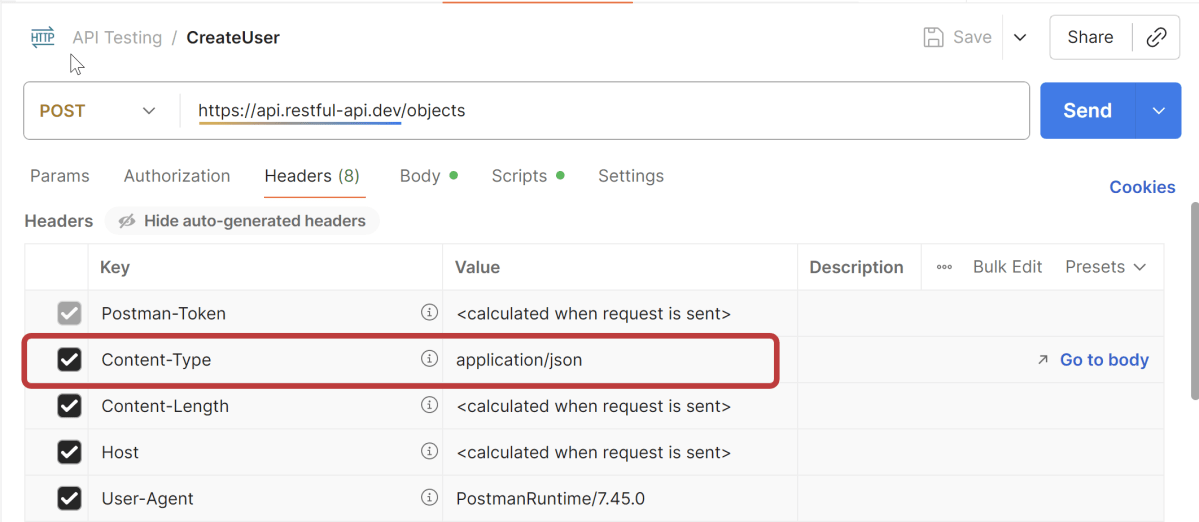
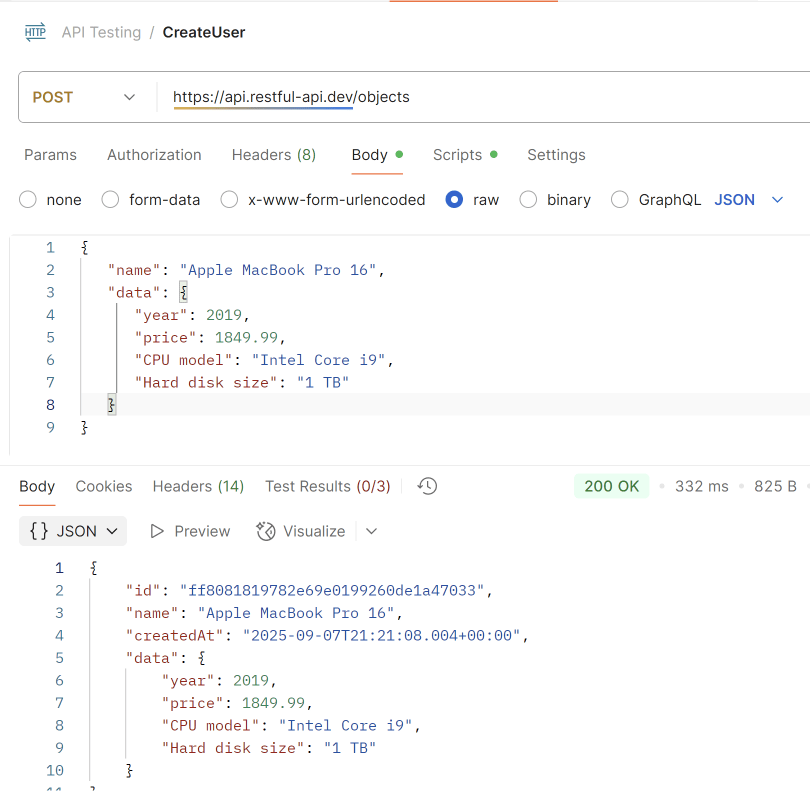
Welcome to the Java Quiz! This blog post features 25 multiple-choice questions that explore concepts of Methods, Method Overloading and Method Overriding in Java.
1. Which method can be defined only once in a program?
a) main method
b) finalize method
c) static method
d) private method
Answer 1
a) main method
main() method can be defined only once in a program. Program execution begins from the main() method by java runtime system.
2. What is the return type of a method that does not return any value?
a) int
b) float
c) void
d) double
Answer 2
c) void
Return type of a method must be made void if it is not returning any value.
