Generating and passing an access token in Postman involves a few steps, typically for use with APIs that require authentication.
Implementation Steps
Step 1: Create a Request to Generate the Auth Token
- Open Postman and create a new request (e.g., POST/token).
- Enter the API endpoint that generates the token.
- Go to the Body tab → select raw → choose JSON → add the request body.
- Send the request.
- In the response, you’ll usually get a JSON with the access_token:
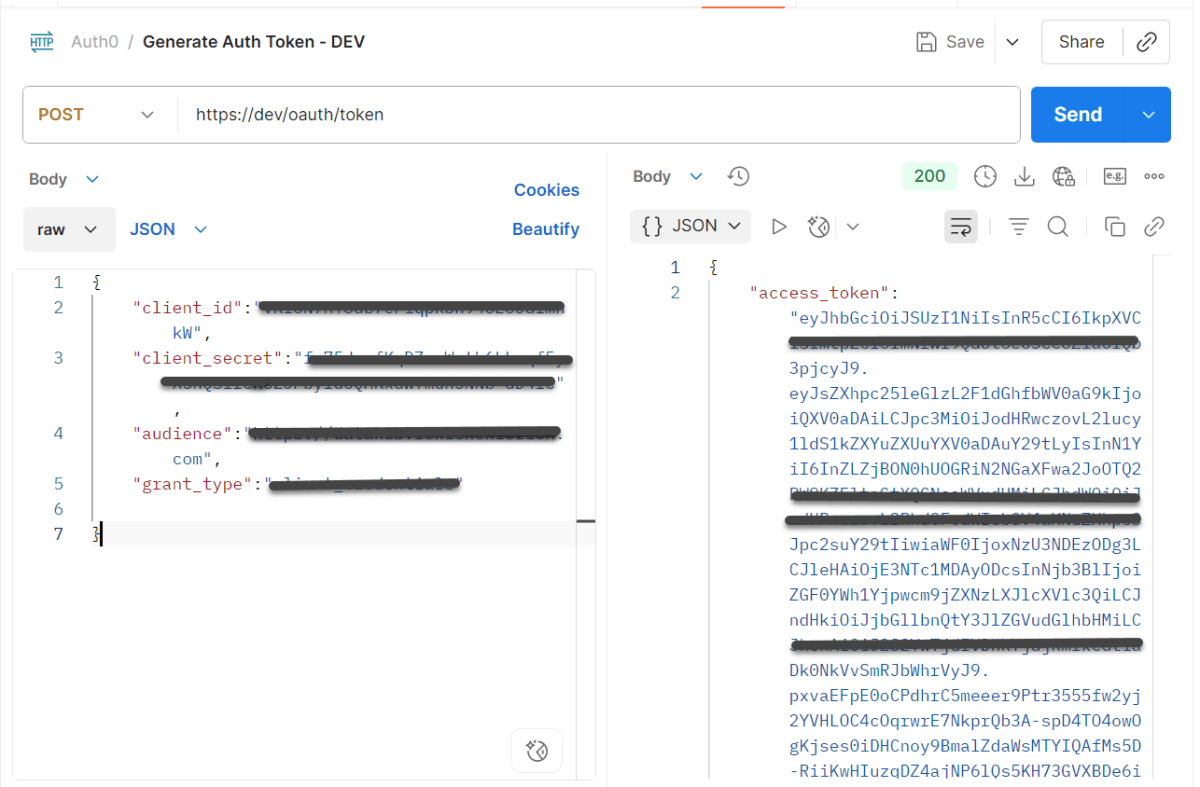
Step 2: Save the Token in an Environment Variable
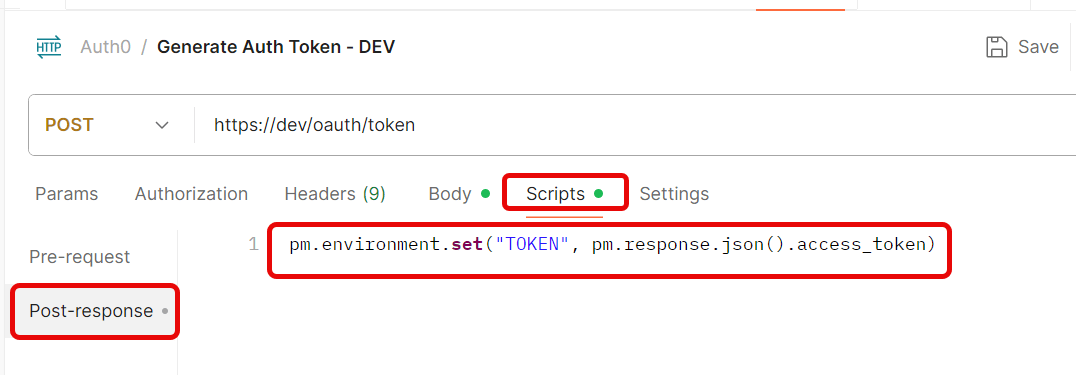
After sending the request, go to the Scripts tab (next to Body/Headers).
