equalToIgnoringCase;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.startsWith;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.equalToIgnoringWhiteSpace;
public class HamcrestStringAssertions {
public String endpoint = "https://restful-booker.herokuapp.com/booking/1";
@Test
public void stringAssertions() {
RestAssured.given().contentType(ContentType.JSON)
.when().get(endpoint)
.then().body("firstname",equalTo("Mary"));
RestAssured.given().contentType(ContentType.JSON)
.when().get(endpoint)
.then().body("firstname",equalToIgnoringCase("mary"));
RestAssured.given().contentType(ContentType.JSON)
.when().get(endpoint)
.then().body("firstname",containsString("Mary"));
RestAssured.given().contentType(ContentType.JSON)
.when().get(endpoint)
.then().body("firstname",startsWith("M"));
RestAssured.given().contentType(ContentType.JSON)
.when().get(endpoint)
.then().body("firstname",endsWith("y"));
RestAssured.given().contentType(ContentType.JSON)
.when().get(endpoint)
.then().body("firstname",equalToIgnoringWhiteSpace(" Mary "));
}
}
The output of the above program is
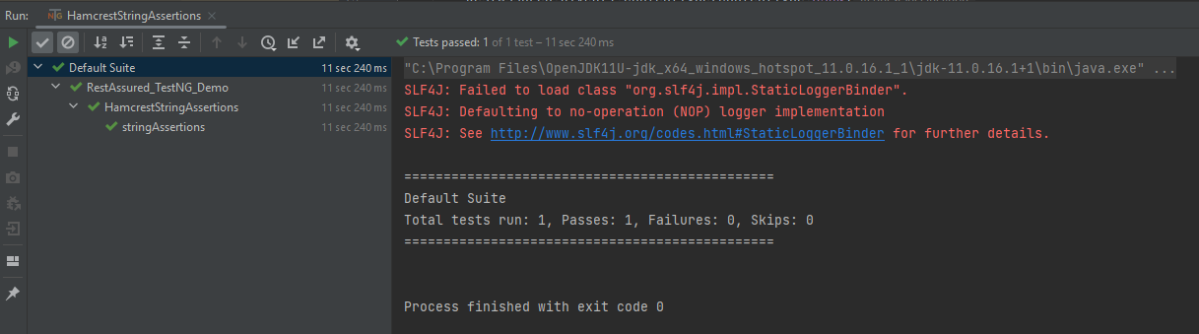
nullValue
It checks whether the extracted response from JSON is NULL or Not.
Below assertions are imported from the package shown below:-
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.hasKey;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.is;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.nullValue;
Below are examples to show the use of collection-related assertions.
import io.restassured.RestAssured;
import io.restassured.http.ContentType;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.is;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.nullValue;
public class HamcrestNullAssertion {
public String endpoint = "https://restful-booker.herokuapp.com/booking/1";
@Test
public void nullAssertion() {
RestAssured.given().contentType(ContentType.JSON)
.when().get(endpoint)
.then().body("totalprice1", is(nullValue()));
}
}
The output of the above program is
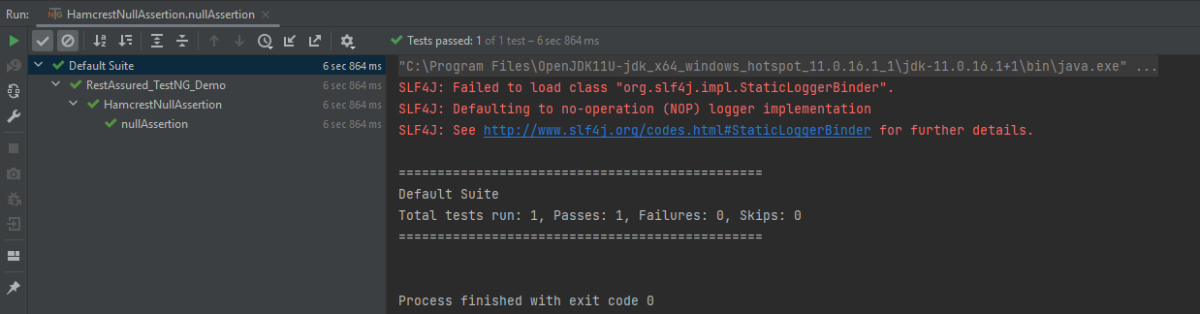
hasKey
It checks whether the extracted map has an expected key.