3. What will be the output of the following Java code?
class box
{
int width;
int height;
int length;
int volume;
void volume(int height, int length, int width)
{
volume = width*height*length;
}
}
class Prameterized_method
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
box obj = new box();
obj.height = 1;
obj.length = 5;
obj.width = 5;
obj.volume(3,2,1);
System.out.println(obj.volume);
}
}
Choose one option
a) 0
b) 1
c) 6
d) 25
Answer 3
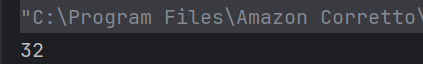
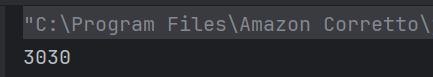
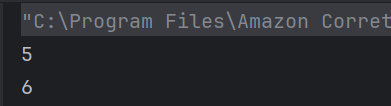
c) 6
The volume() method calculates the product of the parameters passed to it (3, 2, 1) and assigns it to the object’s volume field. Hence, the output is 3 * 2 * 1 = 6.
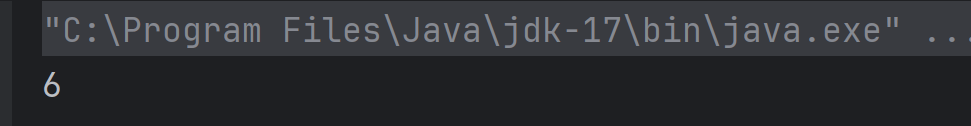
4. What will be the output of the following Java program?
class equality
{
int x;
int y;
boolean isequal()
{
return(x == y);
}
}
class Output
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
equality obj = new equality();
obj.x = 5;
obj.y = 5;
System.out.println(obj.isequal());
}
}
Choose one option
a) true
b) Runtime error
c) false
d) 0
Answer 4
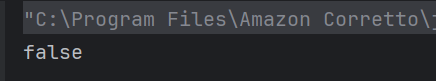
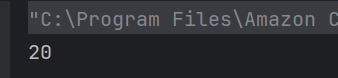
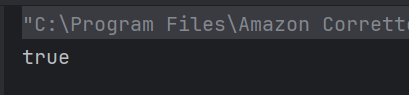
a) true
The method isequal() compares x and y using ==. Since both are set to 5, the condition x == y is true, so the method returns true, which gets printed.
5. Which of the following is a method having same name as that of it’s class?
a) finalize
b) delete
c) class
d) constructor
Answer 5
d) constructor
A constructor is a method that initializes an object immediately upon creation. It has the same name as that of class in which it resides.
6. What will be the output of the following Java program?
class overload
{
int x;
int y;
void add(int a)
{
x = a + 1;
}
void add(int a, int b)
{
x = a + 2;
}
}
class Overload_methods
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
overload obj = new overload();
int a = 0;
obj.add(6);
System.out.println(obj.x);
}
}
Choose one option
a) 5
b) 6
c) 7
d) Runtime error
Answer 6
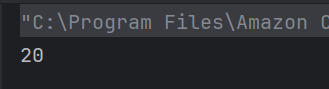
c) 7
Due to method overloading when the add() method is called with a single argument the value of x is set to argument passed i.e. 6 + 1 is returned. Hence the result is 7.
7. What will be the output of the following Java program?
class overload
{
int x;
int y;
void add(int a)
{
x = a + 1;
}
void add(int a , int b)
{
x = a + 2;
}
}
class Overload_methods
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
overload obj = new overload();
int a = 0;
obj.add(6, 7);
System.out.println(obj.x);
}
}
Choose one option
a) 6
b) 7
c) 8
d) 9
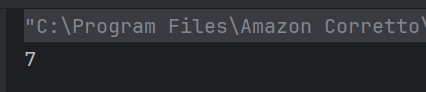
Answer 7
c) 8
Due to method overloading when the add() method is called with two arguments the value of x is set to the first argument passed i.e. 6 + 2 is returned. Hence the result is 8.
8. What will be the output?
class overload
{
int x;
double y;
void add(int a , int b)
{
x = a + b;
}
void add(double c , double d)
{
y = c + d;
}
overload()
{
this.x = 0;
this.y = 0;
}
}
class Overload_methods
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
overload obj = new overload();
int a = 2;
double b = 3.2;
obj.add(a, a);
obj.add(b, b);
System.out.println(obj.x + " " + obj.y);
}
}
Choose one option
a) 6 6
b) 6.4 6.4
c) 6.4 6
d) 4 6.4
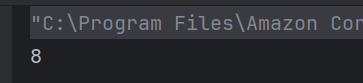
Answer 8
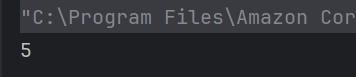
d) 4 6.4
For obj.add(a,a); ,the function in line number 4 gets executed and value of x is 4. For the next function call, the function in line number 7 gets executed and value of y is 6.4.
