Last Updated On
Playwright can be used to get access to the REST API of the application.
In this tutorial, I will go through the steps to execute the PUT requests in Playwright.
What is PUT Request?
A PUT request is an HTTP method used to update a resource at a specified URL, or to create the resource if it does not exist. A key feature of PUT requests is idempotency. This means that multiple identical PUT requests will have the same effect as a single request.
1. Setup Your Playwright Testing Environment:
Verify that the Playwright installed in your project. If you haven’t yet installed it, you can use:
npm install playwright
2. Update playwright.config.ts
Playwright Test comes with a few built-in reporters for different needs and ability to provide custom reporters. We will add detail in playwright.config.ts to generate the html report, once the test execution is finished.
import { defineConfig } from '@playwright/test';
export default defineConfig({
reporter: 'html',
});
3. Writing the API Test
Here’s an example script demonstrating API testing for PUT operation using Playwright:
import { test, expect } from '@playwright/test';
test('API Testing - PUT with Playwright', async ({ request }) => {
// Perform a GET request
const response = await request.get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1');
// Check the response status code
expect(response.status()).toBe(200);
// Parse the response data
const responseBody = await response.json();
console.log(responseBody);
// Perform a PUT request
const putResponse = await request.put('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1', {
data: {
title: 'Manager',
body: 'Test',
userId: 1
}
});
// Check the response status code
expect(putResponse.status()).toBe(200);
// Parse the response data
const putResponseBody = await putResponse.json();
console.log(putResponseBody);
// Validate the response
expect(putResponseBody).toHaveProperty('title', 'Manager');
expect(putResponseBody).toHaveProperty('body', 'Test');
expect(putResponseBody).toHaveProperty('userId', 1);
});
Explanation:
In the above example, first I have sent a GET request to see the body structure of the response. Then I sent a PUT request to see the changes in the response body.
1. Imports
This line imports the test and expect functions from Playwright’s testing library. These functions provide a structure for writing tests and asserting conditions within them.
import { test, expect } from '@playwright/test';
2. Test Definition
This defines an asynchronous test case named “API Testing – PUT with Playwright”. The test receives a request object as a parameter, which is used to perform HTTP requests.2.
test('API Testing - PUT with Playwright', async ({ request })
3. Performing a GET Request
// Perform a GET request
const response = await request.get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1');
// Check the response status code
expect(response.status()).toBe(200);
// Parse the response data
const responseBody = await response.json();
console.log(responseBody);
4. Performing a PUT Request
Sends a PUT request to the specified URL. data transmits the body of the request.
const putResponse = await request.put('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1', {
data: {
title: 'Manager',
body: 'Test',
userId: 1
}
});
5. Checking the Response Status Code
Retrieve HTTP status code for response validation.
expect(putResponse.status()).toBe(200);
6. Parsing the Response Data
Parse response data into JSON format
const putResponseBody = await putResponse.json();
7. Logging the Response
This outputs the response body to the console, allowing you to see the returned JSON data.
console.log(putResponseBody);
8. Perform assertions on the response
expect(putResponseBody).toHaveProperty('title', 'Manager');
expect(putResponseBody).toHaveProperty('body', 'Test');
expect(putResponseBody).toHaveProperty('userId', 1);
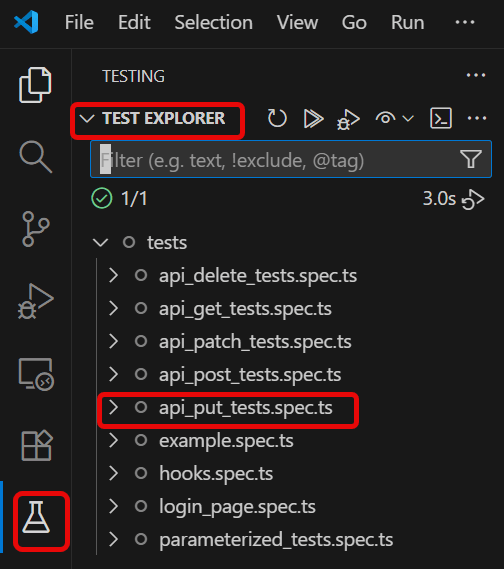
4. Execute the tests through Test Explorer View
Go to the funnel shape icon called “Testing” or “Test Explorer View”. You can run the tests from the test Explorer view too now. You can run all of the tests in all of the test specs in this directory.
You can also come in and run all of the tests in a particular specification file. Alternatively, run individual tests within a specification file. Here, I want to run the tests of api_put_tests.spec.ts file.
