ETL testing is a critical phase. It ensures the integrity and reliability of data within data warehouses. It also plays a vital role in business intelligence systems. This article explores essential methodologies and best practices in ETL testing. It highlights ETL testing’s role in driving high-quality data management and reliable analytical outcomes in organizations.
Table of Contents
- What is ETL (Extract, Transform, Load)
- What is ETL testing and why do we need it?
- Stages of ETL Testing LifeCycle
- Different types of testing involved in an ETL process
- Various ETL Testing Tools
- ETL testing challenges
What is ETL (Extract, Transform, Load)
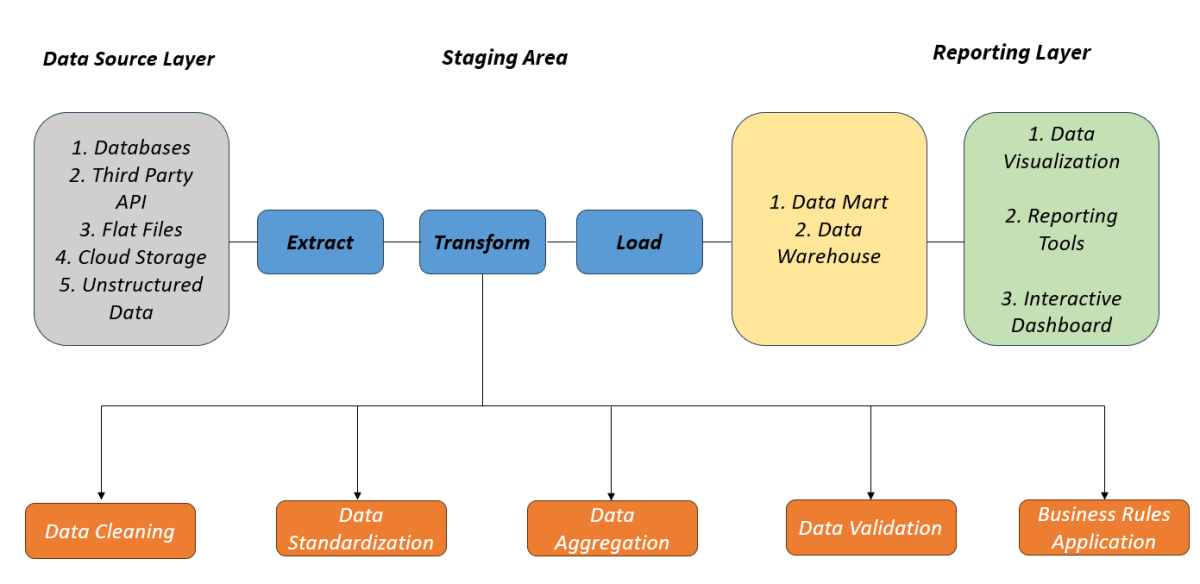
Extract/transform/load (ETL) is a data integration approach. It pulls information from various sources. It transforms the information into defined formats and styles. Finally, it loads the data into a database, a data warehouse, or some other destination.
What is ETL testing and why do we need it?
ETL Testing stands for Extract, Transform, and Load Testing, which is a process used to ensure that the data is correctly extracted from a source system, transformed according to business rules, and loaded accurately into a target system, typically a data warehouse. This testing is crucial for ensuring data integrity, accuracy, and reliability.
It is important to use ETL testing in the following situations:
1. Initial Data Load into a New Data Warehouse: Validate that the entire dataset is accurately transferred, transformed, and loaded into the data warehouse during the initial setup.
2. Adding a New Data Source to an Existing Data Warehouse: Assess compatibility between new data sources and existing systems, ensuring proper integration without quality loss.
3. Data Migration: Validate that all data from old systems is completely and accurately migrated to the new system.
4. High Data Quality for Analytics or Decision-Making: Quality assurance is crucial before using data for analytics and business intelligence. Conduct thorough audits for data quality, check for consistency, accuracy, validity, and correctness across different data sources, and ensure transformations align with business requirements.
Stages of ETL Testing LifeCycle
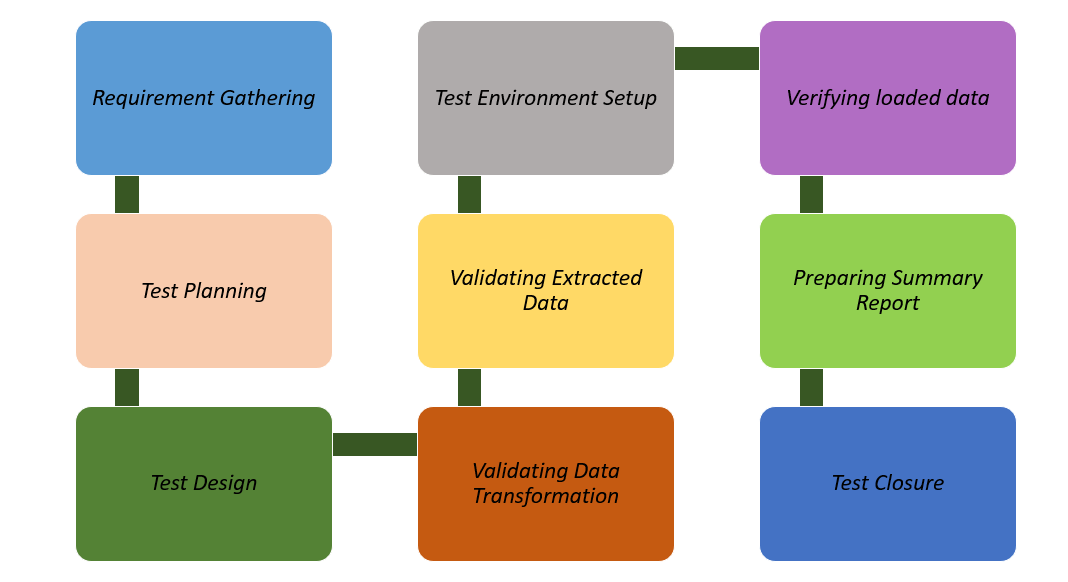
1. Identifying data sources and gathering business requirements: The first step is to understand expectations and the scope of the project. This process includes gathering and analyzing ETL process requirements, including source data, transformation logic, and target data specifications. It’s important to clearly define and document the data model as it will act as a reference for the Quality Assurance (QA) team.
