Last Updated On
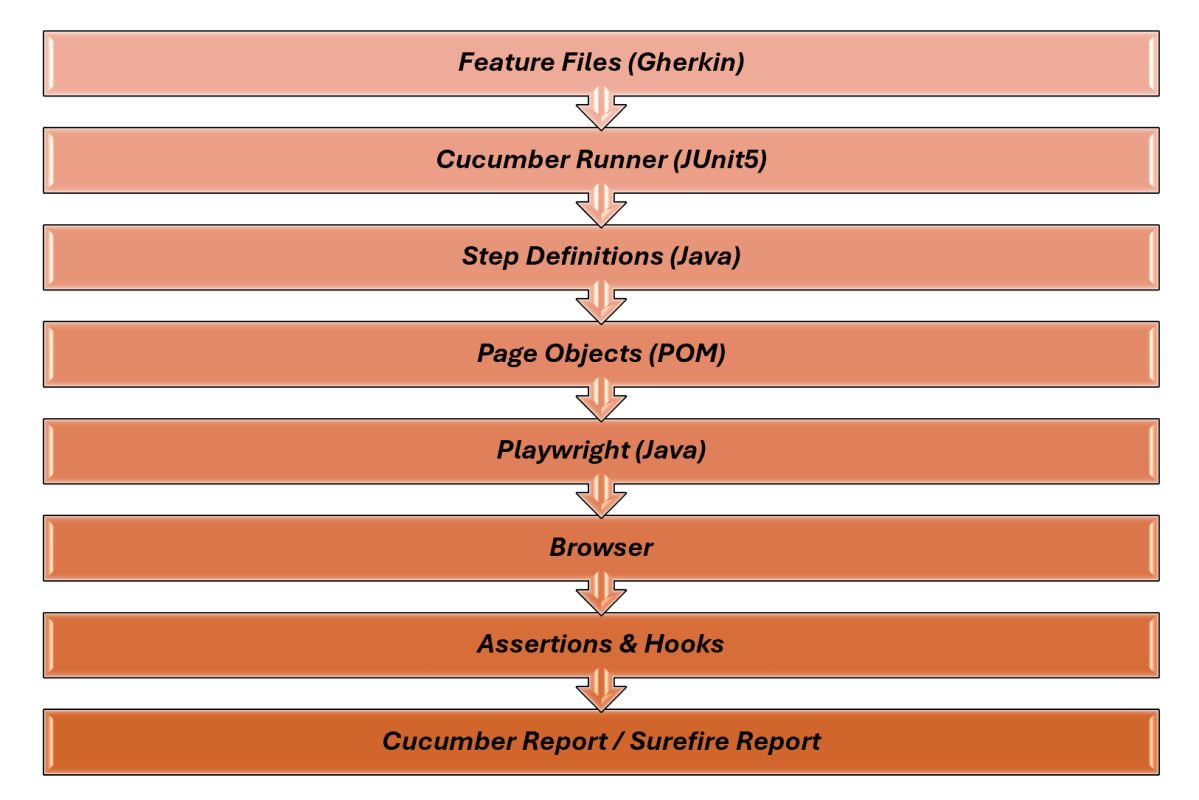
In this blog we will be utilizing Playwright Java for the execution of Parameterized Tests. We can parameterize tests using JUnit5 or TestNG. Here, we are using JUnit5 to parameterize the tests.
Table of Contents
- What is Parameterized testing?
- Why Parameterized testing is important?
- Parameterized Tests using JUnit5
- System requirements
- Implementation Steps
- Summary
What is Parameterized testing?
Parameterized testing is a testing technique. In this technique, the same test method is executed multiple times with different input values. It also has varying expected results.
Instead of writing many separate tests, you write one test and pass different data to it.
Why Parameterized testing is important?
1. Increased Test Coverage: Parameterized testing allows a single test method to run multiple times with different datasets. This ensures that various scenarios, inputs, and edge cases are covered, leading to thorough testing of the application’s functionality.
2. Maintainability: A parameterized test reduces code duplication since the same test logic is applied across different input data. This means fewer test scripts need maintenance. Any changes to the test logic affect all test cases using that method at the same time.
3. Scalability: Tests can be easily scaled by augmenting the set of input data. This helps account for new test scenarios. There is no need for rewriting test logic.
4. Improving Design Quality: Using parameterized tests encourages designing tests that focus on core logic. They foster better test architecture and design practices. These practices can handle diverse scenarios effectively.
Parameterized Tests using JUnit5
JUnit 5 offers robust support for parameterized testing through the @ParameterizedTest annotation. This feature allows us to run a single test method multiple times, each time with a different set of parameters. One of the ways to specify these parameters is by using the @CsvSource annotation.
The @CsvSource annotation allows us to specify the parameter values directly as a list of comma-separated values (CSV) within parentheses. Each line of CSV represents one set of input parameters for the test method.
Below is the example.
@ParameterizedTest
@CsvSource({
"admin123,admin123,Invalid credentials",
"admin,admin12,Invalid credentials",
"Admin,1234,Invalid credentials",
"12345,%^$£56,Invalid credentials"
})
public void unsuccessfulLogin(String username, String password, String expectedErrorMessage) {
LoginPage loginPage = new LoginPage(page);
loginPage.login(username,password);
String actualErrorMessage = loginPage.getErrorMessage();
Assertions.assertEquals(expectedErrorMessage, actualErrorMessage, "");
}
System requirements
The following prerequisites are required to be installed on the machine to begin with a smooth setup and installation.
- Java 11 or higher
- IntelliJ IDE or any other IDE to create a project
- Maven
- Browsers on which tests need to be run, like Chrome, Firefox, etc.
Implementation Steps
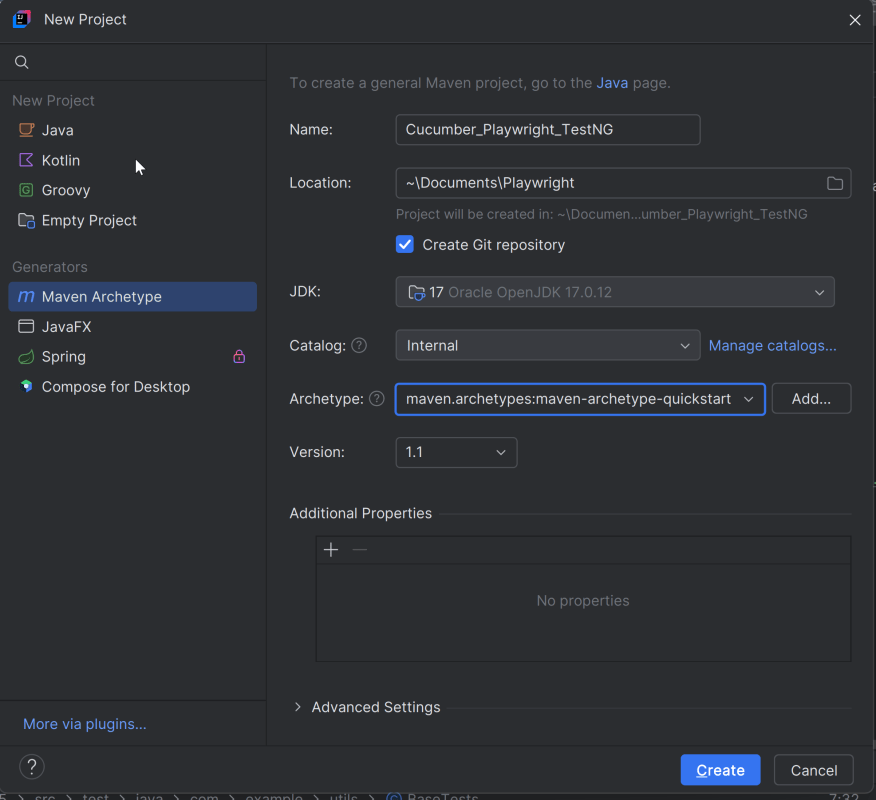
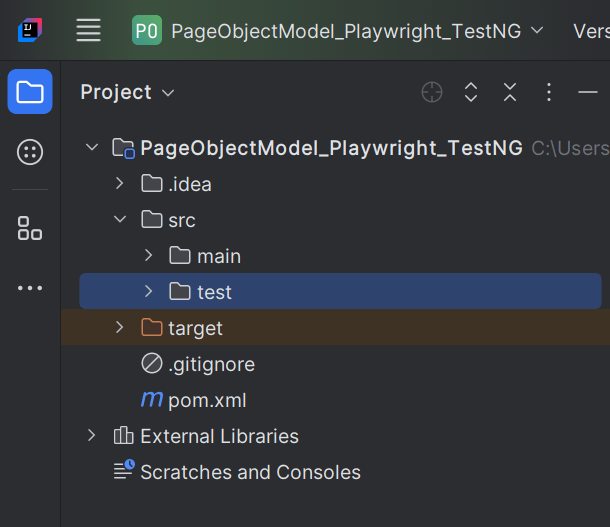
1. Create a new Maven Project
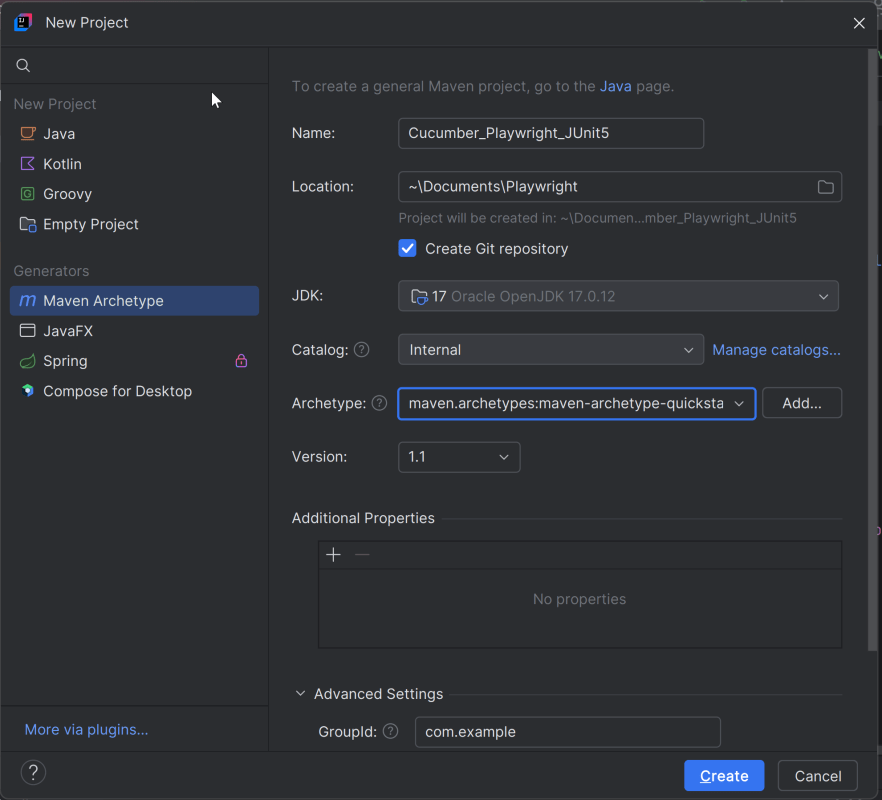
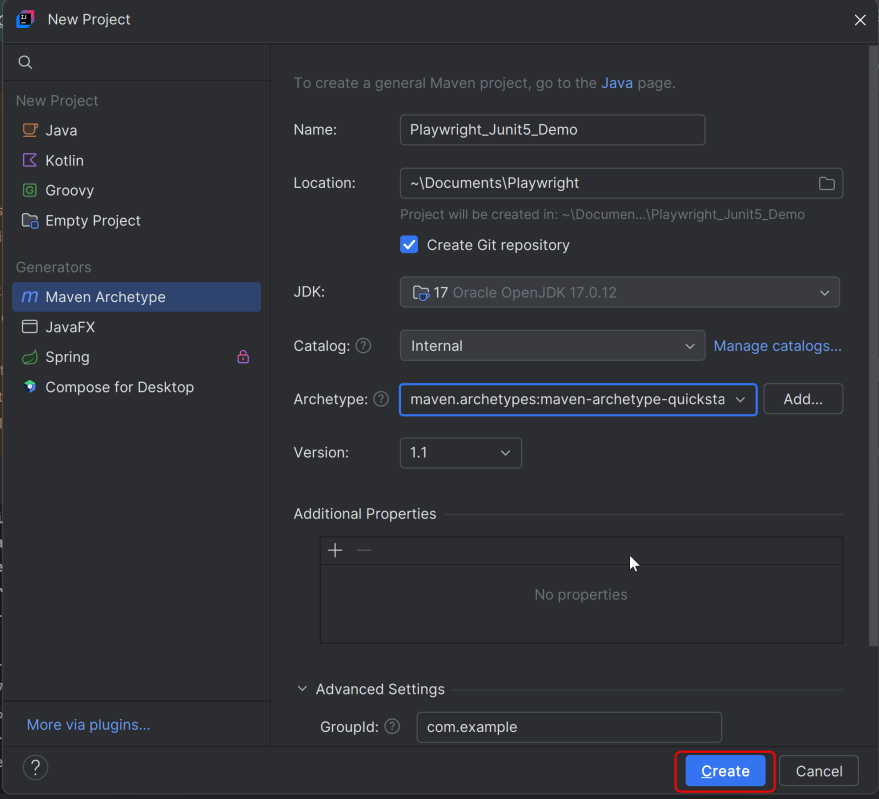
The first step in setup is to create a new Maven project. I will be using IntelliJ in this tutorial. The following steps need to be followed to create a new Maven project :
Open IntelliJ, Navigate to File >> New >> Project

2. In the New Project window, enter the following details:
- Name of the Project – PageObjectModel_Playwright_JUnit5
- Location/path where the project needs to be saved – Documents/Playwright (my location)
- Select JDK version — I am using JDK 17
- Archetype — Search for “quickstart” and select maven-archetype-quickstart from the results
Click on the Create button to create the project.