import io.restassured.RestAssured;
import io.restassured.http.ContentType;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.hasKey;
public class HamcrestHasKeyAssertion {
public String endpoint = "https://restful-booker.herokuapp.com/booking/1";
@Test
public void collectionAssertions() {
RestAssured.given().contentType(ContentType.JSON)
.when().get(endpoint)
.then().body("bookingdates",hasKey("checkin"));
}
}
The output of the above program is
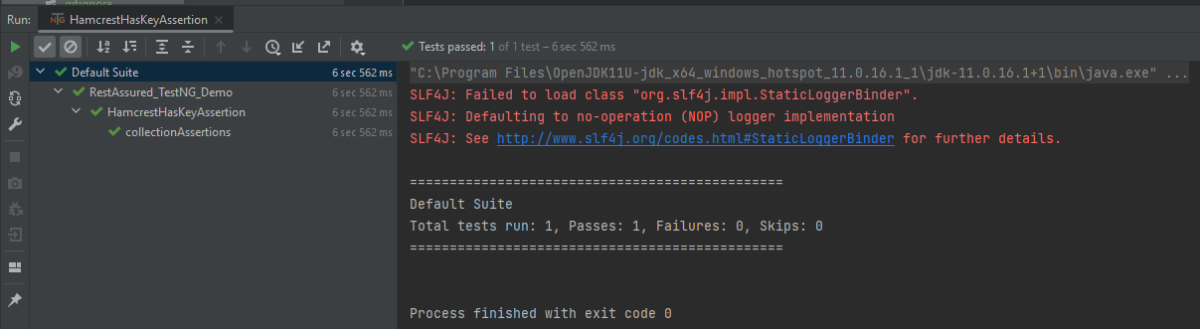
Not Assertion
The not assertion inverts the meaning of the other assertions. For example, if you want to perform negative assertions, then we can use any assertions with NOT.
The below assertion is imported from the package shown below:-
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.equalTo;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.not;
Below are examples to show the use of negative assertions.
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.equalTo;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.not;
import io.restassured.RestAssured;
import io.restassured.http.ContentType;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class HamcrestNotAssertion {
public String endpoint = "https://restful-booker.herokuapp.com/booking/1";
@Test
public void negativeAssertions() {
RestAssured.given().contentType(ContentType.JSON)
.when().get(endpoint)
.then().body("totalprice",not(equalTo(874)));
}
}
The output of the above program is
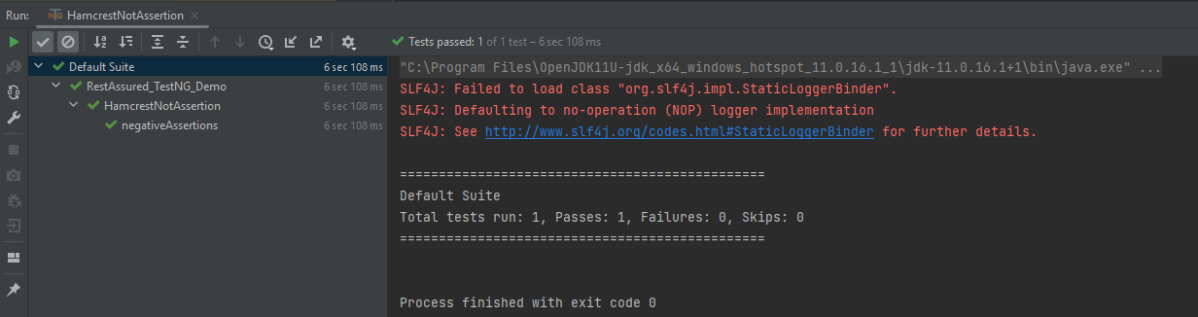
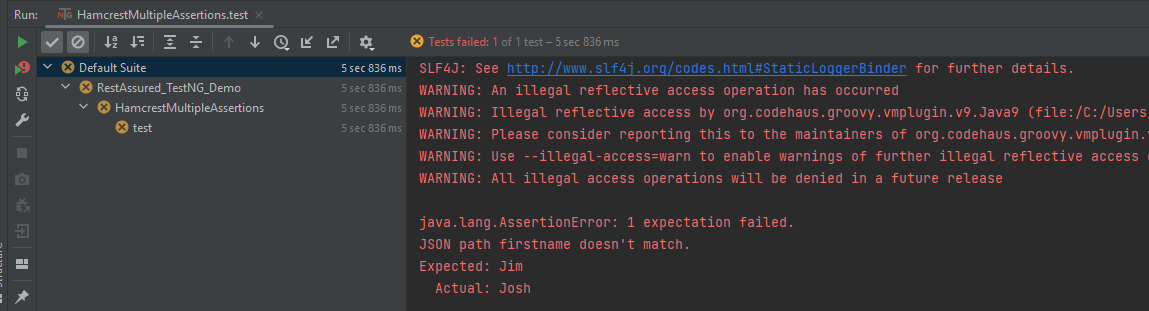
Multiple Assert Statements
In the below example, all 3 assertions will fail. It will only execute the first assertion. If the first assertion fails, then other assertions will not be executed.