9. Which of the following best defines method overloading in Java?
a) Redefining a method with the same name and same parameters in child class.
b) Defining multiple methods with the same name but different parameter lists in the same class.
c) Using a method of the parent class in the child class.
d) Declaring a method as static multiple times.
Answer 9
b) Defining multiple methods with the same name but different parameter lists in the same class.
Overloading occurs when methods have the same name but different parameter lists (number or type).
10. Which of the following is NOT a valid way to overload methods in Java?
a) Different number of parameters.
b) Different types of parameters.
c) Different return types only.
d) Different order of parameters.
Answer 10
c) Different return types only
Overloading cannot be achieved by changing only the return type
11. What will be the output?
class area
{
int width;
int length;
int volume;
area()
{
width=5;
length=6;
}
void volume()
{
volume = width*length*height;
}
}
class cons_method
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
area obj = new area();
obj.volume();
System.out.println(obj.volume);
}
}
Choose one option
a) 0
b) 30
c) 1
d) error
Answer 11
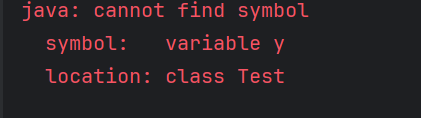
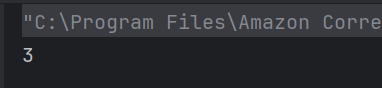
d) error
Variable height is not defined

12. Which of the following allows method overriding?
Choose one option
a) Same method name and parameter list in subclass.
b) Same method name but different parameters in subclass.
c) Same method name but different return type in subclass.
d) Static methods in subclass.
Answer 12
a) Same method name and parameter list in subclass
Overriding requires the same method signature (name + parameters) in superclass and subclass
13. What is the default return type of a method in Java if not specified?
Choose one option
a) int
b) void
c) Object
d) Compilation error
Answer 13
d) Compilation error
Java requires an explicit return type. If omitted, it results in a compilation error.
14. What will be the output of the following code?
class test
{
int a;
int b;
test(int i, int j)
{
a = i;
b = j;
}
void meth(test o)
{
o.a *= 2;
o.b /= 2;
}
}
class Output
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
test obj = new test(10 , 20);
obj.meth(obj);
System.out.println(obj.a + " " + obj.b);
}
}
Choose one option
a) 20 10
b) 10 20
c) 20 40
d) 40 20
Answer 14
a) 20 10
Class objects are always passed by reference, therefore changes done are reflected back on original arguments. obj.meth(obj) sends object obj as parameter whose variables a & b are multiplied and divided by 2 respectively by meth() function of class test. a & b becomes 20 & 10 respectively.
15. What will be the result of this expression?
class Output {
public static int sum(int... x) {
int total = 0;
for (int num : x) {
total += num;
}
return total;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println(sum(10));
System.out.println(sum(10, 20));
System.out.println(sum(10, 20, 30));
System.out.println(sum(10, 20, 30, 40));
}
}
Choose one option
a) only sum(10)
b) only sum(10,20)
c) only sum(10) & sum(10,20)
d) all of the mentioned
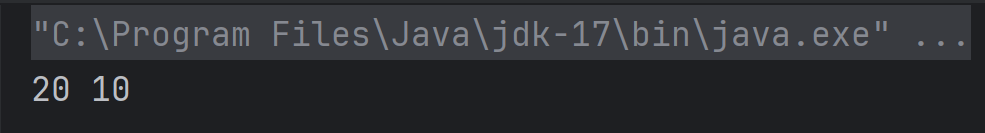
Answer 15
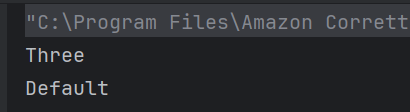
d) all of the mentioned
sum is a variable argument method and hence it can take any number as an argument.
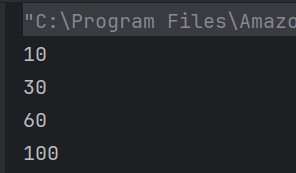
16. What is the result of the following code snippet?
class Test
{
public void m1 (int i,float f)
{
System.out.println(" int float method");
}
public void m1(float f,int i)
{
System.out.println("float int method");
}
public static void main(String[]args)
{
Test test =new Test();
test.m1(20,20);
}
}
Choose one option
a) int float method
b) float int method
c) compile time error
d) run time error
Answer 16
c) compile time error
While resolving overloaded method, compiler automatically promotes if exact match is not found. But in this case, which one to promote is an ambiguity.