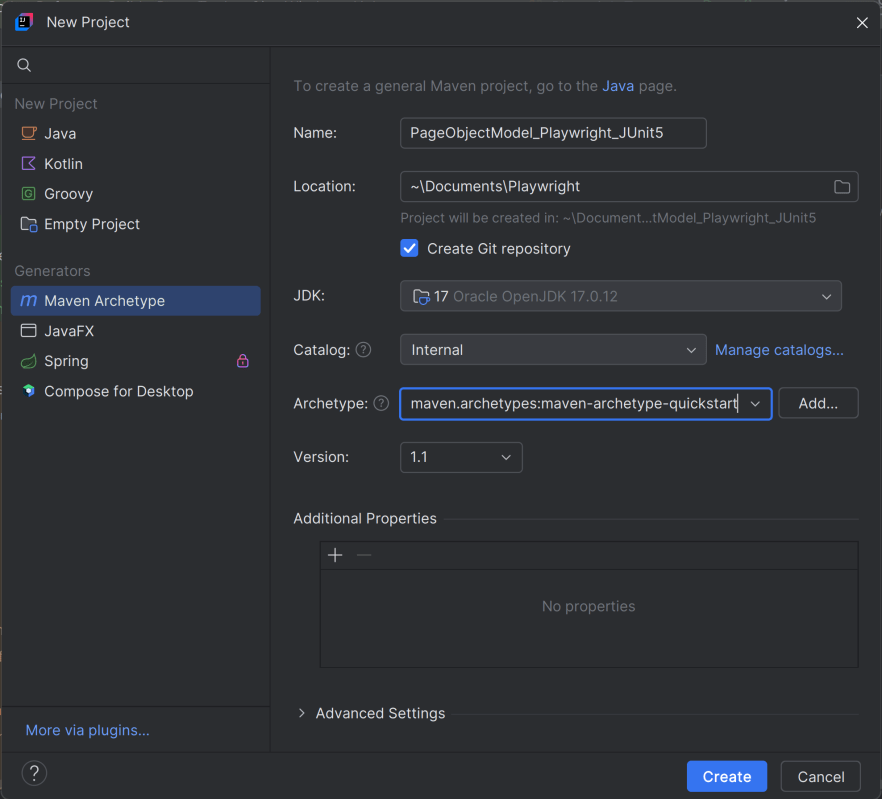
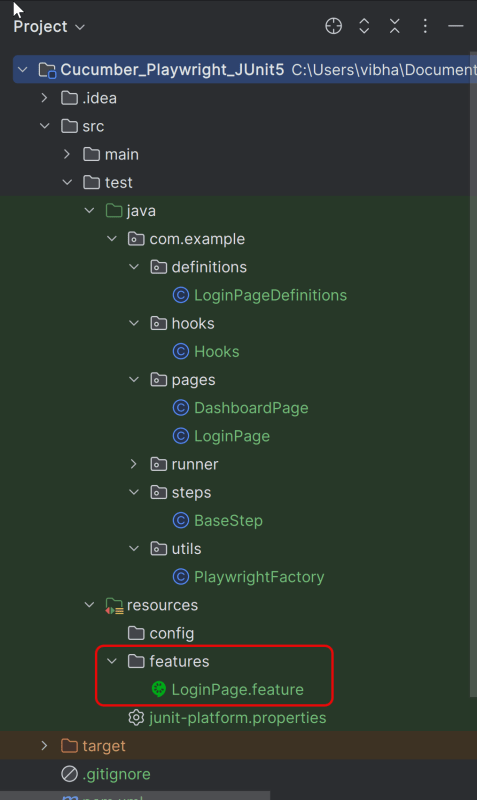
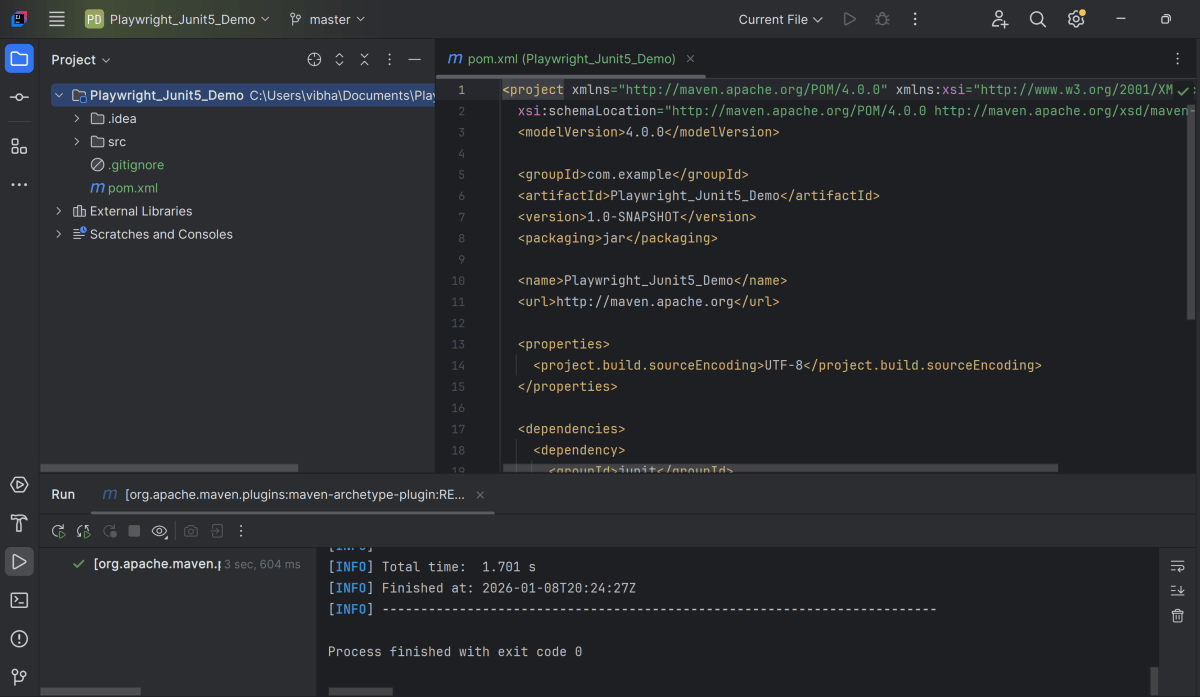
This will create a project as shown below in the IntelliJ.
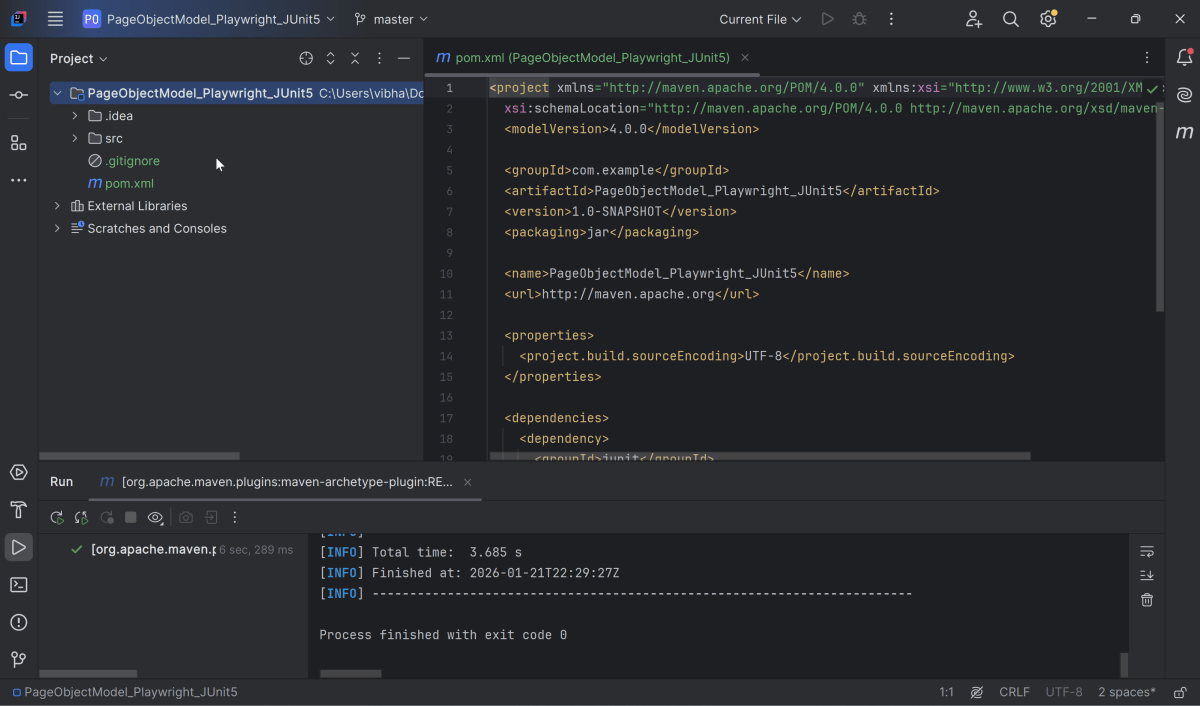
2. Setup Playwright with Java and JUnit5
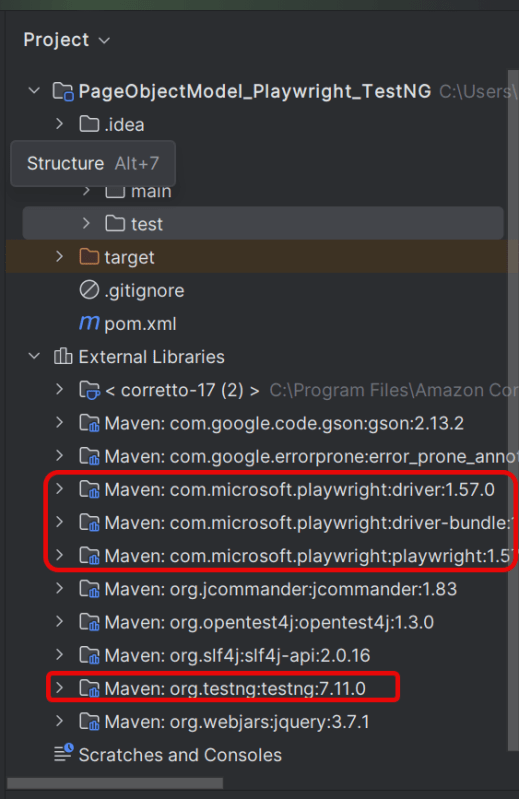
Add the Playwright and JUnit5 dependencies to the pom.xml. The latest dependency can be found from here.
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>PageObjectModel_Playwright_JUnit5</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>PageObjectModel_Playwright_JUnit5</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<playwright.version>1.57.0</playwright.version>
<junit.jupiter.engine.version>6.1.0-M1</junit.jupiter.engine.version>
<junit.jupiter.api.version>6.1.0-M1</junit.jupiter.api.version>
<junit.jupiter.params.version>6.1.0-M1</junit.jupiter.params.version>
<maven.compiler.plugin.version>3.14.1</maven.compiler.plugin.version>
<maven.compiler.source.version>17</maven.compiler.source.version>
<maven.compiler.target.version>17</maven.compiler.target.version>
<maven.surefire.plugin.version>3.5.4</maven.surefire.plugin.version>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
<maven.site.plugin.version>4.0.0-M16</maven.site.plugin.version>
<maven.surefire.report.plugin.version>3.5.4</maven.surefire.report.plugin.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.microsoft.playwright</groupId>
<artifactId>playwright</artifactId>
<version>${playwright.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-engine</artifactId>
<version>${junit.jupiter.engine.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId>
<version>${junit.jupiter.api.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-params</artifactId>
<version>${junit.jupiter.params.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.compiler.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<source>${maven.compiler.source.version}</source>
<target>${maven.compiler.target.version}</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.surefire.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<testFailureIgnore>true</testFailureIgnore>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-site-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.site.plugin.version}</version>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
<reporting>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-report-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven.surefire.report.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<outputName>JUnit5 Report</outputName>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</reporting>
</project>
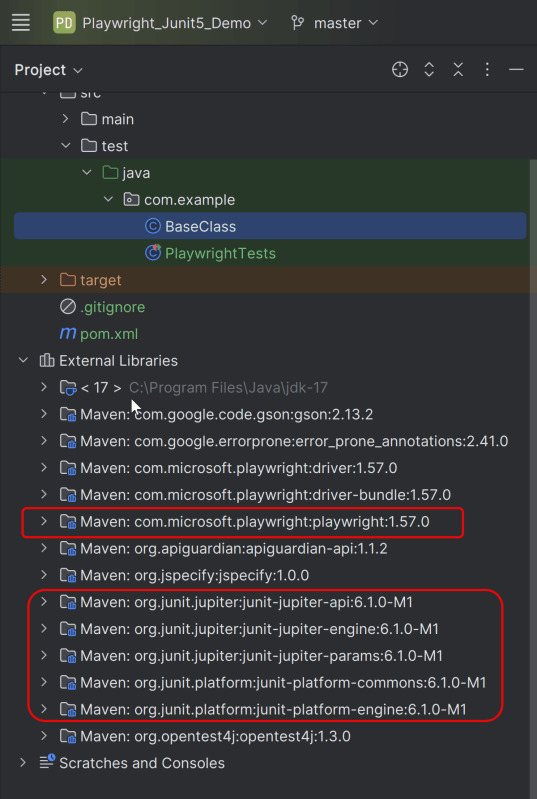
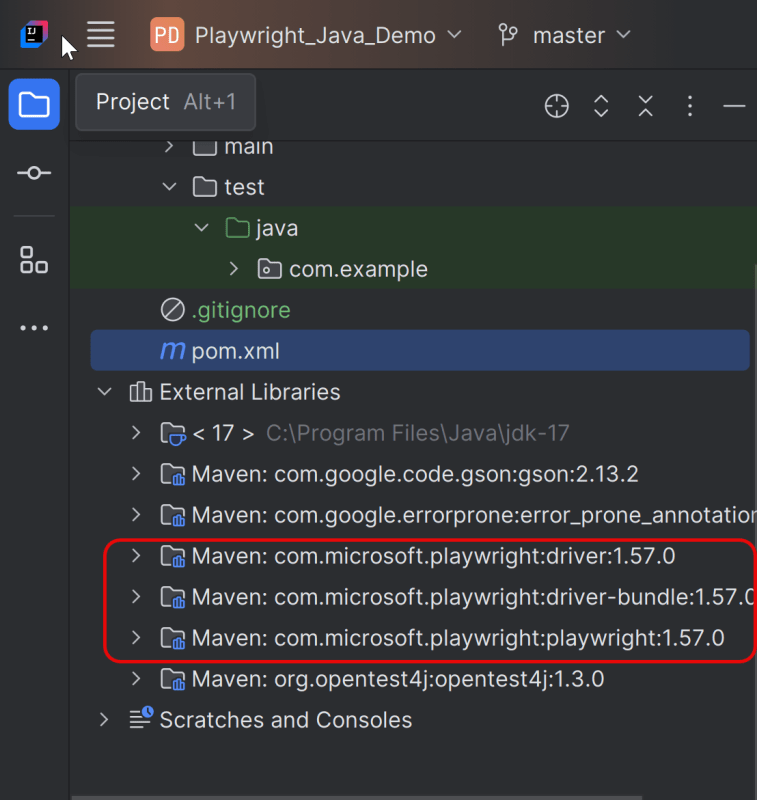
After adding the dependency, refresh the project. We will see that the Playwright jar files are downloaded in External Libraries.
