In this tutorial, we will send a request performing the PATCH method in Postman.
Table of Contents
What is PATCH method?
The PATCH method is used to partially modify an existing resource. This operation updates an existing resource but does not require sending the entire body with the request. PUT modifies a record’s information and creates a new record if one is not available, and PATCH updates a resource without sending the entire body of the request. Unlike PUT Request, PATCH does partial update e.g. Fields that need to be updated by the client, only that field is updated without modifying the other field.
We will use the following URL for this Postman tutorial.
https://reqres.in/api/users/2
Sample Request Body
{
"name": "Patch_Test"
}
Implementation Steps:
To create the first PATCH request in Postman, follow the following steps:
Create a Collection
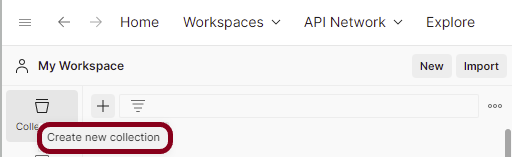
Step 1: Create a Collection, click on Collections, and then click on the “+” plus button.
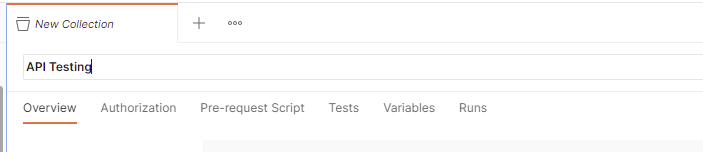
Step 2: Provide a name to the collection – “API Testing”.
Add a request to the Collection
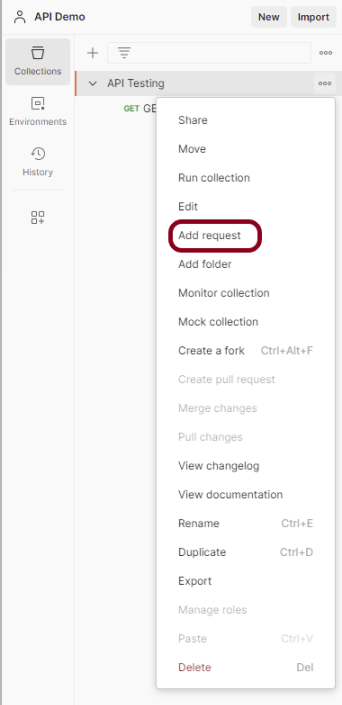
Step 3: To create a new request, click on “Add a request” if it is a new Collection. Otherwise, click on the 3 dots and select “Add request”.
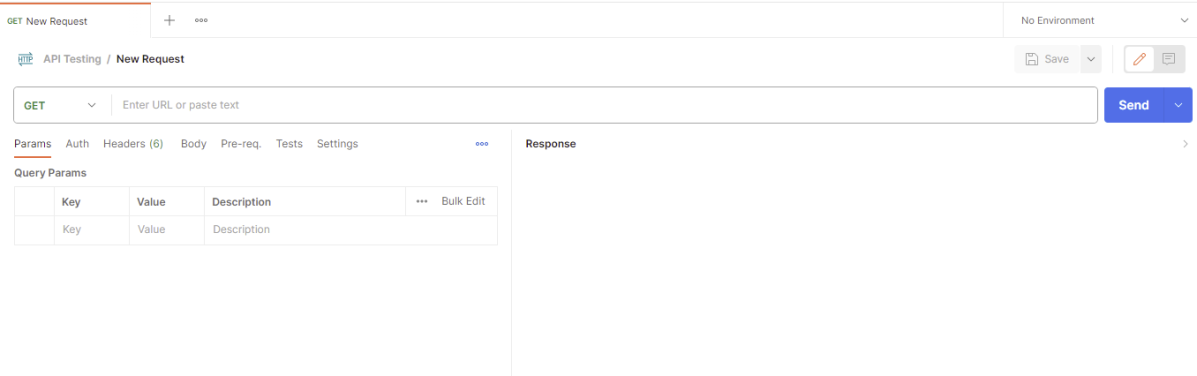
Step 4: Once you create a new request, then you will get the following window:
Enter the details of request
Step 5: Enter the “name” in the request. Here, the name is “PartiallyUpdateUser”.
Step 6: Enter the “URL” in the address bar.
Step 7: Now, select the “PATCH” request from the list of request methods.
Step 8: Add a Request body to the Post request
For this, select the Body tab.
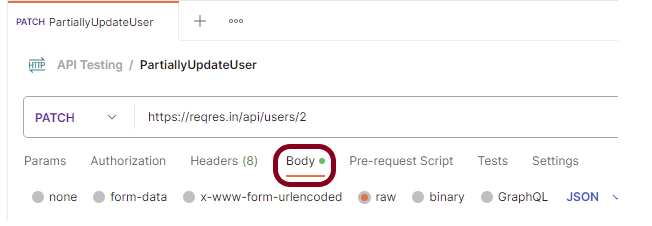
Now in the Body tab, select raw and select JSON as the format type from the drop-down menu, as shown in the image below. This is done because we need to send the request in the appropriate format that the server expects. Copy and paste the request body example mentioned at the beginning of the tutorial to the postman request Body.