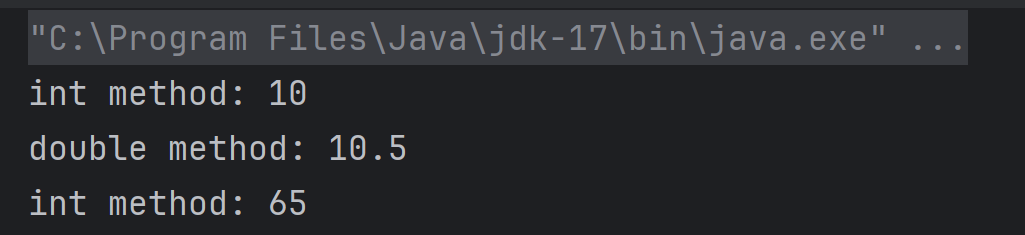
17. What will be printed?
class Test {
void show(int a) {
System.out.println("int method: " + a);
}
void show(double a) {
System.out.println("double method: " + a);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test obj = new Test();
obj.show(10); // Line 1
obj.show(10.5); // Line 2
obj.show('A'); // Line 3
}
}
Choose one option
a) int method: 10
double method: 10.5
int method: 65
b) int method: 10
double method: 10.5
double method: 65.0
c) Compilation error
d) Runtime error
Answer 17
a) int method: 10
double method: 10.5
int method: 65
obj.show('A') → 'A' is a char (ASCII 65). Char can be promoted to int, so it calls show(int) and prints 65.
18. Which principle of OOP is demonstrated by method overriding?
a) Encapsulation
b) Abstraction
c) Polymorphism
d) Inheritance only
Answer 18
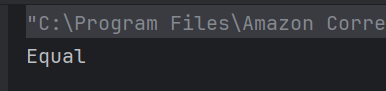
c) Polymorphism
19. If a class has two methods: void add(int a, int b) and int add(int x, int y), what happens?
a) Valid overloading
b) Compile-time error
c) Runtime error
d) Both methods are executed
Answer 19
b) Compile-time error
Same parameter list but different return type only results in compile-time error
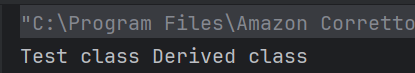
20. What is the output of the following code?
class Derived
{
public void getDetails()
{
System.out.printf("Derived class ");
}
}
public class Test extends Derived
{
public void getDetails()
{
System.out.printf("Test class ");
super.getDetails();
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Derived obj = new Test();
obj.getDetails();
}
}
Choose one option
a) Test class Derived class
b) Derived class Test class
c) Runtime error
d) Compilation error
Answer 20
a) Test class Derived class
Since getDetails() is overridden in the Test class and super.getDetails() is called inside it, both methods are executed in order.
21. What is the output of this switch statement?
import java.io.IOException;
class Derived {
public void getDetails() throws IOException { // Line 4
System.out.println("Derived class");
}
}
public class Test extends Derived {
public void getDetails() throws Exception { // Line 10
System.out.println("Test class");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // Line 14
Derived obj = new Test();
obj.getDetails();
}
}
a) Compilation error due to line 4
b) Compilation error due to line 10
c) Compilation error due to line 14
d) All the above
Answer 21
b) Compilation error due to line 10
The exception thrown by the overriding method should not be new or more broader checked exception.

22. What will be the output of this while loop?
class Derived
{
protected final void getDetails()
{
System.out.println("Derived class");
}
}
public class Test extends Derived
{
protected final void getDetails()
{
System.out.println("Test class");
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Derived obj = new Derived();
obj.getDetails();
}
}
a) Derived class
b) Test class
c) Runtime error
d) Compilation error
Answer 22
d) Compilation error
Final and static methods cannot be overridden.

23. What is the output of the following if-else block?
public class Test
{
public int getData(String temp) throws IOException
{
return 0;
}
public int getData(String temp) throws Exception
{
return 1;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Test obj = new Test();
System.out.println(obj.getData("Happy"));
}
}
a) 0
b) 1
c) Compilation error
d) Runtime error
Answer 23
c) Compilation error
Methods that throws different exceptions are not overloaded as their signature are still the same.

24. Can constructors be overridden in Java?
a) Yes
b) No
c) Only in abstract classes
d) Only for default constructors
Answer 24
b) No
Constructors cannot be inherited, hence cannot be overridden.
25. Which of these statements is correct?
a) Overloading is runtime polymorphism, overriding is compile-time.
b) Overloading is compile-time polymorphism, overriding is runtime.
c) Both overloading and overriding are compile-time polymorphism.
d) Both are runtime polymorphism.
Answer 25
b) Overloading is compile-time polymorphism, overriding is runtime.
We would love to hear from you! Please leave your comments and share your scores in the section below