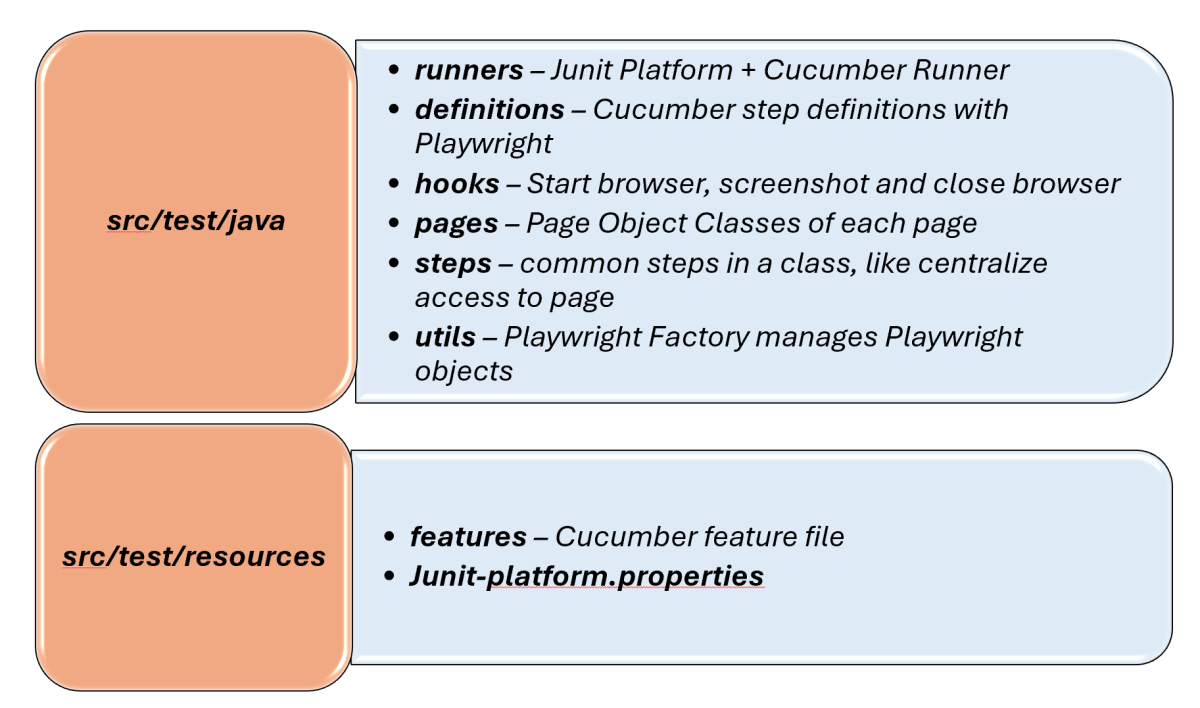
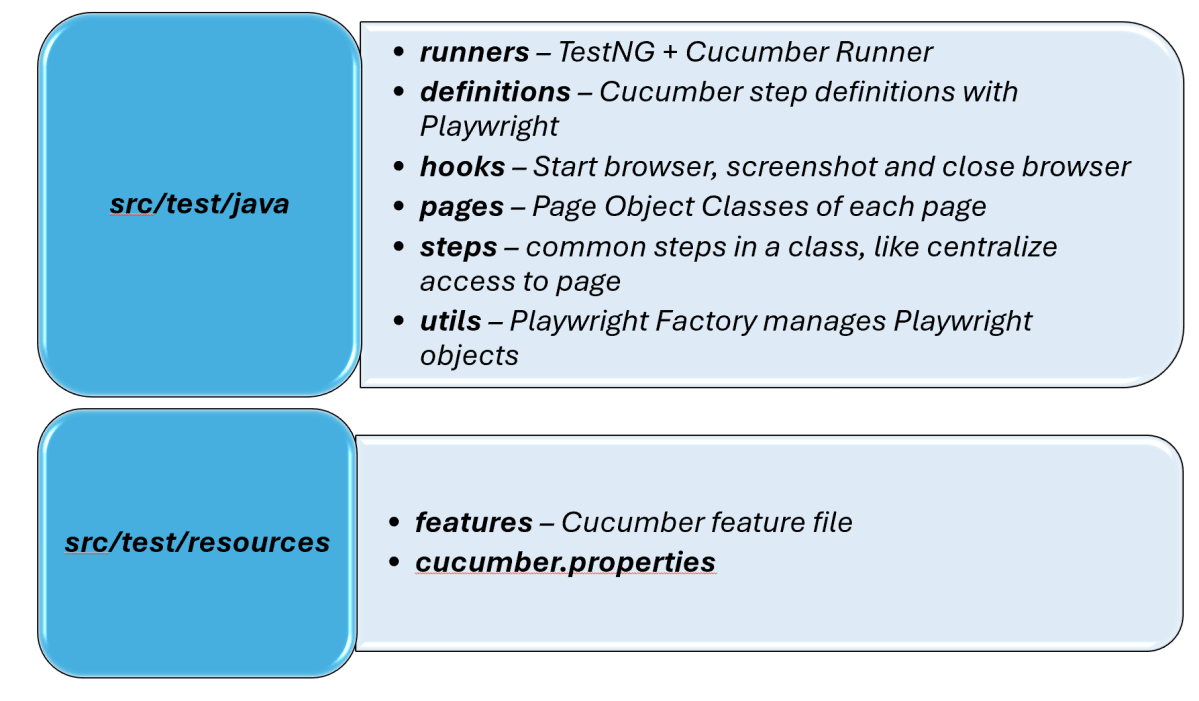
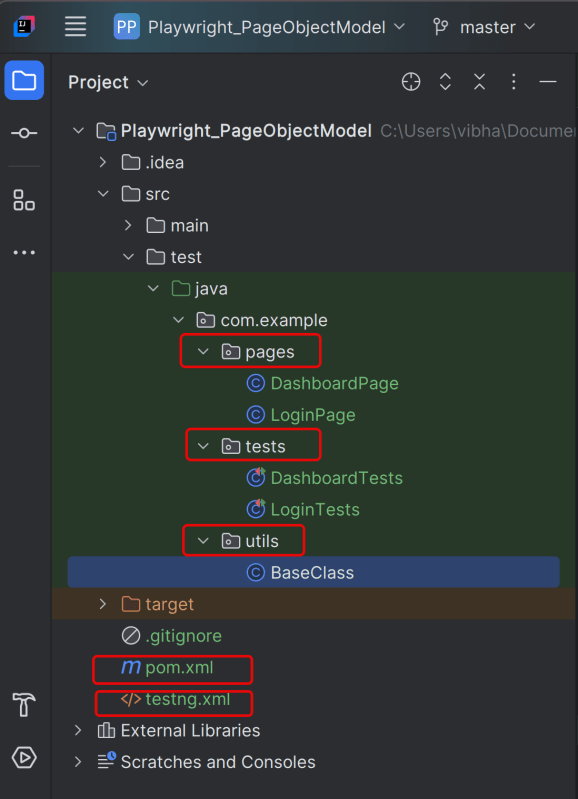
3. Project Structure for Maintainability
Creating a well-organized project structure is crucial for maintaining a scalable and efficient automation framework.
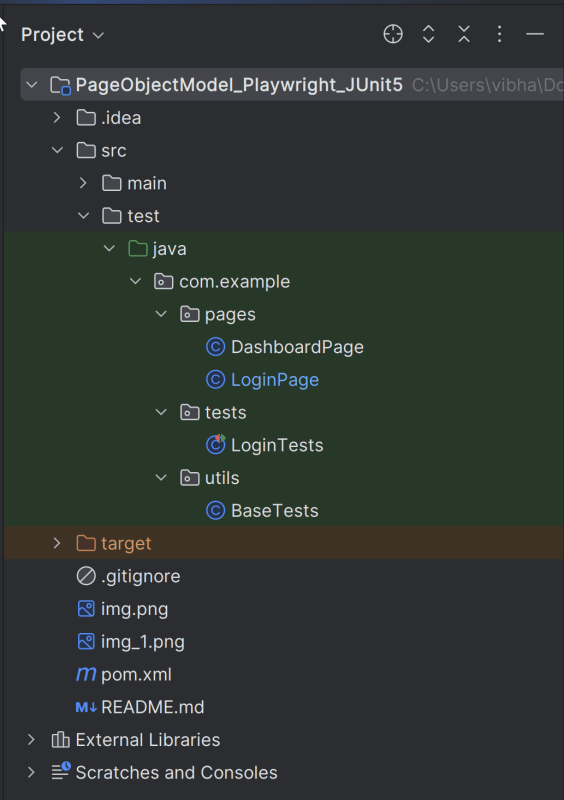
Page Classes (src/main/java/.../pages/): Each web page in your application should have a corresponding page class. This class encapsulates all the functionalities of the web page, following the Page Object Model.
Utility Classes (src/main/java/.../utils/): These classes can include various utilities like configuration readers, helper methods for common tasks, etc.
Test Classes (src/test/java/.../tests/): Here, you write your actual test cases, utilizing the page classes.
Maven Configuration (pom.xml): This file manages project dependencies, plugins, and other configurations.
4. Creating Page Object Classes
Page classes serve as an interface to a web page’s UI elements. Each page class corresponds to a page in your application, encapsulating the actions that can be performed on that page.
- Identify the UI Elements: Determine all the elements on the web page that your test will interact with, such as text boxes, buttons, and links.
- Define Selectors: Store the selectors for these elements in your page class. It’s a best practice to externalize these selectors, but for simplicity, we’ll define them directly in the class.
- Implement Actions: Create methods for each action that can be performed on the page, like entering text, clicking buttons, etc.
Creating LoginPage Class
import com.microsoft.playwright.Page;
public class LoginPage {
private Page page;
//Locators
private final String usernameLocator = "input[name='username']";
private final String passwordLocator = "input[name='password']";
private final String submitButton = "button[type='submit']";
private final String errorMessage = "//p[contains(@class, 'oxd-text oxd-text--p oxd-alert-content-text')]";
//Constructor
public LoginPage(Page page){
this.page = page;
}
public void login(String username, String password) {
page.fill(usernameLocator,username);
page.fill(passwordLocator,password);
page.click(submitButton);
}
public String getErrorMessage(){
return page.textContent(errorMessage);
}
}
Creating DashboardPage Class
package org.example.pages;
import com.microsoft.playwright.Page;
public class DashboardPage {
private Page page;
//Locators
private final String dashboardHeading = "//h6[contains(@class, 'oxd-topbar-header-breadcrumb-module')]";
//Constructor
public DashboardPage(Page page) {
this.page = page;
}
// Methods
public String getHeading() {
return page.textContent(dashboardHeading);
}
}
5. Write the Test Scripts
Create a Test files under src/test/java. Use these page classes in your test scripts to perform end-to-end scenarios. This will keep your tests clean and focused on logic rather than details about the UI elements.
A typical test class includes:
- Setup Method: Initializes the Playwright browser and other prerequisites before each test.
- Test Methods: Individual test cases, each representing a different scenario.
- Teardown Method: Closes the browser and performs any cleanup after each test.
Creating BaseTests
This class contains the common variables and methods used throughout the project, like setup and teardown methods.
package org.example.utils;
package com.example.utils;
import com.microsoft.playwright.*;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.*;
// Subclasses will inherit PER_CLASS behavior.
@TestInstance(TestInstance.Lifecycle.PER_CLASS)
public class BaseTests {
// Shared between all tests in the class.
static Playwright playwright;
static Browser browser;
// New instance for each test method.
BrowserContext context;
protected Page page;
@BeforeAll
public static void launchBrowser() {
playwright = Playwright.create();
browser = playwright.chromium().launch(new BrowserType.LaunchOptions().setHeadless(false));
}
@AfterAll
public static void closeBrowser() {
playwright.close();
}
@BeforeEach
public void createContextAndPage() {
context = browser.newContext();
page = context.newPage();
page.navigate("https://opensource-demo.orangehrmlive.com/web/index.php/auth/login");
}
@AfterEach
public void closeContext() {
context.close();
}
}
Explanation
In JUnit you can initialize Playwright and Browser in @BeforeAll method and destroy them in @AfterAll. Use @TestInstance(TestInstance.Lifecycle.PER_CLASS) annotation to make JUnit create one instance of a class for all test methods within that class (by default each JUnit will create a new instance of the class for each test method). Store Playwright and Browser objects in instance fields. They will be shared between tests. Each instance of the class will use its own copy of Playwright.
1. Playwright playwright:
Initialized to manage the browser automation session, allowing interactions with different browsers.
2. Browser browser:
Declared to store the browser instance that will be shared across test methods within the class.
Playwright playwright;
Browser browser = null;
3. BrowserContext context:
Created anew for each test method to simulate independent browser sessions. This ensures that the browser state doesn’t carry over between tests.
4. Page page:
Represents a single tab or window in a browser used for performing actions and assertions.
BrowserContext context;
Page page;
5. @BeforeAll launchBrowser():
This method is annotated with @BeforeAll, indicating it runs once before any test methods in the current class.
The browser is launched in non-headless mode (setHeadless(false)), meaning an actual browser window is opened.
@BeforeAll
public void launchBrowser() {
playwright = Playwright.create();
browser = playwright.chromium().launch(new BrowserType.LaunchOptions().setHeadless(false));
}
6. @BeforeEach createContextAndPage()
This method runs before each test method in the class, as indicated by the @BeforeEach annotation.
It creates a new BrowserContext and a Page, ensuring each test runs in a clean, isolated state.
The method also navigates to a login page (“https://opensource-demo.orangehrmlive.com/web/index.php/auth/login”), setting up the initial state for each test.
@BeforeMethod
void createContextAndPage() {
context = browser.newContext();
page = context.newPage();
page.navigate("https://opensource-demo.orangehrmlive.com/web/index.php/auth/login");
}
7. @AfterAll closeContext()
Runs after each test method, annotated with @AfterMethod.
Closes the BrowserContext, effectively closing the browser tab and cleaning up resources.
@AfterAll
public static void closeBrowser() {
playwright.close();
}
8. @AfterEach closeContext()
Runs once after all test methods in the current class have executed, as indicated by the @AfterEach annotation.
Closes the Playwright instance, freeing up all resources used for automation.
@AfterEach
public void closeContext() {
context.close();
}
Creating a Login Page Test Class:
We will be automating the following test scenario using Playwright Java and run them in Chromium
- Verify that the user is able to login to the application successfully.
- Verify the invalid username generates error message “Invalid credentials” for multiple set of incorrect credentials.
package com.example.tests;
import com.example.pages.DashboardPage;
import com.example.pages.LoginPage;
import com.example.utils.BaseTests;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
public class LoginTests extends BaseTests {
@ParameterizedTest
@CsvSource({
"admin123,admin123,Invalid credentials",
"admin,admin12,Invalid credentials",
"Admin,1234,Invalid credentials",
"12345,%^$£56,Invalid credentials"
})
public void unsuccessfulLogin(String username, String password, String expectedErrorMessage) {
LoginPage loginPage = new LoginPage(page);
loginPage.login(username,password);
String actualErrorMessage = loginPage.getErrorMessage();
Assertions.assertEquals(expectedErrorMessage, actualErrorMessage, "");
}
@Test
public void successfulLogin() {
LoginPage loginPage = new LoginPage(page);
loginPage.login("Admin","admin123");
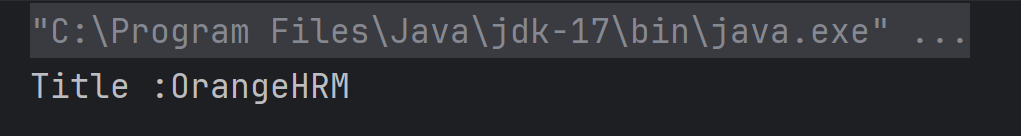
DashboardPage dashboardPage = new DashboardPage(page);
String actualHeading = dashboardPage.getDashboardPageHeading();
Assertions.assertEquals("Dashboard",actualHeading, "Unable to login to the application");
}
}
Explanation
1. successfulLogin
This method enters correct credentials and login to the application.
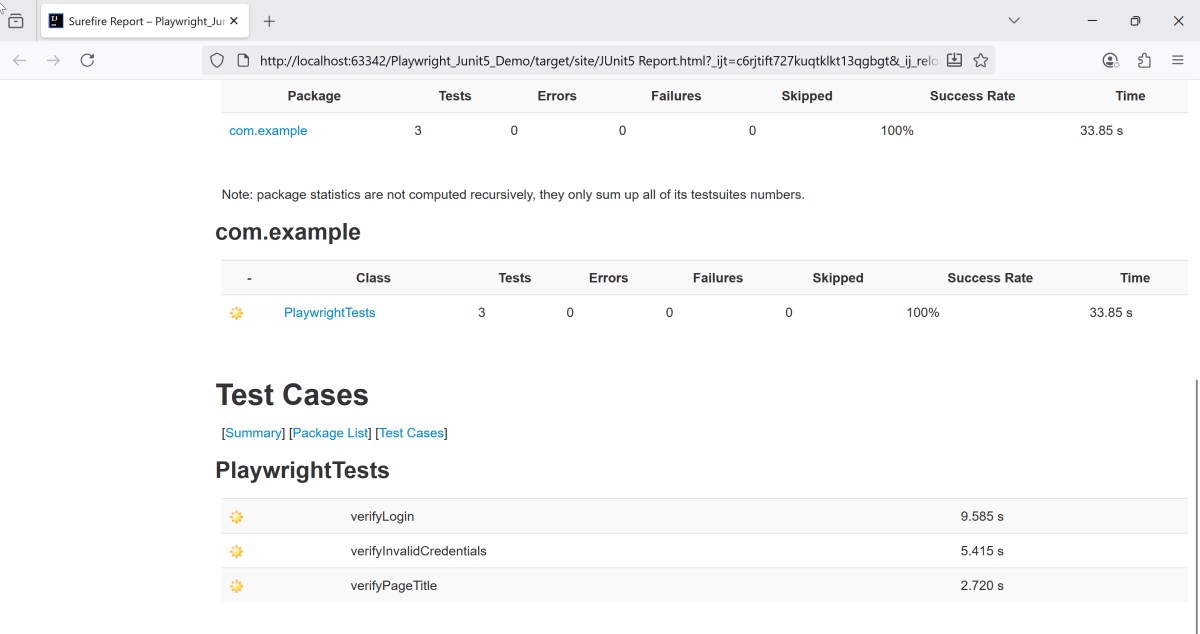
2. unsuccessfulLogin
This method enter the invalid username and password and click on the Submit button. Then, it assert that the error message generated by the application is equal to “Invalid credentials”. Below code is used to parameterize the tests.