2. Test Planning: This step involves developing a comprehensive test plan outlining the scope of testing, objectives, resources, timelines, and risk factors. Here, we choose the appropriate testing tools and frameworks that will be used for automation or manual testing.
3. Test Design: The next step is designing ETL mapping for various scenarios. The design contains creating detailed test cases and test scenarios based on the requirements defined in the previous steps. The testing team is also required to write SQL scripts and define the transformational rules.
4. Test Environment Setup: This step involves preparing the test environment, which includes setting up the required source and target systems, configuring the ETL tools, and ensuring data accessibility. Make sure that necessary permissions and network configurations are in place.
5. Validating extracted data: The first step of ETL is extraction, and at this stage, the testers ensure that all the data have been extracted cleanly and completely. It’s essential to detect defects and fix bugs at the initial stage to lessen the chances of a misleading analysis.
6. Validating data transformation: The transformed data matches the schema of the target repository. The QA team makes sure that the data type syncs with the mapping document.
7. Verifying loaded data: The data is taken from the primary source system and converted into the desired format. After conversion, it is loaded to the target warehouse. Here, the testers reconcile the data and check for data integrity.
8. Preparing summary report: After the test, the QA team prepares a summary report. It contains all the findings of the tests and documents bugs and errors that were detected during the testing process.
9. Test Closure: Filing and submitting ETL test closure report.
Different types of testing involved in an ETL process
1.Source to target count testing – In this testing, we verifies that the number of records loaded into the target database matches the expected record count.
2. Source to target data testing – It ensures projected data is added to the target system without loss or truncation, and that the data values meet expectations after transformation.
3. Metadata testing – It performs data type, length, index, and constraint checks of ETL application metadata (load statistics, reconciliation totals, and data quality metrics).
4. Data Transformation Testing – It ensures that all transformations applied to the source data are accurate and correctly implemented according to the business requirements.
5. Data quality testing – It runs syntax tests (invalid characters, pattern, case order) and reference tests (number, date, precision, null check) to make sure the ETL application accepts default values and rejects and reports invalid data.
6. Data integration testing – It confirms that the data from all sources has loaded to the target data warehouse correctly and checks threshold values.
7. Performance Testing – Assesses the performance of the ETL process, ensuring that it completes within acceptable time limits and that the system can handle expected data volumes and loads.
8. Data Integration Testing – Validates that data from different sources is integrated as expected and that relationships among data entities are maintained correctly in the target system.
9. Scalability Testing – Evaluates the ETL system’s ability to scale up and handle increased data volumes and loads without performance degradation.
10. End-to-End Testing – Validates the entire ETL process from data extraction to loading and ensures the integration of data across the full data pipeline.
11. Report testing – It reviews data in summary report, verifying layout and functionality are as expected, and makes calculations.
Various ETL Testing Tools
1. Informatica Data Validation: Informatica is a widely used tool. It provides automated testing capabilities for data validation and transformation. This ensures data integrity within the ETL process.
2. QuerySurge: QuerySurge leverage AI to automate and scale data validation process. QuerySurge uses AI-powered test creation. It employs a scalable architecture and offers seamless CI/CD integration. These features ensure data integrity at every stage of the pipeline. They accelerate delivery, reduce risk, and drive confident decision-making.
3. Talend Open Studio for Data Integration: Talend is a powerful ETL tool. It also supports testing functionalities. Users can build and automate data pipelines. They can verify data transformations and integrations.
4. Tricentis Tosca: Tricentis is known for its model-based testing approach. Tosca enables organizations to automate end-to-end testing processes, including ETL testing, and ensure comprehensive data quality checks.
5. ETL Validator: This tool is specifically designed for ETL testing. It automates ETL/ELT testing to ensure data integrity. It reduces migration time. It also improves quality with low-code, AI-driven validation across cloud and on-prem pipelines.
6. Datagaps ETL Validator: Datagaps ETL Validator is enterprise-grade tool offers extensive testing capabilities. It includes comparison of source and target data. It also validates transformation logic, which further ensures data accuracy after ETL processes.
7. IBM InfoSphere DataStage: DataStage is primarily an ETL tool. It provides integrated testing functionalities. These ensure data accuracy and consistency during ETL operations.
ETL testing challenges
- Potential complexity of data transformations – Transformations of large datasets can be time-consuming and complex.
- Data Quality Issues – Data is often messy and full of errors; ETL testing needs clean, accurate data to have healthy results.
- Lack of Standardization – Different formats and standards across various source systems complicate the testing process, requiring extensive validation efforts.
- Resource intensiveness – ETL testing can be resource intensive when dealing with large, complex source systems.
- Data source changes – Changes to data sources impact the completeness and accuracy of data quality.
- Complex processes – Complex data integrations and business processes can cause problems.
- Slow performance – Slow processing or slow end-to-end performance caused by massive data volumes can impact data accuracy and completeness.
- Resource Constraints – Difficulty finding people with skilled testing personnel and technical infrastructure and data health expertise.