Welcome to the Java Quiz! This blog post features 25 multiple-choice questions that explore the concepts of Arrays in Java.
1. What is an array in Java?
a) A data structure that can hold elements of different types
b) A class that allows storing single data type elements in a contiguous memory location
c) A collection of elements in no specific order
d) A method for sorting elements
Answer 1
b) A class that allows storing single data type elements in a contiguous memory location
Arrays in Java are used to store multiple values of the same data type in a contiguous memory location.
2. How do you instantiate an array of integers with 10 elements in Java?
a) int[] arr = new int[10];
b) int arr = new int(10);
c) int arr[10] = new int[];
d) int(10) arr = new int[];
Answer 2
a) int[] arr = new int[10];
3. What is the default value of an element in an int array in Java?
Choose one option
a) 1
b) 0
c) null
d) Undefined
Answer 3
b) 0
In Java, arrays of primitive types like int are initialized to their default values. The default value for int is 0
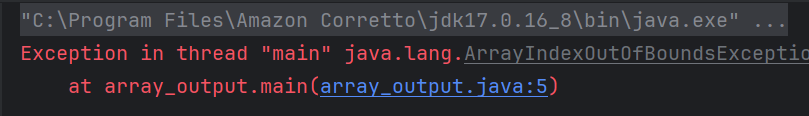
4. What will be the output of the following Java program?
class array_output
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int array_variable [] = new int[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
{
array_variable[i] = i;
System.out.print(array_variable[i] + " ");
i++;
}
}
}
Choose one option
a) 0 2 4 6 8
b) 1 3 5 7 9
c) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
d) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Answer 4
a) 0 2 4 6 8
When an array is declared using new operator then all of its elements are initialized to 0 automatically. for loop body is executed 5 times as whenever controls comes in the loop i value is incremented twice, first by i++ in body of loop then by ++i in increment condition of for loop.
5. What is the maximum number of dimensions an array can have in Java?
a) 1
b) 255
c) 2
d) No theoretical limit
Answer 5
b) 255
Java allows arrays to have up to 255 dimensions.
6. What will be the output of the following Java program?
public class array_output {
public static void main(String args[])
{
char array_variable [] = new char[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
{
array_variable[i] = 'i';
System.out.print(array_variable[i] + "");
}
}
}
Choose one option
a) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
b) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
c) i j k l m n o p q r
d) i i i i i i i i i i
Answer 6
d) i i i i i i i i i i
When an array is declared using the new operator, all of its elements are automatically initialized to default values—0 for numeric types, null for reference types, and ‘\0’ (null character) for char.

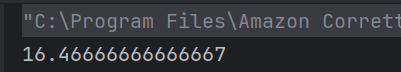
7. What will be the output of the following Java program?
public class array_output {
public static void main(String args[])
{
double num[] = {5.5, 10.1, 11, 12.8, 56.9, 2.5};
double result;
result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 6; ++i)
result = result + num[i];
System.out.print(result/6);
}
}
Choose one option
a) 16.34
b) 16.566666644
c) 16.46666666666667
d) 16.46666666666666
Answer 7
c) 16.46666666666667
8. What happens if you try to access an index of an array that is out of bounds?
Choose one option
a) Compile-time error
b) Returns null
c) Throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
d) None of the above
Answer 8
c) Throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
9. How do you declare an array of strings?
a) String[] arr;
b) String arr[];
c) String arr();
d) String arr{};
Answer 9
a) String[] arr;
This is the standard way of declaring an array of strings in Java.
10. Which of the following is a valid declaration and initialization of String array in Java
a) String[] names ={“Tim”,”Mark”,”Charlie”}
b) String names[] ={“Tim”,”Mark”,”Charlie”}
c) String[3] names ={“Tim”,”Mark”,”Charlie”}
d) Both a) and b)
e) Both a) and c)
Answer 10
d) Both a) and b)
String[3] names = {“Tim”, “Mark”, “Charlie”};` is incorrect because Java does not allow specifying the size of the array within square brackets during initialization in this manner.
11. What will be the output?
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] arr = {"Java", "Python", "C++"};
System.out.println(arr[1]);
}
}
Choose one option
a) Java
b) Python
c) C++
d) Compilation error
Answer 11
b) Python
arr[1] accesses the second element of the array, which is “Python”.