@CsvSource – This annotation specifies the input data for the parameterized test. Each line within the annotation is a pair of input strings followed by an expected result string, separated by commas.
@ParameterizedTest
@CsvSource({
"admin123,admin123,Invalid credentials",
"admin,admin12,Invalid credentials",
"Admin,1234,Invalid credentials",
"12345,%^$£56,Invalid credentials"
})
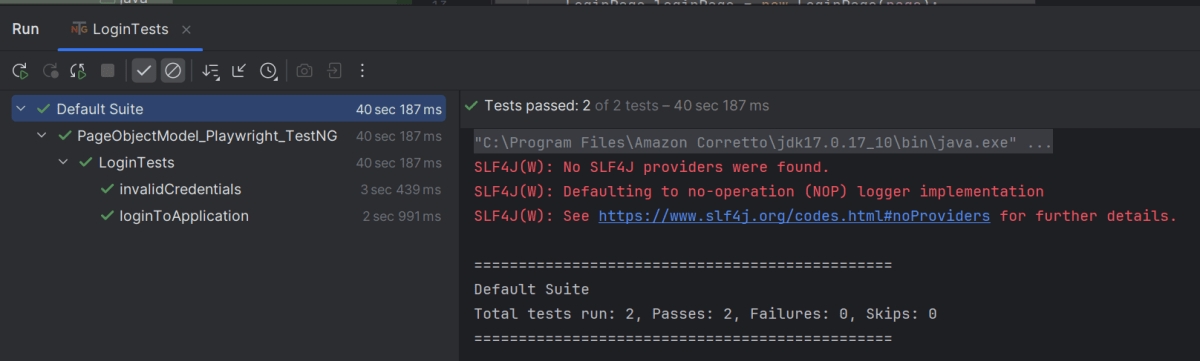
7. Test Execution through IntelliJ
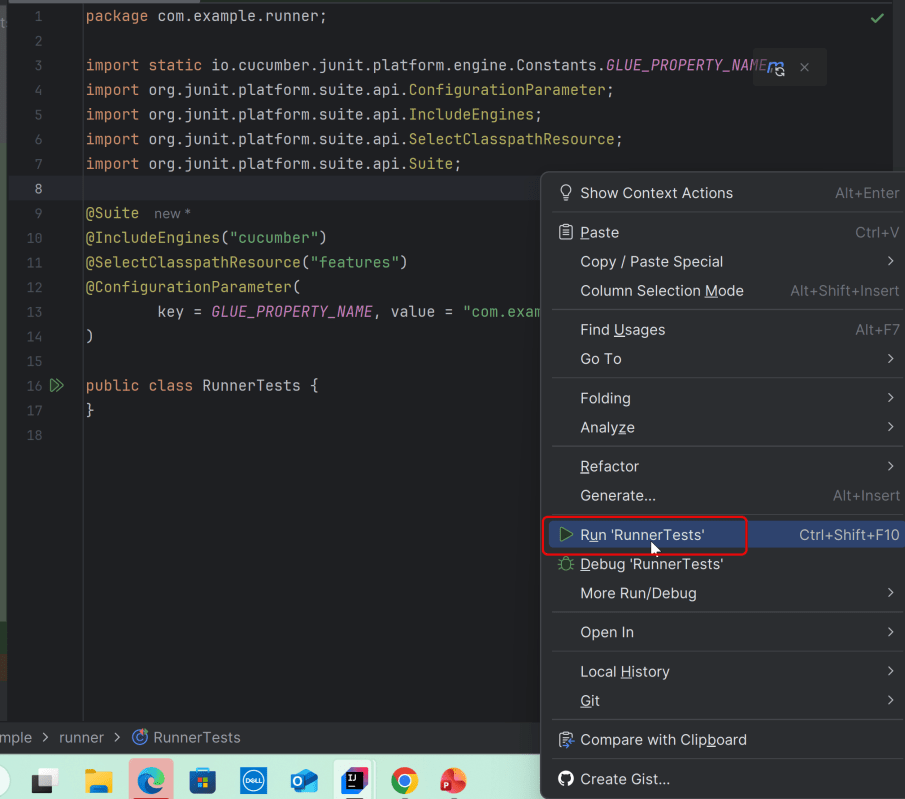
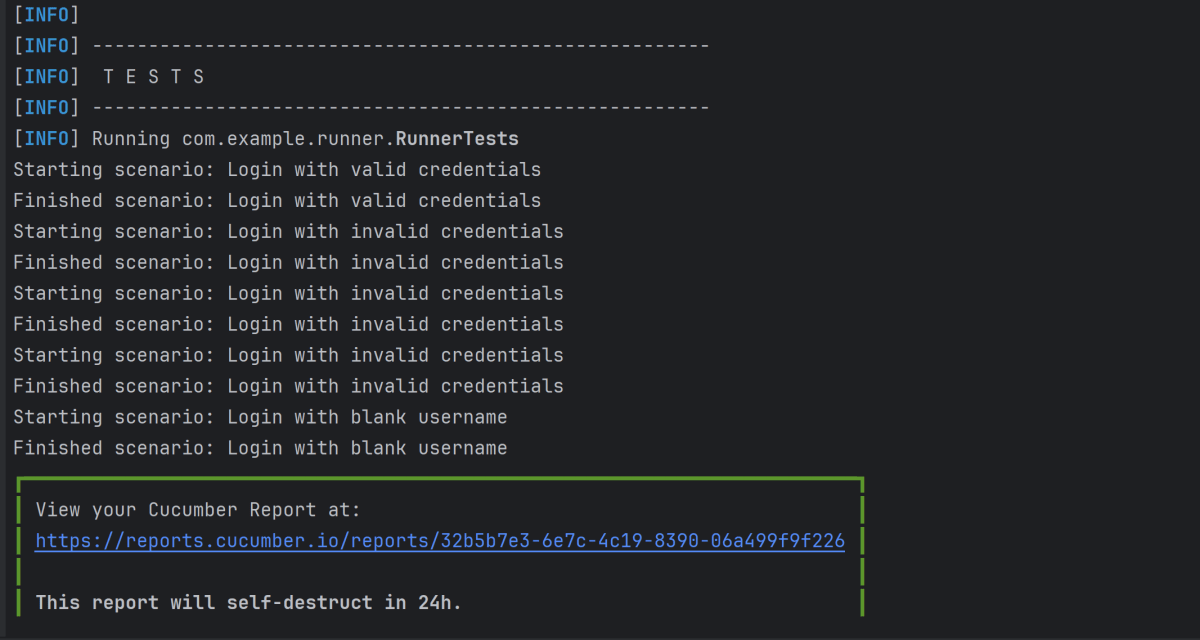
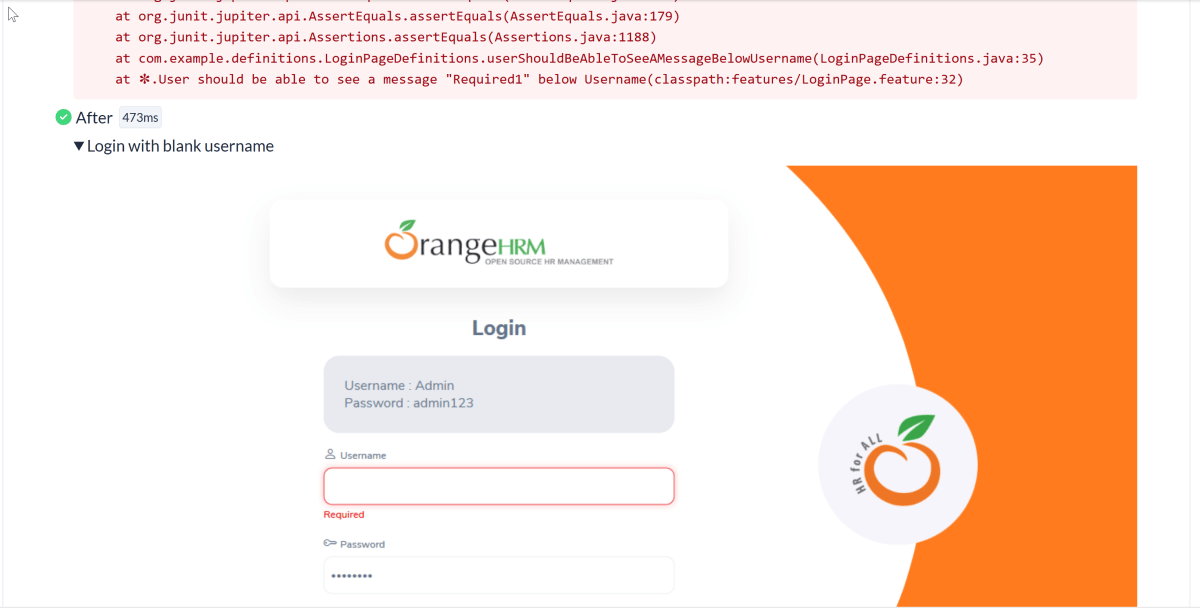
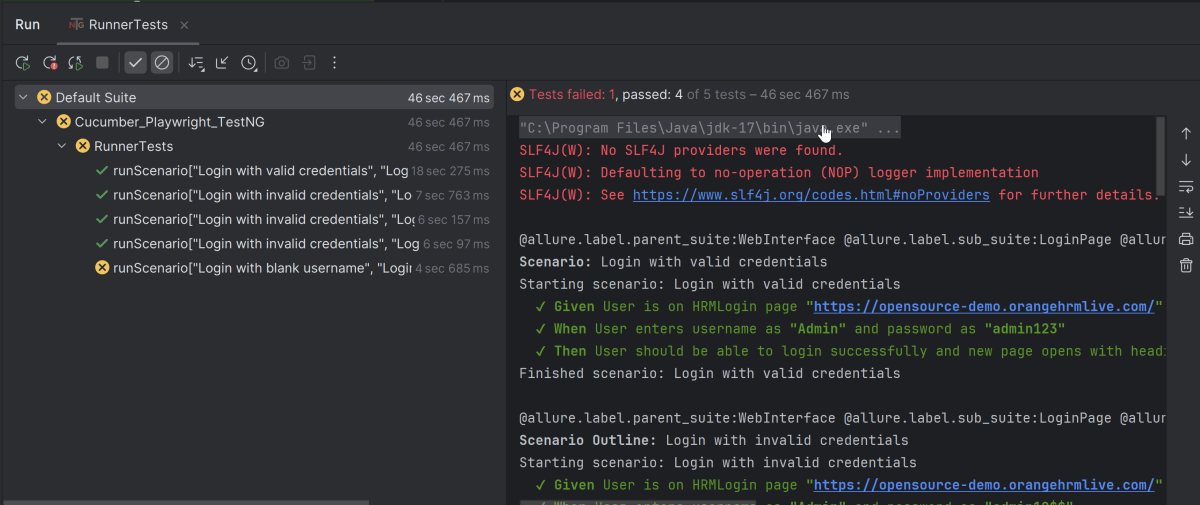
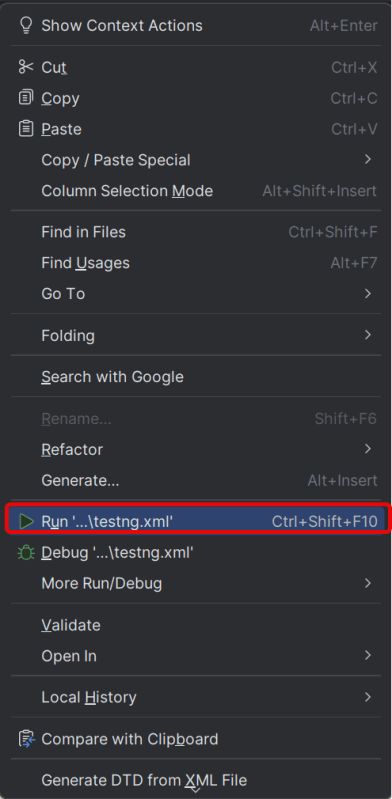
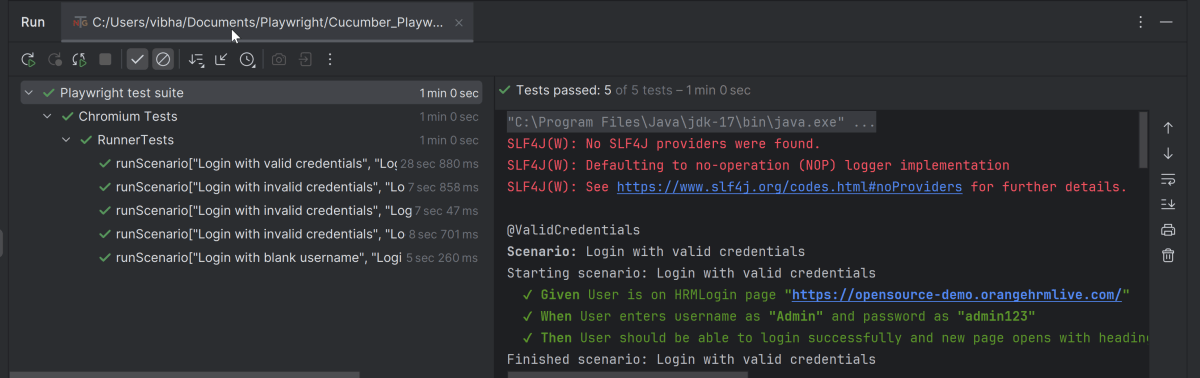
