Last Updated On
In this tutorial, we’ll learn how to use Postman to test an endpoint secured with Basic Authentication.
Table of Contents
What is an authorization token?
An authorization token, often referred to as an access token, is a piece of data or credential that is used to authenticate and authorize access to protected resources or operations in a system. It is a Base64-encoded string of username:password. We can send it in the Authorization header like this:
Authorization: Basic YWRtaW46cGFzc3dvcmQ=
Where YWRtaW46cGFzc3dvcmQ= = Base64 of admin:password
We will use the following URL for this Postman tutorial.
https://postman-echo.com/basic-auth
Implementation Steps
Below are the steps to use Basic Auth in Postman:
Create a Collection
Step 1: Create a Collection, click on Collections, and then click on the “+” plus button.
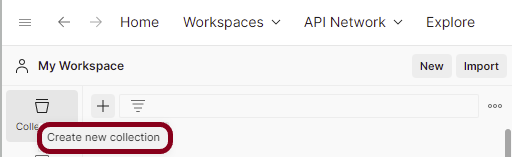
Step 2: Provide a name to the collection – “Authentication”.

Add a request to the Collection
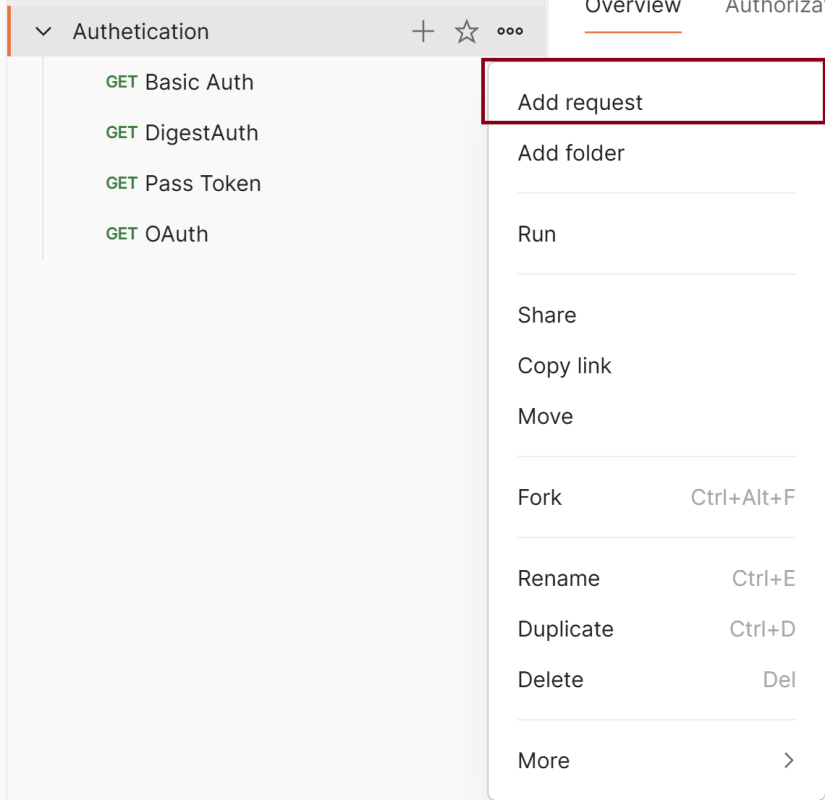
Step 3: To create a new request, click on “Add a request”, if it is a new Collection. Otherwise, click on the 3 dots and select “Add request”.
Enter the details – URL, Method, Authorization
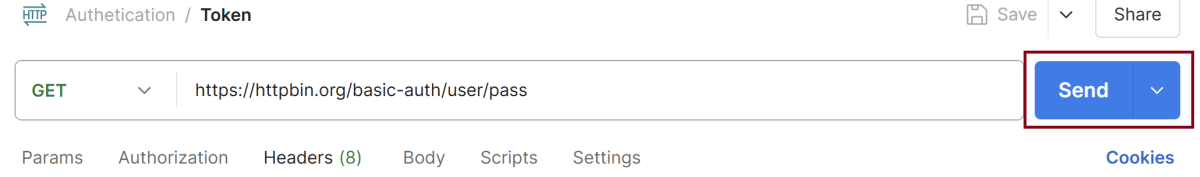
Step 4: Enter the “name” in the request. Here, the name is “Token”.

Step 5: Enter the “URL” in the address bar.
https://httpbin.org/basic-auth/user/pass

Step 6: Now, select the “GET” request from the list of request methods.

Step 7: Now, go to the “Headers “ Tab.

Step 8: We need to add a new key-value pair

Step 9: Now, click on the Send button in Postman. The server will respond with the protected resource response message.
Verify the Response
Step 10: Once you press the send button, you will get the response from the server. Make sure you have a proper internet connection; otherwise, you will not get a response.

Status
You can check the status code. Here, we got the status code 200, which means we got a successful response to the request.

Body
In the Body tab of the response box, we have multiple options to see the response in a different format.

Important Notes
- Credentials are delivered in plain text and encoded using Base64, which leaves them open to interception if not properly secured. Using Basic Authentication over unencrypted channels is not advised due to this vulnerability.
- Always encrypt the entire communication channel, including credentials, using HTTPS to guard against man-in-the-middle attacks and eavesdropping.
We are done! Congratulations on making it through this tutorial and hope you found it useful! Happy Learning!!