12. Which of the following statements is true?
Choose one option
a) Arrays are immutable
b) Arrays are objects
c) Arrays store elements of any data type
d) Arrays automatically grow
Answer 12
b) Arrays are objects
In Java, arrays are objects and are part of the java.lang package.
13. What is the primary use of the `System.arraycopy()` method in Java?
Choose one option
a) To copy one array to another
b) To reverse an array
c) To sort an array
d) To find an element in an array
Answer 13
a) To copy one array to another
System.arraycopy() is used to copy elements from one array to another.
14. What is printed by the following code snippet?
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[5];
System.out.println(arr[1]);
}
}
Choose one option
a) 0
b) null
c) undefined
d) Compilation error
Answer 14
a) 0
Integer arrays are initialized to 0 by default.
15. What will be the result of this program?
public class array_output {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4};
System.out.println(arr.length);
}
}
Choose one option
a) 0
b) 3
c) 4
d) Compilation error
Answer 15
c) 4
arr.length returns the number of elements in the array, which is 4.
16. What exception is thrown by Java code when trying to store values in a sufficiently large dimension of an array but with the wrong data type?
Choose one option
a) ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
b) IllegalArgumentException
c) ClassCastException
d) ArrayStoreException
Answer 16
d) ArrayStoreException
ArrayStoreException occurs when attempting to store incorrect types into arrays of object types.
17. Which of the following is not a valid way to declare a two-dimensional array in Java?
Choose one option
a) int[][] arr = new int[3][3];
b) int arr[][] = new int[3][3];
c) int[] arr = new int[3][];
d) int[][] arr = new int[][];
Answer 17
d) int[][] arr = new int[][];
Option D is invalid because while it declares a two-dimensional array, it does not specify the size of either dimension at the time of declaration.
18. What is the correct way to iterate over a Java array using an enhanced for loop?
a) for (int i : arr)
b) for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++)
c) for (arr : int i)
d) for (arr i : int)
Answer 18
a) for (int i : arr)
The enhanced for loop in Java is written as for (type variable : array).
19. What will happen if you try to store a double value into an int array?
a) The value will be rounded
b) The value will be truncated
c) A ClassCastException will be thrown
d) A compile-time error
Answer 19
d) A compile-time error
You cannot store a double value in an int array without explicit casting, leading to a compile-time error.
20. What is the output of the following code?
public class array_output {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int[] arr = {2, 4, 6, 8};
System.out.println(arr[arr.length]);
}
}
Choose one option
a) 8
b) 4
c) 0
d) ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
Answer 20
d) ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
Since array indices are 0-based, accessing arr[arr.length] is out of bounds. The valid indices for this array are from 0 to arr.length – 1.
21. What is the output of the following code?
public class array_output {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = arr[i] * 2;
}
System.out.println(arr[2]);
}
}
Choose one option
a) 3
b) 6
c) 8
d) 10
Answer 21
b) 6
The loop multiplies each element by 2. Therefore, arr[2] becomes 3 * 2 = 6.
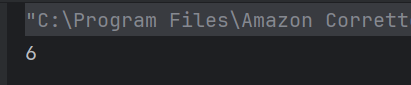
22. What will be the output of the below program?
public class array_output {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[] arr = {10, 20, 30, 40};
System.out.println(arr[1] + arr[2]);
}
}
Choose one option
a) 30
b) 50
c) 60
d) 70
Answer 22
b) 50
arr[1] is 20 and arr[2] is 30, so the sum is 20 + 30 = 50.
23. Can you resize an array in Java after it is created?
Choose one option
a) Yes
b) No
Answer 23
b) No
24. How can you access the element at the second row and third column of a two-dimensional array “matrix”?
a) matrix[3][2]
b) matrix[2, 3]
c) matrix[1][2]
d) matrix[2:3]
Answer 24
c) matrix[1][2]
Array indexing starts at 0 in Java, so the second row is index 1, and the third column is index 2.
25. What will be the default value of the elements in a two-dimensional array of type `int[][]` in Java?
a) null
b) 0
c) undefined
d) Compilation error
Answer 25
b) 0
For arrays of primitive data types like int, the default value of the elements is 0.
We would love to hear from you! Please leave your comments and share your scores in the section below