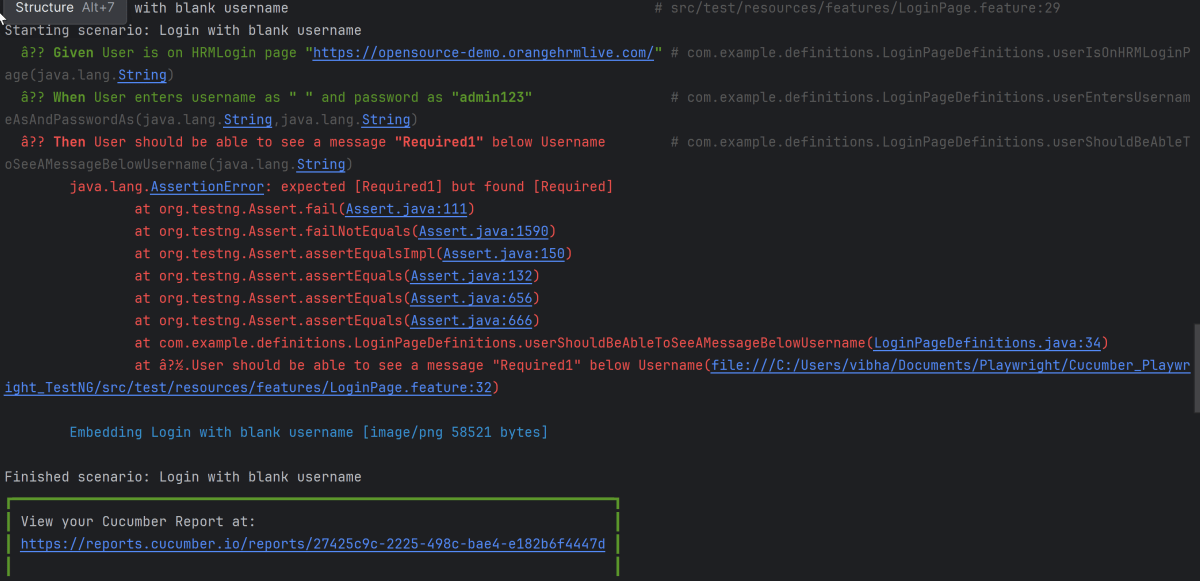
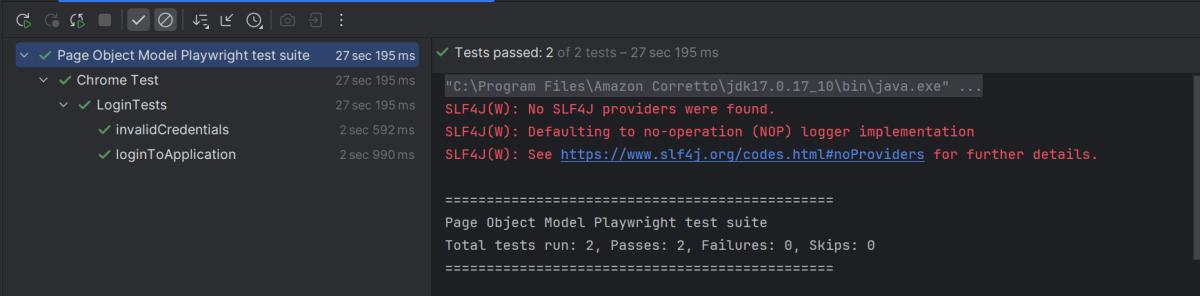
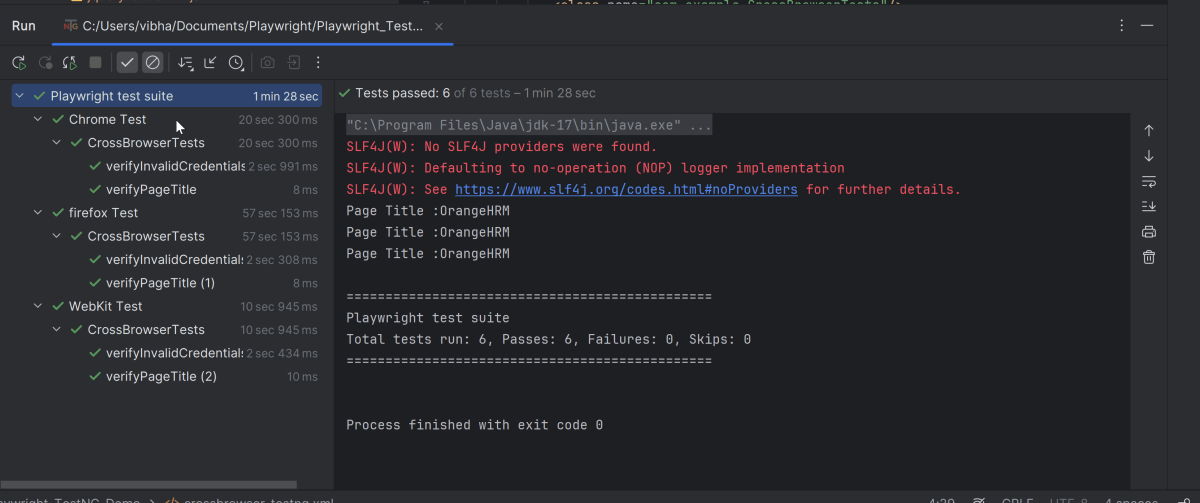
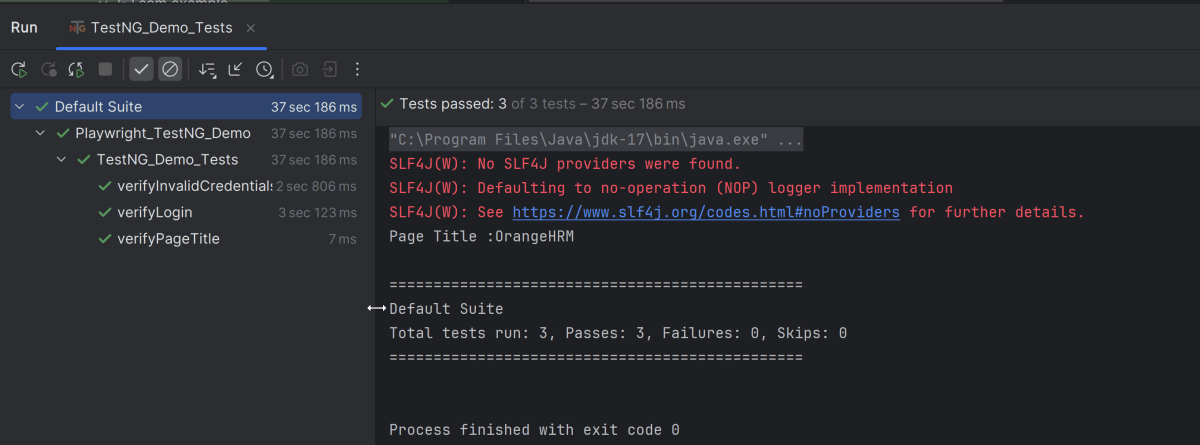
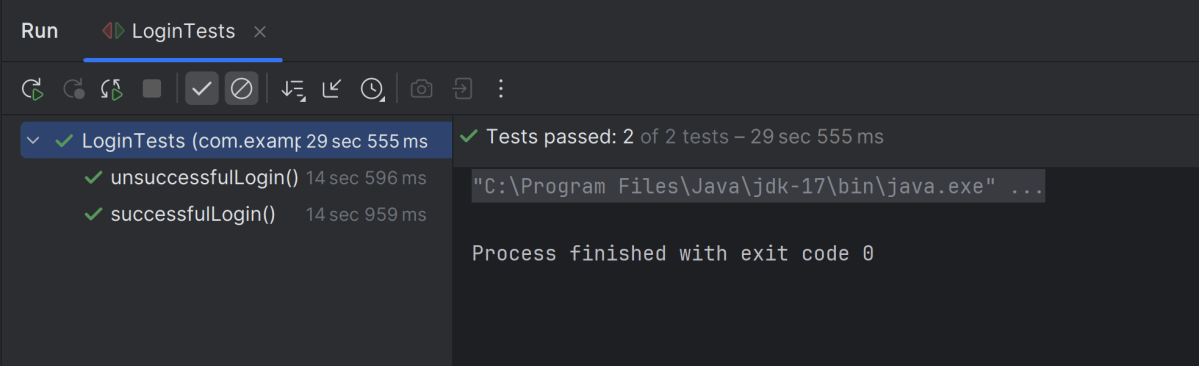
Go to the Test class and right-click and select Run ‘LoginTests’. The tests will run as JUnit5 tests (in IntelliJ).
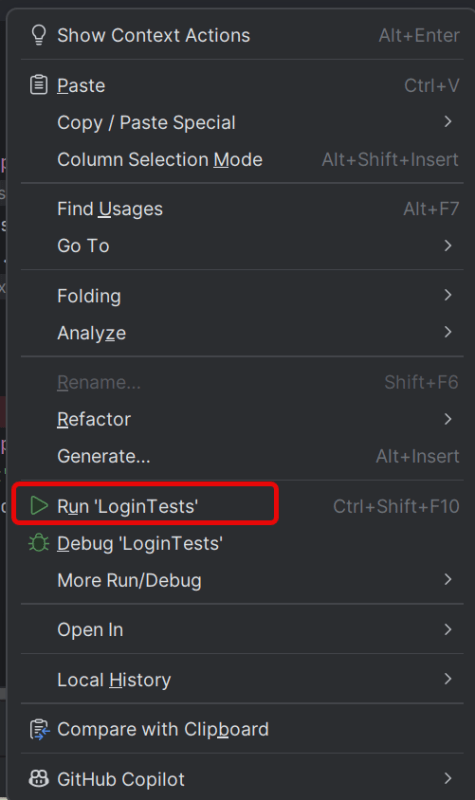
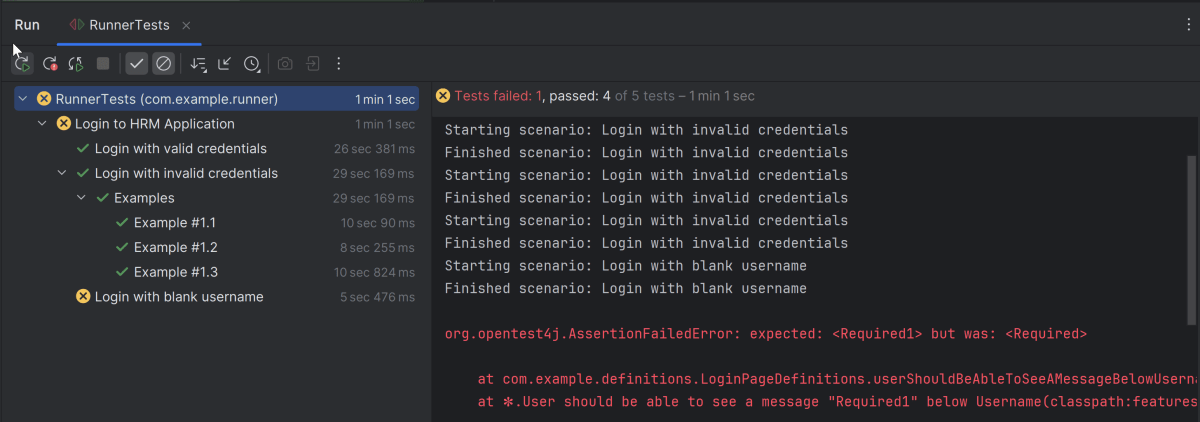
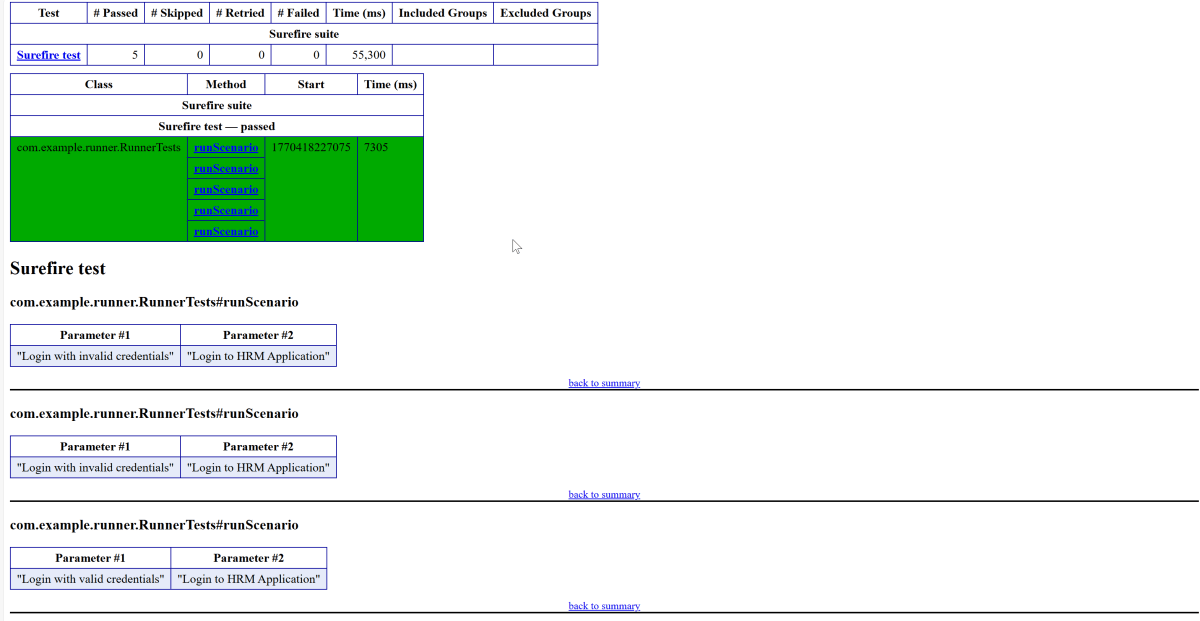
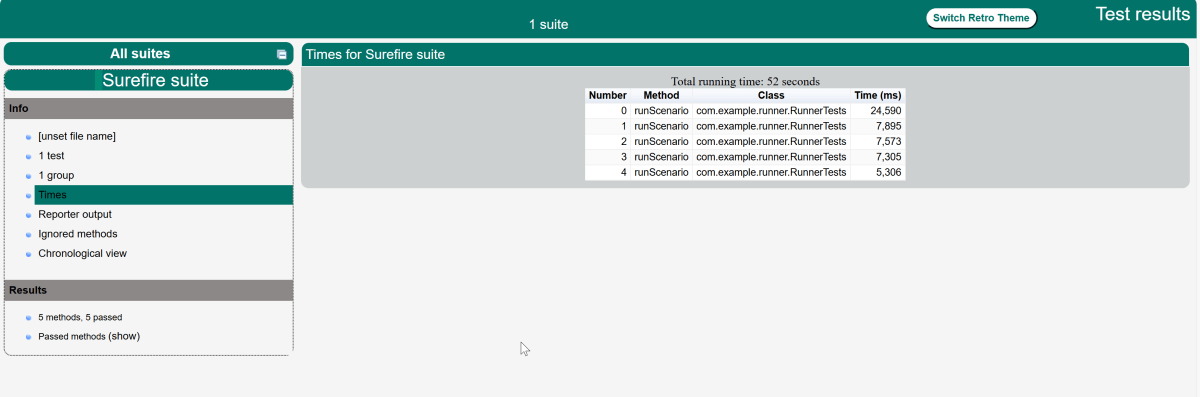
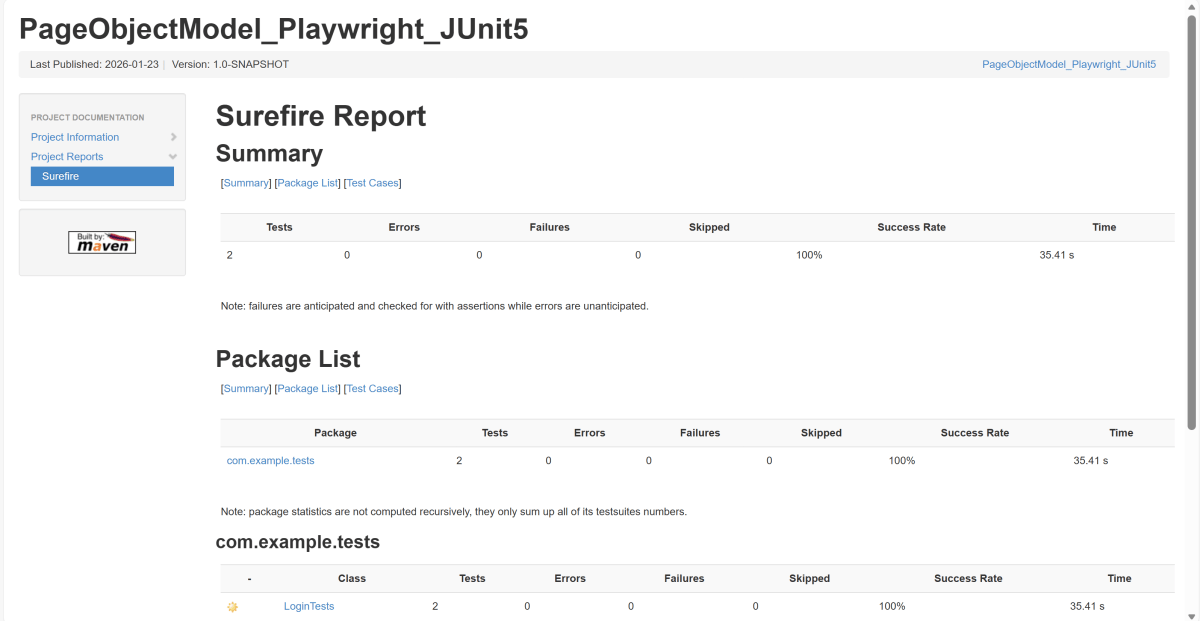
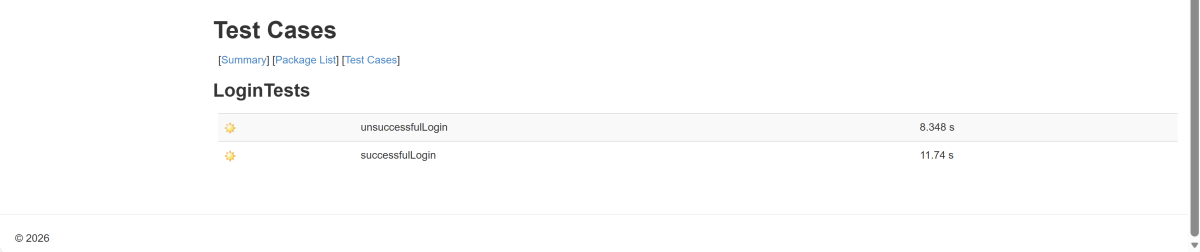
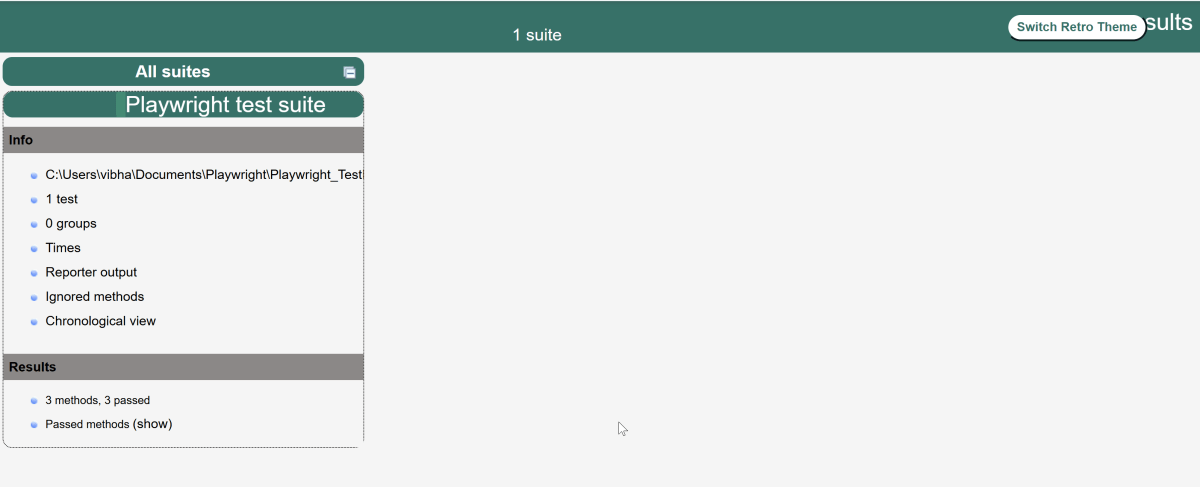
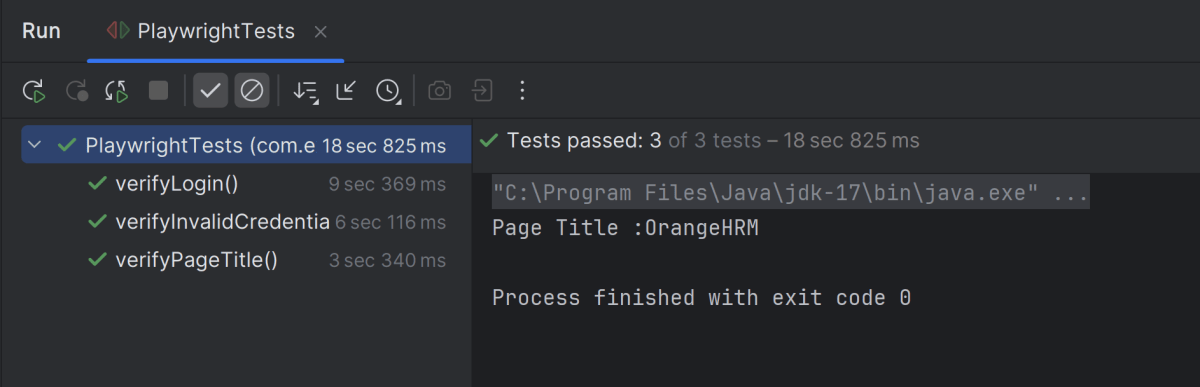
Below is the test execution result.