Add the below script to capture and store the token:
pm.environment.set("TOKEN", pm.response.json().access_token)
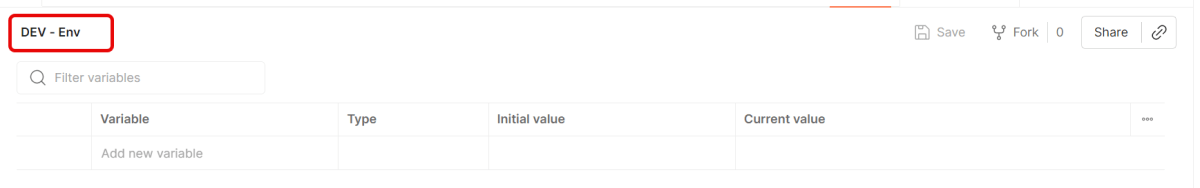
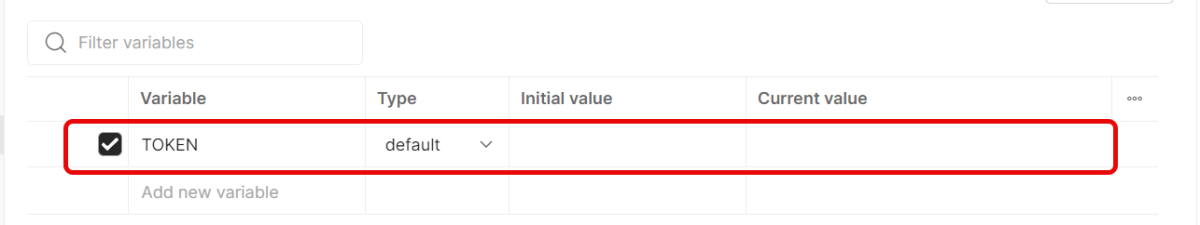
Create a new Environment in Postman (top right → Environments → Add
Save the request.
Step 3: Use the Token in Another Request
- Create a new request.
- Go to the Headers tab.
- Add this header:
Key: Authorization
Value: Bearer {{Token}}
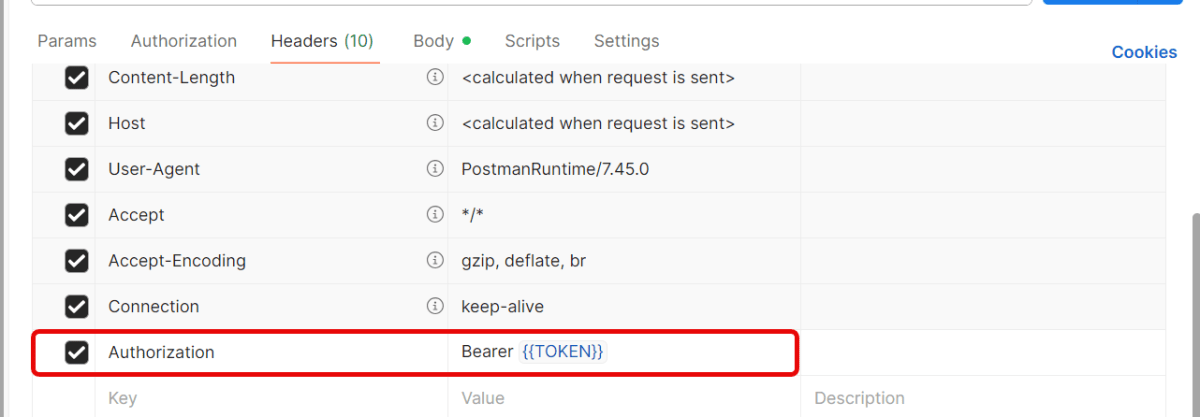
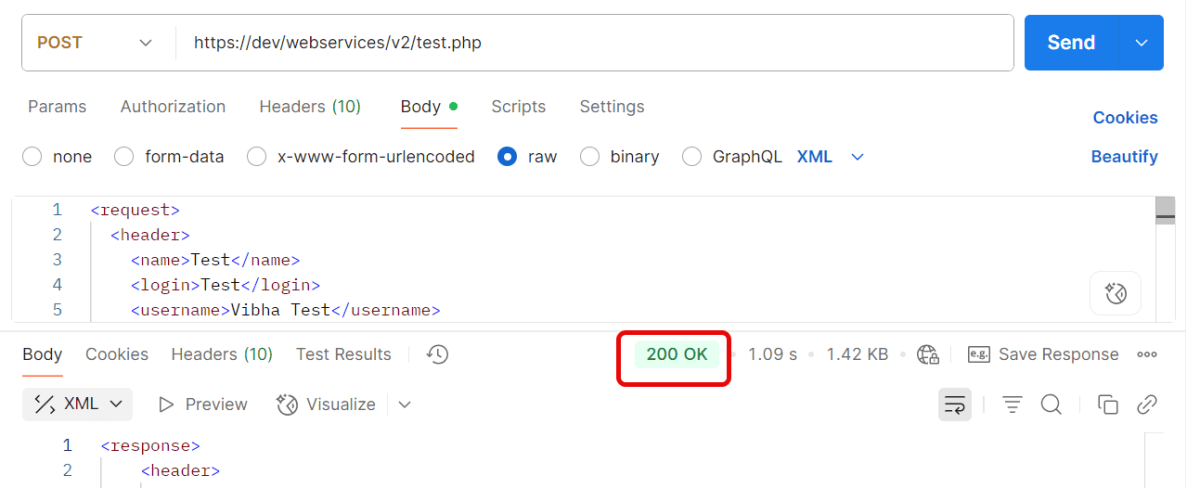
Send the request — Postman will automatically insert the token from the environment variable.
Quick Troubleshooting Checklist
1.Is the token saved correctly in environment variables? Token saved in one environment, but request uses another. Make sure you’ve selected the same environment (top-right dropdown in Postman).
2. Is the Authorization: Bearer {{Token}} header present?
3. Does the account have the correct permissions/scopes? Token is valid, but the user doesn’t have permission for that endpoint. Verify that your account has the right role/permissions.
4. Correct Content-Type is sent. Set header → Content-Type: application/json.