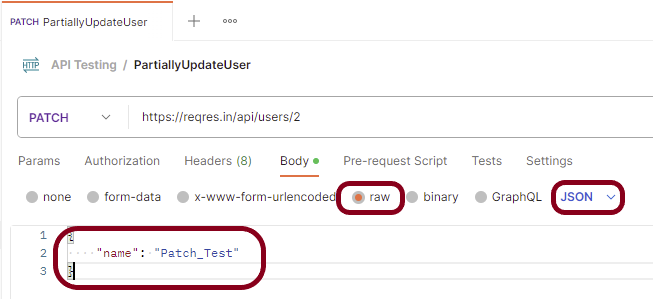
Step 9: Press the “Send” button.
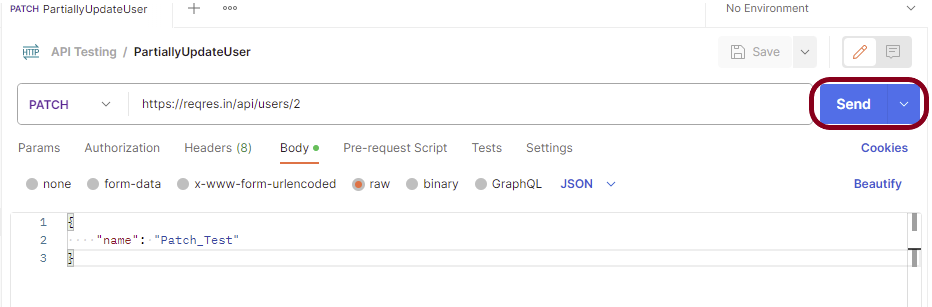
Verify the Response
Step 10: Once you press the send button, you will get the response from the server. Make sure you have a proper internet connection; otherwise, you will not get a response.
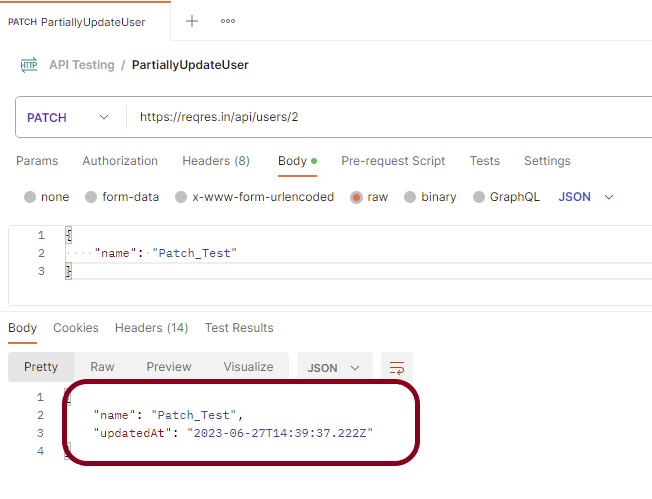
Status
You can check the status code. Here, we got the status code 200, which means we got a successful response to the request. In the case of new resource creation, the status code should be 201. But as this is a dummy API, we are getting a status code of 200.

Body
In the Body tab of the response box, we have multiple options to see the response in a different format.
Format Type
Each request has a defined response to it as defined by the Content-Type header. That response can be in any format. Such as in the above example, we have JSON code file.
Below are the various format type present in Postman.
XML
HTML
Text
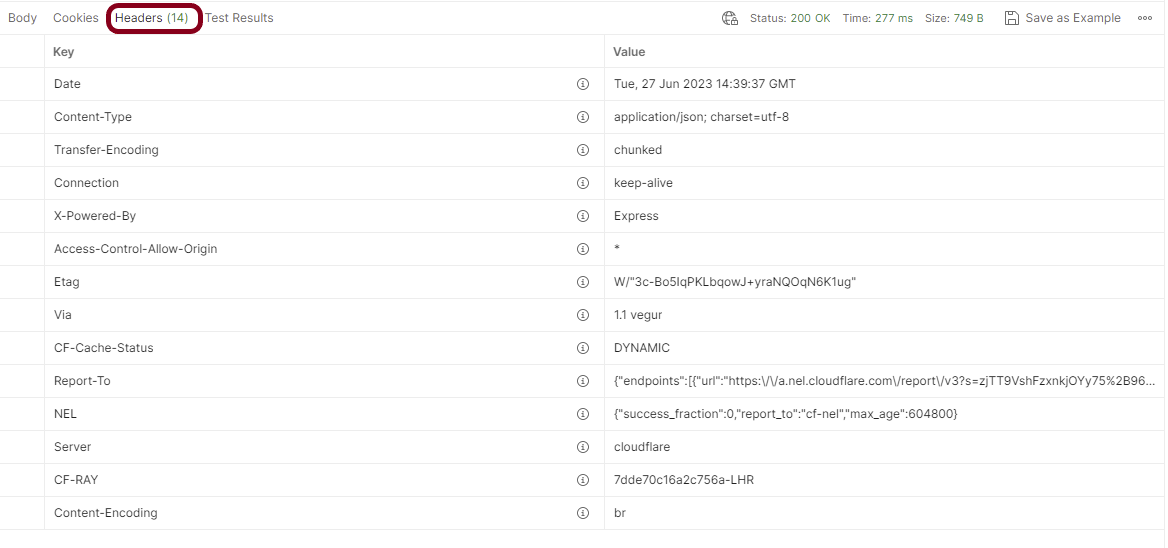
Headers
Headers are the extra information that is transferred to the server or the client. In Postman, headers will show like key-value pairs under the headers tab. Click on the Headers link as shown in the below image:
We are done! Congratulations on making it through this tutorial and hope you found it useful! Happy Learning!!