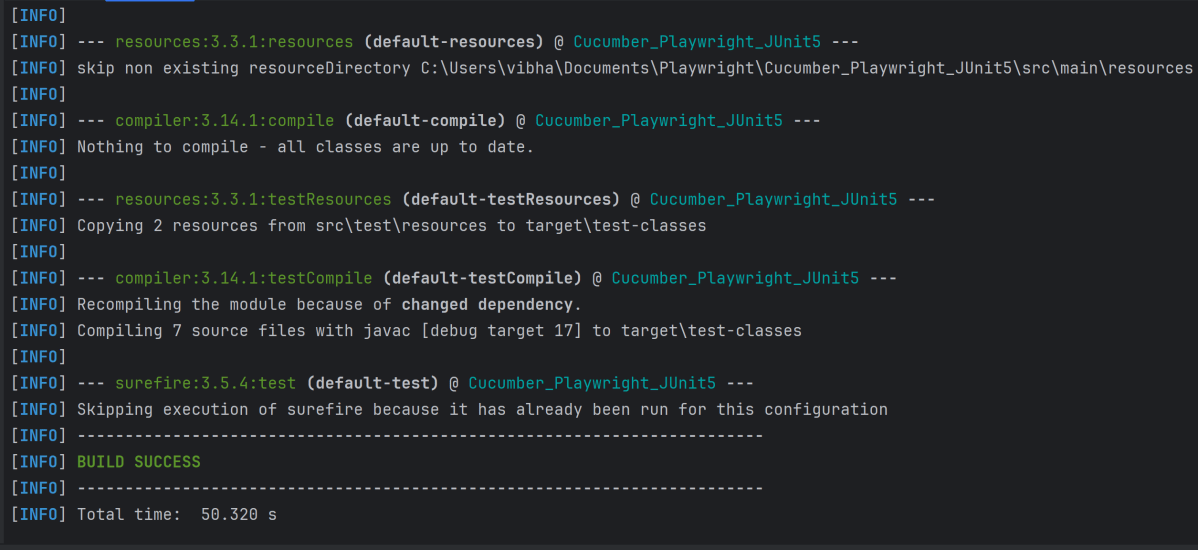
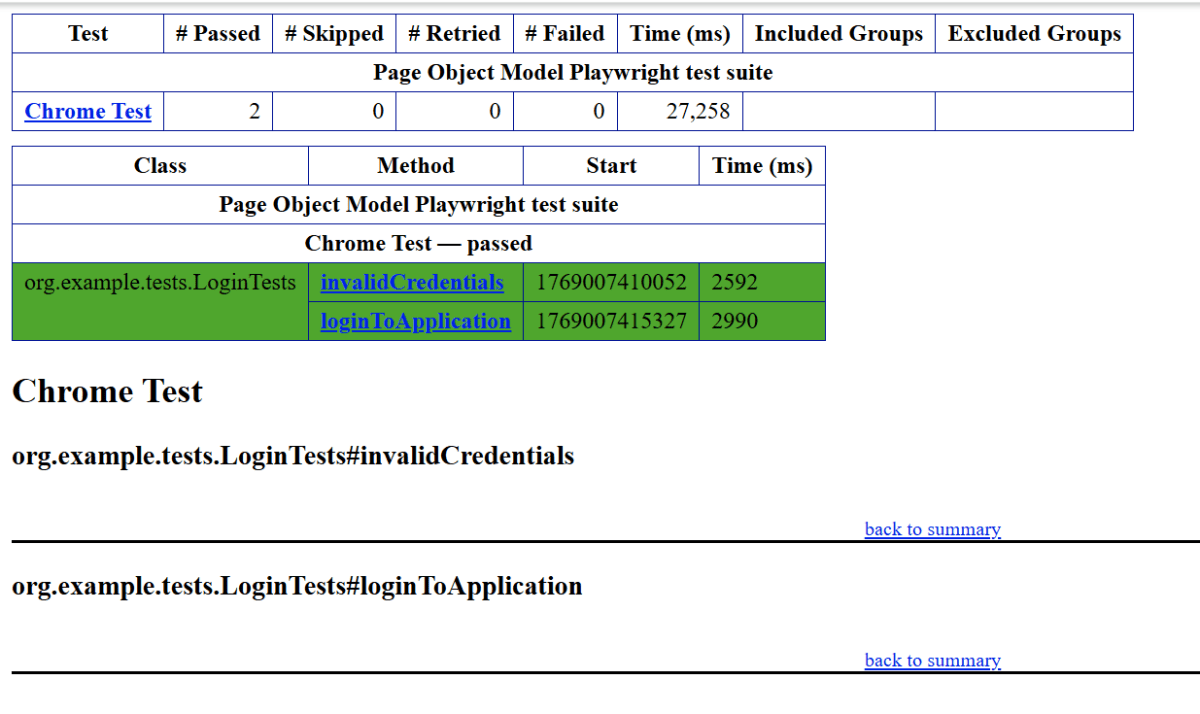
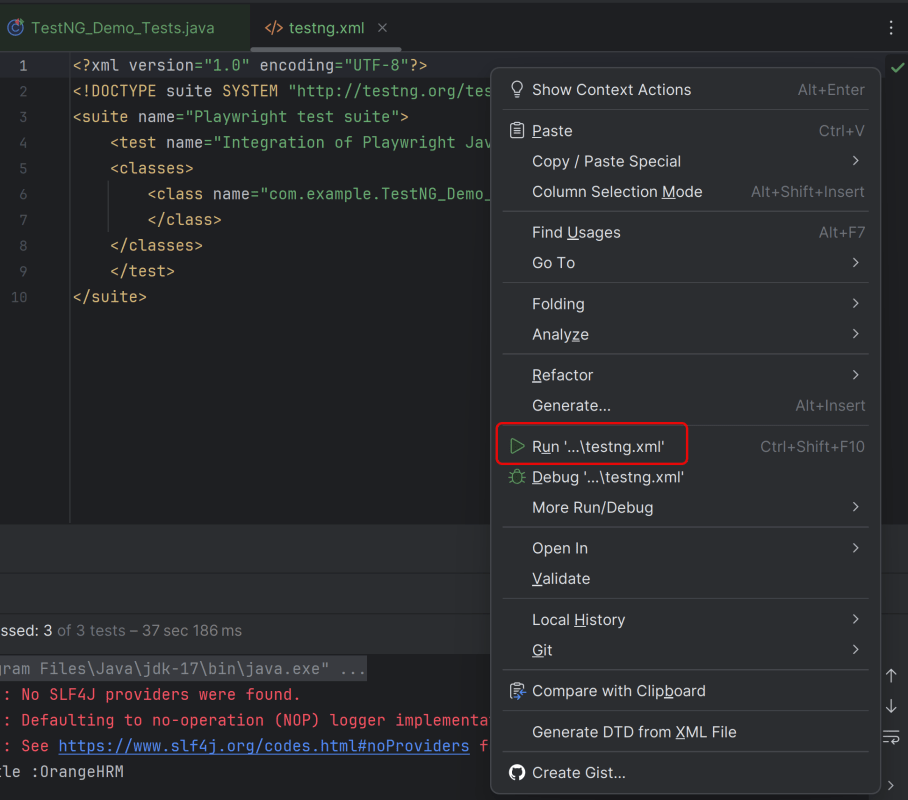
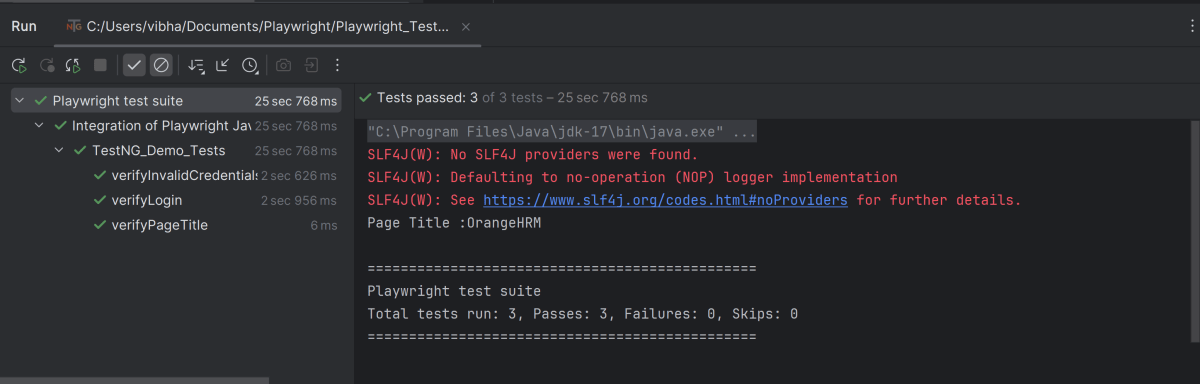
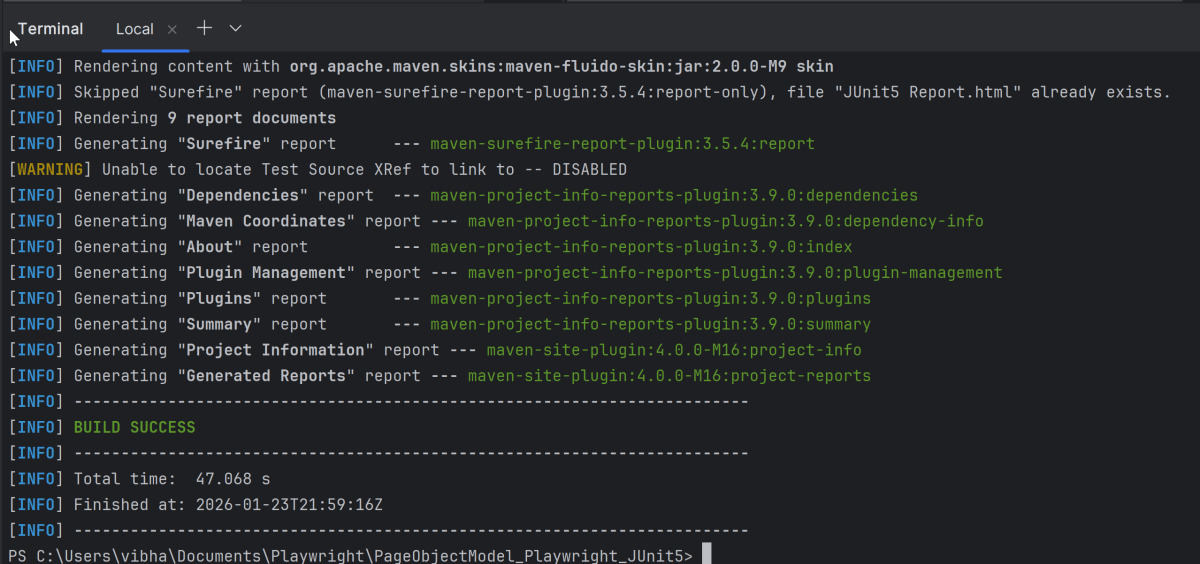
8. Run the tests using the command line
Use the below command to run the tests using the command line.