import io.restassured.RestAssured;
import io.restassured.http.ContentType;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.equalTo;
public class HamcrestMultipleAssertions {
public String endpoint = "https://restful-booker.herokuapp.com/booking/1";
@Test
public void test1() {
RestAssured.given().contentType(ContentType.JSON)
.when().get(endpoint).then()
.body("firstname", equalTo("Jim"), // will fail
"lastname", equalTo("Smith"), // will fail
"totalprice", equalTo(314)); // will fail
}
}
The output of the above program is
To execute all the assertions in the test case, combine them into a single body. This should be done just like it is shown below. You can see that all the assertions failed, and they are shown in the response.
import io.restassured.RestAssured;
import io.restassured.http.ContentType;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.equalTo;
public class HamcrestMultipleAssertions {
public String endpoint = "https://restful-booker.herokuapp.com/booking/1";
@Test
public void test1() {
RestAssured.given().contentType(ContentType.JSON)
.when().get(endpoint).then()
.body("firstname", equalTo("Jim"), // will fail
"lastname", equalTo("Smith"), // will fail
"totalprice", equalTo(314)); // will fail
}
}
The output of the above program is
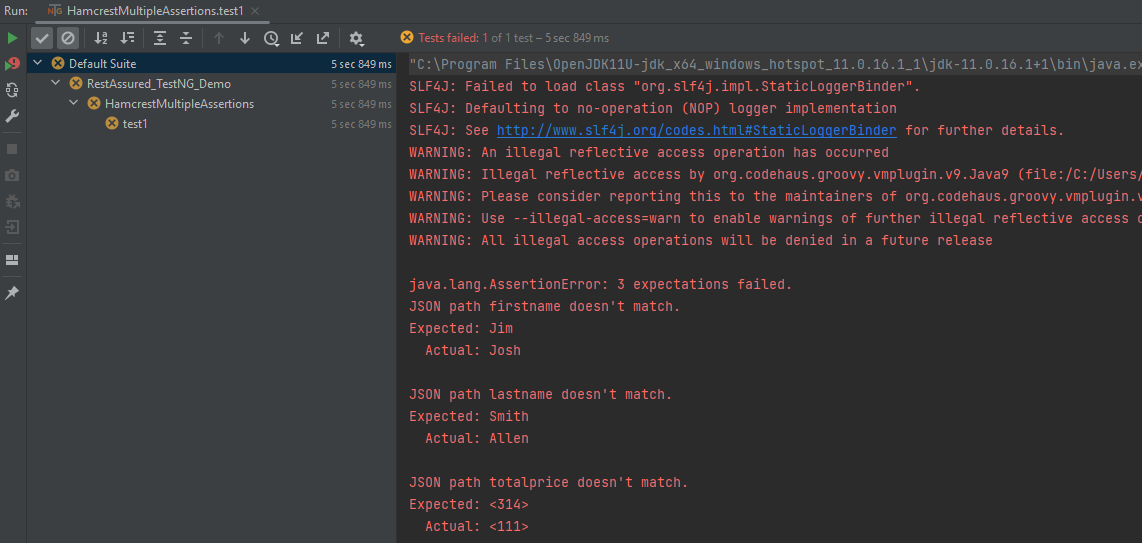
I have tried to show the use of a few of the most commonly used assertion methods. There are many more methods available in Hamcrest package. To know about other methods, write import static org.hamcrest.Matchers and add (.) at the end, it will show the list of all the methods available in Hamcrest.
To know more details related to Hamcrest assertion, you can refer the official website – Hamcrest
Points to Remember:
- Hamcrest is commonly used in JUnit, RestAssured, and Mockito for API and unit testing
- It offers a variety of matchers for different data types, such as: Numbers: greaterThan(), lessThan(), Strings: containsString(), startsWith(), endsWith()
- You can combine multiple matchers using logical operators: assertThat(score, allOf(greaterThan(50), lessThan(100)))
- Encourages fluent and expressive test writing with assertThat() instead of assertEquals()
We are done! Congratulations on making it through this tutorial and hope you found it useful! Happy Learning!!
Additional Tutorials