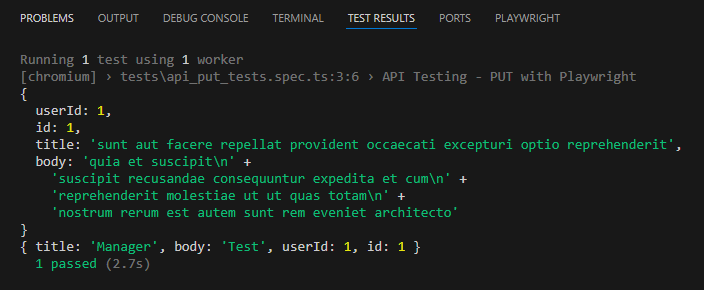
The output of the above program is
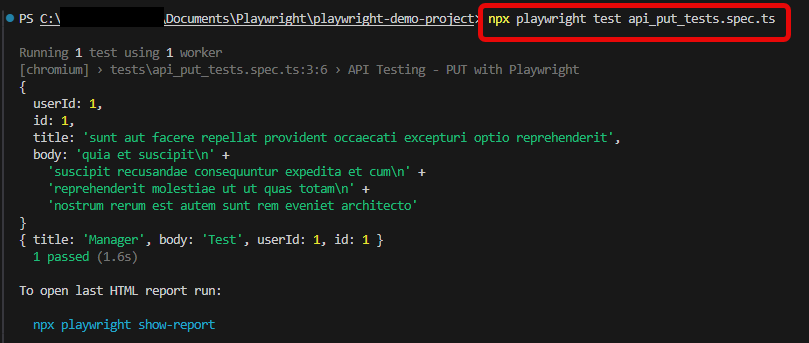
5. Execute the tests through Command Line
You can also run the tests through the command line. Go to the terminal and use the below command:-
npx playwright test api_put_tests.spec.ts
This command runs all the tests present in this file.
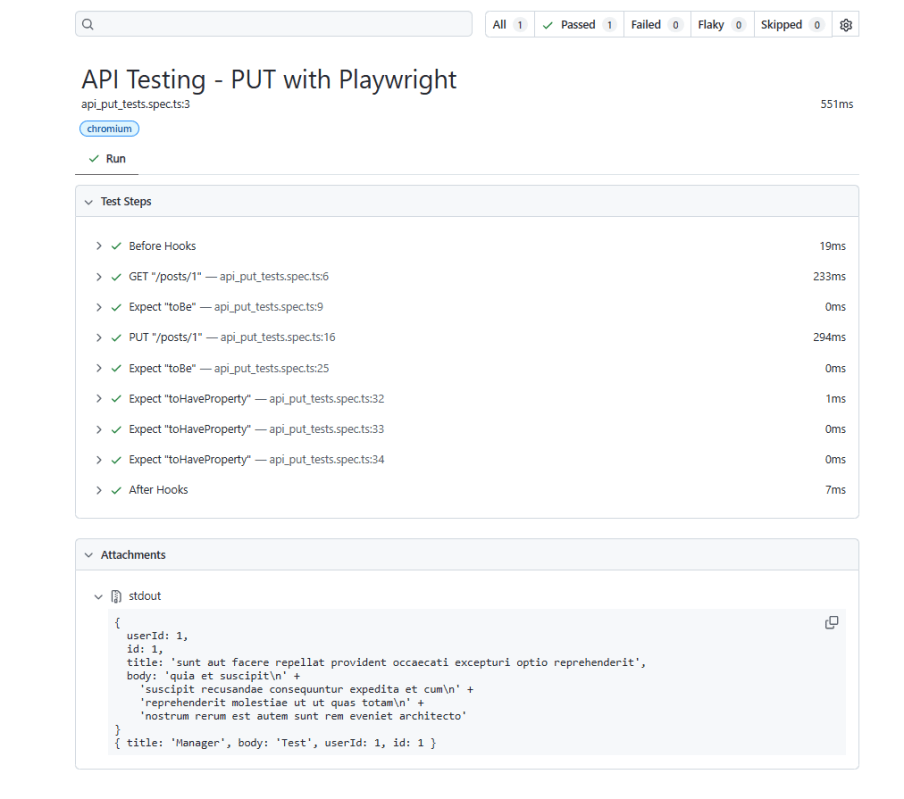
6. Evaluate Test Results
Analyze console outputs and assertions to validate the response data, ensuring that your API endpoints are functioning as designed.
Playwright generates a test report after the execution of the tests. This test report can be viewed by using the below command:
npx playwright show-report
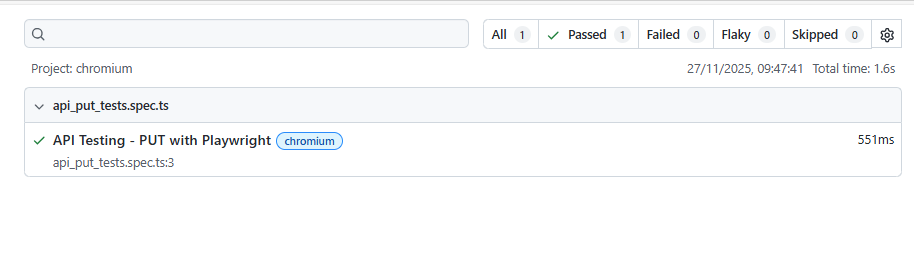
The output of the above command is
Below is the Test Report generated by Playwright.
To know more about Playwright UI mode, please refer to this website – https://playwright.dev/docs.