mvn clean test site
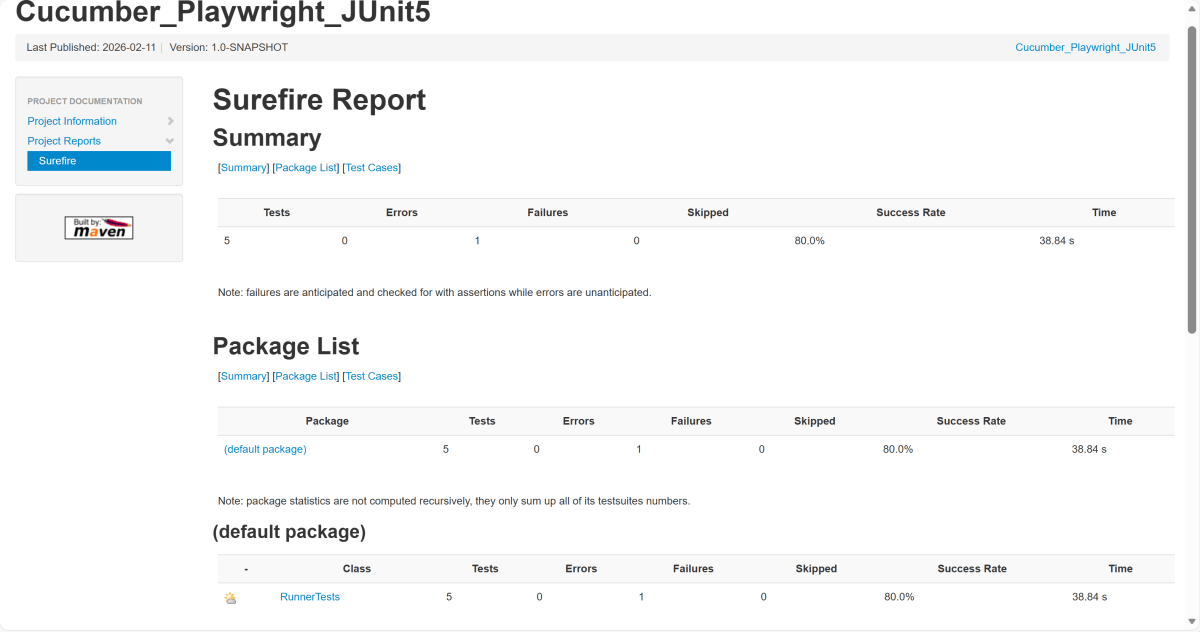
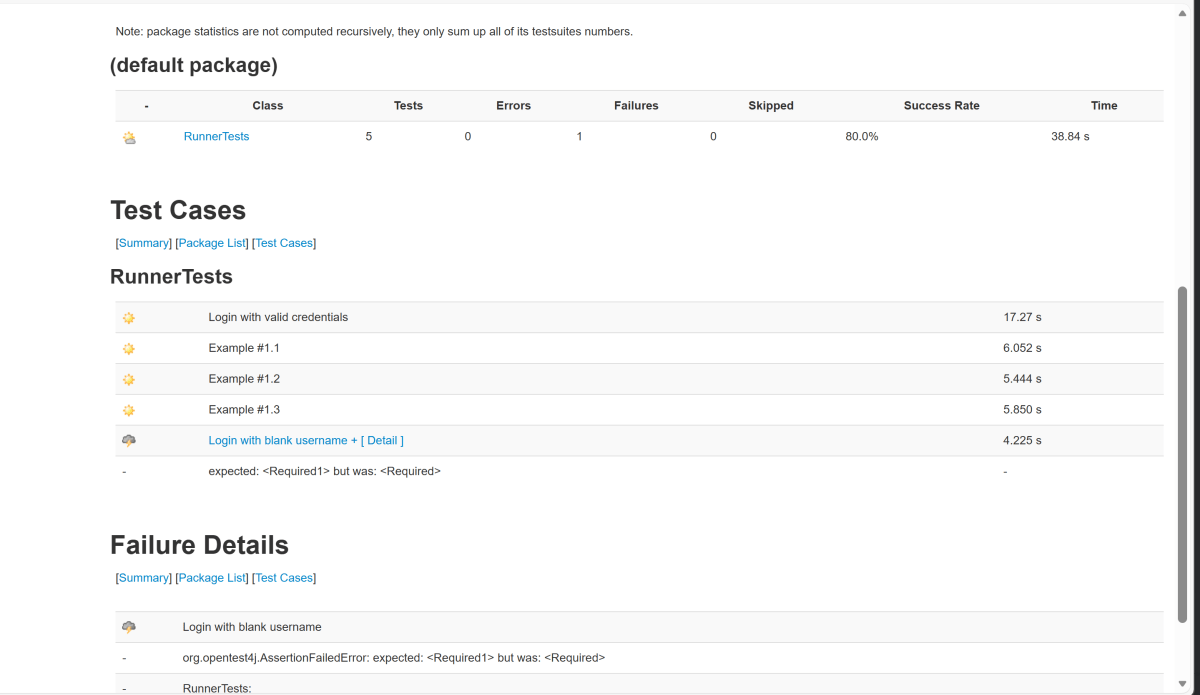
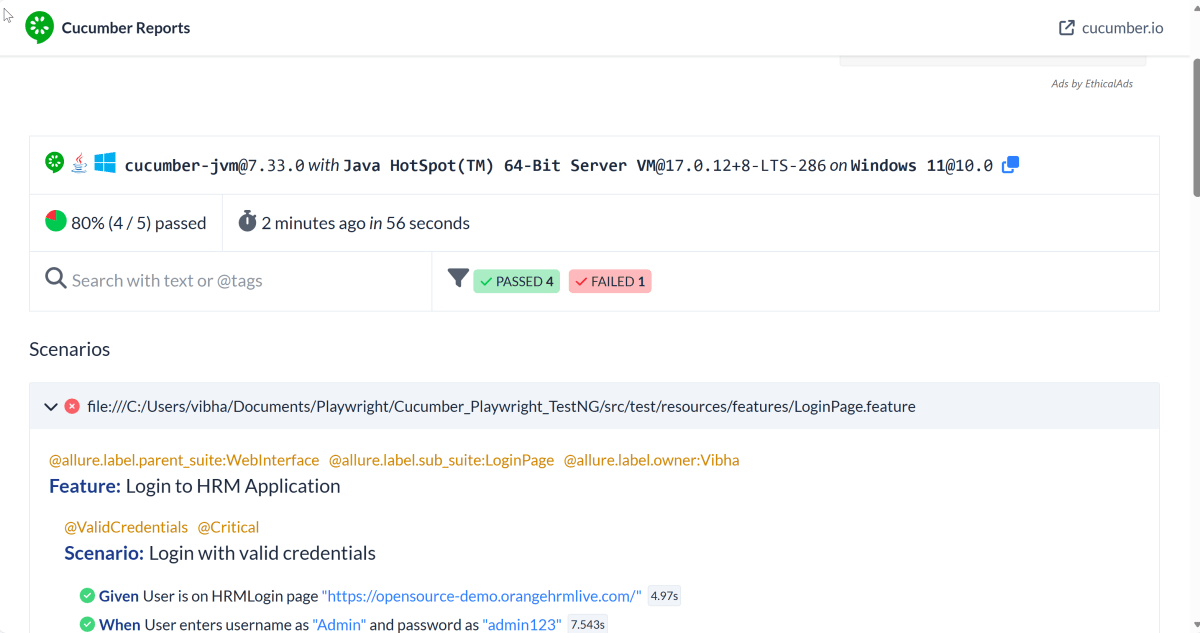
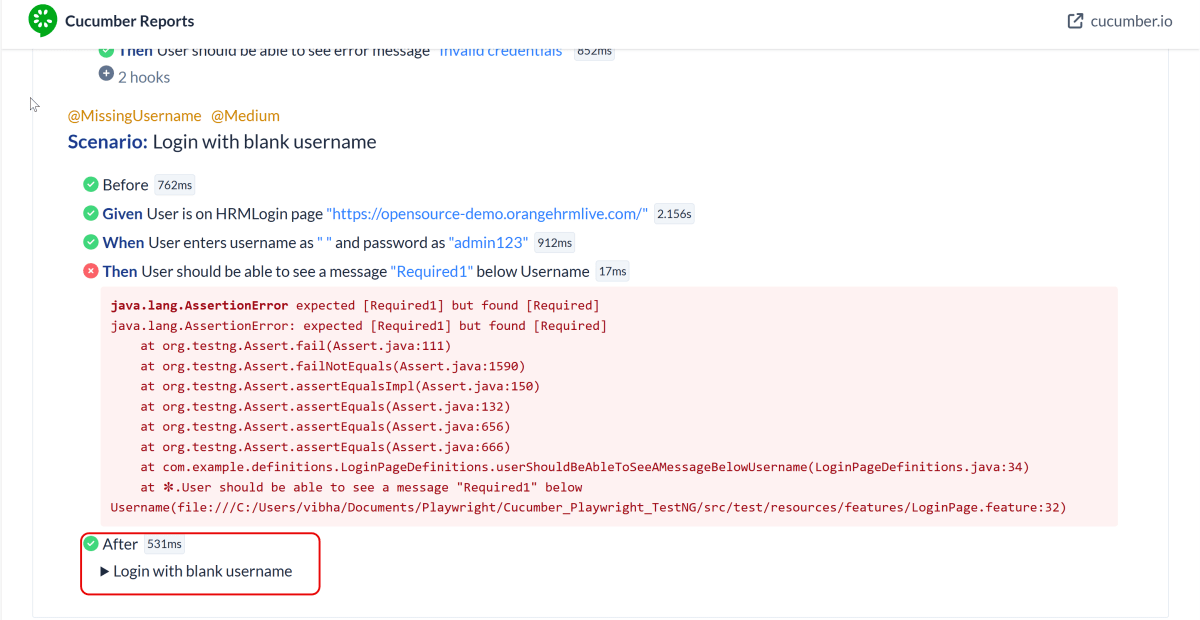
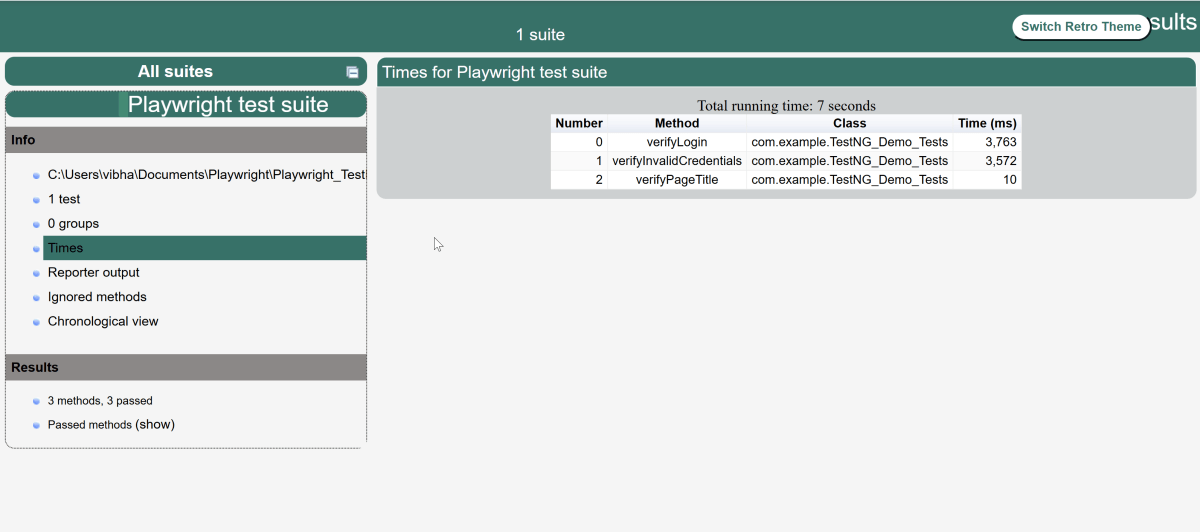
The output of the above program is
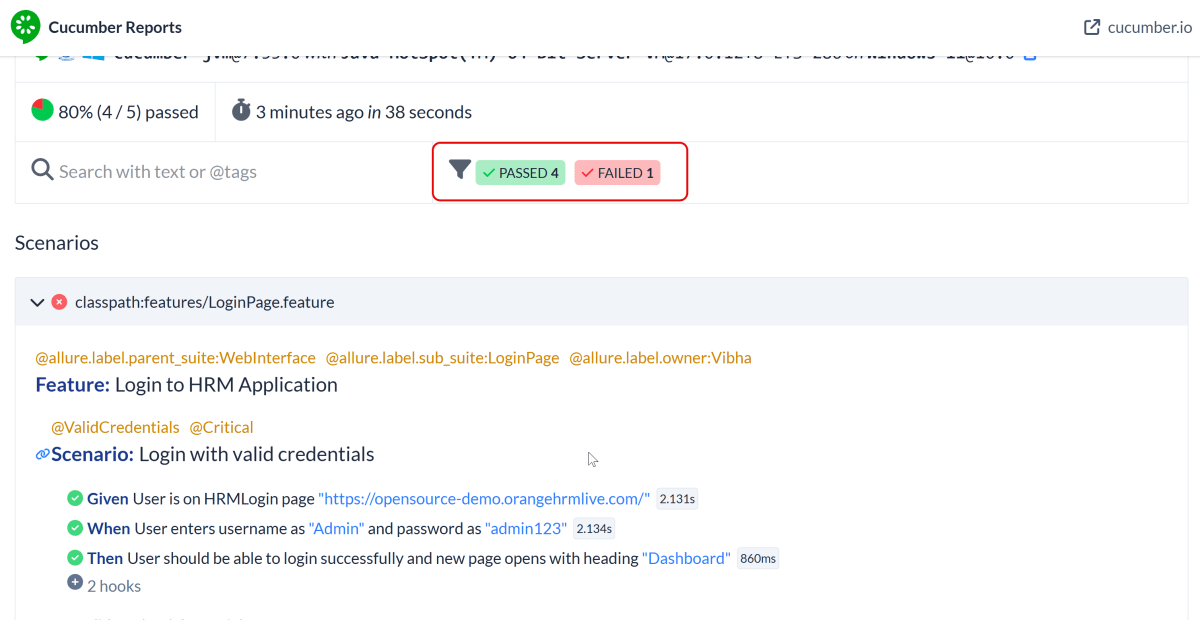
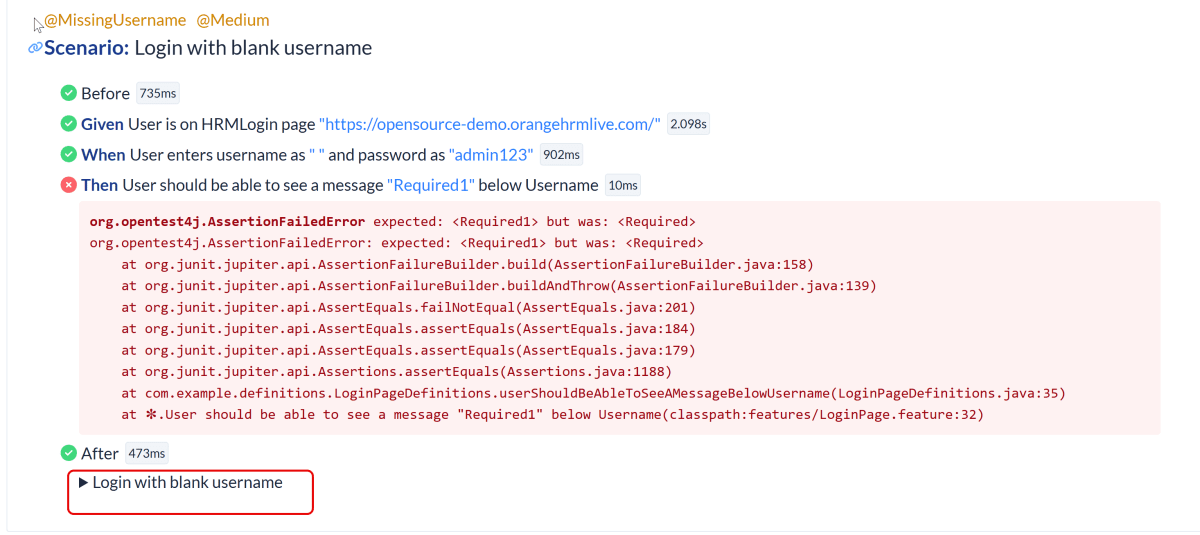
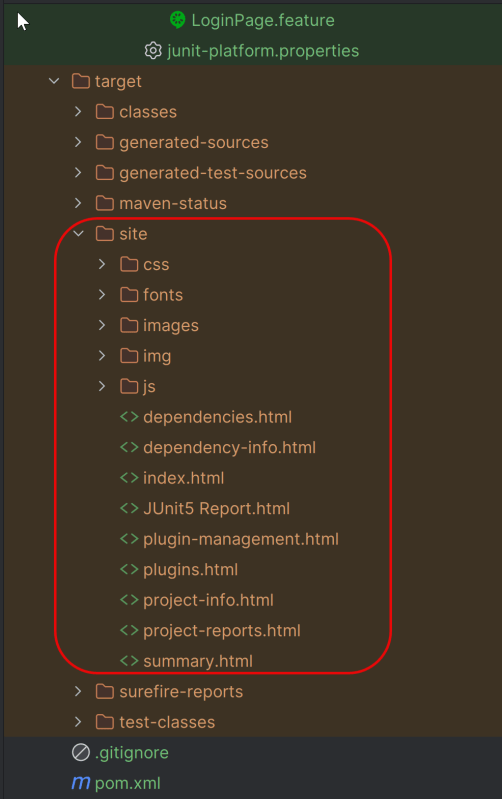
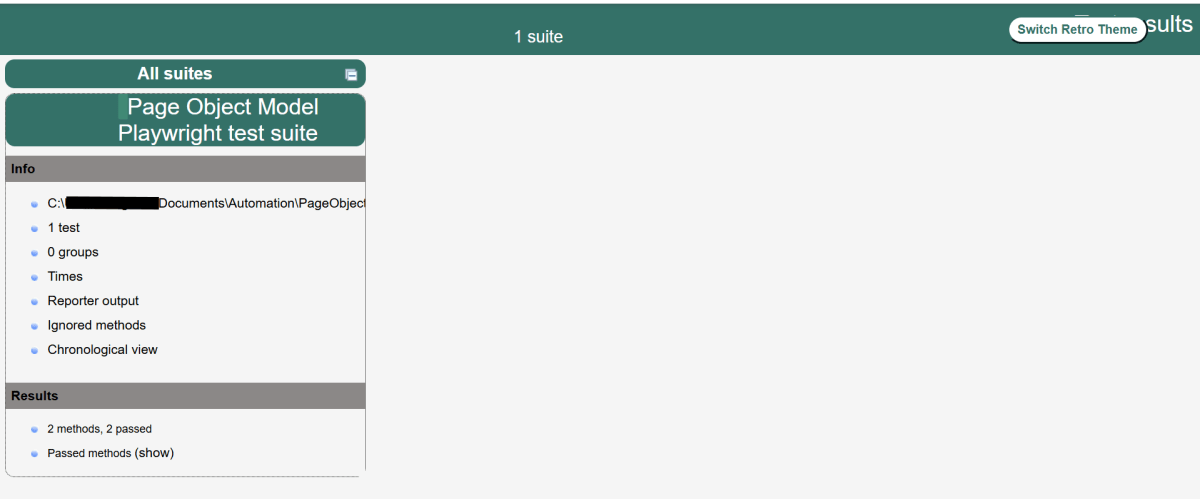
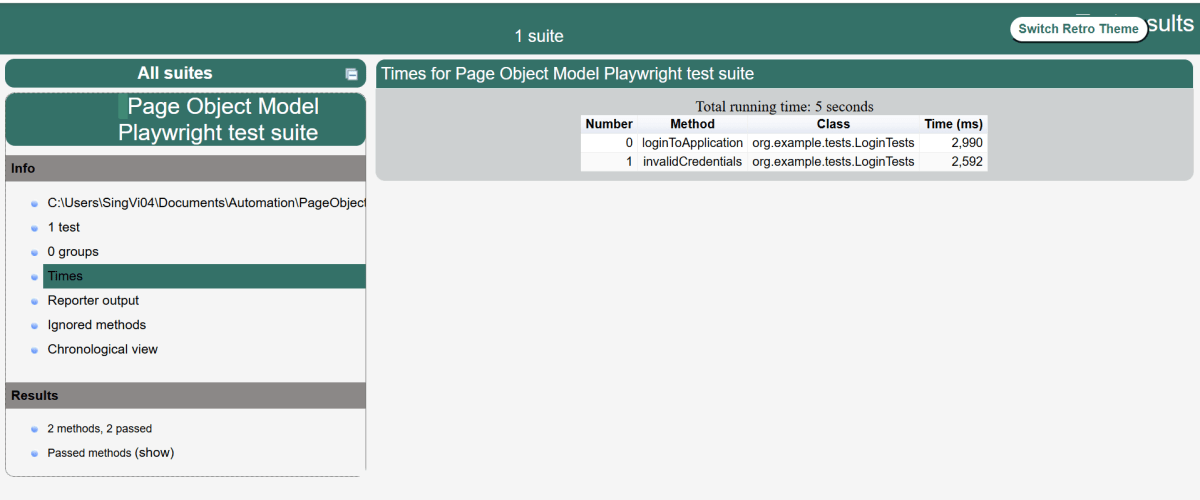
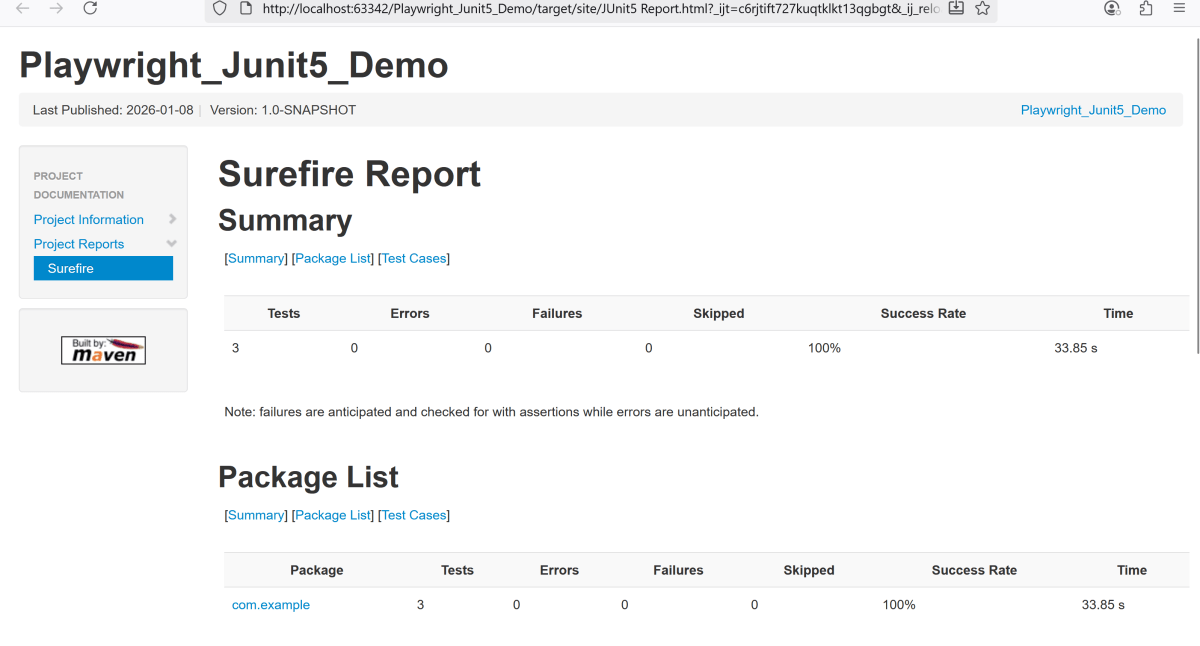
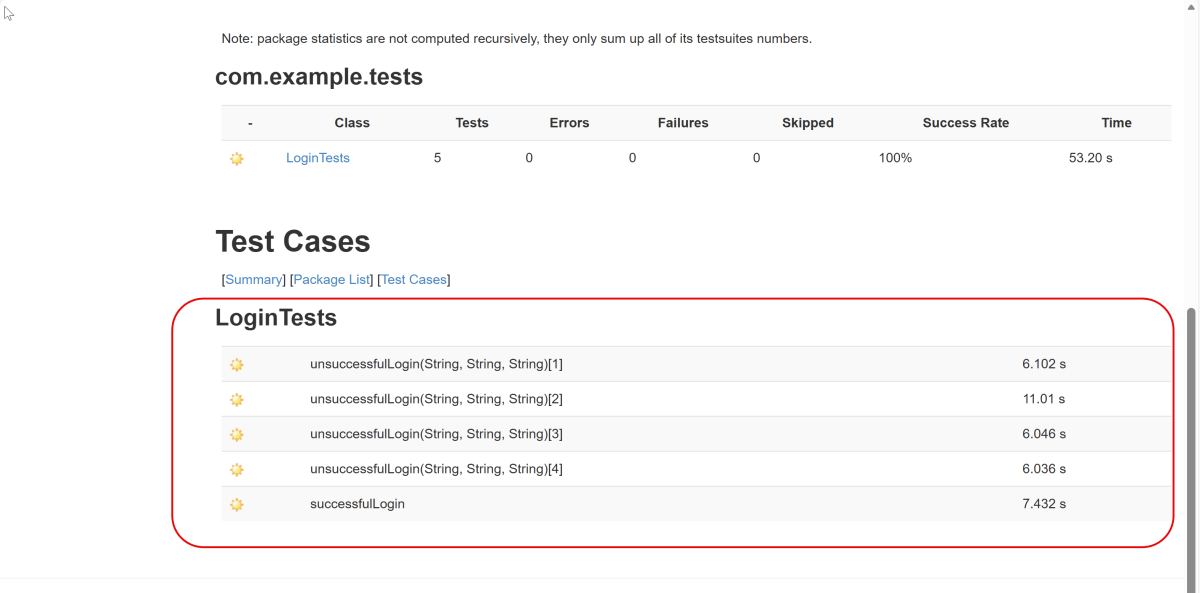
9. JUnit5 Report Generation
Maven Site Plugin creates a folder – site under the target directory.
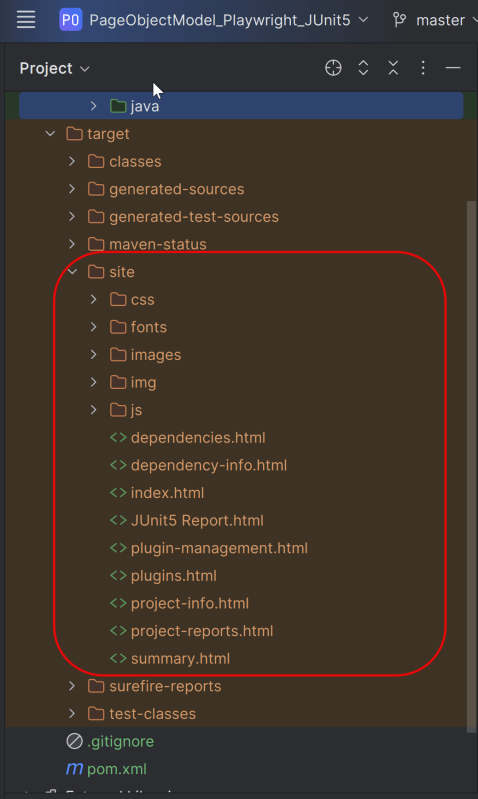
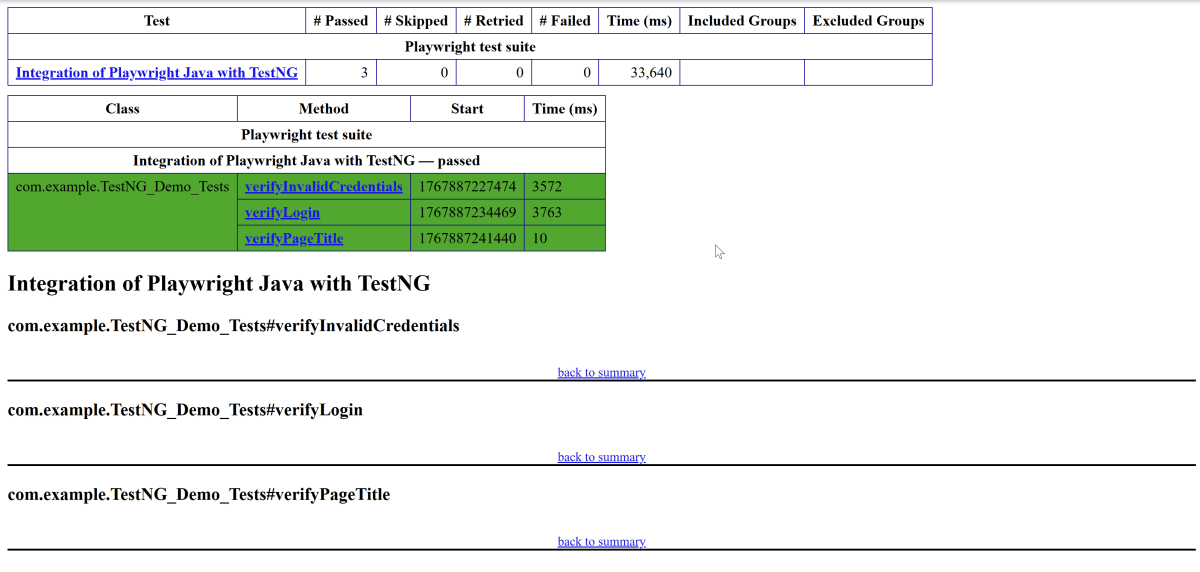
Right-click on the Junit5 Report.html and open it in the browser.
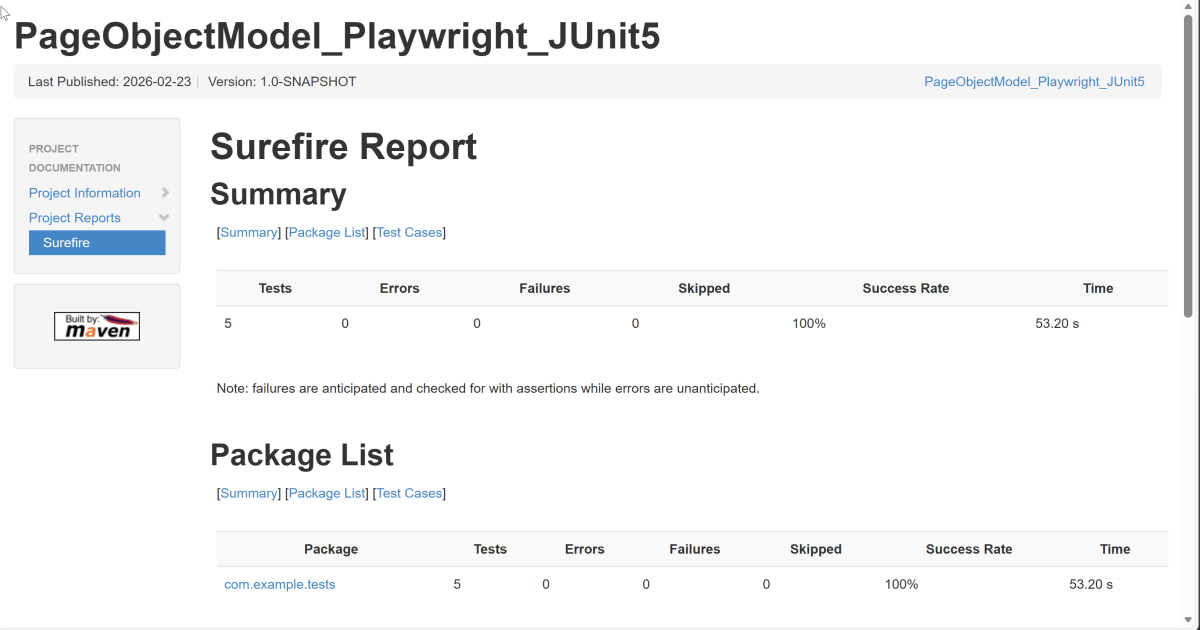
Summary:
1. Utilize the `@ParameterizedTest` annotation to indicate that a method is a parameterized test.
2. Use the `@ValueSource`, `@CsvSource`, `@CsvFileSource`, or custom `@MethodSource` annotations to provide different sets of input data for each test run.
3. @CsvSource: Allows us to provide comma-separated values directly in the annotation for more complex parameter sets.